
官方的定义如下:
MCP is an open protocol that standardizes how applications provide context to LLMs.
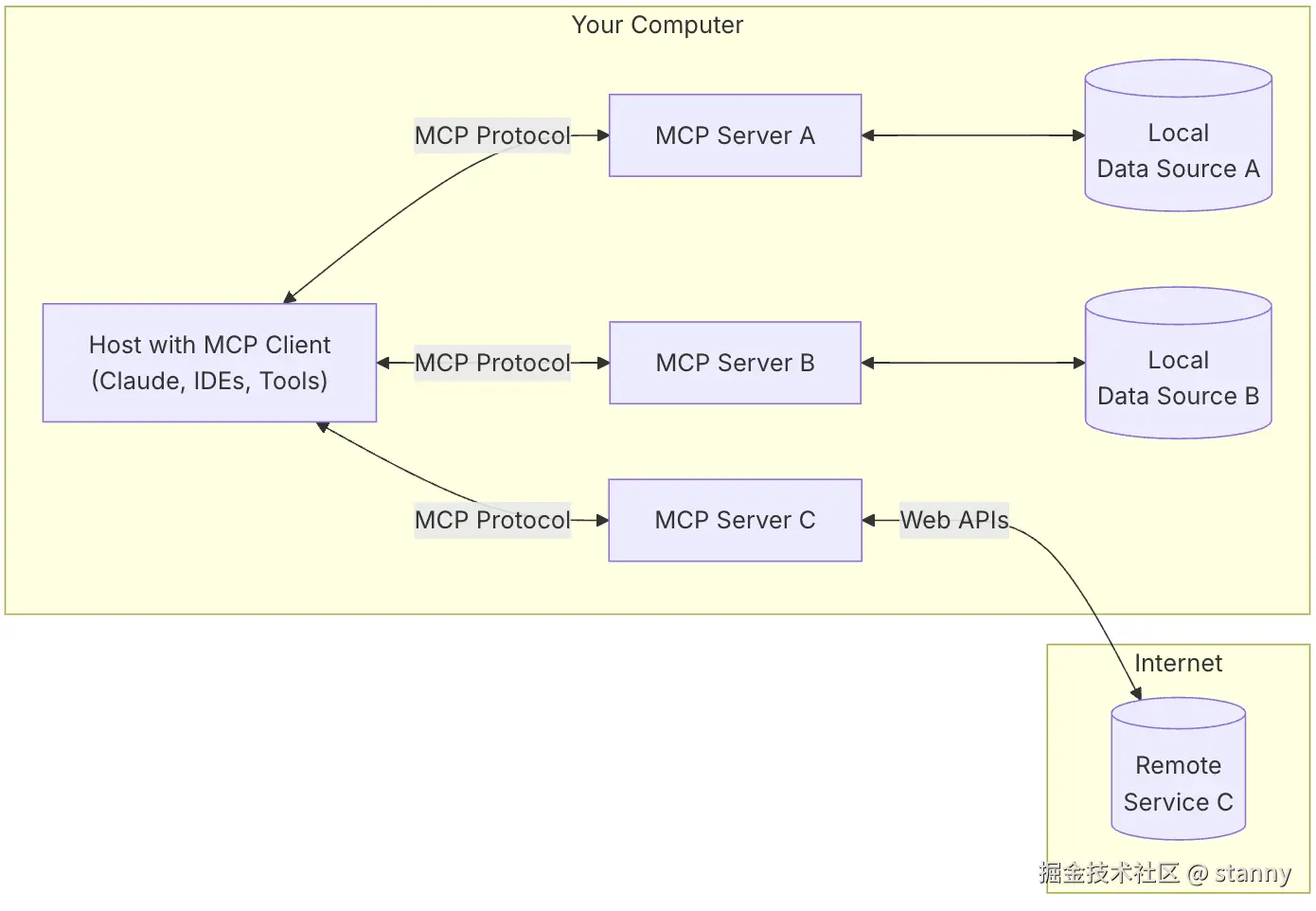
初见这些图和概念,理解上还是云里雾里。
要想理解透彻什么是 MCP,我觉得至少要分为几个部分来学习:
- 理解 function call 是什么
- function call 是怎么被执行的
- 动手实现一个 mcp 示例
为此我也计划写三篇文章来总结一下我对于 MCP 的理解:
- 《MCP(上)------function call 是什么》
- 《MCP(中)------自动化执行 funciton call》
- 《MCP(下)------跟着官方实现一个MCP》
本文是该系列的第一篇,让我们先从调用 llm 开始着手。
使用 api 调用 llm, 启用流式请求
前文我们手写了一个 http 请求直接调用 llm,openai 官方提供了一个封装我们可以拿来直接用:
js
// 这里本质上就是发起一个post请求,使用 api 更方便,他帮我们处理了一些优化,比如重试、错误处理等
const stream = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "qwq-plus",
messages,
stream: true,
});我们去通义模型广场选用一个支持流式返回的模型来调用一探究竟
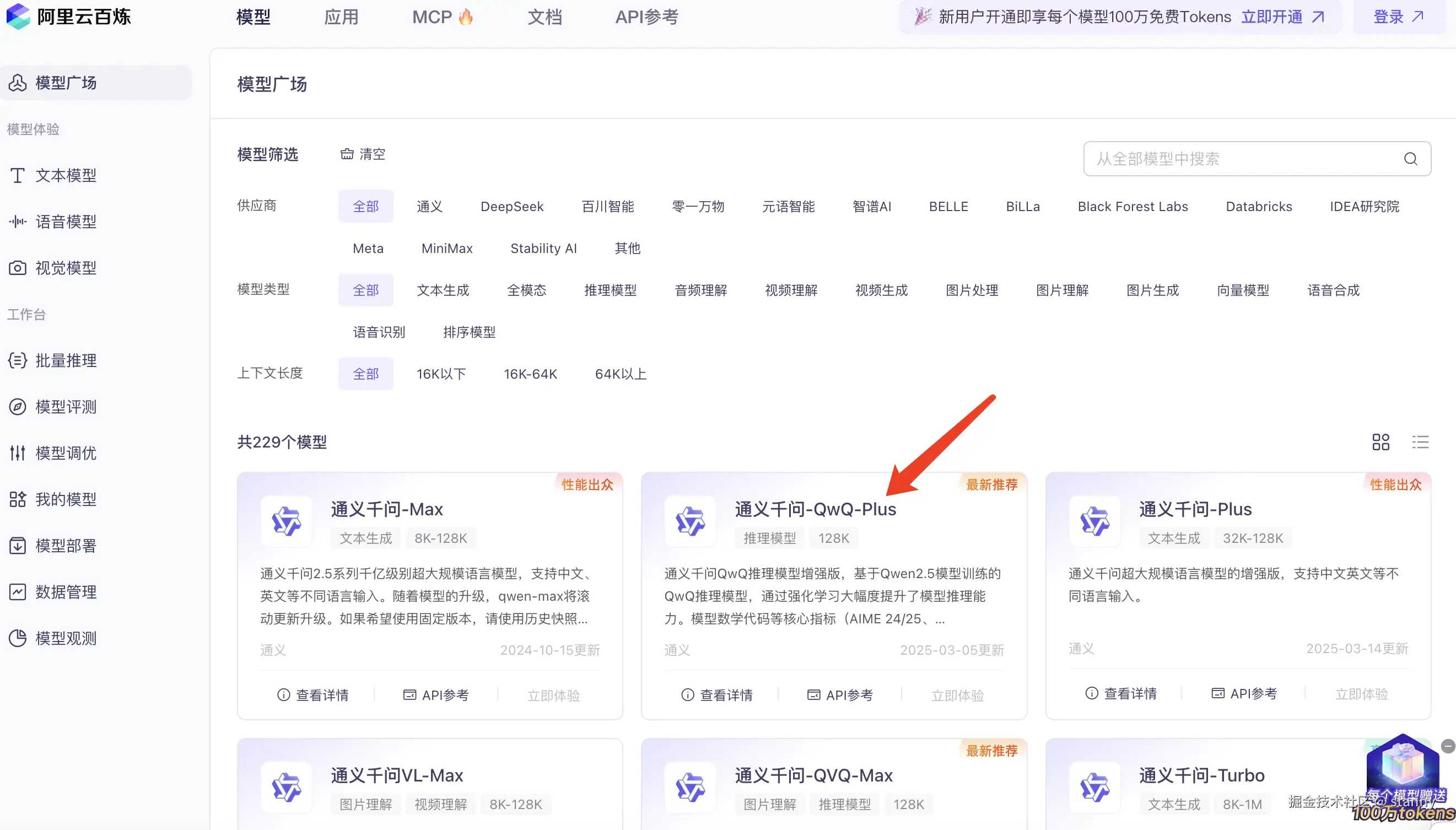
点开【API 参考】文档,我们看到支持调用方式,这里我们选择 nodejs 调用的案例来跑测试。
js
import OpenAI from "openai";
