当我刚开始接触编程的时候,第一个接触的语言是C#,开发网站使用的是.net,因为是在职校学习的所以在技术学习范围就变的很狭隘,连接数据库要写一长串代码直连,并且每个语句都要写出来 加上拼接自己的参数去实现查询。后来接触了第一个orm框架Hibernate 再到上班接触学习了TypeORM、Sequelize。
今天我们讲解一下如何sequelize的基本使用,解放你写原生语句的烦恼
一、连接mysql
首先在mysql上创建一个测试用的库 sequelize 推荐使用的数据库管理工具(navicat)
注意:电脑上要已安装了mysql服务才有用!
shell
cnpm install --save sequelize mysql2 moment编写测试连接的代码:
javascript
// 引入库
const { Sequelize } = require("sequelize");
// 连接数据库
const sequelize = new Sequelize({
// 选择使用的数据库 'mysql' | 'postgres' | 'sqlite' | 'mariadb' | 'mssql' | 'db2' | 'snowflake' | 'oracle'
dialect: "mysql",
// 连接本机mysql
host: "localhost",
port: 3306,
// 输入mysql的账号密码 并指定数据库
username: "root",
password: "root",
database: "sequelize",
});
// 测试连接
async function authenticate() {
try {
await sequelize.authenticate();
console.log("数据库连接成功");
} catch (error) {
console.error("无法连接数据库", error);
return process.exit(1);
}
}
authenticate();二、编写表模型代码
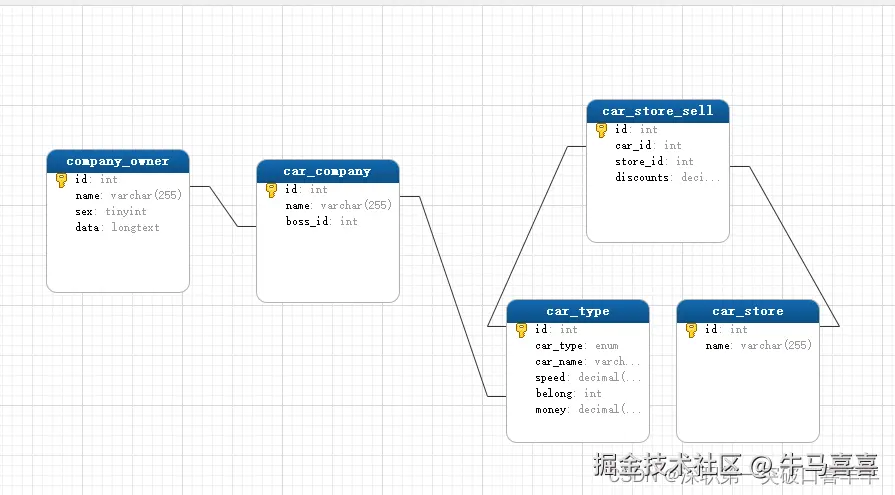
编写代码之前我们先要想我们的数据表 这是最重要的部分
我们创建一个model.js的文件 根据创建的模型想法 写入代码
javascript
const { Sequelize, DataTypes, NOW } = require("sequelize");
const moment = require("moment");
const { STRING, INTEGER, DECIMAL, DATE, BOOLEAN, ENUM, TEXT } = DataTypes;
/**
* @description:创建数据库表用
* @param {Sequelize} sequelize // IDE检测不到 这个参数是啥 我们用的又是js 所以使用这个方式就能让IDE知道这个参数的类型 VsCode插件:koroFileHeader
*/
module.exports = (sequelize) => {
// 学生啊 班级啊 教师啊 那些表都用烂了 男人的浪漫还是要车子 我们就以车子为例
// 属性介绍
// type(字段类型)
// primaryKey(主键)
// autoIncrement(自动增长)
// allowNull(是否允许为Null)
// defaultValue(默认值)
// get(获取时的操作)
// set(设置时的操作)
// values(枚举允许使用的值)
// comment(注释)
const common_config = {
// Model 对应的表名将与model名相同
freezeTableName: true,
// 时间戳开启 并且开启sequelize为我们预设的关于时间的字段
timestamps: true,
deletedAt: true,
createdAt: true,
updatedAt: true,
// 偏执表 开启后 删除记录都是软删除 防止误删
paranoid: true,
};
// 格式化创建时间
const createdAt = {
type: DATE,
defaultValue: NOW,
get() {
return moment(this.getDataValue("createdAt")).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm");
},
};
// 车企老板
const CompanyOwner = sequelize.define(
"company_onwer",
{
id: { type: INTEGER, primaryKey: true, autoIncrement: true },
name: { type: STRING, allowNull: false, comment: "老板名称" },
sex: { type: BOOLEAN, allowNull: false, comment: "性别", defaultValue: 1 },
// 一些特殊的用法 比如塞一个json数据到里面 我想获取和设置的时候不需要额外处理
data: {
type: TEXT("long"),
allowNull: false,
get() {
// 如果使用raw 去获取的话会失效
return JSON.parse(this.getDataValue("data"));
},
set(value) {
this.setDataValue("data", JSON.stringify(value));
},
},
createdAt,
},
common_config
);
// 车企
const CarCompany = sequelize.define(
"car_company",
{
id: { type: INTEGER, primaryKey: true, autoIncrement: true },
name: { type: STRING, allowNull: false, comment: "厂家名称" },
boss_id: { type: INTEGER, allowNull: false, comment: "boss的id" },
