文章目录
- [1. 继承Thread类](#1. 继承Thread类)
- [2. 实现Runnable接口](#2. 实现Runnable接口)
- [3. 匿名内部类](#3. 匿名内部类)
- [4. lambda表达式](#4. lambda表达式)
- [5. 实现Callable接口](#5. 实现Callable接口)
- [6. 使用线程池(ExecutorService)](#6. 使用线程池(ExecutorService))
1. 继承Thread类
示例:
java
public class myThread extends Thread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
myThread thread = new myThread();
thread.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("这是通过继承Thread类创建的线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}输出:

重写的是run()方法,而不是start()方法,但是占用了继承的名额,java中的类是单继承的。
底层也是实现Runable接口,如下图:

2. 实现Runnable接口
java
public class myRunnable implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new myRunnable());
thread.start();
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("这是通过实现Runnable接口创建的线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}总结:实现Runnable接口,实现run()方法,使用依然要用到Thread,这种方式更常用
有时候,我们会直接使用匿名内部类的方式或者Lambda表达式的方式:
3. 匿名内部类
示例:
java
public class myThread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
System.out.println("这是通过使用匿名内部类创建的线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
thread.start();
}
}输出:

4. lambda表达式
java
public class myThread{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> System.out.println("这是通过使用lambda表达式创建的线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()));
thread.start();
}
}输出:

5. 实现Callable接口
结合FutureTask
java
class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
public Integer call() {
System.out.println("Thread is running: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return 42; // 返回值
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
MyCallable callable = new MyCallable();
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(callable);
new Thread(futureTask).start(); // 启动线程
Integer result = futureTask.get(); // 获取返回值
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
}
}输出:

FutureTask本质上还是继承了Runnable接口
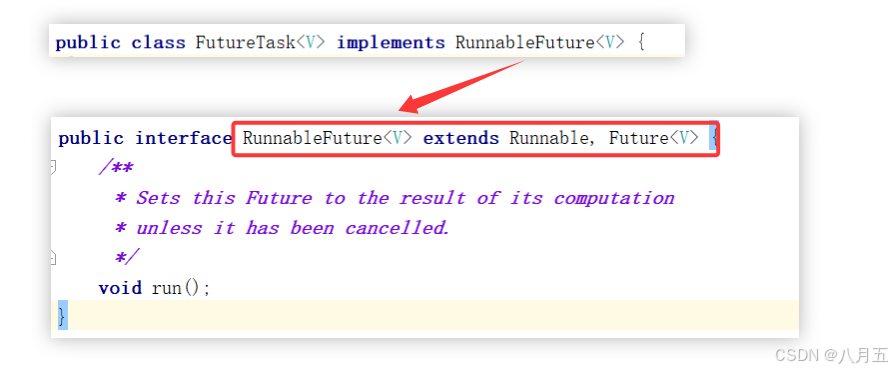
Java中,类和类是单继承的,接口之间是多继承的
6. 使用线程池(ExecutorService)
线程池是一种更高效、更灵活的线程管理方式,可以复用线程,避免频繁创建和销毁线程的开销。
java
public class MyThread implements Runnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
executorService.execute(new MyThread());
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello guys!");
}
}输出:

实现
Callable接口或者Runnable接口都可以,由ExecutorService来创建线程。
以上几种方式,底层都是基于Runnable。
