547. Number of Provinces
There are n cities. Some of them are connected, while some are not. If city a is connected directly with city b, and city b is connected directly with city c, then city a is connected indirectly with city c.
A province is a group of directly or indirectly connected cities and no other cities outside of the group.
You are given an n x n matrix isConnected where isConnected[i][j] = 1 if the i^th city and the jth city are directly connected, and isConnected[i][j] = 0 otherwise.
Return the total number of provinces.
Example 1:
Input: isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 2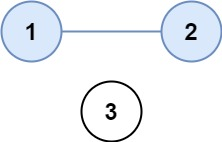
Example 2:
Input: isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3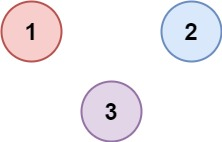
问题描述
给定一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。省份是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有连接的城市。要求返回省份的总数。
解决思路
一眼"并查集",这个sense是要有的。不熟悉的同学可以复习并查集(Union-Find)数据结构详解。简单地说,在计算机科学中,并查集 (Disjoint-set data structure,直译为不交集数据结构)是一种数据结构,用于处理一些不交集(Disjoint sets,一系列没有重复元素的集合)的合并及查询问题。
并查集支持如下操作:
- 查询:查询某个元素属于哪个集合,通常是返回集合内的一个"代表元素"。这个操作是为了判断两个元素是否在同一个集合之中。
- 合并:将两个集合合并为一个。
- 添加:添加一个新集合,其中有一个新元素。
由于支持查询和合并这两种操作,并查集在英文中也被称为联合-查找数据结构 (Union-find data structure)或者合并-查找集合 (Merge-find set),简称并查集。
在省份数量问题中:
- 每个城市最初属于自己独立的省份(即自己是自己的父节点)。
- 当两个城市相连时,我们合并它们所在的省份。
- 最终,剩余的独立集合数量就是省份的总数。
详细步骤解析
-
初始化并查集
cppclass UnionFind { public: UnionFind(int size) : parent(size), count(size) { for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { parent[i] = i; // 每个城市初始时父节点指向自己 } } // ... private: vector<int> parent; // 记录每个节点的父节点 int count; // 记录当前集合/省份的数量 };parent数组:parent[i]表示城市i的父节点count:初始值为n,表示最初有n个独立省份(每个城市一个)
-
Find操作 - 查找根节点cppint find(int x) { if (parent[x] != x) { parent[x] = find(parent[x]); // 路径压缩优化 } return parent[x]; }-
递归地查找
x的根节点 -
路径压缩:在查找过程中将节点直接指向根节点,减少后续查找时间
-
示例:查找城市3的根节点
1 → 2 → 3 → 4 (根节点是4) 查找3后变为: 1 → 2 → 4 3 → 4
-
-
Union操作 - 合并集合cppvoid unionSet(int x, int y) { int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); if (rootX != rootY) { // 只有当两个城市不在同一集合时才合并 parent[rootY] = rootX; --count; // 合并后省份数量减1 } }- 找到两个城市的根节点
- 如果根节点不同,则将其中一个根节点指向另一个
- 减少省份计数
-
主算法流程
cppint findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) { int n = isConnected.size(); UnionFind uf(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) { if (isConnected[i][j] == 1) { uf.unionSet(i, j); // 合并相连的城市 } } } return uf.getCount(); // 返回最终省份数量 }- 遍历所有城市对(只需要遍历矩阵上半部分,避免重复)
- 当两个城市相连时,合并它们所在的集合
- 最终剩余的集合数量就是省份总数
C++ 实现:并查集(Union-Find)
cpp
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(int size) : parent(size), count(size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
}
return parent[x];
}
void unionSet(int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(x);
int rootY = find(y);
if (rootX != rootY) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
--count;
}
}
int getCount() const {
return count;
}
private:
vector<int> parent;
int count;
};
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.size();
UnionFind uf(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1) {
uf.unionSet(i, j);
}
}
}
return uf.getCount();
}
};深度优先搜索(DFS)解法
- 使用递归实现深度优先搜索
- 通过
visited数组避免重复访问 - 每次遇到未访问城市就开始新的DFS,代表发现新省份
cpp
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.size();
vector<bool> visited(n, false); // 访问标记数组
int provinces = 0; // 省份计数器
// DFS递归函数
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int city) {
visited[city] = true;
for (int neighbor = 0; neighbor < n; ++neighbor) {
// 如果相连且未访问,则递归访问
if (isConnected[city][neighbor] == 1 && !visited[neighbor]) {
dfs(neighbor);
}
}
};
// 遍历所有城市
for (int city = 0; city < n; ++city) {
if (!visited[city]) { // 发现未访问的城市
++provinces; // 增加省份计数
dfs(city); // DFS遍历该省份所有城市
}
}
return provinces;
}广度优先搜索(BFS)解法
- 使用队列实现广度优先搜索
- 同样使用
visited数组避免重复访问 - 每次遇到未访问城市就开始新的BFS,代表发现新省份
cpp
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
int n = isConnected.size();
vector<bool> visited(n, false); // 访问标记数组
int provinces = 0; // 省份计数器
queue<int> q; // BFS队列
for (int city = 0; city < n; ++city) {
if (!visited[city]) { // 发现未访问的城市
++provinces; // 增加省份计数
q.push(city); // 当前城市入队
visited[city] = true; // 标记已访问
// BFS遍历
while (!q.empty()) {
int current = q.front();
q.pop();
// 检查所有可能相连的城市
for (int neighbor = 0; neighbor < n; ++neighbor) {
if (isConnected[current][neighbor] == 1 && !visited[neighbor]) {
visited[neighbor] = true; // 标记已访问
q.push(neighbor); // 相连城市入队
}
}
}
}
}
return provinces;
}复杂度分析
| 方法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 |
|---|---|---|
| DFS | O ( n 2 ) O(n²) O(n2) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
| BFS | O ( n ² ) O(n^²) O(n²) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |
| 并查集 | O ( n 2 α ( n ) ) O(n² α(n)) O(n2α(n)) | O ( n ) O(n) O(n) |