继承性是面向对象编程中的一个重要特性,它允许一个类(派生类或子类)继承另一个类(基类或父类)的成员变量和成员函数,从而实现代码的复用和扩展。在 C++ 中,实现继承主要通过以下方式:
定义基类和派生类
- 基类定义:首先定义一个基类,它包含了一些通用的成员变量和成员函数。例如:
cpp
class Vehicle {
public:
int wheels;
void start() {
cout << "Vehicle started." << endl;
}
};- 派生类定义 :使用
:符号和public、private或protected关键字来指定继承方式,然后定义派生类。例如:
cpp
class Car : public Vehicle {
public:
void drive() {
cout << "Car is driving." << endl;
}
};继承的格式:子类 :继承方式 父类,比如 class A :public B 就表示 A 继承 B, 且为公有继承。
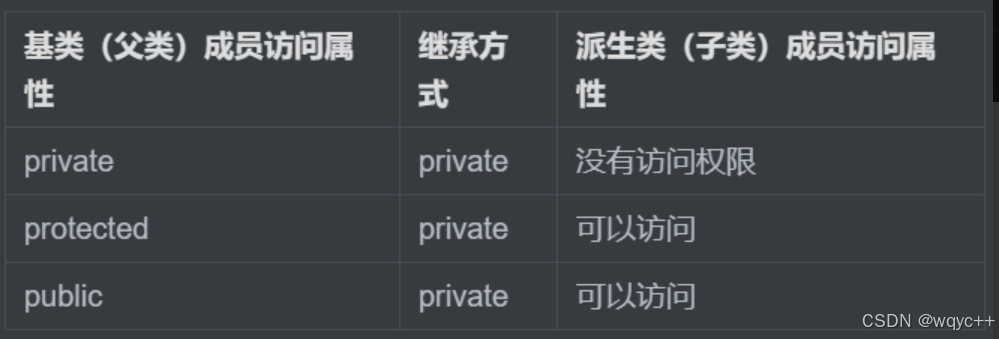
例如:pravite
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
/*
成员属性:
private:私有的 只能在本类内访问
protected:受保护的 类内和子类访问
public:共有的 类内 子类 对象都可访问
*/
//继承只会缩小成员的权限,不会扩大成员的权限
class father {
public:
int a;
protected:
int b;
private:
int c;
};
//私有的方式继承父类,父类中的所有成员在子类中都是私有的
class son:private father{
void fun() {
a = 1;
b = 1;
//c = 1;在父类中c是私有的所以不能在子类中访问
}
};
//因为son以私有的方式继承了father,所以father中的成员在son中都是私有的,所以son的子类grandson不能访问a和b
class grandson :public son {
void fun() {
// a = 1;
// b = 1;
}
};
int main() {
return 0;
}多继承
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class father {
public:
int a;
};
class father1 {
public:
int a;
};
class son :public father ,public father1{
public:
int a;
};
int main() {
//多继承会产生二义性,用作用域进行解决
son aa;
aa.father::a;
return 0;
}菱形继承(钻石继承)
我们首先还是模拟一个菱形继承,Person类,Student类,Teacher类,Assistant类
但是我们在Student类和Teacher类继承Person类时,使用虚继承------关键字virtual
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
class father {
public:
int a;
};
class father1 : public father {
public:
int a;
};
class father2 : public father {
public:
int a;
};
class son :public father ,public father1,public father2{
public:
int a;
};
int main() {
//菱形继承也会产生二义性,通过作用域进行解决或者用关键字虚继承
son bb;
bb.father2::a;
return 0;
}