Transformer
- Transformer是基于Encoder-Decoder结构的,将Seq2Seq中的RNN/GRU部分更换为Self-Attention部分
位置编码
- Positional Encoding
Self-attention丢失了位置信息
-
CNN 卷积神经网络可以保存相邻的位置信息
-
RNN 是顺序输入的,是包含了位置信息的
-
Self-Attention 是并行计算的,丢失了位置信息,位置编码为Self-Attention补充位置信息
为什么不用token的索引直接作为位置编码:
- 序列的长度是可以变化的,如果出现句子非常长的情况,模型的泛化能力较差,因此使用索引作为位置编码会损害模型的泛化能力,缺乏处理没见过的长度的能力
- 如果用norm对序列长度进行归一化,会出现相同的位置编码在不同的长度中对应不同的位置,不利于计算
位置编码希望达到的情况:
- 为每个时间步骤(单词在句子中的位置)输出唯一的编码。
- 任何两个时间步骤之间的距离在不同长度的句子之间应该是一致的。
- 我们的模型应该方便地推广到更长的句子。它的值应该是有界的。
- 位置信息必须是确定性的。
位置编码的方式:
- 固定位置编码
- 可学习位置编码
固定位置编码
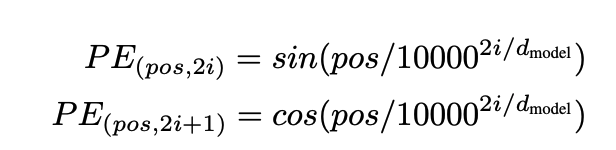
pos是位置,i是维度索引,d_model是嵌入总维度.
频率和波长呈反比关系,波长越长,变化越慢,频率越低
很明显波长的计算和 10000^2i / d_model 有关系
py
"""
位置编码
"""
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_hiddens, dropout, max_len=1000):
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# 创建一个全为0的足够长的P
self.P = torch.zeros((1, max_len, num_hiddens))
# 根据上面的公式进行计算
X = torch.arange(max_len, dtype=torch.float32).reshape(-1, 1) /
torch.pow(10000, torch.arange(0, num_hiddens, 2, dtype=torch.float32)
/ num_hiddens)
# 计算后引入Sin Cos
self.P[:, :, 0::2] = torch.sin(X)
self.P[:, :, 1::2] = torch.cos(X)
def forward(self, X):
# 将计算好的Positional Encoding和原始的X即嵌入进行融合
X = X + self.P[:, :X.shape[1], :].to(X.device)
# dropOut(X)
return self.dropout(X)网络模块
AddNorm
-
使用 self.ln(self.dropout(Y) + X) 实现
-
Residual connection and LayerNormalization 残差链接和层归一化
py
"""
残差连接后进行层规范化
"""
class AddNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, normalized_shape, dropout, **kwargs):
super(AddNorm, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.ln = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape)
def forward(self, X, Y):
return self.ln(self.dropout(Y) + X)Positional-wise Feed-Forward Network
位置前馈网络是Transformer模型中的一个重要组成部分,它通过提供额外的非线性变换和深度,增强了模型对输入序列的理解能力,从而提高了模型在各种自然语言处理任务上的性能。
- Positional-wise Feed-Forward Network
使用基于位置的前馈网络对所有位置进行变换
- 基于多层感知机MLP
- 输入X ( batch_size,time_steps,hidden_num ),被两层的感知机转换为(batch_size,time_steps,ffn_num_outputs)
- 可以实现,对所有的位置进行变换,相同的输入和相同的位置得到的输出也是相同的
py
#@save
class PositionWiseFFN(nn.Module):
"""基于位置的前馈网络"""
def __init__(self, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, ffn_num_outputs,**kwargs):
super(PositionWiseFFN, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dense1 = nn.Linear(ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.dense2 = nn.Linear(ffn_num_hiddens, ffn_num_outputs)
def forward(self, X):
return self.dense2(self.relu(self.dense1(X)))Q:位置前馈网络的作用
- 增加模型的非线性能力
- 增强表示能力:FFN通过两层全连接层(线性变换)来增加模型的深度
- 保持位置不变性:虽然FFN本身对每个位置独立地应用相同的变换,但它并不改变序列中元素的相对位置关系。
- 与自注意力机制互补:在Transformer模型中,FFN通常与自注意力机制(Self-Attention)一起使用。自注意力机制允许模型在处理序列时考虑不同位置之间的关系,而FFN则提供了一种方式来进一步处理这些关系,以生成更丰富的特征表示。
Q:位置前馈网络和位置编码的关系?
