标准IO

源于Unix。对与系统IO ,当我们调用read,write读写数据的时候,操作系统会进入到内核来去调用这些api,但是如果是多次循环读写的话频繁的进入内核是和消耗性能的。所以标准的IO(fopen、fread、fwrite)会有一个用户buffer来缓存文件的数据,当使用fread或者fwrite的时候会直接在这个buffer里面读取,而不需要去频繁的进入内核。当buffer被用满了之后,才会调用read或者write进入到内核读取数据放到buffer中。
一、打开文件
cpp
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <error.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 打开文件
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int fd;
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: %s <file>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
printf("errno = %d\n", errno); // 打印错误信息
printf("err: %s\n", strerror(errno));
// 这里更加简单,效果等同于上面两个
perror("open");
}
else {
printf("fd: %d\n", fd);
}
while (1)
{
sleep(10);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}二、创建文件
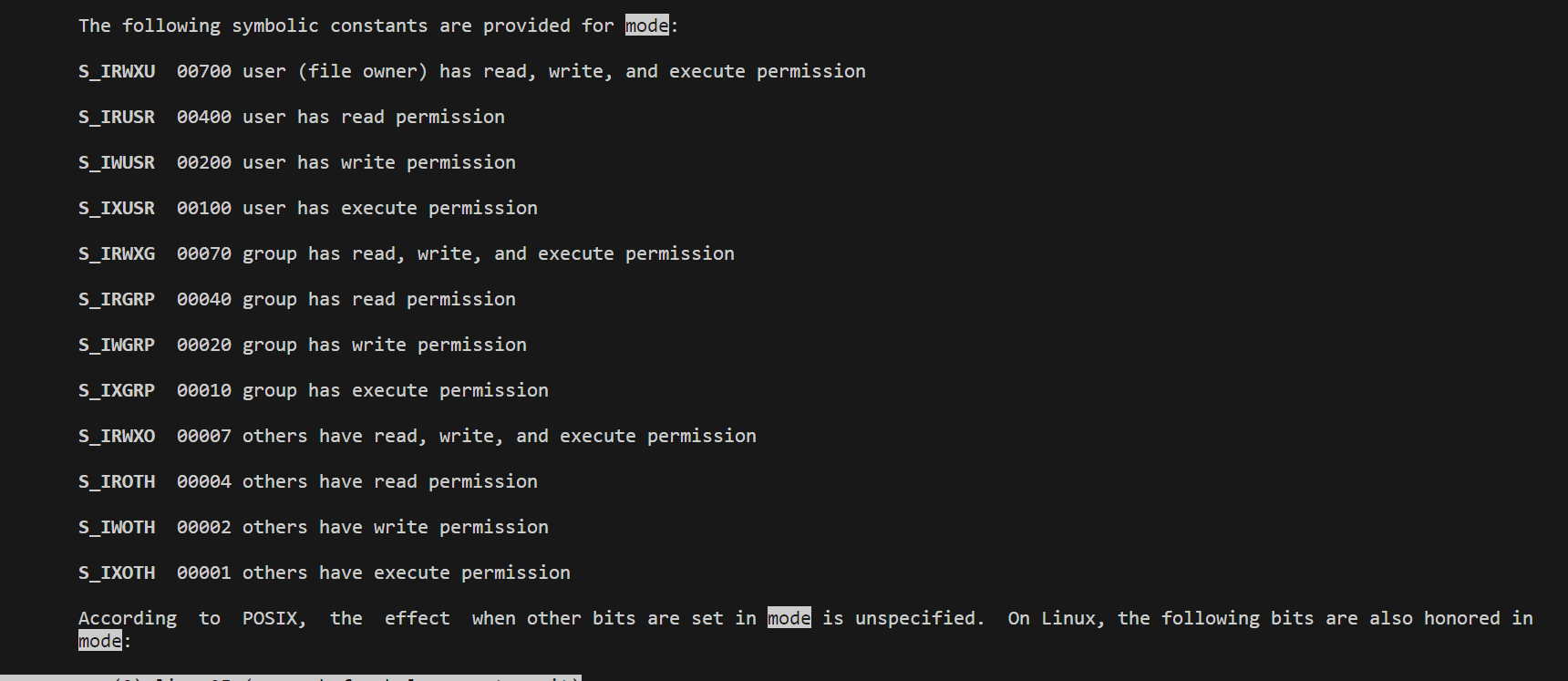
mode模式,权限。
左边是宏,右边是表示对应的八进制
umask指令,查看文件权限。

三、写入文件
cpp
