定时器的功能
在Java中,定时器用于在预定的时间执行任务,两种方式可以实现定时功能:Timer和TimerTask类,还有ScheduledExecutorService接口。
1.Timer和TimerTask
TimerTask是一个抽象类,需要创建它的子类并重写run()方法,这个方法可以在定时任务被执行时调用,Timer用于调度任务。
java
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello run");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
MyTimerTask task = new MyTimerTask();
System.out.println("hello main");
timer.schedule(task, 1000, 2000);
}
}其中Java的Timer类中,schedule方法用于安排任务的执行,schdule(TimeTask task,long delay):其中task是要执行的任务,delay是任务首次执行的时间,单位是毫秒,且该任务只能被执行一次;schedule(TimeTask task,long delay,long period):period是任务连续执行之间的时间间隔,单位是毫秒,表示该任务首次执行是delay毫秒,之后每隔period毫秒重复执行。
当然,也可以使用匿名内部类的写法.TimerTask()创建了一个TimerTask的匿名内部类实例
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 3000");
}
},3000);
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 2000");
}
},2000);
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 1000");
}
},1000);
System.out.println("hello main");
}Timer和TimerTask遇到的问题
-
单线程执行:Timer使用单个后台程序来顺序地执行所有的定时任务,这意味着如果一个任务执行时间过长,那么它会延迟其他任务执行,如果一个任务抛出未捕获异常,那么整个Timer将会被终止,并且不会执行任何后续任务。
javaimport java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; public class TimerExample { public static void main(String[] args) { Timer timer = new Timer(); DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); // 执行时间过长的任务 TimerTask longRunningTask = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { String formattedDateTime = getCurrentTime(formatter); System.out.println("长任务开始: " + formattedDateTime); try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } formattedDateTime = getCurrentTime(formatter); System.out.println("长任务结束: " + formattedDateTime); } }; // 正常的任务 TimerTask normalTask = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { String formattedDateTime = getCurrentTime(formatter); System.out.println("正常任务: " + formattedDateTime); } }; // 抛出异常的任务 TimerTask exceptionThrowingTask = new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { String formattedDateTime = getCurrentTime(formatter); System.out.println("抛异常任务开始时间 " + formattedDateTime); throw new RuntimeException("这是一个未抛出的异常"); } }; // 安排任务 timer.schedule(longRunningTask, 0); timer.schedule(normalTask, 2000); timer.schedule(exceptionThrowingTask, 4000); try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } timer.cancel(); } private static String getCurrentTime(DateTimeFormatter formatter) { return LocalDateTime.now().format(formatter); } }长任务立即开始执行,并在5s后完成,正常任务本再2s后执行,但是由于长任务占据线程,被延迟到长任务完成后执行,抛异常任务本再4s执行,但是长任务占用线程,在长任务和正常任务完成后执行,没有执行抛出异常时,Timer会被终止后续任务不在执行
-
对系统时间敏感:系统时间被任务调整,那么会影响到Timer的调度逻辑,可能导致错过执行时间或者提前执行。
-
不适合长时间运行任务:如果任务执行时间超过了两次任务间隔的时间,那么下一层任务执行将会被推迟,直到当前任务完成,可能导致任务积压。
-
缺乏灵活性:Timer不支持复杂的调度需求。
-
资源管理:不取消不再需要的TimeTask或者关闭不再使用Timer,可能导致资源泄露
-
线程安全问题:Timer是线程安全的,但是TimerTask是非线程安全的。
解释:TimerTask本身并不是非线程安全的,而是Timer的设计和使用方式导致潜在的线程安全问题,当涉及到共享资源或者状态时,可能存在线程安全问题。
2.ScheduledExecutorService接口
ScheduledExecutorService就是为了解决Timer&TimerTask的问题。它基于多线程机制,因此任务之间不会相互影响,内部使用了延时队列,基于等待/唤醒机制实现,因此CPU不会一直繁忙,同时多线程带来的CPU资源复用极大的提升性能
java
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class MyScheduledTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello run");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
MyScheduledTask task = new MyScheduledTask();
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("hello main");
