抛砖引玉
-
让你统计1小时内每种商品的销售额,用Flink 该怎么实现。
-
还是让你统计1小时内每种商品的销售额,但是要过滤掉退款的订单,用Flink 该怎么实现。
学了本文两个操作,不信你还不会。
AggregateFunction
❝
通常用于对数据流中的数据进行分组聚合。它可以将一组数据逐步合并、计算,最终得到一个聚合结果。
AggregateFunction 接口包含几个关键的方法,这些方法定义了如何进行状态初始化、累加、合并和获取结果:
createAccumulator():该方法在聚合前被调用,用于初始化聚合状态。
add(value, accumulator)该方法将新的输入值加到累加器上。在每个事件到达时调用会调用该方法。
getResult(accumulator):该方法用于返回最终聚合结果。这在聚合操作结束时被调用。
merge(acc1, acc2)(可选):该方法作用是,在并行流处理情况下,需要合并不同实例的聚合结果。
以下示例模拟统计每小时各商品的销售额
java
public class AggregateFunctionDemo {
public static class Order{
String goods;
int amount;
public Order(String goods, int amount) {
this.goods = goods;
this.amount = amount;
}
}
public static class OrderACC{
String goods;
int amount;
public OrderACC(String goods, int amount) {
this.goods = goods;
this.amount = amount;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderACC{" +
"goods='" + goods + '\'' +
", amount=" + amount +
'}';
}
}
public static class OrderACCFunction implements AggregateFunction<Order, OrderACC, OrderACC> {
@Override
public OrderACC createAccumulator() {
return new OrderACC(null,0);
}
@Override
public OrderACC add(Order value, OrderACC accumulator) {
if (accumulator.goods == null) {
accumulator.goods = value.goods;
}
accumulator.amount += value.amount;
return accumulator;
}
@Override
public OrderACC getResult(OrderACC accumulator) {
return accumulator;
}
@Override
public OrderACC merge(OrderACC a, OrderACC b) {
a.amount += b.amount;
return a;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Order> dataStream = env.addSource(new SourceFunction<Order>() {
boolean running = true;
List<String> goods = Arrays.asList("书包","本子","笔");
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<Order> ctx) throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
while (running){
int goodsIndex = random.nextInt(goods.size());
int amount = random.nextInt(1000);
Order order = new Order(goods.get(goodsIndex), amount);
ctx.collect(order);
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
running = false;
}
});
DataStream<OrderACC> resultStream =
dataStream.keyBy(order -> order.goods).
window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.hours(5))).
aggregate(new OrderACCFunction());
resultStream.print();
env.execute();
}
}AggregateFunction 小结
- AggregateFunction 常用于对窗口内的数据进行聚合计算。
例如,你可能需要计算某个时间窗口内某个指标的平均值、总和、最大值或最小值等。
- 在分布式计算环境中,通过实现 merge 方法,Flink 可以在不同的节点上并行地执行聚合计算,并在最后将结果合并。
ProcessWindowFunction
ProcessWindowFunction 是 Flink 提供的一个强大的窗口函数接口,允许开发者对窗口中的元素进行自定义处理,包括访问窗口的元数据和状态。
来看看ProcessWindowFunction中 process方法的定义
java
void process(KEY key, Context context, Iterable<IN> elements, Collector<OUT> out) throws Exception;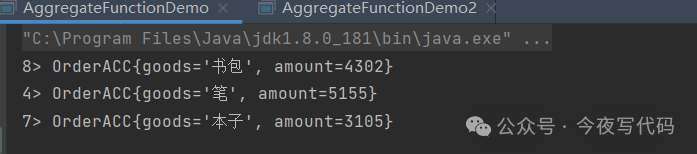
从上面方法定义我们基本可以推断ProcessWindowFunction 的特点
-
Iterable<IN> elements窗口中所有元素 ,这与 ReduceFunction 或 AggregateFunction 不同,后者主要关注于元素之间的聚合操作。我们可以遍历elements,实现自己的聚合逻辑。 -
Context context:你可以通过Context获取到窗口的元数据,如窗口的开始和结束时间戳。甚至进行状态管理
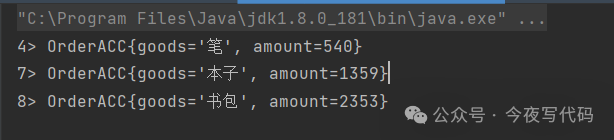
ProcessWindowFunction 的使用
java
public class AggregateFunctionDemo2 {
public static class Order{
String goods;
int amount;
boolean refund;
public Order(String goods, int amount, boolean refund) {
this.goods = goods;
this.amount = amount;
this.refund = refund;
}
}
public static class OrderACC{
String goods;
int amount;
public OrderACC(String goods, int amount) {
this.goods = goods;
this.amount = amount;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderACC{" +
"goods='" + goods + '\'' +
", amount=" + amount +
'}';
}
}
public static class OrderProcessWindowFunction extends ProcessWindowFunction<Order,OrderACC,String, TimeWindow> {
@Override
public void process(String key, ProcessWindowFunction<Order, OrderACC, String, TimeWindow>.Context context, Iterable<Order> elements, Collector<OrderACC> out) throws Exception {
int sum = 0;
for(Order order : elements){
if(!order.refund){
sum += order.amount;
}
}
out.collect(new OrderACC(key,sum));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<Order> dataStream = env.addSource(new SourceFunction<Order>() {
boolean running = true;
List<String> goods = Arrays.asList("书包","本子","笔");
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<Order> ctx) throws Exception {
Random random = new Random();
while (running) {
int goodsIndex = random.nextInt(goods.size());
int amount = random.nextInt(1000);
boolean refund = random.nextBoolean();
Order order = new Order(goods.get(goodsIndex), amount, refund);
ctx.collect(order);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
running = false;
}
});
DataStream<OrderACC> resultStream = dataStream.keyBy(order -> order.goods).
window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(5))).process(new OrderProcessWindowFunction());
resultStream.print();
env.execute();
}
}
ProcessWindowFunction小结
-
可以实现复杂的聚合逻辑,比如对窗口内元素进行过滤、排序之后 再进行聚合。
-
可以获取窗口的状态信息,(如窗口的开始和结束时间)来满足一些特定的需求
总结
本文介绍了如何使用ProcessWindowFunction/AggregateFunction 完成一些聚合操作。通过对比两端代码,相信聪明的你已经体会到两者差异。再回到开头的问题,相信已经不是问题,信手拈来了。