createdAt,
},
common_config
);
// 车子
const CarType = sequelize.define(
"car_type",
{
id: { type: INTEGER, primaryKey: true, autoIncrement: true },
car_type: { type: ENUM, allowNull: false, values: ["轿车", "suv"], comment: "车子类型" },
car_name: { type: STRING, allowNull: false, comment: "车辆名称" },
speed: { type: DECIMAL, allowNull: false, comment: "0-100加速" },
belong: { type: INTEGER, allowNull: false, comment: "所属厂家" },
money: { type: DECIMAL, allowNull: false, comment: "指导价" },
createdAt,
},
common_config
);
// 4S店
const CarStore = sequelize.define(
"car_store",
{
id: { type: INTEGER, primaryKey: true, autoIncrement: true },
name: { type: STRING, allowNull: false, comment: "4s名称" },
createdAt,
},
common_config
);
// 4S与车子的连接表
const CarStoreSell = sequelize.define(
"car_store_sell",
{
id: { type: INTEGER, primaryKey: true, autoIncrement: true },
car_id: { type: INTEGER, allowNull: false, comment: "车辆id" },
store_id: { type: INTEGER, allowNull: false, comment: "4S店的id" },
discounts: { type: DECIMAL, allowNull: false, comment: "优惠价格" },
createdAt,
},
common_config
);
// 定义关联情况
// 关联讲解
// 一对一 就是你的车架号和你的车 是绑定的 不会有相同的车架号
// 一对多 就是一个车企 可以有很多子品牌 比如 吉利下有 领克 极氪等 但他们都是属于吉利下的
// 多对多 就是你买车的时候 可以去A4S店 也可以去B4S店买 但是A、B店不止卖这一款车 而且优惠力度也不一样
// 配置项还可以使用 constraints:false 虚拟绑定不创建外键 防止删除表的时候一直很恶心
// 一对一 一个公司 一个老板 这里只是为了把三种关联关系都绑上 一个老板可以有很多个公司
CompanyOwner.hasOne(CarCompany, { foreignKey: "boss_id", sourceKey: "id", constraints: false });
CarCompany.belongsTo(CompanyOwner, { as: "bossInfo", foreignKey: "boss_id", targetKey: "id", constraints: false });
// 一对多 一个公司可以生产很多车型
CarCompany.hasMany(CarType, { foreignKey: "belong", constraints: false });
CarType.belongsTo(CarCompany, { foreignKey: "belong", constraints: false });
// 多对多 一个4S可以卖多种类的车 一个种类的车也可以被多个4S店卖
CarStore.belongsToMany(CarType, { through: CarStoreSell, sourceKey: "id", foreignKey: "store_id", constraints: false });
CarType.belongsToMany(CarStore, { through: CarStoreSell, sourceKey: "id", foreignKey: "car_id", constraints: false });
// 初始化表 创建完记得注释掉 使用alter属性还会重复创建外键 所以 只有初始化的时候用就好了
// sequelize.sync();
return {
CarCompany,
CarStore,
CarType,
CompanyOwner,
CarStoreSell,
};
};三、增删改查
1.代码修改
我们先对原来的代码进行修改 后续代码统一写入transaction里
javascript
// 引入库
const { Sequelize, Op, fn, col, literal } = require("sequelize");
// 连接数据库
const sequelize = new Sequelize({
// 选择使用的数据库 'mysql' | 'postgres' | 'sqlite' | 'mariadb' | 'mssql' | 'db2' | 'snowflake' | 'oracle'
dialect: "mysql",
// 连接本机mysql
host: "localhost",
port: 3306,
// 输入mysql的账号密码 并指定数据库
username: "root",
password: "root",
database: "sequelize",
logging: false,
});
// 测试连接
async function authenticate() {
try {
await sequelize.authenticate();
console.log("数据库连接成功");
