一、概要
资料来源《机械工程师Python编程:入门、实战与进阶》安琪儿·索拉·奥尔巴塞塔 2024年6月
- 点和向量:向量的缩放、范数、点乘、叉乘、旋转、平行、垂直、夹角
- 直线和线段:线段中点、离线段最近的点、线段的交点、直线交点、线段的垂直平分线
- 多边形:一般多边形、圆、矩形
- 仿射变换
书中强调了单元测试的重要性。
二、点和向量
数字比较
python
# geom2d/nums.py
import math
def are_close_enough(a,b,tolerance=1e-10):
return math.fabs(a-b)<tolerance
def is_close_to_zero(a,tolerance=1e-10):
return are_close_enough(a,0.0,tolerance)
def is_close_to_one(a,tolerance=1e-10):
return are_close_enough(a,1.0,tolerance)点
python
# geom2d/point.py
import math
from geom2d import nums
from geom2d.vector import Vector
class Point:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.x = x
self.y = y
# 计算两点间的距离
def distance_to(self, other):
delta_x = other.x - self.x
delta_y = other.y - self.y
return math.sqrt(delta_x ** 2 + delta_y ** 2)
# 对点进行加操作
def __add__(self, other):
return Point(
self.x + other.x,
self.y + other.y
)
# 对点进行减操作
def __sub__(self, other):
return Vector(
self.x - other.x,
self.y - other.y
)
# 用向量移动点
def displaced(self, vector: Vector, times=1):
scaled_vec = vector.scaled_by(times)
return Point(
self.x + scaled_vec.u,
self.y + scaled_vec.v
)
# 比较点是否相等
def __eq__(self, other):
if self is other:
return True
if not isinstance(other, Point):
return False
return nums.are_close_enough(self.x, other.x) and \
nums.are_close_enough(self.y, other.y)
def __str__(self):
return f'({self.x},{self.y})'向量
python
# geom2d/vector.py
import math
from geom2d import nums
class Vector:
def __init__(self, u, v):
self.u = u
self.v = v
# 向量的加法
def __add__(self, other):
return Vector(
self.u+other.u,
self.v+other.v
)
# 向量的减法
def __sub__(self, other):
return Vector(
self.u-other.u,
self.v-other.v
)
# 向量的缩放
def scaled_by(self,factor):
return Vector(factor*self.u,factor*self.v)
# 计算向量的范数
@property
def norm(self):
return math.sqrt(self.u**2+self.v**2)
# 验证向量是否为单位向量
@property
def is_normal(self):
return nums.is_close_to_one(self.norm)
