=====欢迎来到编程星辰海的博客讲解======
看完可以给一个免费的三连吗,谢谢大佬!

目录
[1. Hooks 是什么?](#1. Hooks 是什么?)
[2. useState 的作用](#2. useState 的作用)
[3. 基本语法解析](#3. 基本语法解析)
[4. 工作原理](#4. 工作原理)
[5. 参数详解](#5. 参数详解)
a) 初始值设置方式 初始值设置方式)
b) 更新函数特性 更新函数特性)
[6. 注意事项](#6. 注意事项)
[7. 类组件对比](#7. 类组件对比)
[8. 常见问题解答](#8. 常见问题解答)
一、知识讲解
1. Hooks 是什么?
React Hooks 是 React 16.8 引入的革命性特性,它允许开发者在函数组件中使用状态(state)和其他 React 特性。Hooks 的诞生解决了以下问题:
- 类组件中生命周期函数带来的逻辑分散
- 高阶组件带来的嵌套地狱(Wrapper Hell)
- 函数组件无法使用状态的局限
- 状态逻辑难以复用的问题
2. useState 的作用
useState 是最基础且重要的 Hook,它让函数组件具备管理局部状态的能力。其核心功能包括:
- 声明组件内部状态
- 提供状态更新方法
- 触发组件重新渲染
- 保持状态在多次渲染间的持久性
3. 基本语法解析
JAVASCRIPT
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
initialState:状态的初始值,可以是任何数据类型state:当前状态值setState:用于更新状态的函数
4. 工作原理
- 初始化阶段:组件首次渲染时,useState 会读取初始值并保存
- 更新阶段 :调用 setState 后:
- 将新值加入更新队列
- 触发组件重新渲染
- 在下次渲染时返回更新后的状态
- 渲染机制:每次渲染都有独立的状态快照(闭包特性)
5. 参数详解
a) 初始值设置方式
JAVASCRIPT
// 直接值初始化 const [count, setCount] = useState(0); // 函数式初始化(惰性初始化) const [count, setCount] = useState(() => { const initialValue = calculateExpensiveValue(); return initialValue; });
b) 更新函数特性
-
支持直接赋值更新: JAVASCRIPT
setCount(5); -
支持函数式更新(推荐用于依赖前值的场景): JAVASCRIPT
setCount(prevCount => prevCount + 1);
6. 注意事项
- 异步更新:状态更新是异步的,不能立即获取到新值
- 合并更新:React 会自动合并多个 setState 调用
- 性能优化:使用函数式更新避免闭包陷阱
- 不可变原则:始终返回新值而不是修改原值
7. 类组件对比
| 特性 | 类组件 | 函数组件 + useState |
|---|---|---|
| 状态初始化 | constructor | useState 参数 |
| 状态更新方式 | this.setState() | setState 函数 |
| 状态访问 | this.state | 直接使用状态变量 |
| 生命周期依赖 | 需要 | 无需 |
| 代码组织 | 分散在各个生命周期方法中 | 逻辑集中 |
8. 常见问题解答
Q:useState 和类组件的 state 有何不同?
A:useState 不会自动合并对象类型的状态,需要手动合并
Q:为什么 setCount(count + 1) 在异步操作中不可靠?
A:由于闭包特性,异步回调中的 count 可能不是最新值,应该使用函数式更新
Q:可以在条件语句中使用 useState 吗?
A:不行,所有 Hooks 都必须保证每次渲染的调用顺序一致
Q:如何存储复杂对象?
