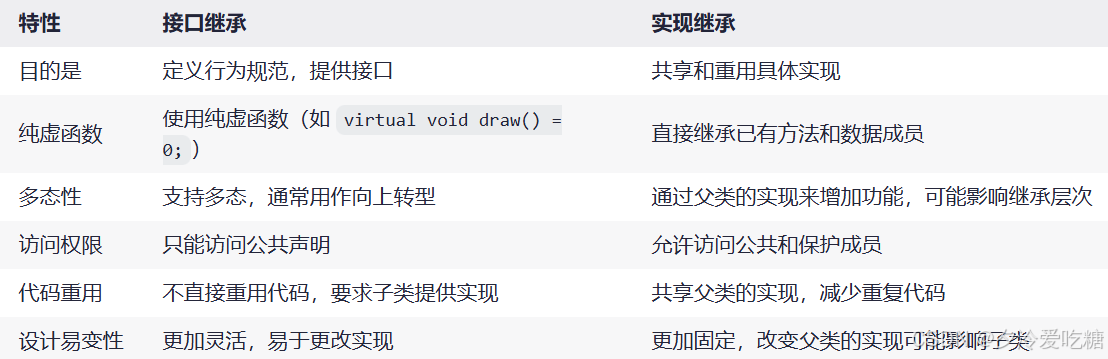
概念
在 C++ 中,接口继承和实现继承是两种不同的继承方式,它们在设计模式、代码复用和多态性方面有着不同的应用。下面将分别解释这两者的概念、实现方式及其区别。
接口继承
接口继承指的是只继承类的接口(即公共的成员函数声明)而不实现这些函数。通常通过纯虚函数来实现。这样做的目的是约定一个行为规范,而具体的实现则留给派生类去完成。
示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
// 定义一个接口
class Drawable {
public:
virtual void draw() const = 0; // 纯虚函数
virtual ~Drawable() {} // 虚析构函数以保证正确的析构
};
class Circle : public Drawable {
public:
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a circle." << std::endl;
}
};
class Square : public Drawable {
public:
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a square." << std::endl;
}
};
void render(const Drawable& shape) {
shape.draw(); // 调用接口的实现
}
int main() {
Circle circle;
Square square;
render(circle); // 输出: Drawing a circle.
render(square); // 输出: Drawing a square.
return 0;
}- 输出
cpp
Drawing a circle.
Drawing a square.代码解析
- 接口定义
cpp
class Drawable {
public:
virtual void draw() const = 0; // 纯虚函数
virtual ~Drawable() {} // 虚析构函数以保证正确的析构
};-
类 Drawable 是一个接口类,使用大写字母开头的名称有助于表明它是一个接口。
-
virtual void draw() const = 0; 声明了一个纯虚函数 draw(),这意味着 Drawable 类没有实现此函数,任何派生类必须实现这个函数。这里的 = 0 表示这是一个纯虚函数,任何包含它的类都被视为抽象类,无法直接实例化。
-
virtual ~Drawable() {} 是一个虚析构函数,允许使用基类指针删除派生类实例时确保资源正确释放。这是接口设计的良好实践。
-
实现接口的派生类
cpp
class Circle : public Drawable {
public:
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a circle." << std::endl;
}
};- class Circle : public Drawable 表示 Circle 类继承自 Drawable 接口,派生类必须实现所有的纯虚函数。
- void draw() const override 这是对基类 Drawable 中 draw() 的实现。通过 override 关键字指示这是对基类虚函数的重写。
- 在 draw() 方法中,我们使用 std::cout 输出 "Drawing a circle."。
cpp
class Square : public Drawable {
public:
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "Drawing a square." << std::endl;
}
};-
Square 类实现与 Circle 类类似,只是输出的信息不同。它同样继承了 Drawable 接口并实现 draw() 方法。
-
渲染函数
cpp
void render(const Drawable& shape) {
shape.draw(); // 调用接口的实现
}-
render 函数 接受一个常量引用类型的 Drawable 对象,这允许传入任何实现了 Drawable 接口的对象。
-
在函数内部调用 shape.draw(),通过多态的机制,这将调用传入对象的具体 draw() 实现,打印出形状信息。
-
主函数
cpp
int main() {
Circle circle;
Square square;
render(circle); // 输出: Drawing a circle.
render(square); // 输出: Drawing a square.
