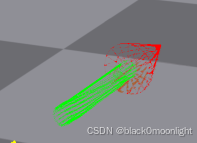
在这里发布一个ISAAC GYM可以使用的箭头绘制类。
gymutil默认有WireframeBoxGeometry,WireframeBBoxGeometry, WireframeSphereGeometry三个线段集生成函数,可以绘制盒子和球体。绘制函数分别有draw_lines和draw_line。
同理,使用以下方法绘制3D箭头:
python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
------------------------------------------------------------------
@File Name: WireframeGeometry
@Created: 2024 2024/11/22 16:01
@Software: PyCharm
@Author: Jiayu ZENG
@Email: jiayuzeng@asagi.waseda.jp
@Description:
------------------------------------------------------------------
'''
from __future__ import print_function, division, absolute_import
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
import math
import numpy as np
import argparse
from bisect import bisect
from isaacgym import gymtorch, gymapi, gymutil
import numpy as np
import math
class WireframeArrowGeometry(gymutil.LineGeometry):
def __init__(self, start_point, direction, length=1.0, arrow_head_length=0.2, arrow_head_width=0.1, shaft_radius=0.05, shaft_segments=8, pose=None, color=None, color2=None):
if color is None:
color = (1, 0, 0)
if color2 is None:
color2 = color
# Normalize direction
direction = np.array(direction, dtype=float)
# Calculate main arrow shaft endpoint
shaft_end_point = start_point + length * direction
arrow_tip = start_point + (length+arrow_head_length) * direction
# Arrow shaft
verts = []
colors = []
# Generate perpendicular vectors to direction for shaft
perp1 = np.cross(direction, np.array([1, 0, 0]))
if np.linalg.norm(perp1) < 1e-6:
perp1 = np.cross(direction, np.array([0, 1, 0]))
perp1 = perp1 / np.linalg.norm(perp1) * shaft_radius
perp2 = np.cross(direction, perp1)
perp2 = perp2 / np.linalg.norm(perp2) * shaft_radius
# Generate shaft lines in a circular pattern
angle_step = 2 * math.pi / shaft_segments
shaft_base_points = []
arrow_base_points = []
for i in range(shaft_segments):
angle = i * angle_step
next_angle = (i + 1) * angle_step
offset1 = math.cos(angle) * perp1 + math.sin(angle) * perp2
offset2 = math.cos(next_angle) * perp1 + math.sin(next_angle) * perp2
start_circle = start_point + offset1
end_circle = shaft_end_point + offset1
shaft_base_points.append(end_circle)
verts.append((start_circle, end_circle))
colors.append(color)
verts.append((start_circle, start_point + offset2))
colors.append(color)
verts.append((end_circle, shaft_end_point + offset2))
colors.append(color)
# Arrow head base point
arrow_base = shaft_end_point
# Generate perpendicular vectors to direction for arrow head
perp1_head = perp1 / shaft_radius * arrow_head_width
perp2_head = perp2 / shaft_radius * arrow_head_width
# Generate arrow head lines to represent a cone
for i in range(shaft_segments):
angle = i * angle_step
next_angle = (i + 1) * angle_step
offset1 = math.cos(angle) * perp1_head + math.sin(angle) * perp2_head
offset2 = math.cos(next_angle) * perp1_head + math.sin(next_angle) * perp2_head
base_point1 = arrow_base + offset1
base_point2 = arrow_base + offset2
arrow_base_points.append(base_point1)
# Lines from tip to base circle
verts.append((arrow_tip, base_point1))
colors.append(color2)
# Lines around the base circle
verts.append((base_point1, base_point2))
colors.append(color2)
# Connect corresponding points on the shaft end and arrow base
for shaft_point, arrow_point in zip(shaft_base_points, arrow_base_points):
verts.append((shaft_point, arrow_point))
colors.append(color2)
# Convert verts and colors to numpy arrays
num_lines = len(verts)
verts_np = np.empty((num_lines, 2), gymapi.Vec3.dtype)
colors_np = np.empty(num_lines, gymapi.Vec3.dtype)
for idx, (v_start, v_end) in enumerate(verts):
verts_np[idx][0] = (v_start[0], v_start[1], v_start[2])
verts_np[idx][1] = (v_end[0], v_end[1], v_end[2])
colors_np[idx] = colors[idx]
# Apply pose transformation if provided
if pose is None:
self.verts = verts_np
else:
self.verts = pose.transform_points(verts_np)
self._colors = colors_np
def vertices(self):
return self.verts
def colors(self):
return self._colors同样调用gymutil.draw_lines绘制。以下代码仅作参考。
python
start_point = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
direction[2] = start_point[2]
color = (0, 1, 0)
color2 = (1, 0, 0)
length *= 0.5
shaft_radius = 0.02
shaft_segments = 16
arrow_head_length = 0.2
arrow_head_width = shaft_radius * 3
arrow = WireframeArrowGeometry(start_point, direction, length, arrow_head_length, arrow_head_width,
shaft_radius, shaft_segments, color=color, color2=color2)
sphere_pose = gymapi.Transform(gymapi.Vec3(pos[0],
pos[1],
pos[2] + 0.2), r=None)
gymutil.draw_lines(arrow, self.gym, self.viewer, env, sphere_pose)绘制效果: