简介说明
spring-data-elasticsearch是比较好用的一个elasticsearch客户端,本文介绍如何使用它来操作ES。本文使用spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch,它内部会引入spring-data-elasticsearch。
Spring Data ElasticSearch有下边这几种方法操作ElasticSearch:
ElasticsearchRepository (传统的方法,可以使用)
ElasticsearchRestTemplate (推荐使用。基于RestHighLevelClient)
ElasticsearchTemplate (ES7中废弃,不建议使用。基于TransportClient)
RestHighLevelClient (推荐度低于ElasticsearchRestTemplate,因为API不够高级)
TransportClient(ES7中废弃,不建议使用)
版本改动
spring-data-elasticsearch:4.0的比较重大的修改:4.0对应支持ES版本为7.6.2,并且弃用 了对TransportClient的使用(默认使用High Level REST Client)。
ES从7.x版本开始弃用 了对TransportClient 的使用,并将会在8.0版本开始完全删除TransportClient。
TransportClient:使用9300端口通过TCP与ES连接,不好用,且有高并发的问题。
High Level REST Client:使用9200端口通过HTTP与ES连接,很好用,性能高。
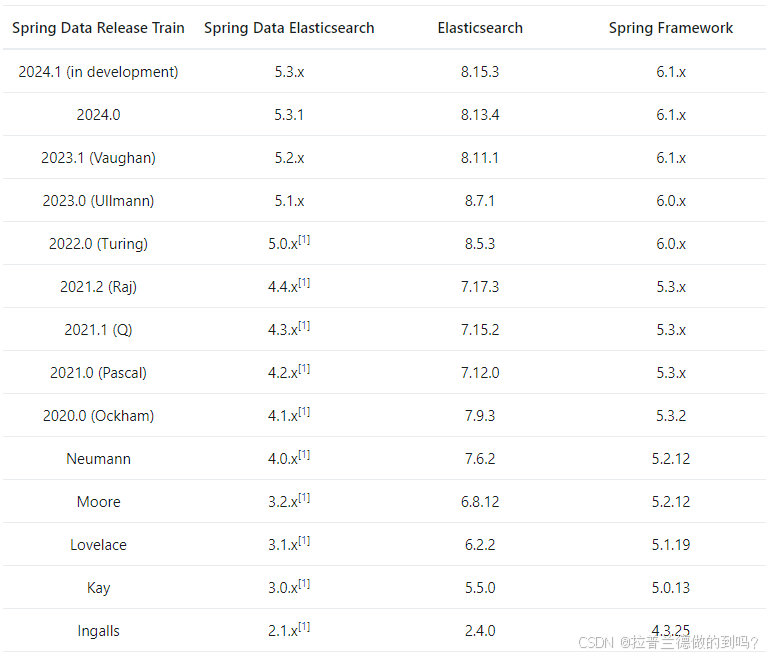
版本对应
Elasticsearch 对于版本的兼容性要求很高,大版本之间是不兼容的。
spring-data-elasticsearch与ES、SpringBoot的对应关系如下:
依赖及配置
XML
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>配置(application.yml )
XML
spring:
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://127.0.0.1:9200
# username: xxx
# password: yyy
# connection-timeout: 1
# read-timeout: 30实例索引结构:
XML
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 5,
"number_of_replicas": 1
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type":"long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"author":{
"type": "text"
},
"category":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"createTime": {
"type": "date",
"format":"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS||yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS||yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||epoch_millis"
},
"updateTime": {
"type": "date",
"format":"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS||yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS||yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||epoch_millis"
},
"status":{
"type":"integer"
},
"serialNum": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}Entity
XML
package com.example.demo.entity;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.DateFormat;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
@Document(indexName = "blog", shards = 1, replicas = 1)
public class Blog {
//此项作为id,不会写到_source里边。
@Id
private Long blogId;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String title;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String content;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String author;
//博客所属分类。
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String category;
//0: 未发布(草稿) 1:已发布 2:已删除
@Field(type = FieldType.Integer)
private int status;
//序列号,用于给外部展示的id
@Field(type = FieldType.Keyword)
private String serialNum;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")