return 0;
}- Circle circle; 和 Square square; 创建了 Circle 和 Square 对象。
- render(circle); 和 render(square); 调用了 render 函数,分别传入 circle 和 square 对象。
- 由于 render 函数使用了接口类型 Drawable 的引用,因此可以通过多态机制实现适当的函数调用。
关键点
- Drawable 类是一个接口,它定义了一个纯虚函数 draw()。
- Circle 和 Square 类实现了接口,重写了 draw() 函数。
- 可以通过接口类型的引用或指针来实现多态。
总结
- 接口继承的灵活性:通过使用抽象类(接口),我们可以定义统一的行为规范(draw())。不同的实现类(Circle 和 Square)可以各自实现该接口的函数,从而提供特定的行为。这种设计模式使得代码的可扩展性和可维护性得以提高。
- 多态性:使用指向接口类的指针或引用可以实现多态,允许我们在不修改 render 函数的情况下轻松添加新的形状类。
- 虚构造和释放:使用虚析构函数确保在删除基类指针时能够正确地调用派生类的析构函数,从而避免内存泄露。
实现继承
实现继承指的是继承一个类的完整实现,而不仅仅是接口。这意味着子类不仅可以使用父类的方法和属性,还可以访问和重用父类的实现。这种方式通常在需要共享代码的场景中使用。
示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
// 基类
class Shape {
public:
void setPosition(int x, int y) {
m_x = x;
m_y = y;
}
protected:
int m_x, m_y; // 保护的成员变量
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
void draw() {
std::cout << "Drawing a circle at (" << m_x << ", " << m_y << ")." << std::endl;
}
};
class Square : public Shape {
public:
void draw() {
std::cout << "Drawing a square at (" << m_x << ", " << m_y << ")." << std::endl;
}
};
int main() {
Circle circle;
circle.setPosition(10, 20);
circle.draw(); // 输出: Drawing a circle at (10, 20).
Square square;
square.setPosition(30, 40);
square.draw(); // 输出: Drawing a square at (30, 40).
return 0;
}- 输出
cpp
Drawing a circle at (10, 20).
Drawing a square at (30, 40).代码解析
- 基类定义
cpp
class Shape {
public:
void setPosition(int x, int y) {
m_x = x;
m_y = y;
}
protected:
int m_x, m_y; // 保护的成员变量
};-
基类 Shape 是一个描述形状的类。
-
setPosition(int x, int y) 方法 是一个公共方法,用于设置形状的坐标。通过设置 m_x 和 m_y 成员变量,基类提供了一个基本的行为。
-
protected 修饰符 表示 m_x 和 m_y 只能在 Shape 类及其派生类中访问。这赋予了派生类对这些成员的访问权限,允许它们读取和修改位置。
-
派生类定义
cpp
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
void draw() {
std::cout << "Drawing a circle at (" << m_x << ", " << m_y << ")." << std::endl;
}
};- class Circle : public Shape 表示 Circle 类派生自 Shape 类,继承了所有公共和保护成员。
- void draw() 方法 在 Circle 类中实现,负责输出当前圆形的坐标信息。
cpp
class Square : public Shape {
public:
void draw() {
std::cout << "Drawing a square at (" << m_x << ", " << m_y << ")." << std::endl;
}
};-
class Square : public Shape 类似于 Circle 类,Square 也继承自 Shape 类。
-
draw() 方法负责输出当前正方形的坐标信息。
-
主函数实现
cpp
int main() {
Circle circle;
circle.setPosition(10, 20);
circle.draw(); // 输出: Drawing a circle at (10, 20).
Square square;
square.setPosition(30, 40);
square.draw(); // 输出: Drawing a square at (30, 40).
return 0;
}- 在 main() 函数中,首先创建了一个 Circle 对象。
- circle.setPosition(10, 20); 调用基类的 setPosition 方法设置圆形的坐标。
- circle.draw(); 调用 Circle 类的 draw() 方法输出圆形的坐标。
- 类似的,对 Square 类进行相同的操作,设置其位置并输出。
关键点
- Shape 类提供了一些具体的实现,比如 setPosition() 方法来设置形状的位置。
- Circle 和 Square 类继承自 Shape,它们可以使用 Shape 中已实现的方法。
- 子类可以重用父类的代码,也可以扩展其功能。
总结
-
实现继承的作用:
- Circle 和 Square 类继承自 Shape 类,能够重用基类的代码,特别是 setPosition 方法,避免了重复实现。
- 通过继承,所有形状类可以共享 Shape 类的成员和方法,简化代码结构。
-
访问控制:
- 使用 protected 修饰符允许派生类访问基类的成员变量,保持数据的封装性,但同时允许派生类访问必要的数据。
-
良好的可扩展性:
- 由于 Shape 类作为基类,可以轻松添加更多形状(例如 Triangle),只需继承 Shape 类并实现 draw() 方法而不需要重复代码。
-
多态性:
- 在这个简单的实现中没有用到多态性,但可以通过把 draw() 方法声明为虚函数和使用基类指针或引用来增强多态特性,这样可以通过基类类型处理不同的派生类对象。
区别