最新学习使用QCustomPlot,这里做了个简单的demo实现瀑布图
实现结果
瀑布图demo
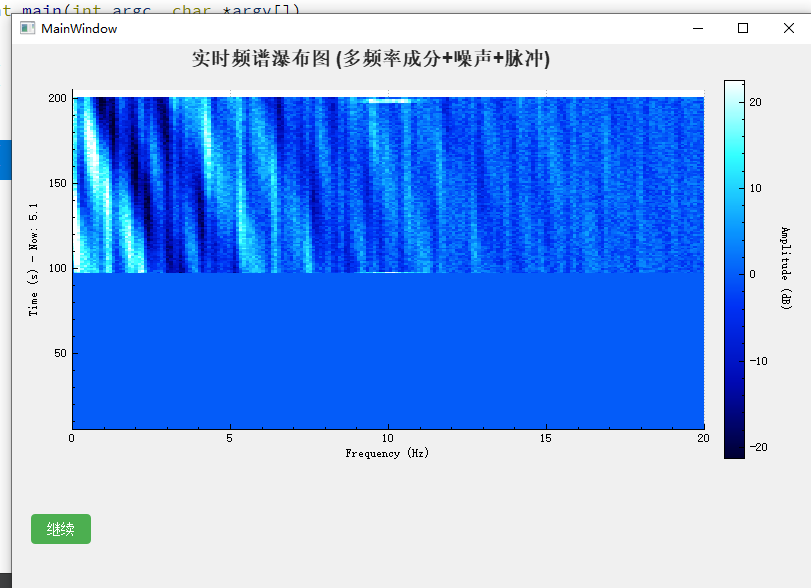
实现过程
1.界面设计
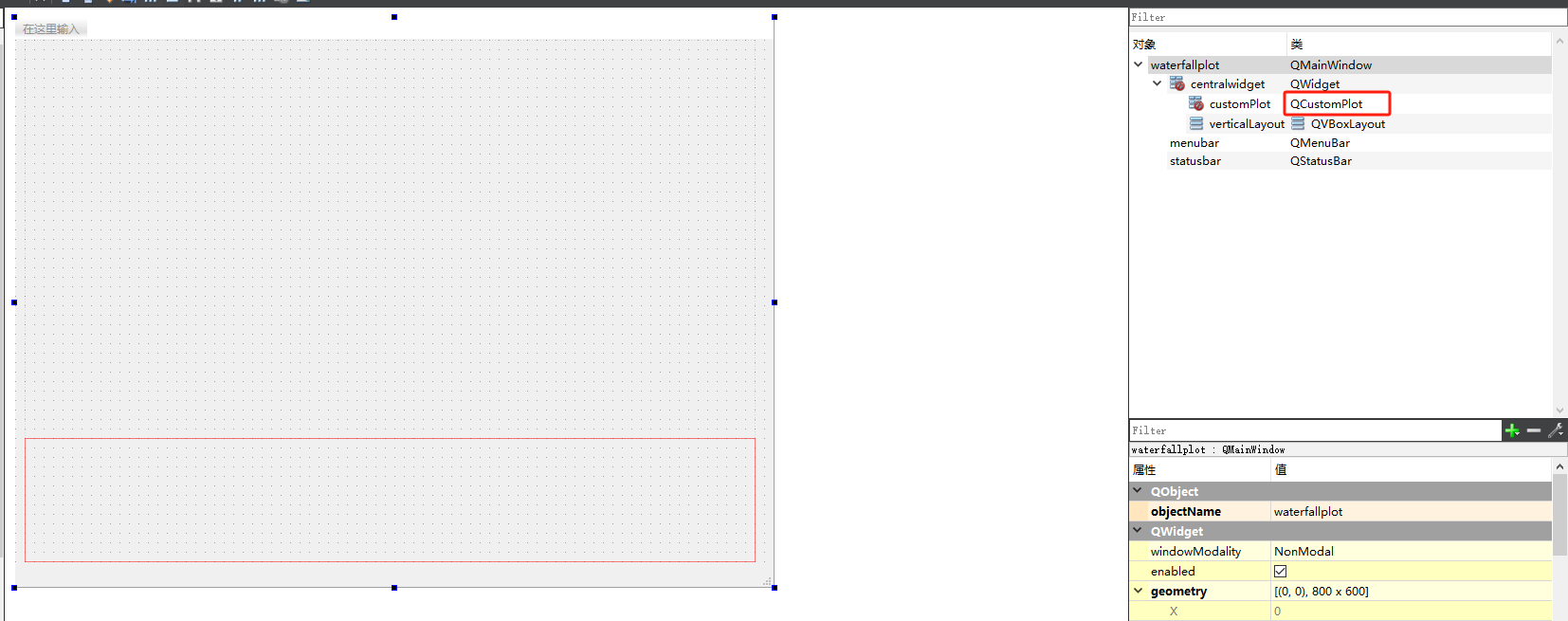
界面较简单,QtDesign里面放置了widget(需要升级为QCustomPlot)和一个verticalLayout(用于放置按钮)
代码初始化瀑布图,步骤为
a.创建颜色映射图
b.设置颜色梯度
c.设置数据范围
d.设置坐标轴
e.设置网格样式
f.设置颜色标尺
g.设置交互功能
h.设置标题及背景样式
代码如下:
void waterfallplot::setupPlot()
{
// 初始化瀑布图显示
// 1. 创建颜色映射图
m_colorMap = new QCPColorMap(ui->customPlot->xAxis, ui->customPlot->yAxis);
m_colorMap->data()->setSize(200, HISTORY_SIZE); // 200列(频率点) x HISTORY_SIZE行(时间历史)
m_colorMap->data()->setRange(QCPRange(0, 20), QCPRange(0, HISTORY_SIZE)); // x:0-20Hz, y:0-HISTORY_SIZE
// 2. 设置更鲜艳的颜色梯度
QCPColorGradient gradient;
gradient.setColorStopAt(0.0, QColor(0, 0, 200)); // 深蓝
gradient.setColorStopAt(0.2, QColor(0, 100, 255)); // 亮蓝
gradient.setColorStopAt(0.4, QColor(0, 255, 255)); // 青色
gradient.setColorStopAt(0.6, QColor(100, 255, 100)); // 亮绿
gradient.setColorStopAt(0.8, QColor(255, 255, 0)); // 黄色
gradient.setColorStopAt(1.0, QColor(255, 50, 50)); // 亮红
m_colorMap->setGradient(gradient);
m_colorMap->setInterpolate(false); // 禁用颜色插值,使颜色边界更清晰
// 3. 设置初始数据范围
m_colorMap->setDataRange(QCPRange(-30, 30));
// 4. 坐标轴设置
ui->customPlot->xAxis->setLabel("Frequency (Hz)");
ui->customPlot->yAxis->setLabel("Time (s)");
ui->customPlot->xAxis->setRange(0, 20); // 0-20Hz
ui->customPlot->yAxis->setRange(0, HISTORY_SIZE);
// 设置网格线样式
ui->customPlot->xAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(QColor(180, 180, 180), 1, Qt::DotLine));
ui->customPlot->yAxis->grid()->setPen(QPen(QColor(180, 180, 180), 1, Qt::DotLine));
// 5. 添加颜色标尺
QCPColorScale *colorScale = new QCPColorScale(ui->customPlot);
ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(0, 1, colorScale); // 添加到右侧
colorScale->setType(QCPAxis::atRight);
m_colorMap->setColorScale(colorScale);