@Field(type= FieldType.Date, format= DateFormat.custom, pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")
private Date createTime;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")
@Field(type=FieldType.Date, format=DateFormat.custom, pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS")
private Date updateTime;
}@Document
用于定义一个类为 Elasticsearch 文档的映射。
-
indexName
-
作用:指定文档的索引名称。
-
示例 :
@Document(indexName = "product") -
说明:索引名称在 Elasticsearch 中是唯一的,用于存储和检索文档。
-
-
type
-
作用:指定文档的类型。
-
示例 :
@Document(type = "product") -
说明:类型在 Elasticsearch 中用于对文档进行分类。在 Elasticsearch 7.x 及更高版本中,类型已被弃用,建议使用单类型索引。
-
-
shards
-
作用:指定索引的分片数。
-
示例 :
@Document(shards = 5) -
说明:分片是 Elasticsearch 分布式存储的基本单位,分片数决定了索引的分布和性能。
-
-
replicas
-
作用:指定索引的副本数。
-
示例 :
@Document(replicas = 1) -
说明:副本是分片的备份,用于提高数据的可用性和查询性能。
-
-
createIndex
-
作用:指定是否在启动时自动创建索引。
-
示例 :
@Document(createIndex = true) -
说明 :如果设置为
true,Spring Data Elasticsearch 会在应用启动时自动创建索引。
-
-
refreshInterval
-
作用:指定索引的刷新间隔。
-
示例 :
@Document(refreshInterval = "1s") -
说明:刷新间隔决定了索引数据何时对搜索可见。
-
-
versionType
-
作用:指定文档的版本类型。
-
示例 :
@Document(versionType = VersionType.EXTERNAL) -
说明 :版本类型用于控制文档的版本管理,支持
INTERNAL和EXTERNAL两种类型。
-
-
useServerConfiguration
-
作用:指定是否使用服务器的配置。
-
示例 :
@Document(useServerConfiguration = true) -
说明 :如果设置为
true,Spring Data Elasticsearch 会使用 Elasticsearch 服务器的配置,而不是应用中的配置。
-
@Id
@Id 是 Spring Data Elasticsearch 中的一个注解,用于标识实体类中的主键字段。在 Elasticsearch 中,每个文档都有一个唯一的标识符(ID),@Id 注解用于指定这个标识符字段。
@Field
-
name
-
作用:指定 Elasticsearch 文档中的字段名称。
-
示例 :
@Field(name = "product_name") -
说明 :如果未指定
name,则使用 Java 字段名作为 Elasticsearch 字段名。
-
-
type
-
作用:指定字段的类型。
-
示例 :
@Field(type = FieldType.Text) -
说明 :支持多种类型,如
Text、Keyword、Integer、Double、Date等。
-
-
index
-
作用:指定字段是否索引。
-
示例 :
@Field(index = true) -
说明 :如果设置为
true,字段将被索引,可以用于搜索;如果设置为false,字段将不会被索引。
-
-
store
-
作用:指定字段是否存储。
-
示例 :
@Field(store = true) -
说明 :如果设置为
true,字段值将被存储在 Elasticsearch 中,可以直接获取;如果设置为false,字段值不会被存储。
-
-
analyzer
-
作用:指定字段的分析器。
-
示例 :
@Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word", searchAnalyzer = "ik_smart") -
说明:分析器用于对文本字段进行分词和处理。
-
-
searchAnalyzer
-
作用:指定搜索时使用的分析器。
-
示例 :
@Field(type = FieldType.Text, analyzer = "ik_max_word", searchAnalyzer = "ik_smart") -
说明:搜索分析器用于在搜索时对查询文本进行分词和处理。
-
-
format
-
作用:指定日期字段的格式。
-
示例 :
@Field(type = FieldType.Date,format= DateFormat.custom, pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS") -
说明:DateFormat.custom表示使用自定义时间格式
-
-
ignoreFields
-
作用:指定忽略的字段。
-
示例 :
@Field(ignoreFields = {"field1", "field2"}) -
说明:用于忽略某些字段,不将其映射到 Elasticsearch 文档中。
-
如果你在 @Field 注解中不指定任何值,Spring Data Elasticsearch 会使用默认值来处理字段。以下是各个属性的默认行为:
默认值
-
name:
-
默认值:Java 字段名。
-
说明 :如果不指定
name,Elasticsearch 字段名将与 Java 字段名相同。
-
-
type:
-
默认值:根据 Java 字段类型自动推断。
-
