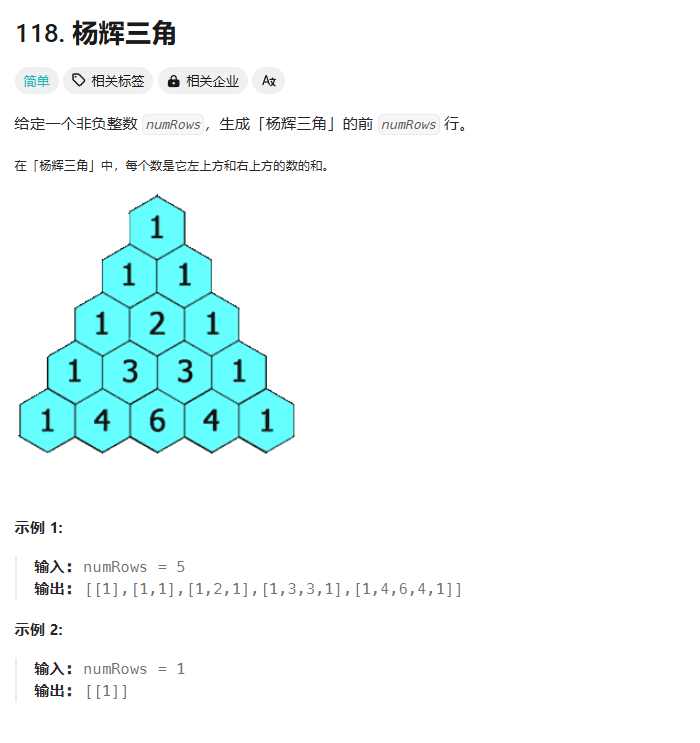
递归:
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
int numRows = 0;
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
this.numRows = numRows;
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int depth) {
List<Integer> nowA = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i <= depth; i++) { // 不需要单独对边界条件处理
if(i == 0 || i == depth) {
nowA.add(1);
continue;
}
nowA.add(ans.get(depth - 1).get(i) + ans.get(depth - 1).get(i - 1));
}
ans.add(nowA);
if (depth + 1 < this.numRows) {
dfs(depth + 1);
}
return;
}
}循环的方式实现:
java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
List<Integer> nowA = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
if (j == 0 || j == i) {
nowA.add(1);
} else {
int lastNum = ans.get(i - 1).get(j) + ans.get(i - 1).get(j - 1);
nowA.add(lastNum);
}
}
ans.add(nowA);
}
return ans;
}
}