colorScale->axis()->setLabel("Amplitude (dB)");
colorScale->axis()->setTickLabels(true);
// 6. 设置交互功能
ui->customPlot->setInteractions(QCP::iRangeDrag | QCP::iRangeZoom | QCP::iSelectPlottables);
// 7. 添加标题
ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->insertRow(0); // 在上方添加一行
QCPTextElement *title = new QCPTextElement(ui->customPlot,
"实时频谱瀑布图 (多频率成分+噪声+脉冲)", QFont("Arial", 14, QFont::Bold));
title->setTextColor(QColor(40, 40, 40)); // 深灰色标题
ui->customPlot->plotLayout()->addElement(0, 0, title);
// 8. 设置背景样式
ui->customPlot->setBackground(QBrush(QColor(240, 240, 240))); // 浅灰色背景
ui->customPlot->axisRect()->setBackground(QBrush(Qt::white)); // 白色绘图区
}初始化按钮ui,代码如下
void waterfallplot::setupControls()
{
// 设置控制UI
// 1. 创建暂停/继续按钮
QPushButton *pauseButton = new QPushButton("暂停", this);
pauseButton->setStyleSheet(
"QPushButton {"
" background-color: #4CAF50;" // 绿色背景
" border: none;"
" color: white;"
" padding: 8px 16px;"
" font-size: 14px;"
" border-radius: 4px;"
"}"
"QPushButton:hover {"
" background-color: #45a049;" // 深绿色悬停效果
"}"
);
// 连接按钮点击信号
connect(pauseButton, &QPushButton::clicked, this, &waterfallplot::onPauseClicked);
// 2. 创建布局
QHBoxLayout *layout = new QHBoxLayout();
layout->addWidget(pauseButton);
layout->addStretch(); // 添加伸缩项使按钮靠左
// 3. 创建容器控件
QWidget *controls = new QWidget(this);
controls->setLayout(layout);
controls->setStyleSheet("background-color: #f0f0f0;"); // 浅灰色背景
// 4. 添加到主布局
ui->verticalLayout->addWidget(controls);
}2.多线程生成数据
为了实现实时效果且不影响ui显示,才去多线程的方法根据当前事件生成模拟数据,使用emit将数据发送出去
主要代码如下:
void DataGenerator::run()
{
// 线程主函数
qDebug() << "数据生成线程启动 - 线程ID:" << QThread::currentThreadId();
QElapsedTimer timer; // 用于计算帧率
timer.start();
int frameCount = 0;
while (m_running) // 主循环
{
// 检查暂停状态
{
QMutexLocker locker(&m_mutex);
if (m_paused)
{
QThread::msleep(100); // 暂停时休眠100ms
continue;