JAVASCRIPT
const [user, setUser] = useState({ name: 'John', age: 25, address: { city: 'New York', zip: '10001' } }); // 正确更新方式 setUser(prev => ({ ...prev, age: 26, address: { ...prev.address, zip: '10002' } }));
二、核心代码示例
JSX
import React, { useState } from 'react'; function Counter() { // 声明状态变量 count 及其更新函数 setCount // 初始值设为 0 const [count, setCount] = useState(0); // 定义增加计数器的方法 const increment = () => { // 使用函数式更新确保基于最新状态值 setCount(prevCount => prevCount + 1); }; // 定义减少计数器的方法 const decrement = () => { setCount(prevCount => prevCount - 1); }; // 定义重置计数器的方法 const reset = () => { setCount(0); }; return ( <div style={styles.container}> <h2>当前计数: {count}</h2> <div style={styles.buttonGroup}> {/* 绑定点击事件 */} <button style={styles.button} onClick={increment}>+</button> <button style={styles.button} onClick={decrement}>-</button> <button style={styles.button} onClick={reset}>重置</button> </div> {/* 条件渲染提示信息 */} {count >= 10 && <p style={styles.tip}>计数已经超过10啦!</p>} </div> ); } // 样式对象 const styles = { container: { textAlign: 'center', padding: '2rem', backgroundColor: '#f0f0f0', borderRadius: '8px', maxWidth: '400px', margin: '2rem auto' }, buttonGroup: { display: 'flex', justifyContent: 'center', gap: '1rem', marginTop: '1rem' }, button: { padding: '0.5rem 1rem', fontSize: '1.2rem', cursor: 'pointer', backgroundColor: '#2196f3', color: 'white', border: 'none', borderRadius: '4px', transition: 'background-color 0.3s' }, tip: { color: '#d32f2f', marginTop: '1rem', fontWeight: 'bold' } }; export default Counter;
三、实现效果
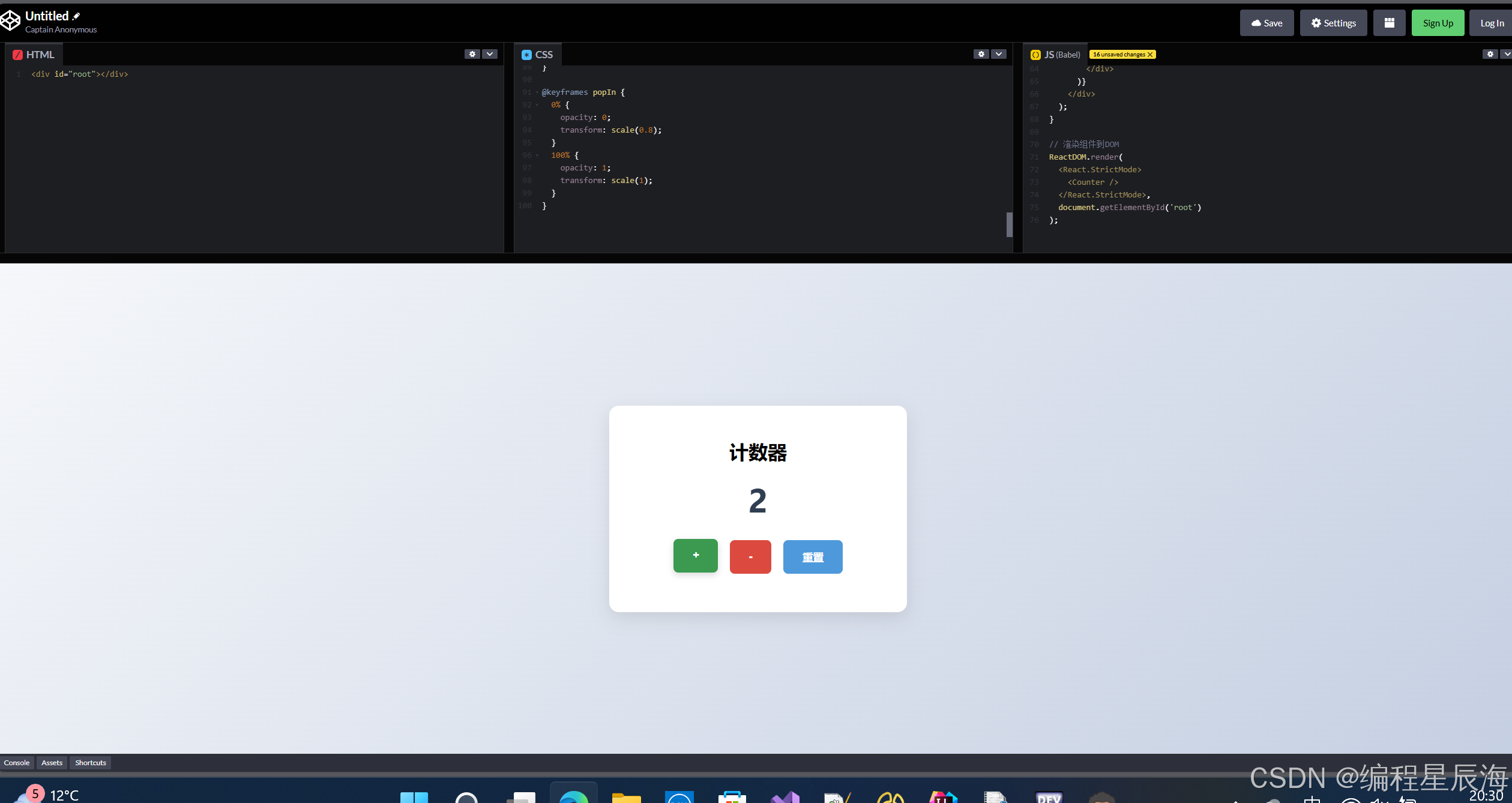
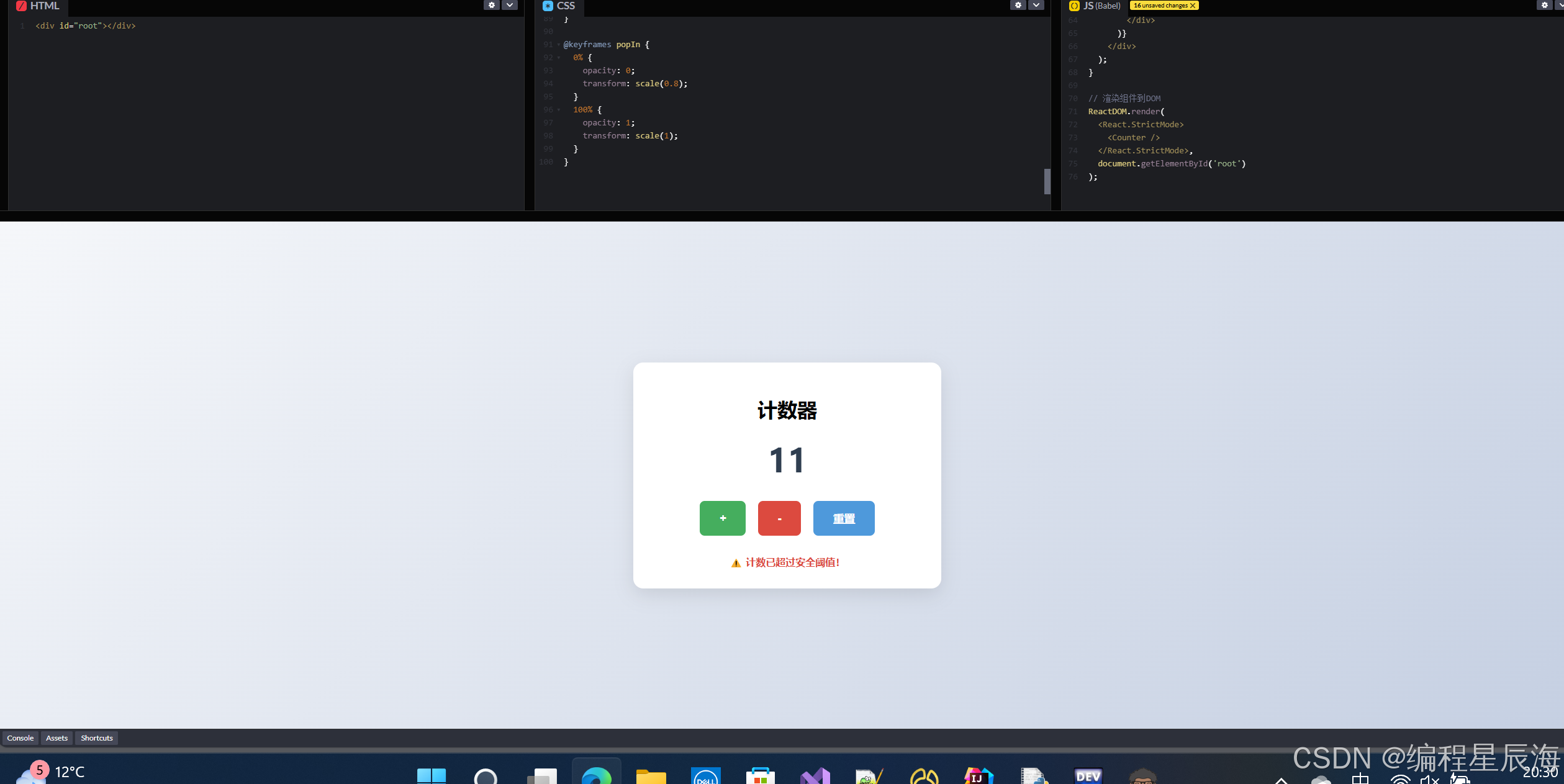
计数器组件包含:
- 显示当前数值的标题
- "+"、"-" 和 "重置" 三个操作按钮
- 当数值 >=10 时显示提示信息
- 按钮悬停时的颜色变化效果
- 整洁的卡片式布局
四、学习要点总结
-
基础概念
- useState 是用于给函数组件添加状态管理的 Hook
- 遵循
const [state, setState] = useState(initialValue)语法
-
使用规则
- 只在组件的顶层调用 Hooks
- 不要在循环、条件或嵌套函数中调用 Hooks
- 遵循不可变原则(immutability)
-
最佳实践
- 对于复杂对象,使用扩展运算符进行合并更新
- 异步操作时使用函数式更新确保获取最新状态
- 拆分多个 useState 管理不同状态
-
性能优化
- 对于昂贵的初始化,使用函数式初始化
- 当更新依赖前值时,必须使用函数式更新
- 使用 React.memo 防止不必要的重新渲染
-
常见错误
- 直接修改状态对象
JAVASCRIPT