}
}MyScheduledTask实现了Runnable接口,必须要重写Runnable的run()方法ScheduledExecutorService是ExecutorService的一个子接口,用于调度任务定时执行,当使用ScheduledExecutorService时,即使没有显式创建一个线程池 ,Java并发API内部也会管理一个线程池执行定时任务。(如上面的代码)
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)创建一个具有指定核心线程数,还可以Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()创建一个单线程ScheduledExecutorService,用于任务调度。
显式创建线程池是直接使用线程池的实现类(例如:ThreadPoolExecutor)来创建和管理线程池的过程,如下:
java
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
corePoolSize,
maximumPoolSize,
keepAliveTime,
unit,
workQueue
);ScheduledExecutorService接口中的四个方法

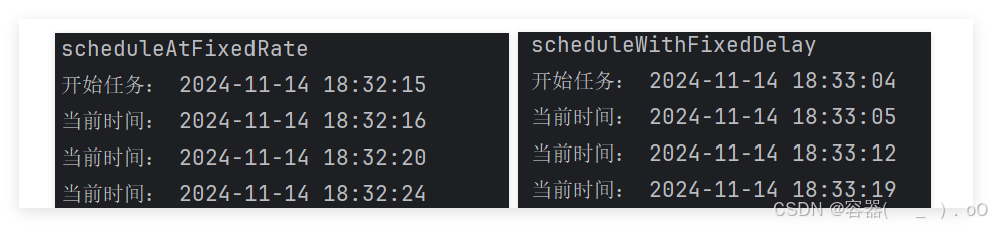
scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay的区别
scheduleAtFixedRate()以固定的(period)频率执行任务,如果任务执行时间超过了peirod,则下一个任务会在前一个任务完成后立即开始,不会等一个周期。如果短于period,则会在下一个period到达时执行任务。
scheduleWithFixedDelay在前一个任务完成后,等待一个固定的延迟时间,然后再执行下一个任务,因此执行任务时间和延时相加。
java
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(8);
Runnable task = () -> {
try {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDateTime = now.format(formatter);
System.out.println("当前时间: " + formattedDateTime);
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// System.out.println("Fixed Delay Task at " + System.currentTimeMillis());
};
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDateTime = now.format(formatter);
System.out.println("开始任务: " + formattedDateTime);
// scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(task, 1, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, 1, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
Thread.sleep(100000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
scheduler.shutdown();
}
模拟实现定时器
1.创建一个类,表示一个任务
任务中含有开始时间以及是什么任务
java
class MyTimerTask2 {
// 持有成员的方式
private Runnable task;
private long time;
public MyTimerTask2 (Runnable task,long time) {
this.task = task;
this.time = time;
}
}2.管理多个任务
由于定时是在某一个未来的时间的进行任务的开启,那么可以使用优先级队列对任务的时间按照任务的时间进行排序,那么就需要比较规则。这里是按照执行时间的先后顺序作为比较规则,需求是能够时间最小的元素能够在队首(小根堆)可以得到如下代码:
java
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask2> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask2 o) {
// 负数:this.time < o.time
// 0 :this.time = o.time
// 正数:this.time > o.time
return Long.compare(this.time,o.time);
}3.实现schedule方法,把任务添加到队列
java
public void schedule(Runnable task,long delay) {
// 不是阻塞队列,不能用put
MyTimerTask2 timerTask2 = new MyTimerTask2(task,System.currentTimeMillis()+delay);
queue.offer(timerTask2);
}4.额外创建一个线程,负责执行队列中的任务
和线程池不同,线程池是只要队列不空,就立即取任务并执行,此处需要看队首元素的时间,时间到了才能执行。
上述的准备工作完成,现在开始创建一个线程去执行任务,如果队列不空,取出队首元素,如果当前任务时间大于系统时间,表明时机未到,不进行执行以及弹出队列。代码如下:
java
public MyTimer() {
// 创建线程,负责执行队列中的任务
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
while(true) {
// 取队首元素
if(!queue.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
MyTimerTask2 task2 = queue.peek();
if(task2.getTime() > System.currentTimeMillis()) {
// 当前任务时间大于比系统时间大,执行时机未到
continue;
}else {
task2.run();
queue.poll();
}
}
});
t.start();
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void run() {
task.run();
}但是当前调用schdule是一个线程,定时器内部又有一个线程,多线程操作一个队列,涉及到了线程安全问题,因此要加锁,对任务进队列和定时器内部进行加锁;
但是可能有关疑问,MyTimer()不是构造方法吗,构造方法本身可以synchronized,但是这里不能这样子写,要保护的逻辑在run里面,和构造方法不是同一个方法
如果此时执行,那么cpu就会高速运转,导致这个情况的原因是下面的代码:

队列空之后,一直在忙等,但是消耗大量CPU资源,为了避免这种情况,可以使用wait 和notify 机制来让线程在队列为空时进入等待状态,而不是忙等
