行为型模式(二):策略模式、命令模式
- 3.策略模式(Strategy)
-
- [3.1 示例](#3.1 示例)
-
- [3.1.1 定义策略接口](#3.1.1 定义策略接口)
- [3.1.2 实现具体策略](#3.1.2 实现具体策略)
- [3.1.3 定义上下文类](#3.1.3 定义上下文类)
- [3.1.4 客户端代码](#3.1.4 客户端代码)
- [3.1.5 输出结果](#3.1.5 输出结果)
- [3.2 总结](#3.2 总结)
-
- [3.2.1 优点](#3.2.1 优点)
- [3.2.2 缺点](#3.2.2 缺点)
- 4.命令模式(Command)
-
- [4.1 组成部分](#4.1 组成部分)
- [4.2 示例](#4.2 示例)
-
- [4.2.1 命令接口](#4.2.1 命令接口)
- [4.2.2 具体命令实现](#4.2.2 具体命令实现)
- [4.2.3 接收者](#4.2.3 接收者)
- [4.2.4 调用者](#4.2.4 调用者)
- [4.2.5 客户端](#4.2.5 客户端)
- [4.2.6 输出结果](#4.2.6 输出结果)
- [4.3 总结](#4.3 总结)
-
- [4.3.1 优点](#4.3.1 优点)
- [4.3.2 缺点](#4.3.2 缺点)
3.策略模式(Strategy)
策略模式(Strategy)是一种行为设计模式,它使你能在运行时改变对象的行为。下面是策略模式的几个关键点:
- 定义一组算法:策略模式定义了一组可互换的算法(或行为)。这些算法封装在独立的类中,每个类实现一个特定的算法。
- 封装变化:将变化的部分从不变的部分中分离出来,封装成独立的类,这样可以更容易地扩展和维护。
- 运行时选择算法:客户端可以根据需要在运行时选择不同的算法(策略)来执行特定任务。
3.1 示例
假设你正在开发一个电商系统,需要根据不同的促销策略计算订单的最终价格。你可以定义一个 PromotionStrategy 接口,然后为不同的促销策略实现该接口,例如:
FixedDiscountStrategy:固定金额折扣PercentageDiscountStrategy:百分比折扣NoDiscountStrategy:无折扣
在订单类中,你可以使用 PromotionStrategy 接口来计算最终价格,并在运行时根据需要选择不同的策略。
3.1.1 定义策略接口
首先,定义一个策略接口 PromotionStrategy,该接口声明了一个计算折扣价格的方法 calculateDiscount。
java
public interface PromotionStrategy {
double calculateDiscount(double originalPrice);
}3.1.2 实现具体策略
接下来,实现不同的促销策略,例如 固定金额折扣 、百分比折扣 和 无折扣。
java
public class FixedDiscountStrategy implements PromotionStrategy {
private double discountAmount;
public FixedDiscountStrategy(double discountAmount) {
this.discountAmount = discountAmount;
}
@Override
public double calculateDiscount(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice - discountAmount;
}
}
public class PercentageDiscountStrategy implements PromotionStrategy {
private double discountRate;
public PercentageDiscountStrategy(double discountRate) {
