目录
[可视化相机pose colmap形式的相机内参外参](#可视化相机pose colmap形式的相机内参外参)
内参外参转换
python
def visualize_cameras(cameras, images):
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
for image_id, image_data in images.items():
qvec = image_data['qvec']
tvec = image_data['tvec']
# Convert quaternion to rotation matrix
rotation = R.from_quat(qvec).as_matrix()
# Plot camera position
ax.scatter(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2], c='r', marker='o')
# Plot camera orientation
camera_direction = rotation @ np.array([0, 0, 1])
ax.quiver(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2], camera_direction[0], camera_direction[1], camera_direction[2], length=0.5, normalize=True)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()这段代码用于在3D坐标系中可视化相机的位置和朝向。以下是逐行解释:
-
提取参数:
qvec = image_data['qvec'] # 相机的旋转四元数 (w, x, y, z 或 x, y, z, w,需确认顺序) tvec = image_data['tvec'] # 相机的平移向量 (x, y, z 坐标) -
四元数转旋转矩阵:
pythonrotation = R.from_quat(qvec).as_matrix() # 将四元数转换为3x3旋转矩阵-
假设
R来自scipy.spatial.transform.Rotation。 -
需确认
qvec的顺序是否为库预期的格式(通常R.from_quat接受(x, y, z, w))。
-
-
绘制相机位置:
pythonax.scatter(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2], c='r', marker='o') # 在3D图中用红点标记相机位置 -
计算并绘制相机朝向:
pythoncamera_direction = rotation @ np.array([0, 0, 1]) # 旋转矩阵乘以Z轴单位向量,得到相机在世界坐标系中的朝向 ax.quiver(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2], camera_direction[0], camera_direction[1], camera_direction[2], length=0.5, normalize=True)-
原理:相机坐标系中默认朝向为Z轴正方向(通常指向拍摄方向),通过旋转矩阵将其转换到世界坐标系。
-
箭头参数:
-
起点为相机位置
(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2])。 -
方向向量为
camera_direction。 -
length=0.5控制箭头显示长度(实际长度可能因归一化调整)。 -
normalize=True确保箭头方向正确,长度统一。
-
-
注意事项:
-
四元数顺序 :确认
qvec是否与R.from_quat兼容(SciPy需(x, y, z, w))。 -
坐标系定义 :假设相机朝向为Z轴正方向,若实际定义相反(如OpenGL使用-Z),需调整为
[0, 0, -1]。 -
3D绘图设置 :确保
ax是3D轴(例如通过fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')创建)。
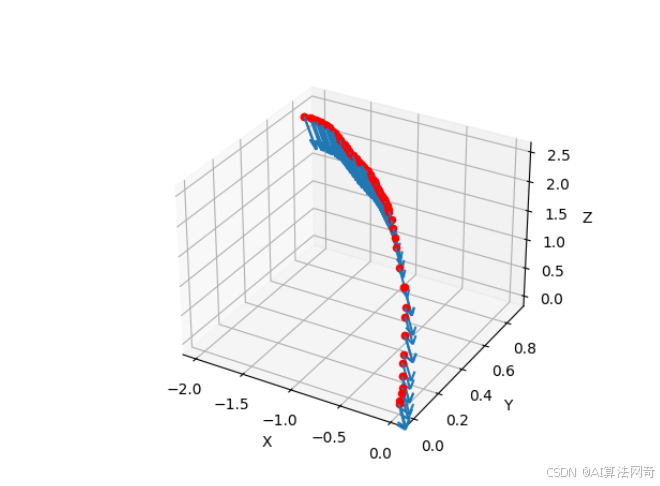
效果:在3D图中,红色圆点表示相机位置,箭头指示其拍摄方向。
可视化相机pose colmap形式的相机内参外参
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation as R
def read_cameras(file_path):
cameras = {}
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
for line in file:
if line[0] == '#':
continue
parts = line.strip().split()
camera_id = int(parts[0])
model = parts[1]
width = int(parts[2])
height = int(parts[3])
params = np.array([float(p) for p in parts[4:]])
cameras[camera_id] = {
'model': model,
'width': width,
'height': height,
'params': params
}
return cameras
def read_images(file_path):
images = {}
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
for line in file:
if line[0] == '#':
continue
parts = line.strip().split()
if len(parts) == 15:
continue
image_id = int(parts[0])
qvec = np.array([float(p) for p in parts[1:5]])
tvec = np.array([float(p) for p in parts[5:8]])
camera_id = int(parts[8])
file_name = parts[9]
images[image_id] = {
'qvec': qvec,
'tvec': tvec,
'camera_id': camera_id,
'file_name': file_name
}
return images
def visualize_cameras(cameras, images):
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
for image_id, image_data in images.items():
qvec = image_data['qvec']
tvec = image_data['tvec']
# Convert quaternion to rotation matrix
rotation = R.from_quat(qvec).as_matrix()
# Plot camera position
ax.scatter(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2], c='r', marker='o')
# Plot camera orientation
camera_direction = rotation @ np.array([0, 0, 1])
ax.quiver(tvec[0], tvec[1], tvec[2], camera_direction[0], camera_direction[1], camera_direction[2], length=0.5, normalize=True)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_zlabel('Z')
plt.show()
# 示例使用
cameras = read_cameras('./cameras.txt')
images = read_images('./images.txt')
visualize_cameras(cameras, images)