// 错误示例 const [user, setUser] = useState({name: 'John'}); user.name = 'Mike'; // 直接修改原对象 setUser(user); // 不会触发更新 // 正确做法 setUser({...user, name: 'Mike'});
- 在渲染函数中执行副作用操作
- 忽视异步更新的特性
五、扩展阅读推荐
官方文档
优质文章
推荐学习路径
- 掌握 useState → useEffect → useContext 基础三件套
- 学习自定义 Hook 实现逻辑复用
- 了解 useReducer 管理复杂状态
- 学习性能优化相关 Hooks(useMemo/useCallback)
- 探索第三方 Hooks 库(如 ahooks)
进阶资源
六、实践步骤
可以以下步骤进行实践:
- 从简单计数器开始
- 实现表单输入控制
- 创建动态列表组件
- 开发带有复杂状态的购物车
- 尝试将业务逻辑抽象为自定义 Hooks
一、表单输入控制
JSX
import React, { useState } from 'react'; function UserForm() { // 使用单个对象管理所有表单字段 const [formData, setFormData] = useState({ username: '', email: '', password: '', newsletter: false }); // 统一处理输入变化 const handleInputChange = (e) => { const { name, value, type, checked } = e.target; setFormData(prev => ({ ...prev, [name]: type === 'checkbox' ? checked : value })); }; // 处理表单提交 const handleSubmit = (e) => { e.preventDefault(); console.log('表单提交数据:', formData); alert(JSON.stringify(formData, null, 2)); }; return ( <form style={formStyles} onSubmit={handleSubmit}> <div style={inputGroup}> <label>用户名:</label> <input type="text" name="username" value={formData.username} onChange={handleInputChange} /> </div> <div style={inputGroup}> <label>邮箱:</label> <input type="email" name="email" value={formData.email} onChange={handleInputChange} /> </div> <div style={inputGroup}> <label>密码:</label> <input type="password" name="password" value={formData.password} onChange={handleInputChange} /> </div> <div style={checkboxGroup}> <label> <input type="checkbox" name="newsletter" checked={formData.newsletter} onChange={handleInputChange} /> 订阅新闻邮件 </label> </div> <button type="submit" style={submitButton}>提交</button> </form> ); } // 样式配置 const formStyles = { maxWidth: '400px', margin: '2rem auto', padding: '2rem', backgroundColor: '#f8f9fa', borderRadius: '8px' }; const inputGroup = { marginBottom: '1rem' }; const checkboxGroup = { margin: '1rem 0' }; const submitButton = { backgroundColor: '#28a745', color: 'white', padding: '0.5rem 1rem', border: 'none', borderRadius: '4px', cursor: 'pointer' }; export default UserForm;
学习要点:
- 使用对象统一管理表单状态
- 处理多种输入类型(文本/复选框)
- 动态属性名更新技巧([name]: value)
- 表单提交时访问最新状态
二、动态列表组件
JSX