this.discountRate = discountRate;
}
@Override
public double calculateDiscount(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice * (1 - discountRate);
}
}
public class NoDiscountStrategy implements PromotionStrategy {
@Override
public double calculateDiscount(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice;
}
}FixedDiscountStrategy、PercentageDiscountStrategy 和 NoDiscountStrategy 实现了 PromotionStrategy 接口,分别实现了固定金额折扣、百分比折扣和无折扣。
3.1.3 定义上下文类
上下文类 Order 使用 PromotionStrategy 接口来计算最终价格。上下文类可以在运行时选择不同的策略。
java
public class Order {
private double originalPrice;
private PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy;
public Order(double originalPrice, PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy) {
this.originalPrice = originalPrice;
this.promotionStrategy = promotionStrategy;
}
public double getFinalPrice() {
return promotionStrategy.calculateDiscount(originalPrice);
}
public void setPromotionStrategy(PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy) {
this.promotionStrategy = promotionStrategy;
}
}3.1.4 客户端代码
客户端代码可以根据需要选择不同的促销策略,并计算订单的最终价格。
java
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double originalPrice = 100.0;
// 固定金额折扣
PromotionStrategy fixedDiscountStrategy = new FixedDiscountStrategy(10.0);
Order order1 = new Order(originalPrice, fixedDiscountStrategy);
System.out.println("Fixed Discount: " + order1.getFinalPrice());
// 百分比折扣
PromotionStrategy percentageDiscountStrategy = new PercentageDiscountStrategy(0.2);
Order order2 = new Order(originalPrice, percentageDiscountStrategy);
System.out.println("Percentage Discount: " + order2.getFinalPrice());
// 无折扣
PromotionStrategy noDiscountStrategy = new NoDiscountStrategy();
Order order3 = new Order(originalPrice, noDiscountStrategy);