import readline from 'node:readline/promises';
import { stdin as input, stdout as output } from 'node:process';
import 'dotenv/config';
// apikey 要自己配置一下
const openai = new OpenAI({
apiKey: process.env.API_KEY,
baseURL: process.env.BASE_URL
});
async function main() {
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input, output });
const question = await rl.question("请输入您的问题:");
rl.close();
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: question }];
try {
const stream = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "qwq-plus",
messages,
stream: true,
});
// 我们来打印看下返回的结果是什么样子的(这里暂时移除了其他代码)
for await (const chunk of stream) {
console.dir(chunk, { depth: null, colors: true });
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("发生错误:", error);
}
}
main();然后在控制台里跑一下这个文件看看输出:
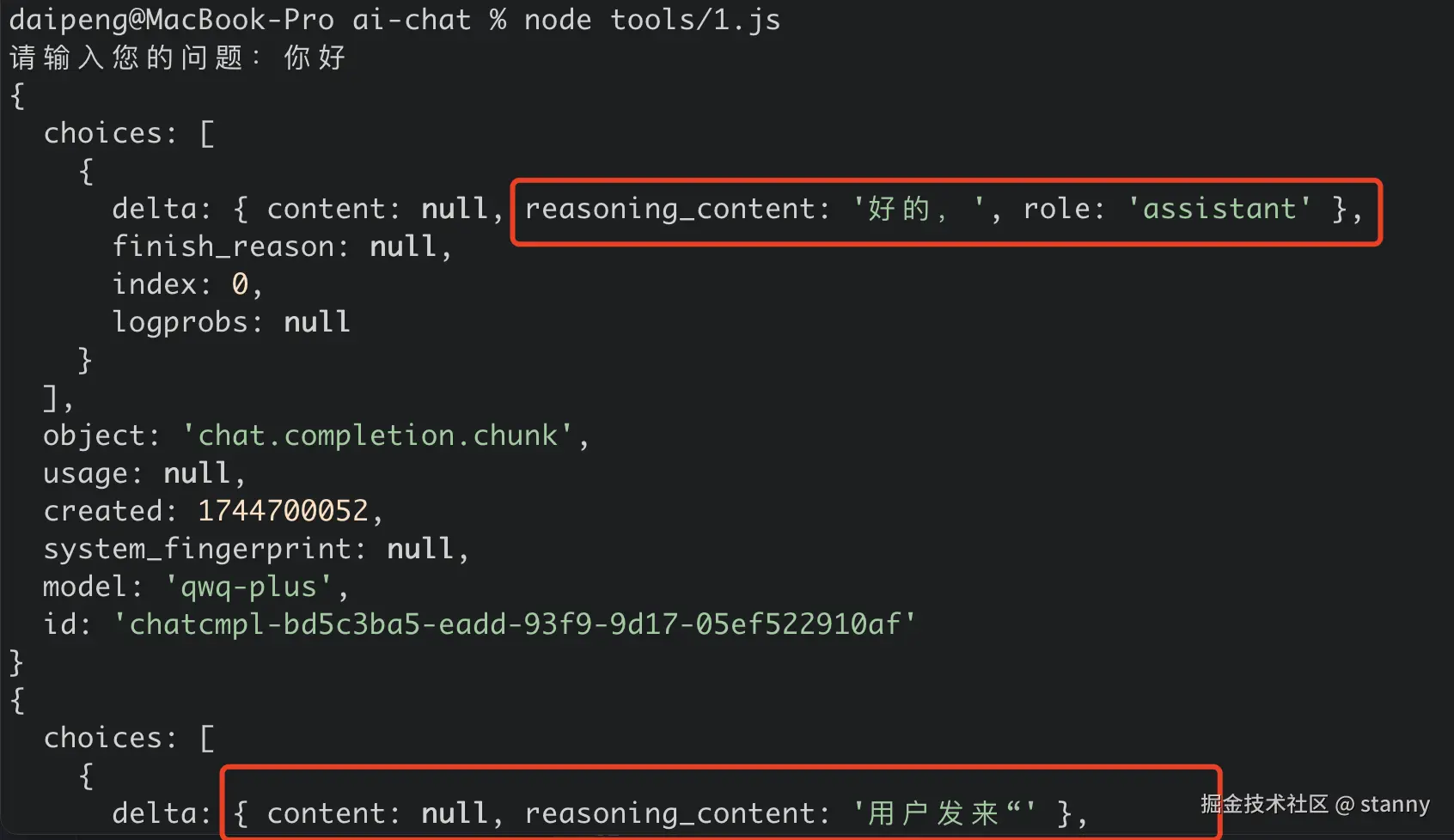
先看一下返回的格式,前半段都是带 reasoning_content 内容,也就是他的 "思考过程"
js
{
choices: [
{
delta: { content: null, role: 'assistant', reasoning_content: '' },
index: 0,
logprobs: null,
finish_reason: null
}
],
object: 'chat.completion.chunk',
usage: null,
created: 1744283860,
system_fingerprint: null,
model: 'qwq-plus',
id: 'chatcmpl-8445fb0f-1479-965b-a0be-6de2e54cb7a2'
}
{
choices: [
{
finish_reason: null,
delta: { content: null, reasoning_content: '好的,用户发' },
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}
{
choices: [
{
delta: { content: null, reasoning_content: '来了"你好",我需要用' },
finish_reason: null,
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}后半段 reasoning_content 为 null,content 开始有内容;
js
{
choices: [
{