位置编码(Positional Encoding)和位置逐元素前馈网络(Position-wise Feed-Forward Network)是Transformer模型中的两个关键组件,它们在模型中扮演着不同的角色,但又相互关联。
- 位置编码(Positional Encoding) :
- 位置编码的主要作用是为模型提供序列中词的位置信息。由于Transformer模型中的自注意力机制本身不包含任何关于词顺序的信息,位置编码通过在每个词的嵌入向量中添加一个唯一的位置向量来解决这个问题。
- 位置编码可以是绝对位置编码,也可以是相对位置编码。在原始的Transformer模型中,通常使用正弦和余弦函数的不同频率来生成位置编码,这种编码方式被称为Sinusoidal Positional Encoding。
- 位置编码通常与词嵌入向量相加,为模型提供关于词位置的信息,帮助模型理解输入序列中的顺序关系。
- 位置逐元素前馈网络(Position-wise Feed-Forward Network) :
- 位置逐元素前馈网络位于自注意力层之后,它对每个序列位置的输出进行独立的线性变换,通常包括两个线性层,中间夹着一个ReLU激活函数。
- 这个网络的目的是捕捉序列中的局部特征,它与自注意力层一起工作,自注意力层负责捕捉序列中的长距离依赖关系,而位置逐元素前馈网络则负责学习更深层次 的特征表示。
- 由于这个网络对每个位置单独应用,因此被称为"位置逐元素"的,意味着它在每个序列位置进行相同的操作,但操作是独立进行的。
在Transformer模型中,位置编码通常在自注意力机制之前添加到输入序列中,而位置逐元素前馈网络则在自注意力机制之后应用。这样,模型首先利用位置编码来理解词的顺序信息,然后通过自注意力机制捕捉词之间的依赖关系,最后通过位置逐元素前馈网络进一步提取特征,从而实现对序列数据的深入理解
Self-Attention
-
每个Q都会关注所有的Key-Value并生成一个注意力输出;
-
如果查询、键和值来自同一组输入,就称为Self-Attention(intra-Attention);
不同的注意力计算方式用于计算α评分函数的方式不同;
加性注意力
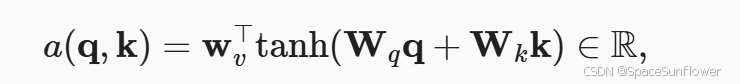
- 其中的Wv Wq Wk都是可以学习的参数
py
class AdditiveAttention(nn.Module):
"""加性注意力"""
def __init__(self, key_size, query_size, num_hiddens, dropout, **kwargs):
super(AdditiveAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.W_k = nn.Linear(key_size, num_hiddens, bias=False)
self.W_q = nn.Linear(query_size, num_hiddens, bias=False)
self.w_v = nn.Linear(num_hiddens, 1, bias=False)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, queries, keys, values, valid_lens):
queries, keys = self.W_q(queries), self.W_k(keys)
# 在维度扩展后,
# queries的形状:(batch_size,查询的个数,1,num_hidden)
# key的形状:(batch_size,1,"键-值"对的个数,num_hiddens)
# 使用广播方式进行求和
features = queries.unsqueeze(2) + keys.unsqueeze(1)
features = torch.tanh(features)
# self.w_v仅有一个输出,因此从形状中移除最后那个维度。
# scores的形状:(batch_size,查询的个数,"键-值"对的个数)
scores = self.w_v(features).squeeze(-1)
self.attention_weights = masked_softmax(scores, valid_lens)
# values的形状:(batch_size,"键-值"对的个数,值的维度)
return torch.bmm(self.dropout(self.attention_weights), values)缩放点积注意力
单个数据的缩放点积注意力:
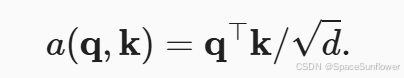
小批次的缩放点积注意力:
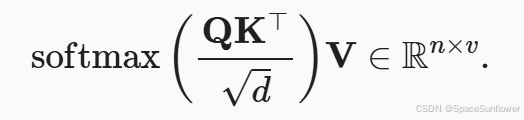
py
class DotProductAttention(nn.Module):
"""缩放点积注意力"""
def __init__(self, dropout, **kwargs):
super(DotProductAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# 缩放点积注意力的实现使用了暂退法进行模型正则化。
# queries的形状:(batch_size,查询的个数,d)
# keys的形状:(batch_size,"键-值"对的个数,d)
# values的形状:(batch_size,"键-值"对的个数,值的维度)
# valid_lens的形状:(batch_size,)或者(batch_size,查询的个数)
def forward(self, queries, keys, values, valid_lens=None):
d = queries.shape[-1]
# 设置transpose_b=True为了交换keys的最后两个维度
scores = torch.bmm(queries, keys.transpose(1,2)) / math.sqrt(d)
self.attention_weights = masked_softmax(scores, valid_lens)
return torch.bmm(self.dropout(self.attention_weights), values)掩码多头注意力
- (Masked) Multi-Head Attention
多头注意力在进行前首先要转换为多头的数据格式:
- transpose_qkv 增加一个num of heads维度
- transpose_output增加一个逆转回去的方式
py
def transpose_qkv(X, num_heads):
"""为了多注意力头的并行计算而变换形状"""
# 输入X的形状:(batch_size,查询或者"键-值"对的个数,num_hiddens)
# 输出X的形状:(batch_size,查询或者"键-值"对的个数,num_heads,
# num_hiddens/num_heads)
X = X.reshape(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], num_heads, -1)