System.out.println("No Discount: " + order3.getFinalPrice());
// 动态更改策略
order1.setPromotionStrategy(percentageDiscountStrategy);
System.out.println("Changed to Percentage Discount: " + order1.getFinalPrice());
}
}客户端代码创建不同的策略对象,并将它们传递给 Order 对象,计算最终价格。还可以在运行时动态更改策略。
3.1.5 输出结果
plain
Fixed Discount: 90.0
Percentage Discount: 80.0
No Discount: 100.0
Changed to Percentage Discount: 80.03.2 总结
3.2.1 优点
- 灵活性:可以在运行时动态选择算法。
- 扩展性:新增策略时,只需实现新的策略类,无需修改现有代码。
- 代码复用:不同的上下文可以共享相同的策略。
3.2.2 缺点
- 类的数量增加:每增加一个策略,就需要增加一个类。
- 客户端需要知道所有策略:客户端需要了解所有可用的策略,并选择合适的策略。
4.命令模式(Command)
命令模式(Command)是一种行为设计模式,它将请求封装成一个对象,从而使你能够用不同的请求、队列或者请求日志来参数化其他对象。命令模式也支持可撤销的操作。
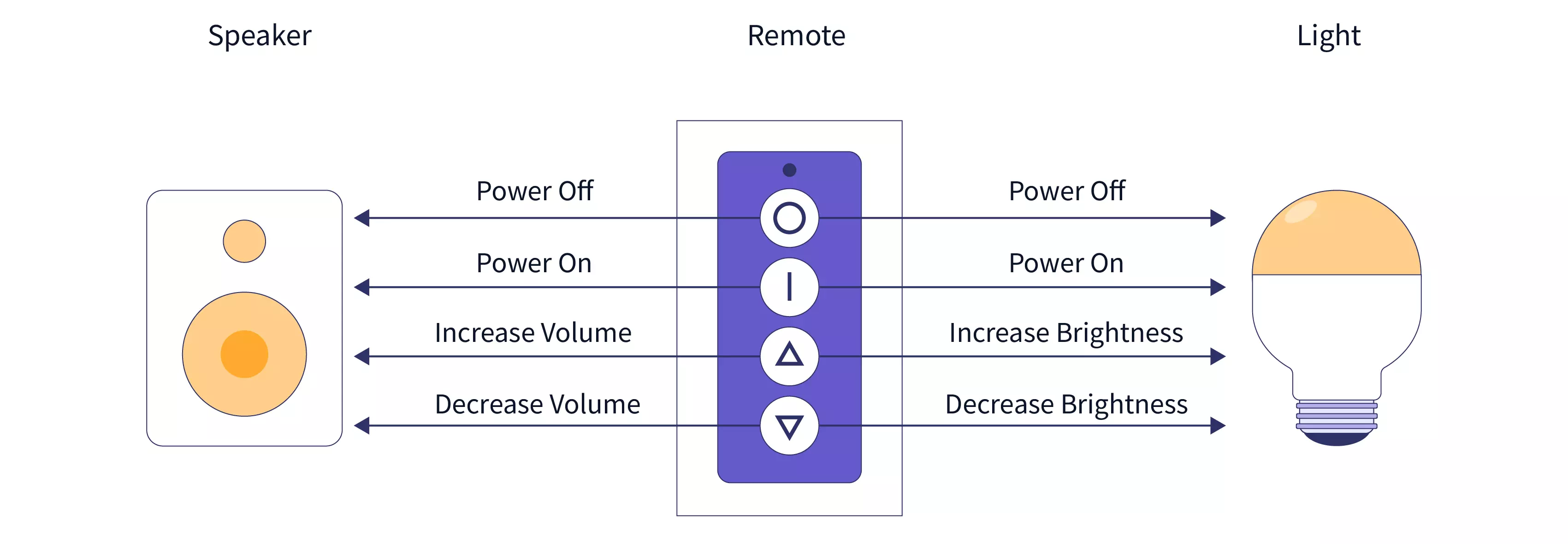
4.1 组成部分
- 命令对象:封装了一个请求,包括执行该请求所需的所有信息(例如,接收者、方法、参数等)。
- 接收者:实际执行命令的对象。
- 调用者:请求的发起者,它将命令对象传递给接收者。
- 客户端:创建命令对象并将其设置到调用者中。
4.2 示例
假设我们正在开发一个智能家居系统,用户可以通过 遥控器 控制不同的设备(如 灯、风扇 等)。我们可以使用命令模式来实现这个功能。
4.2.1 命令接口
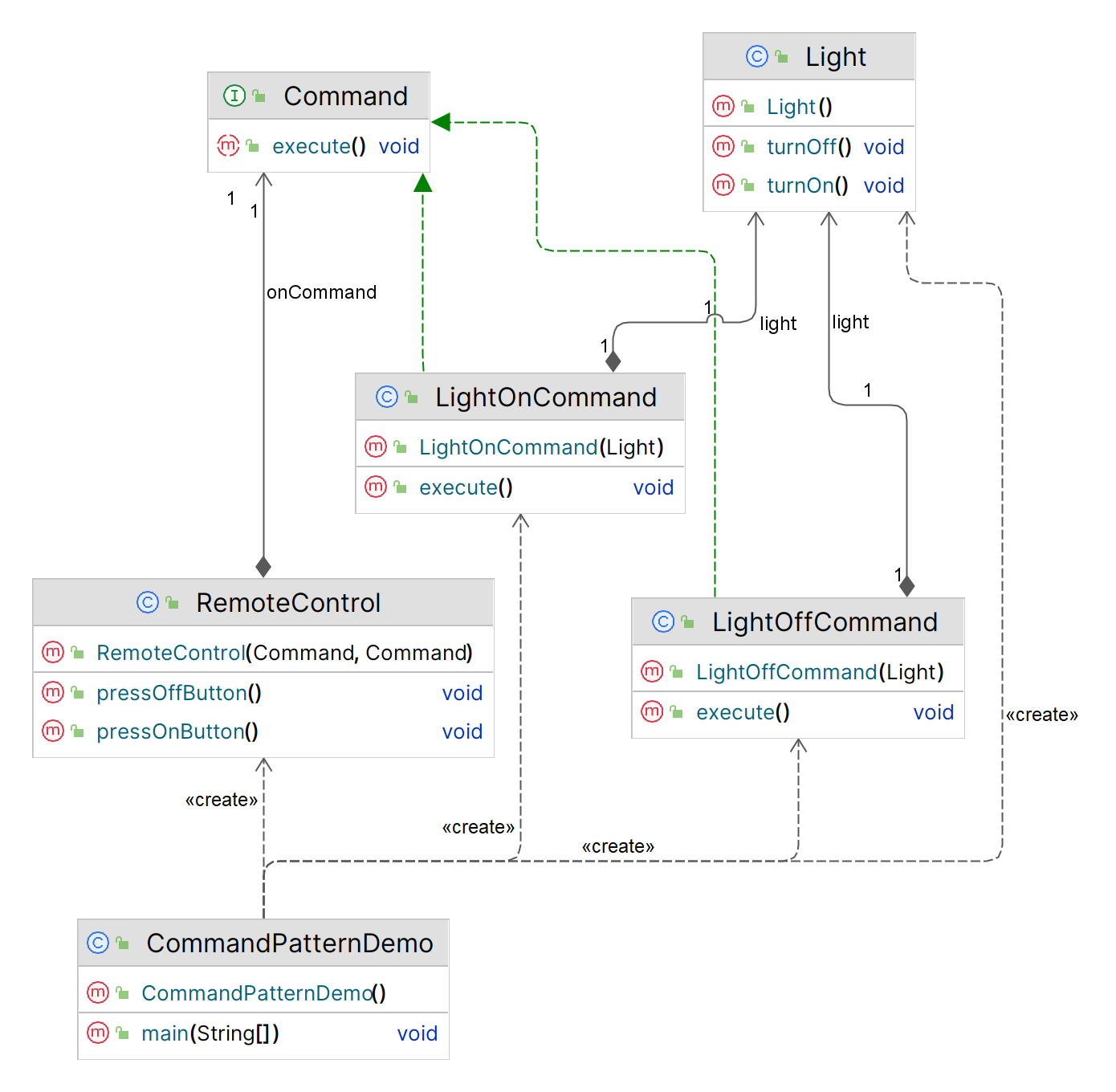
首先,定义一个命令接口 Command,声明一个执行命令的方法 execute。
java
public interface Command {
void execute();
}4.2.2 具体命令实现
接下来,实现不同的命令,例如控制灯的开关和控制风扇的开关。
java
// 开灯
public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOn();
}
}
// 关灯
public class LightOffCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOff();
}
}
// 开风扇
public class FanOnCommand implements Command {
private Fan fan;
public FanOnCommand(Fan fan) {
this.fan = fan;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
fan.turnOn();
}
}
// 关闭风扇
public class FanOffCommand implements Command {
private Fan fan;
public FanOffCommand(Fan fan) {
this.fan = fan;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
fan.turnOff();
}
}LightOnCommand、LightOffCommand、FanOnCommand 和 FanOffCommand 实现了 Command 接口,分别控制灯和风扇的开关。
4.2.3 接收者
接收者是 实际执行命令的对象,例如灯和风扇。