let { CarCompany, CarStore, CarType, CompanyOwner, CarStoreSell } = require("./models")(sequelize);
// 运行前清空所有表数据
await sequelize.truncate({ force: true });
try {
// 使用事务 后续再讲 原子性 要全部语句运行成功 有一个错误就回滚
await sequelize.transaction(async (transaction) => {
// 在此写入代码
});
} catch (err) {
console.log("数据操作的时候出现了错误:");
console.log(err);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("无法连接数据库", error);
return process.exit(1);
}
}
authenticate();2.增的基础使用
javascript
// 增删改查 增的基础使用
const createMethods = async () => {
// 推荐使用findOrCreate 测试途中会重复运行代码 防止重复创建
// xxx.create(结构)
// xxx.findOrCreate 返回结构为[model,created] model代表返回查询或者刚创建的模型 created代表是否是刚刚创建的
// 1.一个叫张三的老板
let boss = await CompanyOwner.create(
{
name: "张三",
data: {
story: "测试数据",
},
},
{
transaction,
}
);
// 2.创建了一个车企
let bwm = await CarCompany.create(
{
name: "别摸我",
boss_id: boss.id,
},
{
transaction,
}
);
// 3.生产了两个车型
let M3 = await CarType.create(
{
car_type: "轿车",
car_name: "M3 雷霆版",
money: 900000,
speed: 4,
belong: bwm.id,
},
{
transaction,
}
);
let GLB200 = await CarType.create(
{
car_type: "suv",
car_name: "GLB200 7座",
money: 300000,
speed: 10,
belong: bwm.id,
},
{
transaction,
}
);
// 4.开了两家4S店 A店只卖M3 B店卖M3和GLB200
let storeA = await CarStore.create(
{ name: "中升海滨店" },
{
transaction,
}
);
let storeB = await CarStore.create(
{ name: "中升讯美店" },
{
transaction,
}
);
// 这个生成的添加关联方法有点难找
// 如果一直提示错误的话 Model.associations 打印出来 看里面的关联 并且将首字母大写
// 如 我获取到的数据 { car_types: car_types } 所以就是addCar_types
await storeA.addCar_types(M3, { through: { discounts: 10000 } });
await storeB.addCar_types(M3, { through: { discounts: 8000 } });
await storeB.addCar_types(GLB200, { through: { discounts: 30000 } });
// 基础的数据生成完毕了
};3.查的基础使用
javascript
// 增删改查 查的基础使用
const readMethods = async () => {
// 为什么查询都要加上事务呢? 因为我们是在同一次事务内操作的 还没提交到数据库中
// 不加上事务的id 无法查找到还未提交
let [current_page, page_size] = [1, 10];
// 查找有几家车企和数据 通常用于分页
let companys = await CarCompany.findAndCountAll({
limit: page_size,
offset: (current_page - 1) * page_size,
transaction,
});
// 返回的结果是 {count:数量,rows:数据}
console.log(companys.count);
// 查找叫别摸我的车企 并且获取它的老板信息
let bwm = await CarCompany.findOne({
where: { name: "别摸我" },
include: {
// 使用模型获取
// model: CompanyOwner,
// 使用别名获取
association: "bossInfo",
// 不写获取所有的字段 写了就仅获取所填的字段
attributes: ["name", "data"],
// 第二种写法 可以排除属性 也可以包含属性
// attributes: {
// include: ["name", "data"],
// exclude: ["id"],
// },
},
transaction,
});
// 能直接获取到老板的名字
// console.log(bwm.company_onwer.name);
console.log(bwm.bossInfo.name);
// 我们之前做了处理 所以拿到的直接是对象 而不是字符串
// { story: '测试数据' }
console.log(bwm.bossInfo.data);
// 查询该车企业有几款车
let cars = await CarCompany.findOne({
where: {
// 使用id查询 其实不需要别的条件的话 直接使用findByPk即可
id: bwm.id,