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <error.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 打开文件
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
int fd;
if (argc < 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <file> <string1> <string2> ......\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
printf("errno = %d\n", errno); // 打印错误信息
printf("err: %s\n", strerror(errno));
// 这里更加简单,效果等同于上面两个
perror("open");
}
else {
printf("fd: %d\n", fd);
}
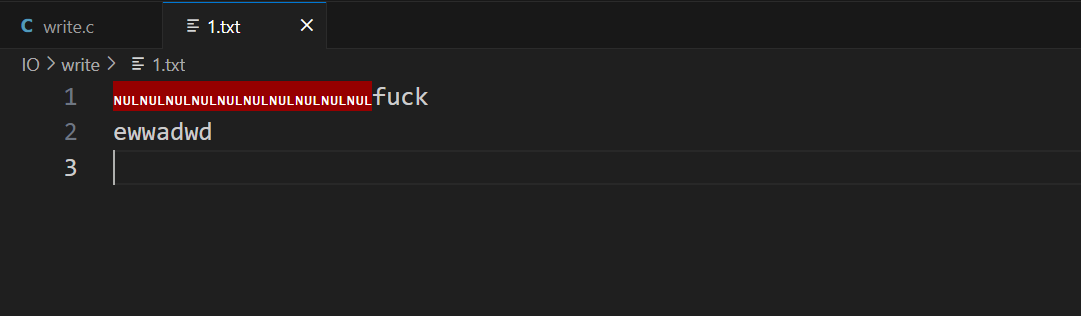
lseek(fd, 10, SEEK_SET);
for (int i = 2;i < argc;i++) {
int len = write(fd, argv[i], strlen(argv[i]));
if (len != strlen(argv[i])) {
perror("write");
break;
}
write(fd, "\r\n", 2);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
四、读取
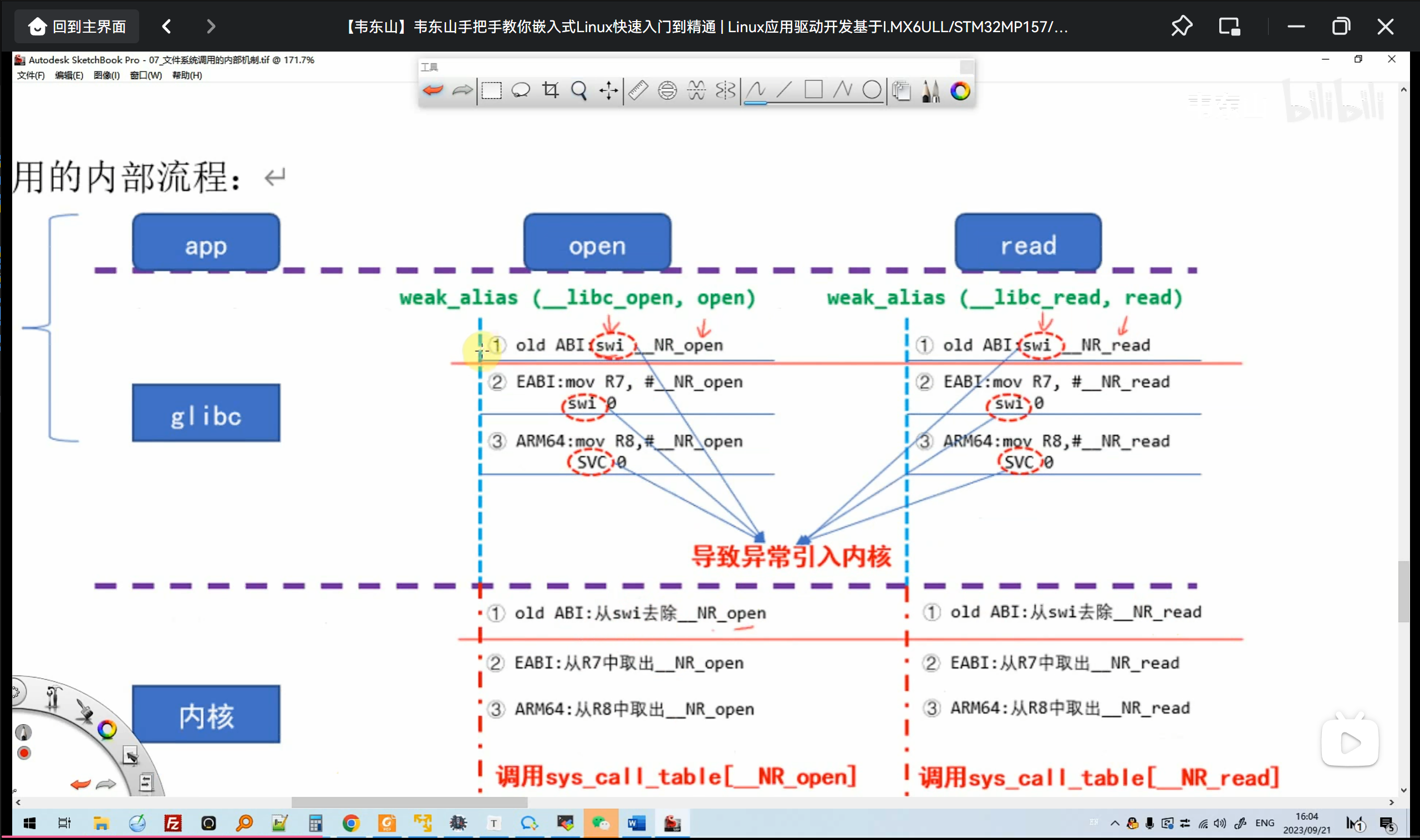
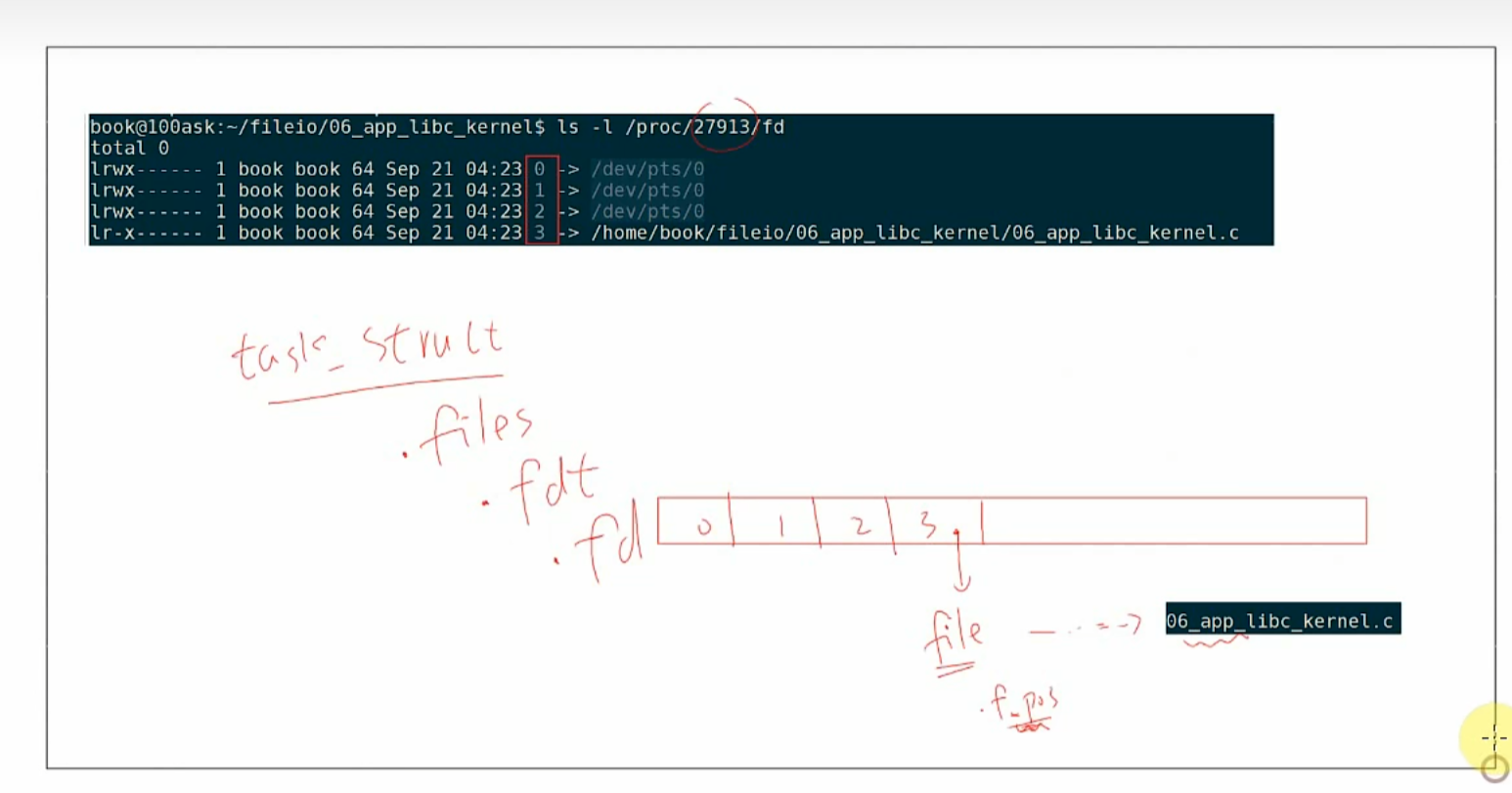
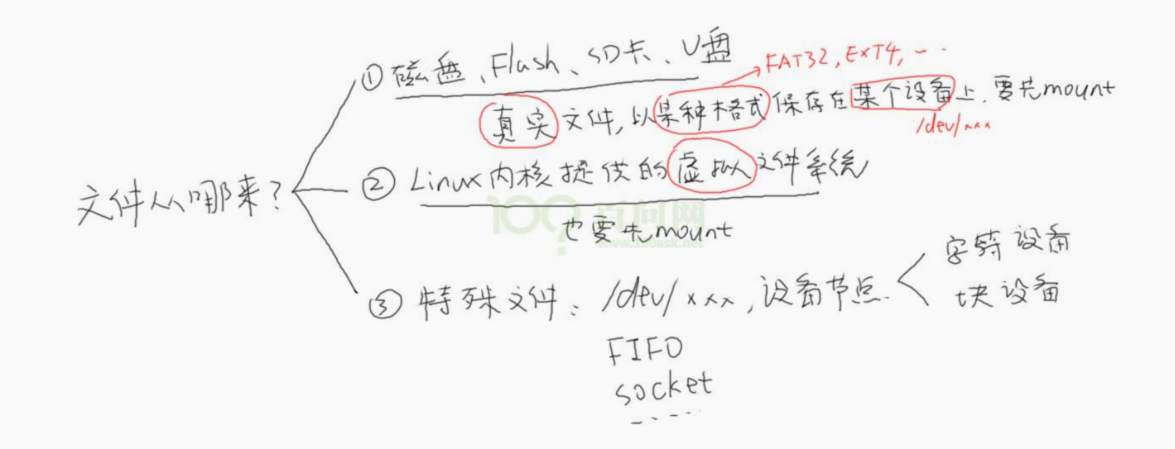
文件IO内部机制
应用层触发异常,传递给内核,内核去处理异常。glibc