java
public class Light {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Light is on");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("Light is off");
}
}
public class Fan {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Fan is on");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("Fan is off");
}
}Light 和 Fan 是实际执行命令的对象。
4.2.4 调用者
调用者是 请求的发起者,它将命令对象传递给接收者。
java
public class RemoteControl {
private Command onCommand;
private Command offCommand;
public RemoteControl(Command onCommand, Command offCommand) {
this.onCommand = onCommand;
this.offCommand = offCommand;
}
public void pressOnButton() {
onCommand.execute();
}
public void pressOffButton() {
offCommand.execute();
}
}RemoteControl 是请求的发起者,它将命令对象传递给接收者并执行命令。
4.2.5 客户端
客户端代码 创建不同的命令对象 ,并将它们设置到 RemoteControl 中,通过调用 RemoteControl 的方法来执行命令。
java
public class CommandPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Light light = new Light();
Fan fan = new Fan();
Command lightOn = new LightOnCommand(light);
Command lightOff = new LightOffCommand(light);
Command fanOn = new FanOnCommand(fan);
Command fanOff = new FanOffCommand(fan);
RemoteControl remoteControl = new RemoteControl(lightOn, lightOff);
remoteControl.pressOnButton(); // 输出: Light is on
remoteControl.pressOffButton(); // 输出: Light is off
remoteControl = new RemoteControl(fanOn, fanOff);
remoteControl.pressOnButton(); // 输出: Fan is on
remoteControl.pressOffButton(); // 输出: Fan is off
}
}
4.2.6 输出结果
plain
Light is on
Light is off
Fan is on
Fan is off通过这个例子,你可以看到命令模式如何将请求的发送者和接收者解耦,使代码更加灵活和可扩展。
4.3 总结
4.3.1 优点
- 解耦:命令模式将请求的发送者和接收者解耦,使两者不直接依赖。
- 扩展性:可以很容易地增加新的命令,而不需要修改现有的代码。
- 支持撤销操作:命令对象可以存储执行前的状态,从而支持撤销操作。
4.3.2 缺点
- 类的数量增加:每个命令都需要一个具体的命令类。
- 复杂性增加:引入了多个对象和接口,可能会使系统变得更复杂。