题目: 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。(两链表节点个数范围[0, 50])
思路:
创建新的空链表,遍历原链表,将节点小的节点拿到新链表中进行尾插操作
下面是我画的示意图,供大家理解
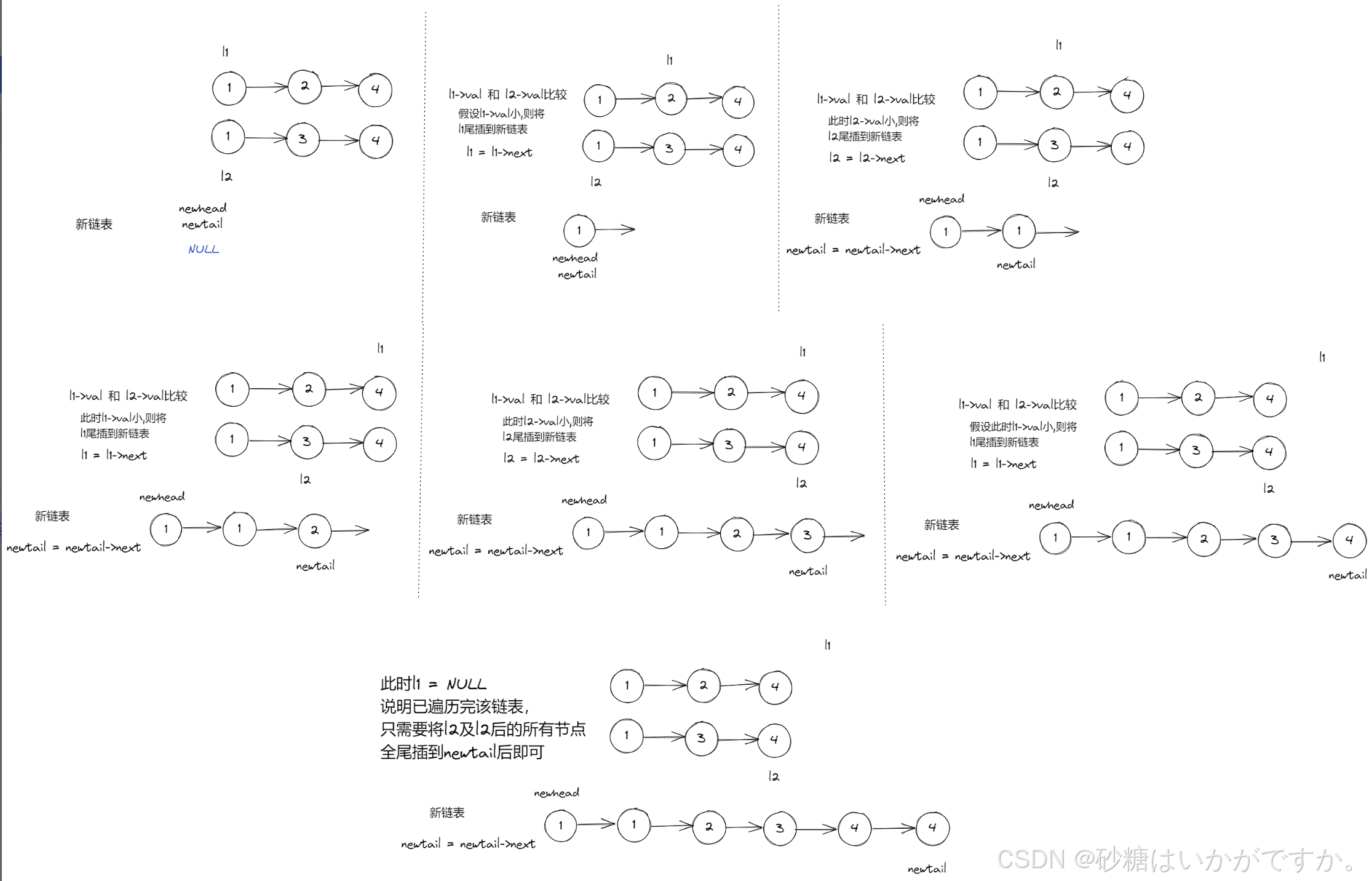
根据示意图,我们将代码搭建好了:
cpp
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2)
{
//判空
if (list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if (list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
ListNode* l1 = list1;
ListNode* l2 = list2;
//创建新链表
ListNode* newhead, *newtail;
newhead = newtail = NULL;
while (l1 && l2)
{
if (l1->val <= l2->val)
{
//l1尾插到新链表
if (newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2尾插到新链表
if (newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环有两种情况,要么 l1 走到空, 要么 l2 走到空
if (l2)
{
newtail->next = l2;
}
if (l1)
{
newtail->next = l1;
}
return newhead;
}代码我们写完了,但是这里有段代码很冗长,存在重复,该如何优化呢?
cpp
if (l1->val <= l2->val)
{
//l1尾插到新链表
if (newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l1;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2尾插到新链表
if (newhead == NULL)
{
newhead = newtail = l2;
}
else
{
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
}
}每次进入循环都要判断新链表是否为空,而实际上只有第一次需要判断,所以浪费运算时间
解决办法为让新链表不为空,即动态的开辟一个空间但不往空间里存放任何数据,这样新链表就是一个非空链表,头尾指针都指向了一个有效的地址(节点)
cpp
//创建新链表
ListNode* newhead, *newtail;
newhead = newtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
cpp
if (l1->val <= l2->val)
{
//l1尾插到新链表
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2尾插到新链表
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}此时的newhead 指向开辟的无数据的结构体指针,所以要return newhead->next
最后要将动态开辟的空间释放掉
最终代码如下:
cpp
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2)
{
//判空
if (list1 == NULL)
{
return list2;
}
if (list2 == NULL)
{
return list1;
}
ListNode* l1 = list1;
ListNode* l2 = list2;
//创建新链表
ListNode* newhead, *newtail;
newhead = newtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
while (l1 && l2)
{
if (l1->val <= l2->val)
{
//l1尾插到新链表
newtail->next = l1;
newtail = newtail->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
//l2尾插到新链表
newtail->next = l2;
newtail = newtail->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
//跳出循环有两种情况,要么 l1 走到空, 要么 l2 走到空
if (l2)
{
newtail->next = l2;
}
if (l1)
{
newtail->next = l1;
}
Listode* ret = newhead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = NULL;
return ret;
}