说明 :Spring Data Elasticsearch 会根据 Java 字段的类型自动推断 Elasticsearch 字段类型。例如,
String类型会映射为Text,Integer类型会映射为Integer,Date类型会映射为Date等。
-
-
index:
-
默认值 :
true。 -
说明:默认情况下,字段会被索引,可以用于搜索。
-
-
store:
-
默认值 :
false。 -
说明:默认情况下,字段值不会被存储在 Elasticsearch 中,查询时需要从原始文档中提取。
-
-
analyzer:
-
默认值 :
standard。 -
说明 :默认使用
standard分析器进行分词和处理。
-
-
searchAnalyzer:
-
默认值 :与
analyzer相同。 -
说明:默认情况下,搜索时使用的分析器与索引时使用的分析器相同。
-
-
format:
-
默认值 :
strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis。 -
说明 :默认情况下,日期字段支持
strict_date_optional_time和epoch_millis两种格式。
-
@Mapping
用于定义索引的映射信息。通过 @Mapping 注解,你可以指定一个 JSON 文件路径,该文件包含了索引的详细映射配置。这使得你可以在实体类中直接定义复杂的映射规则,而不需要在代码中硬编码这些配置。
例:
entity
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Mapping;
@Document(indexName = "product")
@Mapping(mappingPath = "product-mapping.json")
public class Product {
@Id
private String id;
private String name;
private double price;
}json
{
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "standard",
"fields": {
"english": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
},
"price": {
"type": "double"
}
}
}@Setting
用于定义索引的映射信息。通过 @Mapping 注解,你可以指定一个 JSON 文件路径,该文件包含了索引的详细映射配置。这使得你可以在实体类中直接定义复杂的映射规则,而不需要在代码中硬编码这些配置。
例:
{
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 2,
"refresh_interval": "1s",
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"ik_max_word": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_max_word"
},
"ik_smart": {
"type": "custom",
"tokenizer": "ik_smart"
}
}
}
}
}-
number_of_shards:-
作用:指定索引的分片数。
-
示例 :
"number_of_shards": 3 -
说明:索引将分为 3 个分片。
-
-
number_of_replicas:-
作用:指定索引的副本数。
-
示例 :
"number_of_replicas": 2 -
说明:每个分片将有 2 个副本。
-
-
refresh_interval:-
作用:指定索引的刷新间隔。
-
示例 :
"refresh_interval": "1s" -
说明:索引数据每 1 秒刷新一次,使其对搜索可见。
-
-
analysis:-
作用:定义自定义分析器。
-
示例:
{ "index": { "number_of_shards": 3, "number_of_replicas": 2, "refresh_interval": "1s", "analysis": { "analyzer": { "ik_max_word": { "type": "custom", "tokenizer": "ik_max_word" }, "ik_smart": { "type": "custom", "tokenizer": "ik_smart" } } } } }自定义分词器,需要在mapping映射中指定自定义的分词器才会生效。
-
@Score
用于在查询结果中包含评分信息。评分信息表示查询结果的相关性分数,通常用于排序和过滤查询结果。
例:
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Field;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.FieldType;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Score;
@Document(indexName = "product")
public class Product {
@Id
private String id;
@Field(type = FieldType.Text)
private String name;
@Field(type = FieldType.Double)
private double price;
@Score
private Float score;
}@ScriptedField
用于定义脚本字段(Scripted Field)。脚本字段是通过在查询时执行脚本来动态计算的字段,而不是直接从索引中获取的字段。脚本字段可以用于在查询结果中包含动态计算的值,例如根据其他字段的值进行计算。
@GeoPoint
用于定义地理位置字段。地理位置字段用于存储和查询地理位置信息,支持地理空间查询,如距离查询、范围查询等。
@MultiField
用于定义多字段映射。多字段映射允许你为一个字段定义多个子字段,每个子字段可以有不同的分析器和字段类型。这使得你可以根据不同的需求对同一个字段进行不同的处理和查询。
