由于vector和string 非常相似,在这里我们讲简单对其进行讲解,其基本用法都是一样的,只不过是这次不是字符串了而是顺序表
1.遍历vector
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2(10,1); //插入10个1
vector<int>v3 = { 10,20,30,40 };
v1.push_back(1);
v1.push_back(14);
v1.push_back(15);
for (size_t i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i]<<" ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it1 = v3.begin();
while (it1 != v3.end())
{
cout << *it1 << " ";
it1++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : v2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}结果如下:
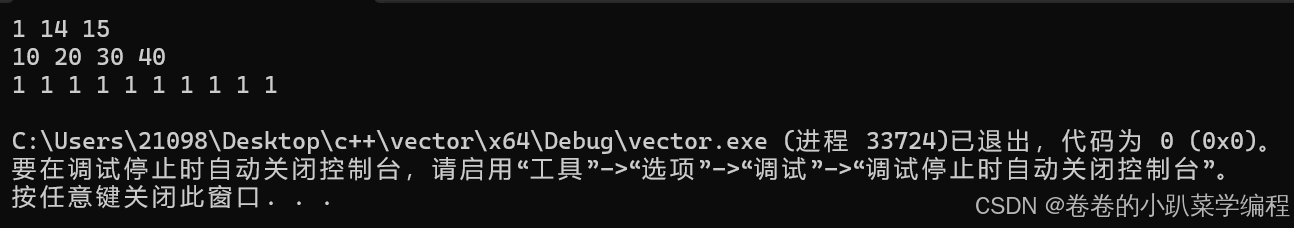
注:只要能用迭代器的地方就能用范围for! 范围for本质就是迭代器!
2.扩容方式
void testvectorexpand()
{
size_t sz;
vector<int>v;
//v.reserve(100);
sz = v.capacity();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
if (sz != v.capacity())
{
sz = v.capacity();
cout << "capacity changed:" << sz << endl;
}
}
}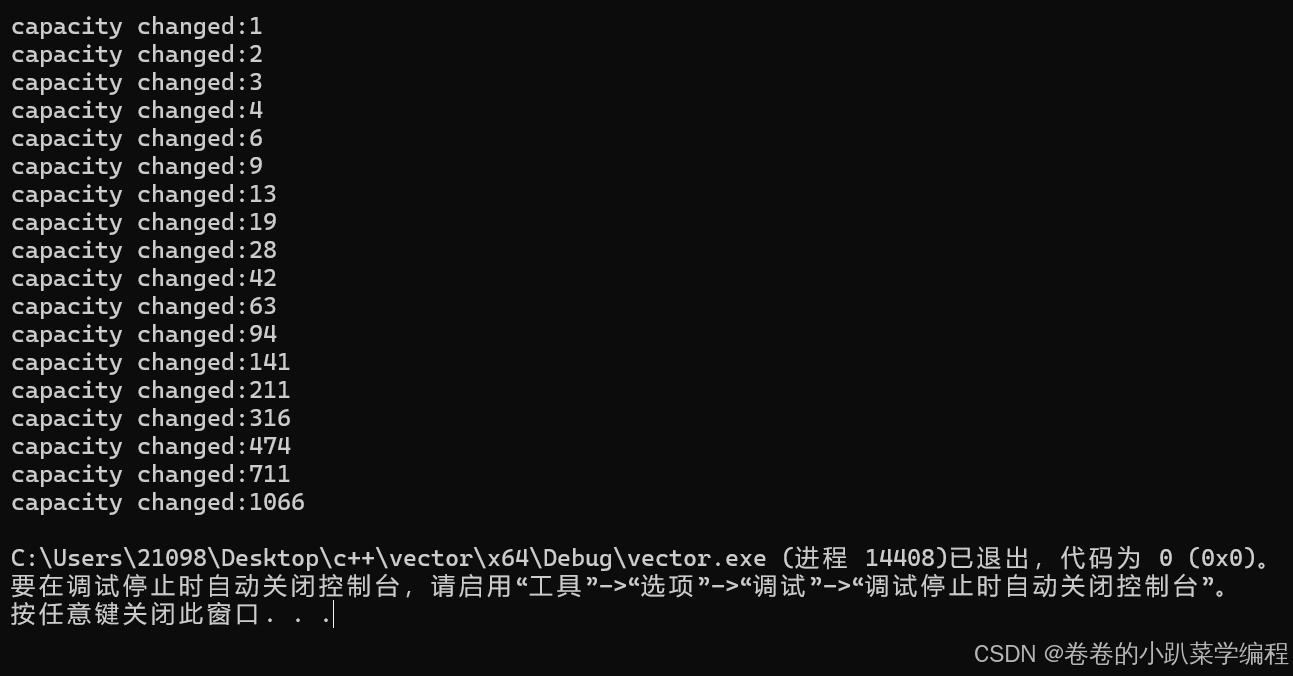
说明是1.5倍扩容
3.简单应用
int main()
{
vector<int>v1 = { 10,20,30,40,50 };
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 1); //在0的位置插入1
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 3, 5);
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<char>v2 = { 'a','b','c' }; //没有\0不兼容C
string s1("abc"); //有\0,可以兼容C
return 0;
}4.排序,查找,以及与<list>的对比
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,5,-6,9,30 };
list<int>lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
vector<string>v2;
vector<vector<int>>v3;
string name1 = "赵刚";
v2.push_back(name1); //有名
v2.push_back(string("李华")); //匿名
v2.push_back("李云龙"); //三种方式均可
for (const auto& e : v2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int x;
cin >> x;
//vector<int>::iterator it1 = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), x);
//上面写法过于冗长,可以简化一下:
auto it1 = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), x);
if (it1 != v1.end())
{
cout << x << " existed!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << x << " never existed!" << endl;
}
int y;
cin >> y;
auto it2 = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), y);
if (it2 != lt1.end())
{
cout<<y<< " existed!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << y << " never existed!" << endl;
}
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), less<int>()); //greater:降序,less:升序
for (const auto& ch : v1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<int>());
for (const auto& ch : v1)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
return 0;
}结果如下:

关于vector的更多应用这里就不在赘述了,基本上与<string>是一样的,仿照即可!