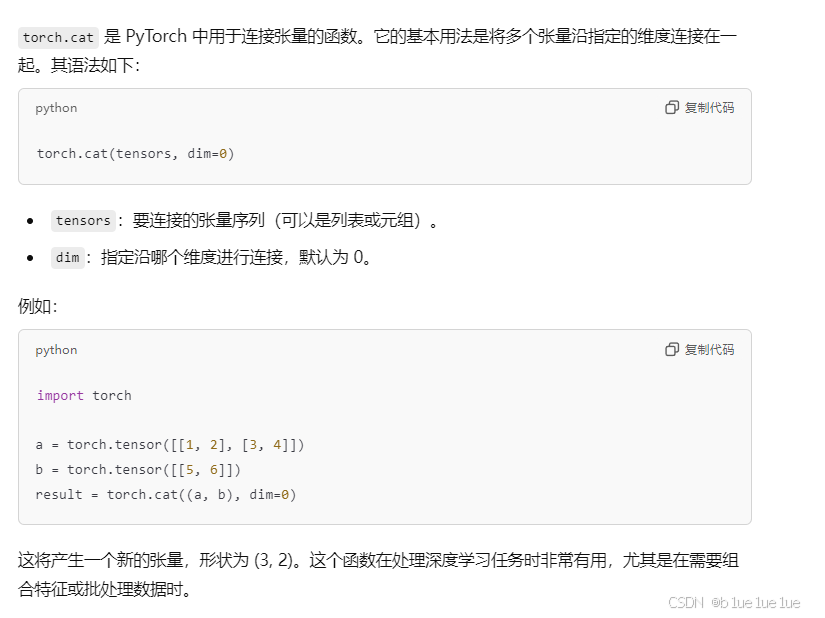
cat函数:
cat函数不会增加维度,默认按照dim=0连接张量
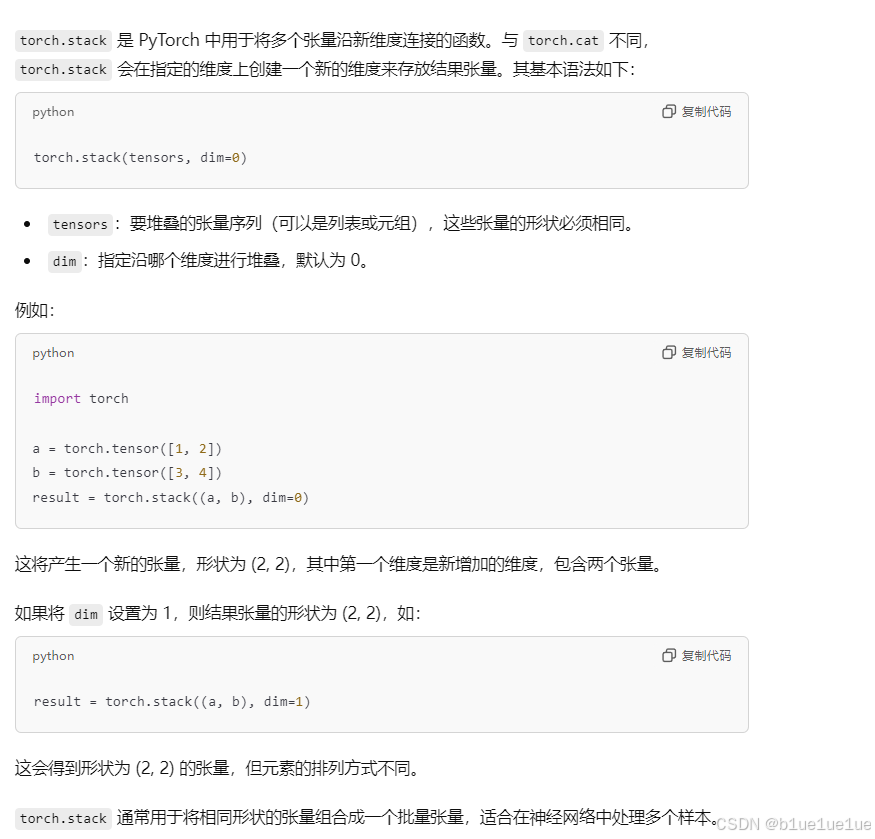
stack函数:
stack函数会增加一个维度
nn.Linear的默认输入:
torch中默认输入一定要为tensor,并且默认是tensor.float32,此外device如果没有model.to(device)放到gpu上面默认会在cpu上运行,如果把模型放到了device上面,那么输入的向量也要放到gpu上面
torch的eval模式和train模式:
使用model.eval模式,模型会进入评估模式,在这个时候,会丢弃以下行为:
-
Dropout:在评估模式下,Dropout 层不会丢弃任何神经元,所有的神经元都会参与计算。
-
Batch Normalization:在评估模式下,Batch Normalization 层会使用训练过程中累积的均值和方差来进行归一化,而不是使用当前批次的数据。
使用model.train模式,模型会进入训练模式,这时候模型会启用Dropout和Batch Normalization
torch.gather函数:
torch.gather(input, dim, index) → Tensor假设input的shape为(a*b*c),index的shape需要为(a*b,x),这时候指定dim=2,就会把dim=2这一维度的向量按照x的下标收集起来1
python
import torch
# 创建一个形状为 (3, 4) 的输入张量
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12]])
# 创建一个形状为 (3, 2) 的索引张量
index = torch.tensor([[0, 1],
[1, 2],
[2, 3]])
# 沿着第 1 维(列)收集元素
output = torch.gather(input, dim=1, index=index)
print(output)
"""
tensor([[ 1, 2],
[ 6, 7],
[11, 12]])
"""torch.distributions.Categorical函数:
torch.distributions.Categorical(probs=None, logits=None)
probs代表概率,要求加起来为1,logits代表对数概率,不一定要加起来为1,torch会自动计算让他们加起来为1,虽然用np.random.choice也能实现这个效果,但是numpy是不能进行梯度计算的
python
action_dist = torch.distributions.Categorical(probs)
action = action_dist.sample()item() 和 detach().cpu().numpy()
在深度学习训练后,需要计算每个epoch得到的模型的训练效果的时候,一般会用到detach() item() cpu() numpy()等函数。
- item():返回的是tensor中的值,且只能返回单个值(标量),不能返回向量,使用返回loss等,得到的值因为是标量所以肯定是在cpu上,因为cuda上只能放tensor
- detach(): 阻断反向传播,返回值任然是tensor
- cpu():将tensor放到cpu上,返回值任然是tensor
- numpy():将tensor转换为numpy,注意cuda上面的变量类型只能是tensor,不能是其他
在pytorch中反向传播只能对计算出的loss进行,loss肯定是一个具体的值,使用detach是为了把拿出的计算图和主图分离,计算出的loss不再对主干进行修改:
python
critic_loss = torch.mean(F.mse_loss(self.critic(states), td_target.detach()))
critic_loss.backward()如上的critic_loss.backward()只会修改critic的参数,并不会修改td_target的参数