// car_type:["suv","轿车"] car_type:"suv" 对车类型进行筛查
// 对价格进行筛查
// money: {
// [Op.lte]: 500000,
// [Op.gte]: 500000,
// [Op.between]: [0, 1000000],
// },
// 更多操作见 https://www.sequelize.cn/core-concepts/model-querying-basics#%E9%AB%98%E7%BA%A7%E6%9F%A5%E8%AF%A2%E4%B8%8D%E4%BB%85%E9%99%90%E4%BA%8E%E5%88%97
},
include: {
model: CarType,
},
transaction,
});
// [ 'M3 雷霆版', 'GLB200 7座' ]
cars.car_types.length && console.log(cars.car_types.map((x) => x.car_name));
// 查找这几款车有几家4S店在卖 指导价 以及优惠过的价格
// 尽量不要在循环里写语句 一次查找出来 再用代码逻辑去操作
let stores = await CarType.findAll({
where: {
id: cars.car_types.map((x) => x.id),
},
include: {
model: CarStore,
// 不希望连接的字段出现
attributes: [],
through: {
model: CarStoreSell,
attributes: [],
},
},
attributes: [
"car_name",
"money",
[col("car_stores.name"), "store_name"],
// [col("`car_stores->car_store_sell`.discounts"), "discounts"]
// 计算优惠后的价格
[literal("`car_type`.`money` - `car_stores->car_store_sell`.`discounts`"), "sell_money"],
],
// 不需要获取模型原型 只要数据
raw: true,
transaction,
});
// 获取到的数组其中一项
// [
// {
// car_name: "GLB200 7座",
// money: "300000",
// store_name: "中升讯美店",
// sell_money: "270000",
// },
// ];
console.log(stores);
// 基本的关联查找功能讲解完毕
};4.改的基础使用
javascript
// 增删改查 改的基础使用
const updateMethods = async () => {
// 修改一些老板的数据
let boss = await CompanyOwner.findOne({ where: { name: "张三" }, transaction });
// 赋值方式1
// boss.setDataValue("data", { story: "修改数据" });
// 赋值方式2
boss.data = { story: "修改数据" };
boss.sex = 0;
boss.name = "李四";
await boss.save({ transaction });
boss = await CompanyOwner.findOne({ include: CarCompany, transaction });
// {name:"李四",sex:false,data:{ story: '修改数据' }}
console.log(boss);
// 车企指导价下降的批量操作
// 自减写法1 自增increment
// await CarType.decrement("money", {
// by: 10000,
// where: {
// belong: boss.car_company.id,
// },
// transaction,
// });
// 自减写法2
await CarType.update(
{
money: literal(`money - 20000`),
},
{
where: {
belong: boss.car_company.id,
},
transaction,
}
);
// 更新的基础操作就做完了
};5.删的基础使用
javascript
// 增删改查 删除的基础使用
const deleteMethods = async () => {
// 4s下架所有车辆
await CarStoreSell.destroy({ transaction, where: {} });
// 车企下架单独某款车
let car = await CarType.findOne({ where: { car_name: "GLB200 7座" }, transaction });
await car.destroy({ transaction });
// 车企倒闭了 所有车辆下架 老板销户了
await CarType.destroy({ transaction, where: {} });
await CarCompany.destroy({ transaction, where: {} });
await CompanyOwner.destroy({ where: { name: "李四" }, transaction });
// 这就是简单的删除应用 操作数据类的代码 最好要用事务去操作 但是事务也有缺陷 可以去看看脏读 幻读 等
};6.完整代码
javascript
// 引入库
const { Sequelize, Op, fn, col, literal } = require("sequelize");
// 连接数据库
const sequelize = new Sequelize({
// 选择使用的数据库 'mysql' | 'postgres' | 'sqlite' | 'mariadb' | 'mssql' | 'db2' | 'snowflake' | 'oracle'
dialect: "mysql",