@CompletionField
用于定义自动补全字段(Completion Field)。自动补全字段用于实现搜索建议(Search Suggestions)功能,即在用户输入搜索关键词时,自动补全功能会根据已有的数据提供可能的搜索建议。
@JoinField
用于定义父子文档关系(Parent-Child Relationship)。父子文档关系允许你在同一个索引中存储具有层次结构的数据,并且可以在查询时根据父子关系进行关联查询。
Dao
package com.example.demo.dao;
import com.example.demo.entity.Blog;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
public interface BlogRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<Blog, Long> {
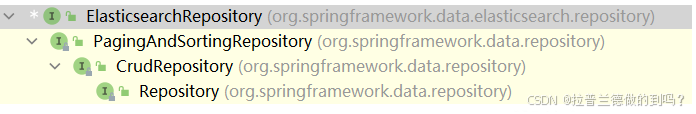
}简介
接口的继承
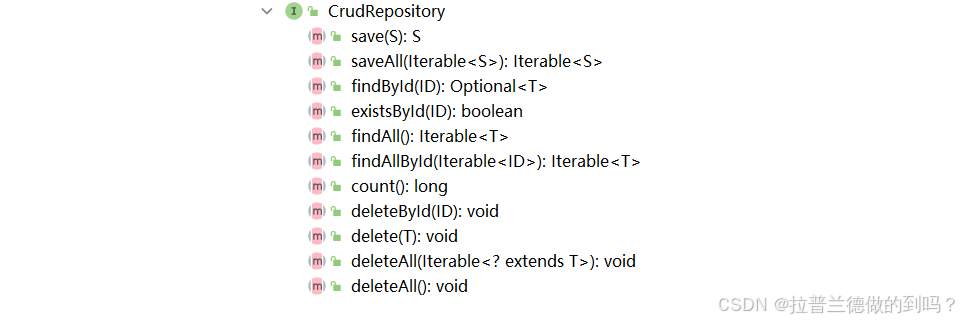
所有方法
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.dao.BlogRepository;
import com.example.demo.entity.Blog;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@Api(tags = "增删改查(文档)")
@RestController
@RequestMapping("crud")
public class CrudController {
@Autowired
private BlogRepository blogRepository;
@ApiOperation("添加单个文档")
@PostMapping("addDocument")
public Blog addDocument() {
Long id = 1L;
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(id);
blog.setTitle("Spring Data ElasticSearch学习教程" + id);
blog.setContent("这是添加单个文档的实例" + id);
blog.setAuthor("Tony");
blog.setCategory("ElasticSearch");
blog.setCreateTime(new Date());
blog.setStatus(1);
blog.setSerialNum(id.toString());
return blogRepository.save(blog);
}
@ApiOperation("添加多个文档")
@PostMapping("addDocuments")
public Object addDocuments(Integer count) {
List<Blog> blogs = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) {
Long id = (long)i;
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(id);
blog.setTitle("Spring Data ElasticSearch学习教程" + id);
blog.setContent("这是添加单个文档的实例" + id);
blog.setAuthor("Tony");
blog.setCategory("ElasticSearch");
blog.setCreateTime(new Date());
blog.setStatus(1);
blog.setSerialNum(id.toString());
blogs.add(blog);
}
return blogRepository.saveAll(blogs);
}
/**
* 跟新增是同一个方法。若id已存在,则修改。
* 无法只修改某个字段,只能覆盖所有字段。若某个字段没有值,则会写入null。
* @return 成功写入的数据
*/
@ApiOperation("修改单个文档")
@PostMapping("editDocument")
public Blog editDocument() {
Long id = 1L;
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setBlogId(id);
blog.setTitle("Spring Data ElasticSearch学习教程" + id);
blog.setContent("这是修改单个文档的实例" + id);
// blog.setAuthor("Tony");
// blog.setCategory("ElasticSearch");
// blog.setCreateTime(new Date());
// blog.setStatus(1);
// blog.setSerialNum(id.toString());
return blogRepository.save(blog);
}
@ApiOperation("查找单个文档")
@GetMapping("findById")
public Blog findById(Long id) {
return blogRepository.findById(id).get();
}
@ApiOperation("删除单个文档")
@PostMapping("deleteDocument")
public String deleteDocument(Long id) {
blogRepository.deleteById(id);
return "success";
}
@ApiOperation("删除所有文档")
@PostMapping("deleteDocumentAll")
public String deleteDocumentAll() {
blogRepository.deleteAll();
return "success";
}
}