随机链表的复制
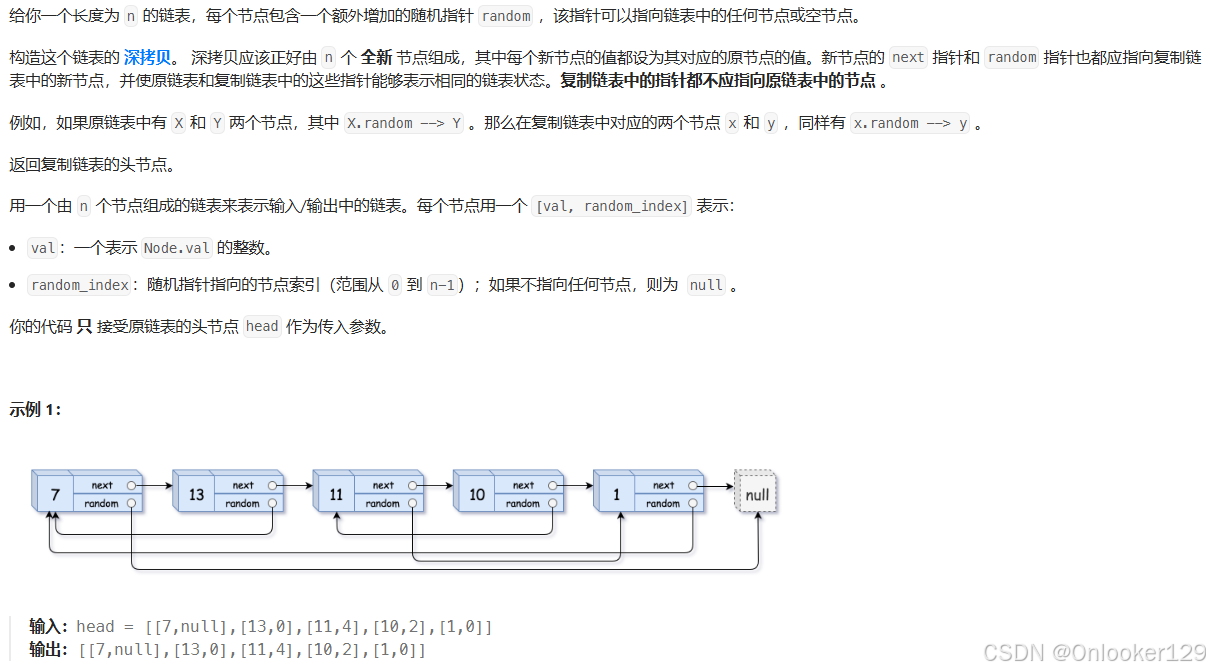
为了在 O(n) 时间复杂度内解决这个问题,并且使用 O(1) 的额外空间,可以利用以下技巧:
- 将新节点插入到原节点后面 :我们可以将复制节点插入到原节点后面。例如,如果链表是
A -> B -> C,我们将链表改为A -> A' -> B -> B' -> C -> C',其中A'、B'、C'是A、B、C的拷贝节点。 - 复制
random指针 :因为复制节点与原节点紧挨在一起,我们可以直接利用原节点的random指针,来为新节点复制random指针。 - 拆分链表:最后,我们将原链表和复制链表拆分成两个独立的链表。
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
//插入新节点到原节点后面
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node copy = new Node(cur.val);//创建新节点
copy.next = cur.next;//新节点的next指向原节点的next
cur.next = copy;//原节点的next指向新节点
cur = copy.next;//移动到原节点的下一个节点
}
//复制random节点
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.random != null){
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;//新节点的random指向原节点random对应的新节点
}
cur = cur.next.next;//跳到下一个原节点
}
//拆分链表,恢复原链表并生成新链表
Node newHead = head.next;
Node copyCur = newHead;
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
cur.next = cur.next.next;//恢复原链表
if(copyCur.next != null){
copyCur.next = copyCur.next.next;//更新新链表的next指针
copyCur = copyCur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return newHead;
}
}排序链表
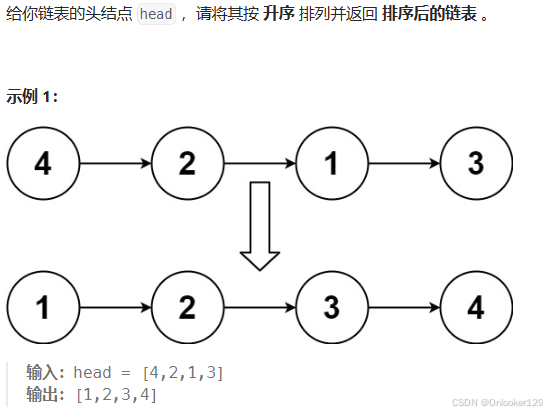
解题思路
- 归并排序:我们可以使用归并排序来对链表进行排序。归并排序的核心思想是将链表递归地分为两半,对两半分别进行排序,然后将排序后的两部分合并。
- 分割链表 :我们可以通过快慢指针的方法找到链表的中间节点,从而分割链表。在
findMiddle方法中,slow应该是慢指针,每次移动一步;fast是快指针,每次移动两步。当fast到达链表末尾时,slow应该正好指向中间节点的前一个节点。 - 合并两个有序链表 :归并排序的合并操作通常是合并两个有序链表。我们可以直接操作链表的
next指针来合并。
步骤
- 递归分割链表:通过快慢指针找到中间节点,将链表分为两部分。
- 排序子链表:对每个子链表递归调用归并排序。
- 合并两个有序链表:将两个排序后的子链表合并。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 递归终止条件:如果链表为空或者只有一个节点,直接返回
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 1. 找到链表的中间节点
ListNode mid = findMiddle(head);
// 2. 将链表分为两部分
ListNode left = head;
ListNode right = mid.next;
mid.next = null; // 切断链表,确保左右两部分互不影响
// 3. 对两部分链表递归排序
left = sortList(left);
right = sortList(right);
// 4. 合并两个有序链表
return merge(left, right);
}
// 找到链表的中间节点(快慢指针)
private ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 合并两个有序链表
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
// 合并两个有序链表
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
// 如果有剩余节点,直接连接
if (l1 != null) {
cur.next = l1;
} else {
cur.next = l2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}合并K个升序链表

使用优先队列(最小堆)
优先队列可以帮助我们高效地获取当前最小的节点。我们将每个链表的头节点加入到优先队列中,然后依次从队列中取出最小的节点,将其加入到新链表中,接着将其下一个节点加入到队列中,直到所有节点都被处理完。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//定义一个最小堆
PriorityQueue<ListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b) -> a.val - b.val);
//将所有链表的头节点加入堆中
for(ListNode list : lists){
if(list != null){
pq.offer(list);
}
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode current = dummy;
//从堆中取出最小节点,并将其后续节点加入堆
while(!pq.isEmpty()){
ListNode node = pq.poll();
current.next = node;
current = current.next;
if(node.next != null){
pq.offer(node.next);//将当前节点的下一个节点加入堆中