# 输出X的形状:(batch_size,num_heads,查询或者"键-值"对的个数,
# num_hiddens/num_heads)
X = X.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
# 最终输出的形状:(batch_size*num_heads,查询或者"键-值"对的个数,
# num_hiddens/num_heads)
return X.reshape(-1, X.shape[2], X.shape[3])
#@save
def transpose_output(X, num_heads):
"""逆转transpose_qkv函数的操作"""
X = X.reshape(-1, num_heads, X.shape[1], X.shape[2])
X = X.permute(0, 2, 1, 3)
return X.reshape(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], -1)多头注意力
py
"""
多头注意力
"""
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens,
num_heads, dropout, bias=False, **kwargs):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.attention = DotProductAttention(dropout)
self.W_q = nn.Linear(query_size, num_hiddens, bias=bias)
self.W_k = nn.Linear(key_size, num_hiddens, bias=bias)
self.W_v = nn.Linear(value_size, num_hiddens, bias=bias)
self.W_o = nn.Linear(num_hiddens, num_hiddens, bias=bias)
def forward(self, queries, keys, values, valid_lens):
# queries,keys,values的形状:
# (batch_size,查询或者"键-值"对的个数,num_hiddens)
# valid_lens 的形状:
# (batch_size,)或(batch_size,查询的个数)
# 经过变换后,输出的queries,keys,values 的形状:
# (batch_size*num_heads,查询或者"键-值"对的个数,num_hiddens/num_heads)
queries = transpose_qkv(self.W_q(queries), self.num_heads)
keys = transpose_qkv(self.W_k(keys), self.num_heads)
values = transpose_qkv(self.W_v(values), self.num_heads)
if valid_lens is not None:
# 在轴0,将第一项(标量或者矢量)复制num_heads次,
# 然后如此复制第二项,然后诸如此类。
valid_lens = torch.repeat_interleave(
valid_lens, repeats=self.num_heads, dim=0)
# output的形状:(batch_size*num_heads,查询的个数,
# num_hiddens/num_heads)
output = self.attention(queries, keys, values, valid_lens)
# output_concat的形状:(batch_size,查询的个数,num_hiddens)
output_concat = transpose_output(output, self.num_heads)
return self.W_o(output_concat)Transformer-Encoder
- 单独的一个Transformer编码器块
py
"""Transformer编码器块"""
class EncoderBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens,
norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads,
dropout, use_bias=False, **kwargs):
super(EncoderBlock, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.attention = d2l.MultiHeadAttention(
key_size, query_size, value_size,
num_hiddens, num_heads, dropout,
use_bias)
self.addnorm1 = AddNorm(norm_shape, dropout)
self.ffn = PositionWiseFFN(
ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_hiddens)
self.addnorm2 = AddNorm(norm_shape, dropout)
def forward(self, X, valid_lens):
Y = self.addnorm1(X, self.attention(X, X, X, valid_lens))
return self.addnorm2(Y, self.ffn(Y))
- 使用Encoder Block组成Transformer Encoder部分
py
#@save
class TransformerEncoder(d2l.Encoder):
"""Transformer编码器"""
def __init__(self, vocab_size, key_size, query_size, value_size,
num_hiddens, norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens,
num_heads, num_layers, dropout, use_bias=False, **kwargs):
super(TransformerEncoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_hiddens = num_hiddens
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, num_hiddens)
self.pos_encoding = PositionalEncoding(num_hiddens, dropout)
self.blks = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(num_layers):
self.blks.add_module("block"+str(i),
EncoderBlock(key_size, query_size,
value_size, num_hiddens,