// 连接本机mysql
host: "localhost",
port: 3306,
// 输入mysql的账号密码 并指定数据库
username: "root",
password: "root",
database: "sequelize",
logging: false,
});
// 测试连接
async function authenticate() {
try {
await sequelize.authenticate();
console.log("数据库连接成功");
let { CarCompany, CarStore, CarType, CompanyOwner, CarStoreSell } = require("./models")(sequelize);
// 运行前清空所有表数据
await sequelize.truncate({ force: true });
try {
// 使用事务 后续再讲 原子性 要全部语句运行成功 有一个错误就回滚
await sequelize.transaction(async (transaction) => {
// 增删改查 增的基础使用
const createMethods = async () => {
// 推荐使用findOrCreate 测试途中会重复运行代码 防止重复创建
// xxx.create(结构)
// xxx.findOrCreate 返回结构为[model,created] model代表返回查询或者刚创建的模型 created代表是否是刚刚创建的
// 1.一个叫张三的老板
let boss = await CompanyOwner.create(
{
name: "张三",
data: {
story: "测试数据",
},
},
{
transaction,
}
);
// 2.创建了一个车企
let bwm = await CarCompany.create(
{
name: "别摸我",
boss_id: boss.id,
},
{
transaction,
}
);
// 3.生产了两个车型
let M3 = await CarType.create(
{
car_type: "轿车",
car_name: "M3 雷霆版",
money: 900000,
speed: 4,
belong: bwm.id,
},
{
transaction,
}
);
let GLB200 = await CarType.create(
{
car_type: "suv",
car_name: "GLB200 7座",
money: 300000,
speed: 10,
belong: bwm.id,
},
{
transaction,
}
);
// 4.开了两家4S店 A店只卖M3 B店卖M3和GLB200
let storeA = await CarStore.create(
{ name: "中升海滨店" },
{
transaction,
}
);
let storeB = await CarStore.create(
{ name: "中升讯美店" },
{
transaction,
}
);
// 这个生成的添加关联方法有点难找
// 如果一直提示错误的话 Model.associations 打印出来 看里面的关联 并且将首字母大写
// 如 我获取到的数据 { car_types: car_types } 所以就是addCar_types
await storeA.addCar_types(M3, { through: { discounts: 10000 } });
await storeB.addCar_types(M3, { through: { discounts: 8000 } });
await storeB.addCar_types(GLB200, { through: { discounts: 30000 } });
// 基础的数据生成完毕了
};
// 增删改查 查的基础使用
const readMethods = async () => {
// 为什么查询都要加上事务呢? 因为我们是在同一次事务内操作的 还没提交到数据库中
// 不加上事务的id 无法查找到还未提交
let [current_page, page_size] = [1, 10];
// 查找有几家车企和数据 通常用于分页
let companys = await CarCompany.findAndCountAll({
limit: page_size,
offset: (current_page - 1) * page_size,
transaction,
});
// 返回的结果是 {count:数量,rows:数据}
console.log(companys.count);
// 查找叫别摸我的车企 并且获取它的老板信息
let bwm = await CarCompany.findOne({
where: { name: "别摸我" },
include: {
// 使用模型获取
// model: CompanyOwner,
// 使用别名获取
association: "bossInfo",
// 不写获取所有的字段 写了就仅获取所填的字段
attributes: ["name", "data"],
// 第二种写法 可以排除属性 也可以包含属性
// attributes: {
// include: ["name", "data"],
// exclude: ["id"],
// },
},
transaction,
});
// 能直接获取到老板的名字
// console.log(bwm.company_onwer.name);
console.log(bwm.bossInfo.name);
// 我们之前做了处理 所以拿到的直接是对象 而不是字符串
// { story: '测试数据' }
console.log(bwm.bossInfo.data);
// 查询该车企业有几款车
let cars = await CarCompany.findOne({
where: {
// 使用id查询 其实不需要别的条件的话 直接使用findByPk即可
id: bwm.id,
