目录
[5.1 第一次显示图片,没有任何缓存](#5.1 第一次显示图片,没有任何缓存)
[5.2 页面被销毁时](#5.2 页面被销毁时)
[5.3 加载内存缓存中已有的图片](#5.3 加载内存缓存中已有的图片)
一,介绍
Glide的缓存机制是非常经典的,它有许多值得我们在项目中去借鉴的地方。
它主要分为了活动缓存,内存缓存,磁盘缓存这三个缓存,也叫三级缓存。
二,活动缓存
活动缓存,也叫弱引用缓存,把正在使用中的图片使用弱引用来进行缓存,什么是弱引用,弱引用就是当垃圾回收器进行垃圾回收时,如果一个对象只被弱引用引用,那么该对象会被回收。也就是说如果当图片没有被强引用的时候,下次垃圾回收的时候就会把它回收掉。
我们看下它的源码:
java
@VisibleForTesting
static final class ResourceWeakReference extends WeakReference<EngineResource<?>> {
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Synthetic
final Key key;
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Synthetic
final boolean isCacheable;
@Nullable
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Synthetic
Resource<?> resource;
@Synthetic
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
ResourceWeakReference(
@NonNull Key key,
@NonNull EngineResource<?> referent,
@NonNull ReferenceQueue<? super EngineResource<?>> queue,
boolean isActiveResourceRetentionAllowed) {
super(referent, queue);
this.key = Preconditions.checkNotNull(key);
this.resource =