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}使用归并思想
归并的思想和合并两个有序链表的方法类似。每次从 k 个链表中合并两个链表,直到最终合并成一个链表。这个方法适用于链表数目较少的情况,因为其时间复杂度为 O(k log k)。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return mergeKListsHelper(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
// 分治法,合并两个链表
private ListNode mergeKListsHelper(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return lists[left];
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
ListNode leftMerged = mergeKListsHelper(lists, left, mid);
ListNode rightMerged = mergeKListsHelper(lists, mid + 1, right);
return mergeTwoLists(leftMerged, rightMerged);
}
// 合并两个有序链表
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode current = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
current.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
current.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
current = current.next;
}
if (l1 != null) {
current.next = l1;
} else {
current.next = l2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}LRU缓存

思路:
- 哈希表(HashMap):用于存储缓存的 key-value 对,通过 key 快速查找对应的值。哈希表中的每个元素将指向双向链表中的一个节点,这样可以在 O(1) 时间内访问链表节点。
- 双向链表(Doubly Linked List):用于表示缓存的使用顺序。最近使用的元素放在链表的头部,最久未使用的元素放在链表的尾部。当缓存达到容量限制时,我们可以从尾部移除最久未使用的元素。
操作:
get(key):- 如果
key存在缓存中,则返回该值,并将该节点移动到双向链表的头部(表示最近使用)。 - 如果
key不存在,返回 -1。
- 如果
put(key, value):- 如果
key已经存在,更新其值,并将该节点移动到链表的头部。 - 如果
key不存在,插入新节点,并将其添加到链表头部。如果缓存已满,移除链表尾部的节点(最久未使用)。
- 如果
设计步骤:
- 构造双向链表 :节点存储
key和value,同时拥有指向前一个节点和后一个节点的指针。 - 哈希表存储 :将
key和对应的链表节点关联起来,以便快速查找。 - 维护链表的顺序:每次访问节点时,将其移动到链表头部。
java
class LRUCache {
class Node{
int key,value;
Node prev,next;
public Node(int key,int value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
public Map<Integer,Node> cache;
private int capacity;
private Node head,tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.cache = new HashMap<>();
head = new Node(0,0);
tail = new Node(0,0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
//从链表中移除节点
private void remove(Node node){
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
//将节点插入到头部
private void insertToHead(Node node){
node.next = head.next;
node.prev = head;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
//获取缓存中的值
public int get(int key) {
if(cache.containsKey(key)){
Node node = cache.get(key);
remove(node);//移除节点
insertToHead(node);//将节点移到头部
return node.value;
}
return -1;
}
//插入或更新节点
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(cache.containsKey(key)){
//更新节点的值
Node node = cache.get(key);
node.value = value;
remove(node);
insertToHead(node);
}else{
if(cache.size() >= capacity){
//缓存已满,删除尾部节点
Node tailNode = tail.prev;
remove(tailNode);
cache.remove(tailNode.key);
}
//插入新节点
Node newNode = new Node(key,value);
cache.put(key,newNode);
insertToHead(newNode);//插入到头部
}
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj.get(key);
* obj.put(key,value);
*/