# 计算单位长度的向量
def normalized(self):
return self.scaled_by(1.0/self.norm)
# 计算指定长度的向量
def with_length(self,length):
return self.normalized().scaled_by(length)
# 向量的投影
def projection_over(self,direction):
return self.dot(direction.normalized())
# 向量点乘
def dot(self,other):
return (self.u*other.u)+(self.v*other.v)
# 向量叉乘
def cross(self,other):
return (self.u*other.v)-(self.v*other.u)
# 检验两向量是否平行,即叉乘是否为0
def is_parallel_to(self,other):
return nums.is_close_to_zero(self.cross(other))
# 检验两向量是否垂直,即点乘是否为0
def is_perpendicular_to(self,other):
return nums.is_close_to_zero(self.dot(other))
# 向量的夹角(角度值)
def angle_value_to(self,other):
dot_product=self.dot(other) # 计算点乘值
norm_product=self.norm*other.norm # 范数的乘积
return math.acos(dot_product/norm_product) # (点乘值/范数乘积)取反余弦,即角度值
# 向量的夹角(带叉乘符号的角度值)
def angle_to(self,other):
value=self.angle_value_to(other)
cross_product=self.cross(other)
return math.copysign(value,cross_product) #math.copysign(x, y)函数返回x的大小和y的符号
# 向量的旋转,旋转一定角度
def rotated_radians(self,radians):
cos=math.cos(radians)
sin=math.sin(radians)
return Vector(
self.u*cos-self.v*sin,
self.u*sin+self.v*cos
)
# 垂直向量,旋转90度
def perpendicular(self):
return Vector(-self.v,self.u)
# 相反向量,旋转180度
def opposite(self):
return Vector(-self.u,-self.v)
# 向量的正旋和余弦
@property
def sine(self):
return self.v/self.norm
@property
def cosine(self):
return self.u/self.norm
# 比较向量是否相等
def __eq__(self, other):
# 检查是否在比较相同的实例
if self is other:
return True
# other不是Vector类的实例
if not isinstance(other,Vector):
return False
return nums.are_close_enough(self.u,other.u) and \
nums.are_close_enough(self.v,other.v)
def __str__(self):
return f'({self.u},{self.v}) with norm {self.norm}'
python
#geom2d/vectors.py
# 向量工厂
from geom2d.point import Point
from geom2d.vector import Vector
# 创建一个从点p到点q的向量
def make_vector_between(p:Point,q:Point):
return q-p