referent.isMemoryCacheable() && isActiveResourceRetentionAllowed
? Preconditions.checkNotNull(referent.getResource())
: null;
isCacheable = referent.isMemoryCacheable();
}
void reset() {
resource = null;
clear();
}
}可以看到,它将资源和它对应的key一起封装成了一个弱引用的 ResourceWeakReference 对象
三,内存缓存
内存缓存,也叫Lrucache内存缓存,它使用lru算法来缓存。
Lru算法也叫最近最少使用算法。顾名思义,它采用双向链表,将最近最少使用的元素都放到链表的尾端,当元素数量超过最大值时,就将尾端的元素删除。
我们来看下Lrucache的源码:
java
public class LruCache<K, V> {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
private int size;
private int maxSize;
private int putCount;
private int createCount;
private int evictionCount;
private int hitCount;
private int missCount;
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
public void resize(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
synchronized (this) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
}
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
previous = map.put(key, value);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.eldest();
if (toEvict == null) {
break;
}
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
protected V create(K key) {
return null;
}
private int safeSizeOf(K key, V value) {
int result = sizeOf(key, value);
if (result < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Negative size: " + key + "=" + value);
}
return result;
}
protected int sizeOf(K key, V value) {
return 1;
}
。。。
}其实它的源码很简单,就是维护了一个LinkedHashMap,根据传入的最大值来限制元素的个数。
四,磁盘缓存
磁盘缓存同样也是采用了LRU算法。
五,缓存流程
了解了三个缓存的原理,那么就来看看它们的工作流程是怎样的。
5.1 第一次显示图片,没有任何缓存
当第一次显示图片,没有任何缓存时,它的流程如下:
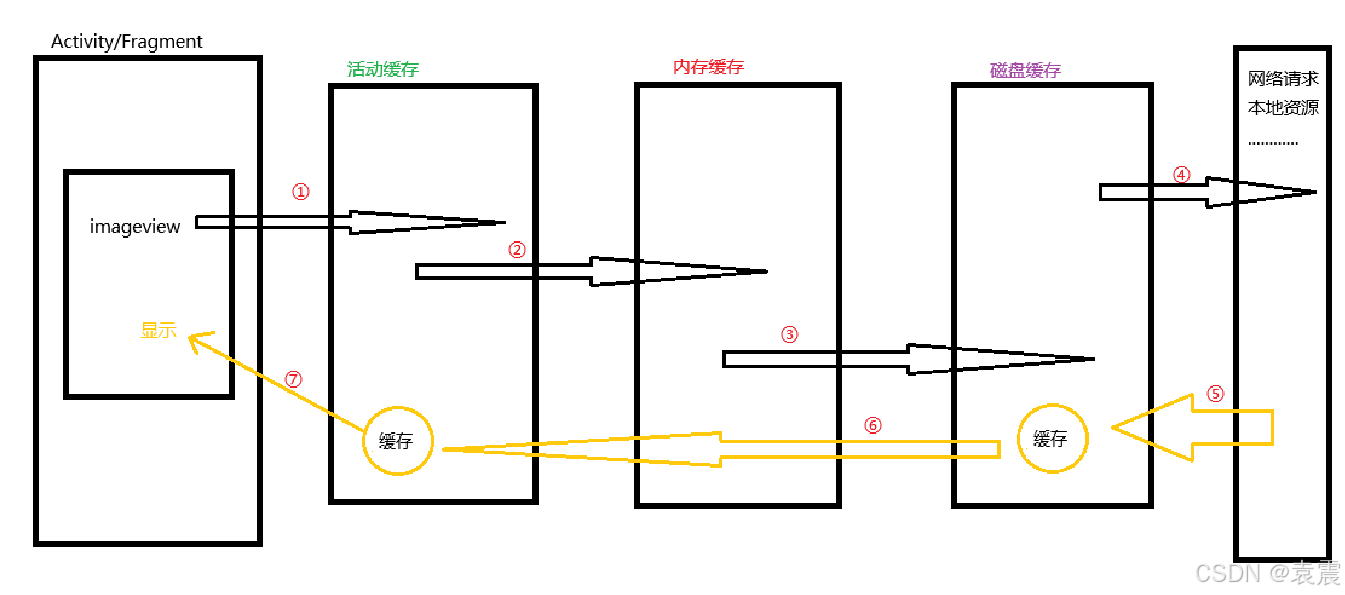
①查找活动缓存中有没有该图片
②活动缓存中没有找到该图片,查找内存缓存中有没有该图片
③内存缓存中没有找到该图片,查找磁盘缓存中有没有该图片
④磁盘缓存中也没有该图片,那就请求网络加载下载图片
⑤网络请求返回的图片缓存到磁盘缓存
⑥磁盘缓存中的图片复制一份到活动缓存
⑦活动缓存中的图片被加载显示到页面
5.2 页面被销毁时
当页面被销毁时,会触发glide的生命周期监控,它的流程如下:
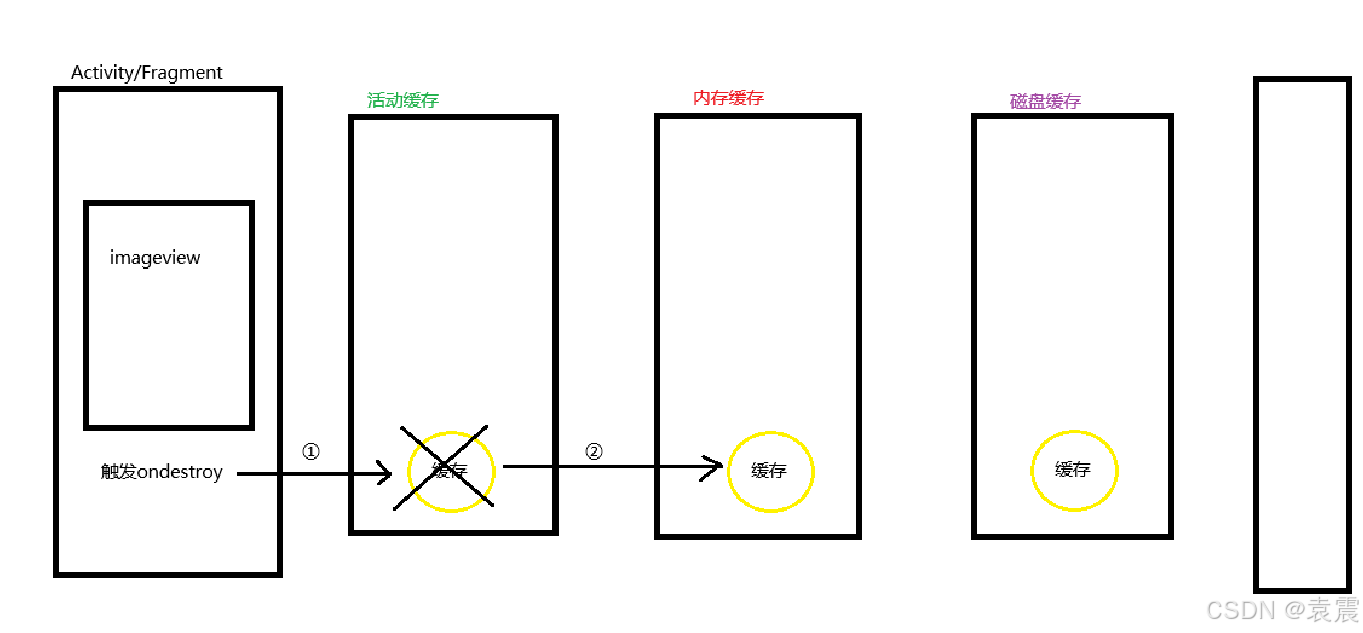
① glide监控生命周期,监控到页面销毁,传递给活动缓存
② 活动缓存将缓存剪切到内存缓存
5.3 加载内存缓存中已有的图片
当加载已经在内存缓存中的图片时,流程如下:
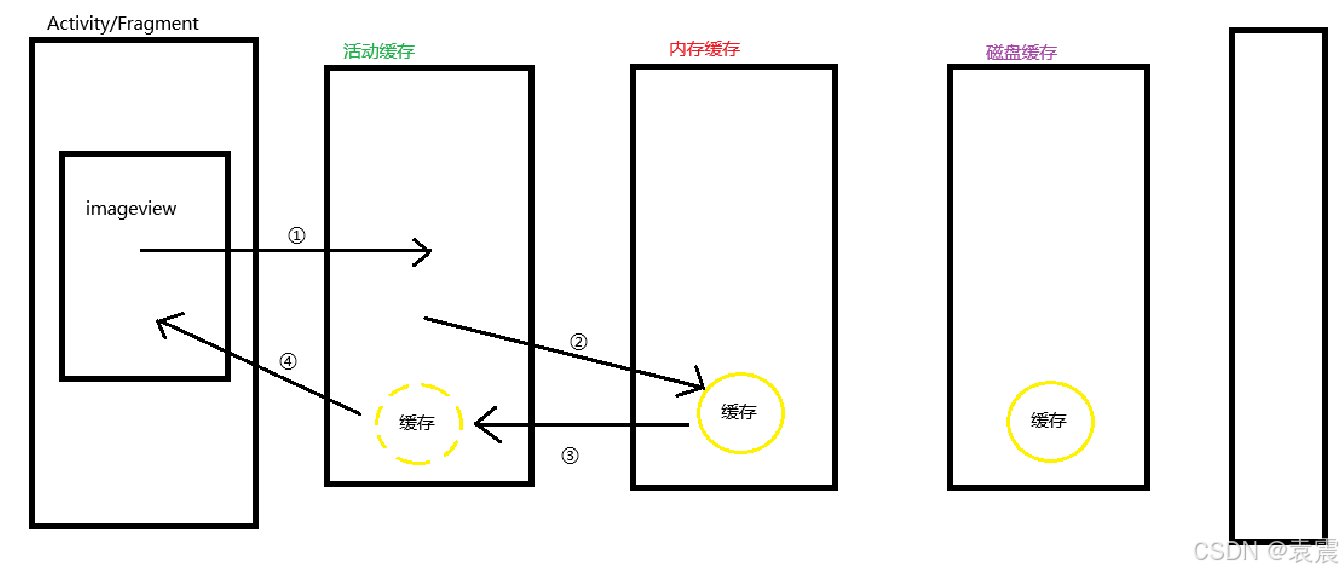
①去活动缓存查到图片
②活动缓存没有找到,去内存缓存查找
③内存缓存中找到了缓存,将 缓存复制到活动缓存中
④将活动缓存中的图片加载到imageview显示
注意:当app进程被杀死时,活动缓存和内存缓存都不存在了,只有磁盘缓存还在。