import React, { useState } from 'react'; function TodoList() { const [todos, setTodos] = useState([ { id: 1, text: '学习React Hooks', completed: false }, { id: 2, text: '练习useState', completed: true } ]); const [newTodo, setNewTodo] = useState(''); // 添加新待办事项 const addTodo = () => { if (newTodo.trim()) { setTodos([...todos, { id: Date.now(), text: newTodo, completed: false }]); setNewTodo(''); } }; // 切换完成状态 const toggleTodo = (id) => { setTodos(todos.map(todo => todo.id === id ? { ...todo, completed: !todo.completed } : todo )); }; // 删除待办事项 const deleteTodo = (id) => { setTodos(todos.filter(todo => todo.id !== id)); }; return ( <div style={container}> <h2>待办事项列表 ({todos.length})</h2> <div style={inputGroup}> <input type="text" value={newTodo} onChange={(e) => setNewTodo(e.target.value)} placeholder="输入新事项" style={inputStyle} /> <button onClick={addTodo} style={addButton}>添加</button> </div> <ul style={listStyle}> {todos.map(todo => ( <li key={todo.id} style={itemStyle(todo.completed)}> <input type="checkbox" checked={todo.completed} onChange={() => toggleTodo(todo.id)} /> <span style={{ flex: 1 }}>{todo.text}</span> <button onClick={() => deleteTodo(todo.id)} style={deleteButton} >删除</button> </li> ))} </ul> </div> ); } // 样式配置 const container = { maxWidth: '600px', margin: '2rem auto', padding: '1rem' }; const inputGroup = { display: 'flex', gap: '0.5rem', marginBottom: '1rem' }; const inputStyle = { flex: 1, padding: '0.5rem' }; const addButton = { backgroundColor: '#17a2b8', color: 'white', border: 'none', padding: '0.5rem 1rem', borderRadius: '4px', cursor: 'pointer' }; const listStyle = { listStyle: 'none', padding: 0 }; const itemStyle = (completed) => ({ display: 'flex', alignItems: 'center', padding: '0.5rem', margin: '0.5rem 0', backgroundColor: completed ? '#d4edda' : '#fff', border: '1px solid #ddd', borderRadius: '4px', opacity: completed ? 0.7 : 1 }); const deleteButton = { backgroundColor: '#dc3545', color: 'white', border: 'none', padding: '0.25rem 0.5rem', borderRadius: '4px', cursor: 'pointer' }; export default TodoList;
学习要点:
- 使用数组管理动态列表
- 列表项的增删改操作
- 正确使用key属性
- 复杂状态对象的更新方法
- 条件样式渲染技巧
三、购物车组件(复杂状态)
JSX