norm_shape, ffn_num_input,
ffn_num_hiddens,
num_heads, dropout, use_bias))
def forward(self, X, valid_lens, *args):
# 因为位置编码值在-1和1之间,
# 因此嵌入值乘以嵌入维度的平方根进行缩放,
# 然后再与位置编码相加。
X = self.pos_encoding(self.embedding(X) * math.sqrt(self.num_hiddens))
self.attention_weights = [None] * len(self.blks)
for i, blk in enumerate(self.blks):
X = blk(X, valid_lens)
"""
当前有i层
保存每一层的多头注意力的注意力权重
"""
self.attention_weights[i] = blk.attention.attention.attention_weights
return XTransformer-Decoder
- Decoder Block
py
class DecoderBlock(nn.Module):
"""解码器中第i个块"""
def __init__(self, key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens,
norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads,
dropout, i, **kwargs):
super(DecoderBlock, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.i = i
self.attention1 = MultiHeadAttention(
key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens, num_heads, dropout)
self.addnorm1 = AddNorm(norm_shape, dropout)
self.attention2 = MultiHeadAttention(
key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens, num_heads, dropout)
self.addnorm2 = AddNorm(norm_shape, dropout)
self.ffn = PositionWiseFFN(ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens,
num_hiddens)
self.addnorm3 = AddNorm(norm_shape, dropout)
def forward(self, X, state):
enc_outputs, enc_valid_lens = state[0], state[1]
# 训练阶段,输出序列的所有词元都在同一时间处理,
# 因此state[2][self.i]初始化为None。
# 预测阶段,输出序列是通过词元一个接着一个解码的,
# 因此state[2][self.i]包含着直到当前时间步第i个块解码的输出表示
if state[2][self.i] is None:
key_values = X
else:
key_values = torch.cat((state[2][self.i], X), axis=1)
state[2][self.i] = key_values
if self.training:
batch_size, num_steps, _ = X.shape
# dec_valid_lens的开头:(batch_size,num_steps),
# 其中每一行是[1,2,...,num_steps]
dec_valid_lens = torch.arange(
1, num_steps + 1, device=X.device).repeat(batch_size, 1)
else:
dec_valid_lens = None
# 自注意力
X2 = self.attention1(X, key_values, key_values, dec_valid_lens)
Y = self.addnorm1(X, X2)
# 编码器-解码器注意力。
# enc_outputs的开头:(batch_size,num_steps,num_hiddens)
Y2 = self.attention2(Y, enc_outputs, enc_outputs, enc_valid_lens)
Z = self.addnorm2(Y, Y2)
return self.addnorm3(Z, self.ffn(Z)), state- 使用Decoder-Block组成TransformerDecoder
- Decoder Block使用state[2]存储预测出来的Token,并在下次输入的时候加以使用
py
class TransformerDecoder(d2l.AttentionDecoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, key_size, query_size, value_size,
num_hiddens, norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens,
num_heads, num_layers, dropout, **kwargs):
super(TransformerDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_hiddens = num_hiddens
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, num_hiddens)
self.pos_encoding = PositionalEncoding(num_hiddens, dropout)
self.blks = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(num_layers):
self.blks.add_module("block"+str(i),
DecoderBlock(key_size, query_size, value_size, num_hiddens,
norm_shape, ffn_num_input, ffn_num_hiddens,
num_heads, dropout, i))
self.dense = nn.Linear(num_hiddens, vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, enc_valid_lens, *args):
"""
enc_outputs包括outputs和state
outputs里面是每个时间步的隐状态
state里面是最后一个时间步的(多层)隐藏状态
使用Encoder的state对Decoder进行初始化
"""