}
}
// 生成数据并发送信号
QVector<double> data = generateSignalData();
emit newDataGenerated(data); // 发射信号到主线程
// 计算并显示帧率
frameCount++;
if (timer.elapsed() >= 1000)
{
qDebug() << "数据生成帧率:" << frameCount << "FPS";
frameCount = 0;
timer.restart();
}
// 按间隔休眠,控制数据生成频率
QThread::msleep(m_updateInterval);
}
qDebug() << "数据生成线程结束";
}3.根据数据更新UI实现瀑布效果
读取数据,然后重新绘制瀑布图,更新y轴显示,实现瀑布效果
代码如下:
void waterfallplot::updatePlot(const QVector<double> &newData)
{
// 更新瀑布图显示
qDebug() << "接收到新数据,数据大小:" << newData.size();
if(newData.isEmpty()) {
qWarning() << "接收到空数据!";
return;
}
// 1. 数据滚动:将旧数据向上移动一行
for (int y = 1; y < HISTORY_SIZE; ++y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < newData.size(); ++x)
{
m_colorMap->data()->setCell(x, y-1, m_colorMap->data()->cell(x, y));
}
}
// 2. 在最后一行添加新数据
for (int x = 0; x < newData.size(); ++x) {
m_colorMap->data()->setCell(x, HISTORY_SIZE-1, newData[x]);
}
// 3. 计算数据范围
auto [minIt, maxIt] = std::minmax_element(newData.constBegin(), newData.constEnd());
double minValue = *minIt;
double maxValue = *maxIt;
// 调试输出
qDebug() << QString("更新瀑布图[%1] - 范围: %2~%3 - 最新数据: %4...%5")
.arg(m_dataIndex)
.arg(minValue, 0, 'f', 2)
.arg(maxValue, 0, 'f', 2)
.arg(newData.first(), 0, 'f', 2)
.arg(newData.last(), 0, 'f', 2);
m_dataIndex++;
// 4. 动态调整颜色映射范围
static QCPRange dataRange(-30, 30); // 初始范围
// 平滑调整范围,避免突变
dataRange.lower = qMin(dataRange.lower * 0.9, minValue * 0.9);
dataRange.upper = qMax(dataRange.upper * 0.9, maxValue * 1.1);
m_colorMap->setDataRange(dataRange);
// 5. 更新时间轴显示
static double timeOffset = 0;
timeOffset += 0.05; // 每次更新增加0.05单位时间
ui->customPlot->yAxis->setRange(timeOffset, HISTORY_SIZE + timeOffset);
ui->customPlot->yAxis->setLabel(QString("Time (s) - Now: %1").arg(timeOffset, 0, 'f', 1));
// 6. 请求重绘(使用队列重绘优化性能)
ui->customPlot->replot(QCustomPlot::rpQueuedReplot);
}希望对大家有所帮助.