import React, { useState } from 'react'; const initialProducts = [ { id: 1, name: '商品A', price: 100, quantity: 1 }, { id: 2, name: '商品B', price: 200, quantity: 2 } ]; function ShoppingCart() { const [cart, setCart] = useState(initialProducts); const [newProduct, setNewProduct] = useState(''); // 计算总价 const total = cart.reduce((sum, item) => sum + (item.price * item.quantity), 0); // 添加新商品 const addProduct = () => { if (newProduct.trim()) { setCart([...cart, { id: Date.now(), name: newProduct, price: Math.floor(Math.random() * 500) + 100, quantity: 1 }]); setNewProduct(''); } }; // 更新商品数量 const updateQuantity = (id, delta) => { setCart(cart.map(item => { if (item.id === id) { const newQuantity = Math.max(1, item.quantity + delta); return { ...item, quantity: newQuantity }; } return item; })); }; // 移除商品 const removeProduct = (id) => { setCart(cart.filter(item => item.id !== id)); }; return ( <div style={container}> <h2>购物车 (总价: ¥{total})</h2> <div style={inputGroup}> <input type="text" value={newProduct} onChange={(e) => setNewProduct(e.target.value)} placeholder="输入商品名称" style={inputStyle} /> <button onClick={addProduct} style={addButton}>添加商品</button> </div> <ul style={listStyle}> {cart.map(item => ( <li key={item.id} style={itemStyle}> <div style={itemInfo}> <span style={itemName}>{item.name}</span> <span>单价: ¥{item.price}</span> </div> <div style={quantityControls}> <button onClick={() => updateQuantity(item.id, -1)} style={controlButton} >-</button> <span style={quantityDisplay}>{item.quantity}</span> <button onClick={() => updateQuantity(item.id, 1)} style={controlButton} >+</button> </div> <div style={itemSubtotal}> 小计: ¥{item.price * item.quantity} <button onClick={() => removeProduct(item.id)} style={removeButton} >删除</button> </div> </li> ))} </ul> </div> ); } // 样式配置 const container = { maxWidth: '800px', margin: '2rem auto', padding: '1rem' }; const inputGroup = { display: 'flex', gap: '0.5rem', marginBottom: '1rem' }; const inputStyle = { flex: 1, padding: '0.5rem' }; const addButton = { backgroundColor: '#007bff', color: 'white', border: 'none', padding: '0.5rem 1rem', borderRadius: '4px', cursor: 