# 创建单位方向向量
def make_versor(u:float,v:float):
return Vector(u,v).normalized()
# 在两点之间创建一个单位方向向量
def make_versor_between(p:Point,q:Point):
return make_vector_between(p,q).normalized()向量范数
向量的范数(norm)是指它的长度。单位范数的长度为一个单位。拥有单位范数的向量在确认向量方向时非常有用,因此,我们经常会想知道一个向量的范数是否为单位范数(它是否是单位向量)。我们也经常需要归一化(normalize)一个向量:方向不变,长度变为1。
向量点乘
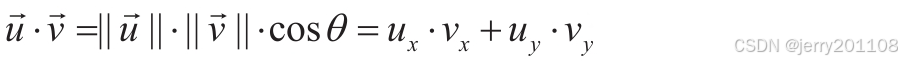
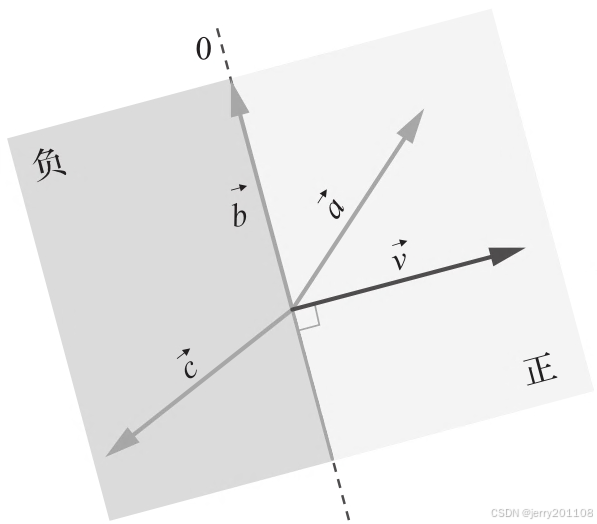
点乘(dot product)会得到一个标量,它可以反映两个向量方向的差异。
图上有一个参考向量和另外三个向量:
、
和
。一条垂直于
的直线将空间分成两个半平面。向量
在直线上,因此
和
的夹角θ等于90°。而cos(90°)=0,因此
。垂直向量的点乘为零。向量
所在的半平面和
相同,因此,
。最后,
在与
相对的半平面上,因此,
。
向量叉乘
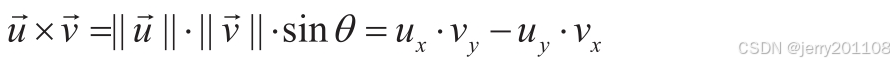
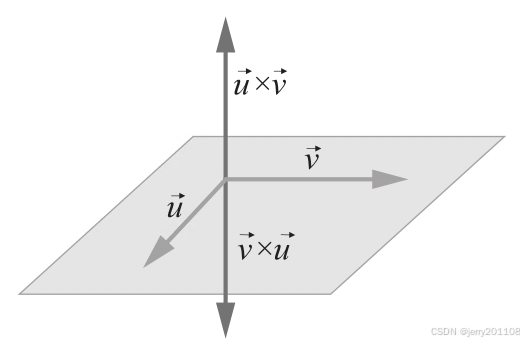
向量叉乘(cross product)会得到一个垂直于这两个向量所在平面的新向量。向量的顺序很重要,它决定了结果向量的方向。可以使用右手法则得到叉乘的方向。
叉乘不满足交换律:
二维向量叉乘的一个重要应用是确定角度的旋转方向。,因为从
到
的角度为正(逆时针)。相反,从
到
的角度为负,因此叉乘
。最后,平行向量的叉乘为0,这很显然,因为sin 0=0。
向量旋转
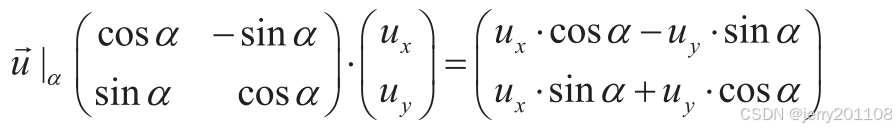
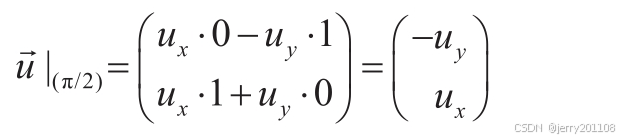
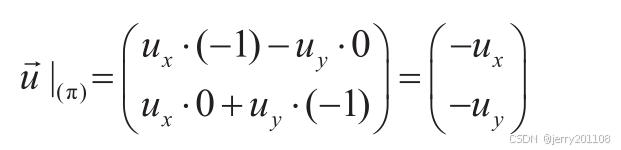
cos(π/2)=0, sin(π/2)=1,cos(π)=-1, sin(π)=0
向量的正弦和余弦
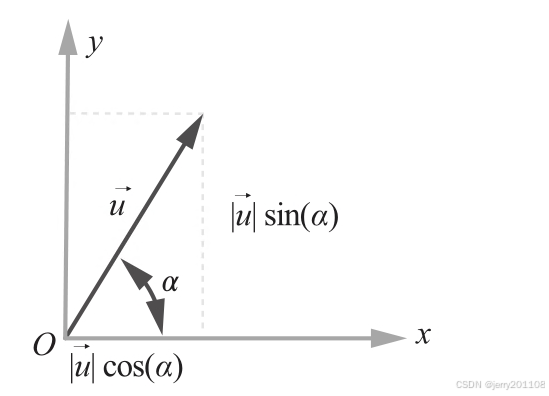

三、直线和线段
线段
python
# geom2d/segment.py
from geom2d.point import Point
from geom2d.vectors import make_vector_between,make_versor_between
from geom2d import tparam
class Segment:
def __init__(self,start:Point,end:Point):
self.start=start
self.end=end
# 线段的方向向量
@property
def direction_vector(self):
return make_vector_between(self.start,self.end)
# 线段的单位方向向量
@property
def direction_versor(self):
return make_versor_between(self.start,self.end)
# 垂直于线段方向的向量,法向量
# 调用self的direction_versor来得到线段的方向向量,同时也是Vector类的实例
# 调用perpendicular方法,返回垂直于线段方向的向量
def normal_versor(self):
return self.direction_versor.perpendicular()
# 线段的长度
@property
def length(self):
return self.start.distance_to(self.end)
# 使用参数t获取线段上的任意一点
def point_at(self,t:float):
tparam.ensure_valid(t) # 验证t值
return self.start.displaced(self.direction_vector,t)