return [enc_outputs, enc_valid_lens, [None] * self.num_layers]
def forward(self, X, state):
X = self.pos_encoding(
self.embedding(X) * math.sqrt(self.num_hiddens))
self._attention_weights = [[None] * len(self.blks) for _ in range (2)]
for i, blk in enumerate(self.blks):
X, state = blk(X, state)
# 解码器自注意力权重
self._attention_weights[0][
i] = blk.attention1.attention.attention_weights
# "编码器-解码器"自注意力权重
self._attention_weights[1][
i] = blk.attention2.attention.attention_weights
return self.dense(X), state
@property
def attention_weights(self):
return self._attention_weightsEncoder-Decoder
py
class EncoderDecoder(nn.Module):
"""编码器-解码器架构的基类"""
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, **kwargs):
super(EncoderDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self, enc_X, dec_X, *args):
enc_outputs = self.encoder(enc_X, *args)
dec_state = self.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, *args)
return self.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)Transformer Train Test
Transformer训练过程:
- Encoder提供上下文信息,Decoder用于使用采用上下文信息和正确的预测结果(Teacher Forcing)进行下一步的预测
- 注意Decoder只能使用当前预测Token之前的Token信息进行下一步的预测,不能使用之后的Token
Transformer测试过程:
- Encoder提供上下文信息,Decoder用于使用Bos作为开始标志结合上下文信息进行解码
训练代码
py
num_hiddens, num_layers, dropout, batch_size, num_steps = 32, 2, 0.1, 64, 10
lr, num_epochs, device = 0.005, 200, d2l.try_gpu()
ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads = 64, 4
train_iter, src_vocab, tgt_vocab = d2l.load_data_nmt(batch_size, num_steps)
encoder = TransformerEncoder(
len(src_vocab), num_hiddens, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout)
decoder = TransformerDecoder(
len(tgt_vocab), num_hiddens, ffn_num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout)
net = EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder)
train_seq2seq(net, train_iter, lr, num_epochs, tgt_vocab, device)- 训练时候传入的 data_iter 引入了< eos >
- enc_X需要< eos >
- dec_X需要< eos >和< bos >
- 训练阶段采用强制教学,使用正确答案进行训练
- 第一次初始化网络使用xavier
- 损失函数使用MaskedSoftmaxCELoss
py
def train_seq2seq(net, data_iter, lr, num_epochs, tgt_vocab, device):
"""训练序列到序列模型"""
net.initialize(init.Xavier(), force_reinit=True, ctx=device)
trainer = gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(), 'adam',
{'learning_rate': lr})
loss = MaskedSoftmaxCELoss()
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', ylabel='loss',
xlim=[10, num_epochs])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
timer = Timer()
metric = Accumulator(2) # 训练损失求和,词元数量
for batch in data_iter:
X, X_valid_len, Y, Y_valid_len = [
x.as_in_ctx(device) for x in batch]
bos = np.array([tgt_vocab['<bos>']] * Y.shape[0],
ctx=device).reshape(-1, 1)
dec_input = np.concatenate([bos, Y[:, :-1]], 1) # 强制教学
with autograd.record():
Y_hat, _ = net(X, dec_input, X_valid_len)
l = loss(Y_hat, Y, Y_valid_len)
l.backward()
d2l.grad_clipping(net, 1)
num_tokens = Y_valid_len.sum()
trainer.step(num_tokens)
metric.add(l.sum(), num_tokens)
if (epoch + 1) % 10 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (metric[0] / metric[1],))
print(f'loss {metric[0] / metric[1]:.3f}, {metric[1] / timer.stop():.1f} '
f'tokens/sec on {str(device)}')测试代码
py
engs = ['go .', "i lost .", 'he\'s calm .', 'i\'m home .']