'pointer' }; const listStyle = { listStyle: 'none', padding: 0 }; const itemStyle = { display: 'flex', justifyContent: 'space-between', alignItems: 'center', padding: '1rem', margin: '0.5rem 0', backgroundColor: '#fff', border: '1px solid #ddd', borderRadius: '4px' }; const itemInfo = { flex: 2, display: 'flex', flexDirection: 'column', gap: '0.5rem' }; const itemName = { fontWeight: 'bold' }; const quantityControls = { display: 'flex', alignItems: 'center', gap: '0.5rem' }; const controlButton = { padding: '0.25rem 0.5rem', minWidth: '32px', backgroundColor: '#6c757d', color: 'white', border: 'none', borderRadius: '4px', cursor: 'pointer' }; const quantityDisplay = { minWidth: '30px', textAlign: 'center' }; const itemSubtotal = { flex: 1, display: 'flex', flexDirection: 'column', alignItems: 'flex-end', gap: '0.5rem' }; const removeButton = { backgroundColor: '#dc3545', color: 'white', border: 'none', padding: '0.25rem 0.5rem', borderRadius: '4px', cursor: 'pointer' }; export default ShoppingCart;
学习要点:
- 多层嵌套状态的管理
- 复杂状态更新模式
- 派生状态(总价)的计算
- 不可变数据更新模式
- 复杂组件的样式组织
四、自定义Hook:useCart
JSX
// useCart.js import { useState } from 'react'; function useCart(initialItems = []) { const [cart, setCart] = useState(initialItems); const total = cart.reduce((sum, item) => sum + (item.price * item.quantity), 0); const addItem = (newItem) => { setCart([...cart, { ...newItem, id: Date.now(), quantity: 1 }]); }; const updateQuantity = (itemId, delta) => { setCart(currentCart => currentCart.map(item => item.id === itemId ? { ...item, quantity: Math.max(1, item.quantity + delta) } : item ) ); }; const removeItem = (itemId) => { setCart(currentCart => currentCart.filter(item => item.id !== itemId)); }; return { cart, total, addItem, updateQuantity, removeItem }; } export default useCart; // 使用示例 function CartComponent() { const { cart, total, addItem, updateQuantity, removeItem } = useCart(); // ...组件实现与前面购物车示例类似 }
学习要点:
- 自定义Hook的命名规范(必须用use开头)
- 状态逻辑的封装
- Hook之间的通信
- 返回可操作的方法集
- 实现业务逻辑复用
推荐练习项目:
- 个人博客系统
- 任务管理系统(类似Trello)
- 电子商务平台
- 实时数据监控仪表盘
学完后建议弄清以下问题:
- 状态更新的原理是什么?
- 如何避免不必要的重新渲染?
- 复杂状态如何组织更合理?
- 如何调试状态变化?
- 如何测试Hook相关逻辑?