# 线段的中点
@property
def middle(self):
return self.point_at(tparam.MIDDLE)
# 线段上的最近点
# 计算从线段的端点S到外部点P的向量v
# 计算在线段方向上投影的单位向量d
# 将投影的长度设为vs
def closest_point_to(self,p:Point):
v=make_vector_between(self.start,p)
d=self.direction_versor
vs=v.projection_over(d)
if vs<0:
return self.start
if vs>self.length:
return self.end
return self.start.displaced(d,vs)线段的方向向量
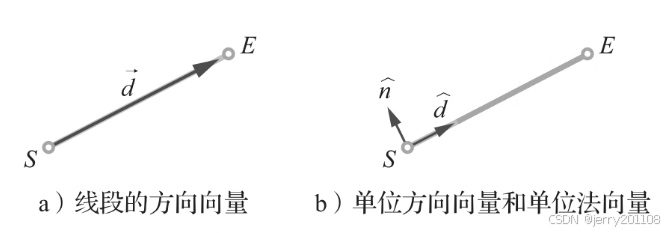
方向(direction)是线段的一个重要性质,定义为从起点S到终点E的向量。用来表示该向量。
方向向量(direction vector)是一个与线段平行且长度相同的向量,其方向是从起点到终点。
单位方向(direction versor)是方向向量的归一化版本,即与方向向量的方向相同,但长度为一个单位。
垂直于线段的方向也同样重要。将单位方向向量**** 旋转方向π/4 rad(90°),就可以得到线段的单位法向量(normalversor)。
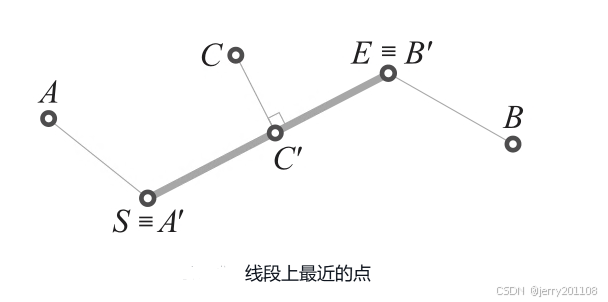
线段上最接近外部点的点
如果外部点没有与线段对齐,穿过该点且垂直于线段的直线不与线段相交,那么最近的点必然是两个端点S或E中的一个。
如果该点与该段对齐,则垂直线与线段的交点就是最近的点。
如图:点S≡A'是离A最近的点,点E≡B'是最接近B的点,C'是最接近C的点。
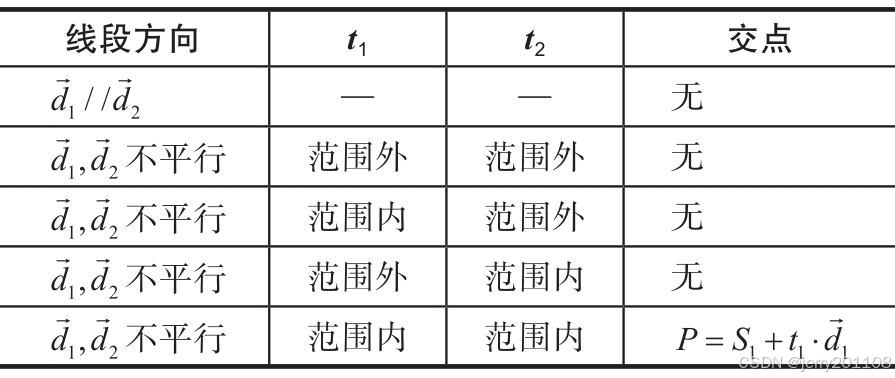
线段的交点
四、多边形
一般多边形------用它们的顶点来定义;
圆是平面内与指定点(圆心)的距离(半径)相同的所有点的集合。因此,圆由圆心C的位置和半径R的值定义
矩形------由原点、宽度和高度定义
多边形中一个重要性质是质心(centroid),即所有顶点坐标的算术平均值。
五、仿射变换
仿射变换:它使我们能够通过缩放、旋转、平移和剪切来改变几何形状。
六、单元测试
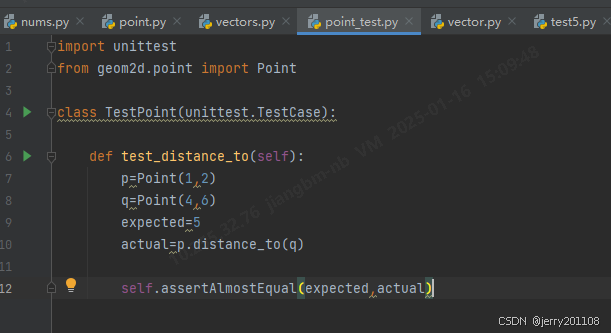
断言方法
| 断言方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| assertAlmostEqual | 定义在我们引用的类unittest.TestCase中,用指定的公差来检查浮点数是否相等,公差用小数点后的位数表示,默认是7。请记住,在比较浮点数时,必须有公差,或者像上述例子,给定小数点后的位数 |
| assertEqual | 使用==操作符来比较这两个参数 |
| assertTrue | 检验给定表达式的计算结果是否为True |
| assertFalse | 检验给定表达式的计算结果是否为False |
| assertRaises | 向其传入三个参数。首先是预期要触发的异常(TParamError)。其次,传入了期望触发异常的方法。最后,传入需要传递给前面的方法(在本例中为point_at)的实参。 |
| assertIsNone | 检查传入的值是否是None(无) |
单元测试的三个规则
1、失败原因须唯一
单元测试应该有且仅有一个失败的原因。如果测试失败只有一个原因,那么很容易找到代码中的错误。如果一个测试失败可能有五个不同的原因。当测试失败时,你会发现自己花费太多时间去阅读错误消息和调试代码。
2、受控环境
测试的输入和输出应该是已知的。发生在测试中的一切都应该是确定的(deterministic),也就是说,不应该出现随机性或依赖任何你无法控制的东西:日期或时间、操作系统、未在测试中设置的机器环境变量,等等。
3、测试独立性
测试不应依赖于其他测试。每个测试都应该独立运行,绝不能依赖于其他测试所设置的运行测试的环境。这至少有三个原因。首先,你需要独立地运行或调试测试。其次,许多测试框架并不能保证测试的执行顺序。最后,不依赖于其他测试的测试要易读得多。