fras = ['va !', 'j\'ai perdu .', 'il est calme .', 'je suis chez moi .']
for eng, fra in zip(engs, fras):
translation, dec_attention_weight_seq = d2l.predict_seq2seq(
net, eng, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps, device, True)
print(f'{eng} => {translation}, ',
f'bleu {d2l.bleu(translation, fra, k=2):.3f}')- 测试阶段,输入的src_tokens
- 首先对src_tokens加上eos
- 然后enc_X = src_tokens
- 然后dec_X = src_tokens + < bos >
- 使用预测的最高可能性的词元,作为解码器下一个时间步的输入
py
def predict_seq2seq(net, src_sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps,
device, save_attention_weights=False):
"""序列到序列模型的预测"""
src_tokens = src_vocab[src_sentence.lower().split(' ')] + [src_vocab['<eos>']]
enc_valid_len = np.array([len(src_tokens)], ctx=device)
src_tokens = d2l.truncate_pad(src_tokens, num_steps, src_vocab['<pad>'])
enc_X = np.expand_dims(np.array(src_tokens, ctx=device), axis=0)
enc_outputs = net.encoder(enc_X, enc_valid_len)
dec_state = net.decoder.init_state(enc_outputs, enc_valid_len)
# 这里是很多的<bos>没有其他内容
dec_X = np.expand_dims(np.array([tgt_vocab['<bos>']], ctx=device),
axis=0)
output_seq, attention_weight_seq = [], []
for _ in range(num_steps):
Y, dec_state = net.decoder(dec_X, dec_state)
# 我们使用具有预测最高可能性的词元,作为解码器在下一时间步的输入
dec_X = Y.argmax(axis=2)
pred = dec_X.squeeze(axis=0).astype('int32').item()
# 保存注意力权重(稍后讨论)
if save_attention_weights:
attention_weight_seq.append(net.decoder.attention_weights)
# 一旦序列结束词元被预测,输出序列的生成就完成了
if pred == tgt_vocab['<eos>']:
break
output_seq.append(pred)
return ' '.join(tgt_vocab.to_tokens(output_seq)), attention_weight_seq评估指标BLEU
使用2、3、4连续的序列的重叠的概率、预测序列和真实序列的长度计算BLEU指标 ,代码就是对公式的复现

py
"""
计算BLEU
"""
def bleu(pred_seq, label_seq, k):
pred_tokens, label_tokens = pred_seq.split(' '), label_seq.split(' ')
len_pred, len_label = len(pred_tokens), len(label_tokens)
score = math.exp(min(0, 1 - len_label / len_pred))
for n in range(1, k + 1):
num_matches, label_subs = 0, collections.defaultdict(int)
for i in range(len_label - n + 1):
label_subs[' '.join(label_tokens[i: i + n])] += 1
for i in range(len_pred - n + 1):
if label_subs[' '.join(pred_tokens[i: i + n])] > 0:
num_matches += 1
label_subs[' '.join(pred_tokens[i: i + n])] -= 1
score *= math.pow(num_matches / (len_pred - n + 1), math.pow(0.5, n))
return score