// car_type:["suv","轿车"] car_type:"suv" 对车类型进行筛查
// 对价格进行筛查
// money: {
// [Op.lte]: 500000,
// [Op.gte]: 500000,
// [Op.between]: [0, 1000000],
// },
// 更多操作见 https://www.sequelize.cn/core-concepts/model-querying-basics#%E9%AB%98%E7%BA%A7%E6%9F%A5%E8%AF%A2%E4%B8%8D%E4%BB%85%E9%99%90%E4%BA%8E%E5%88%97
},
include: {
model: CarType,
},
transaction,
});
// [ 'M3 雷霆版', 'GLB200 7座' ]
cars.car_types.length && console.log(cars.car_types.map((x) => x.car_name));
// 查找这几款车有几家4S店在卖 指导价 以及优惠过的价格
// 尽量不要在循环里写语句 一次查找出来 再用代码逻辑去操作
let stores = await CarType.findAll({
where: {
id: cars.car_types.map((x) => x.id),
},
include: {
model: CarStore,
// 不希望连接的字段出现
attributes: [],
through: {
model: CarStoreSell,
attributes: [],
},
},
attributes: [
"car_name",
"money",
[col("car_stores.name"), "store_name"],
// [col("`car_stores->car_store_sell`.discounts"), "discounts"]
// 计算优惠后的价格
[literal("`car_type`.`money` - `car_stores->car_store_sell`.`discounts`"), "sell_money"],
],
// 不需要获取模型原型 只要数据
raw: true,
transaction,
});
// 获取到的数组其中一项
// [
// {
// car_name: "GLB200 7座",
// money: "300000",
// store_name: "中升讯美店",
// sell_money: "270000",
// },
// ];
console.log(stores);
// 基本的关联查找功能讲解完毕
};
// 增删改查 改的基础使用
const updateMethods = async () => {
// 修改一些老板的数据
let boss = await CompanyOwner.findOne({ where: { name: "张三" }, transaction });
// 赋值方式1
// boss.setDataValue("data", { story: "修改数据" });
// 赋值方式2
boss.data = { story: "修改数据" };
boss.sex = 0;
boss.name = "李四";
await boss.save({ transaction });
boss = await CompanyOwner.findOne({ include: CarCompany, transaction });
// {name:"李四",sex:false,data:{ story: '修改数据' }}
console.log(boss);
// 车企指导价下降的批量操作
// 自减写法1 自增increment
// await CarType.decrement("money", {
// by: 10000,
// where: {
// belong: boss.car_company.id,
// },
// transaction,
// });
// 自减写法2
await CarType.update(
{
money: literal(`money - 20000`),
},
{
where: {
belong: boss.car_company.id,
},
transaction,
}
);
// 更新的基础操作就做完了
};
// 增删改查 删除的基础使用
const deleteMethods = async () => {
// 4s下架所有车辆
await CarStoreSell.destroy({ transaction, where: {} });
// 车企下架单独某款车
let car = await CarType.findOne({ where: { car_name: "GLB200 7座" }, transaction });
await car.destroy({ transaction });
// 车企倒闭了 所有车辆下架 老板销户了
await CarType.destroy({ transaction, where: {} });
await CarCompany.destroy({ transaction, where: {} });
await CompanyOwner.destroy({ where: { name: "李四" }, transaction });
// 这就是简单的删除应用 操作数据类的代码 最好要用事务去操作 但是事务也有缺陷 可以去看看脏读 幻读 等
};
await createMethods();
await readMethods();
await updateMethods();
await deleteMethods();
});
} catch (err) {
console.log("数据操作的时候出现了错误:");
console.log(err);
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("无法连接数据库", error);
return process.exit(1);
}
}
authenticate();