delta: { content: '你好!', reasoning_content: null },
finish_reason: null,
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}
{
choices: [
{
delta: { content: '今天过得怎么样?有什么我可以', reasoning_content: null },
finish_reason: null,
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}
{
choices: [
{
delta: { content: '帮你的吗?😊', reasoning_content: null },
finish_reason: null,
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}最后一个chunk 有一个 finish_reason: 'stop' 的标识;
js
{
choices: [
{
finish_reason: 'stop',
delta: { content: '', reasoning_content: null },
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}总结一下:
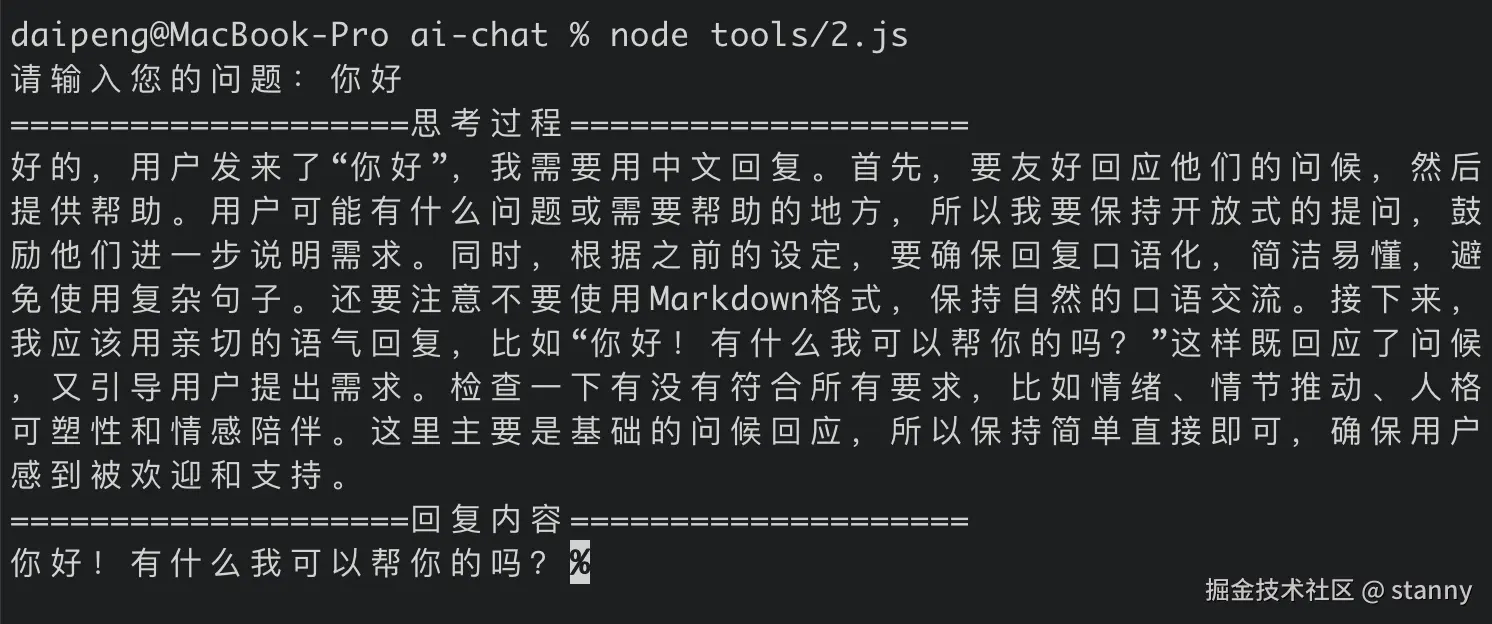
调用一次模型时,QwQ-plus 模型会先返回它的思考过程,然后再返回回答内容。
其实就是将每一句chunk返回的内容拼接起来就是 ai 的全部回答,包含两部分:
- reasoning_content 思考过程(可以选择性的展示给用户)
- content 回答结果
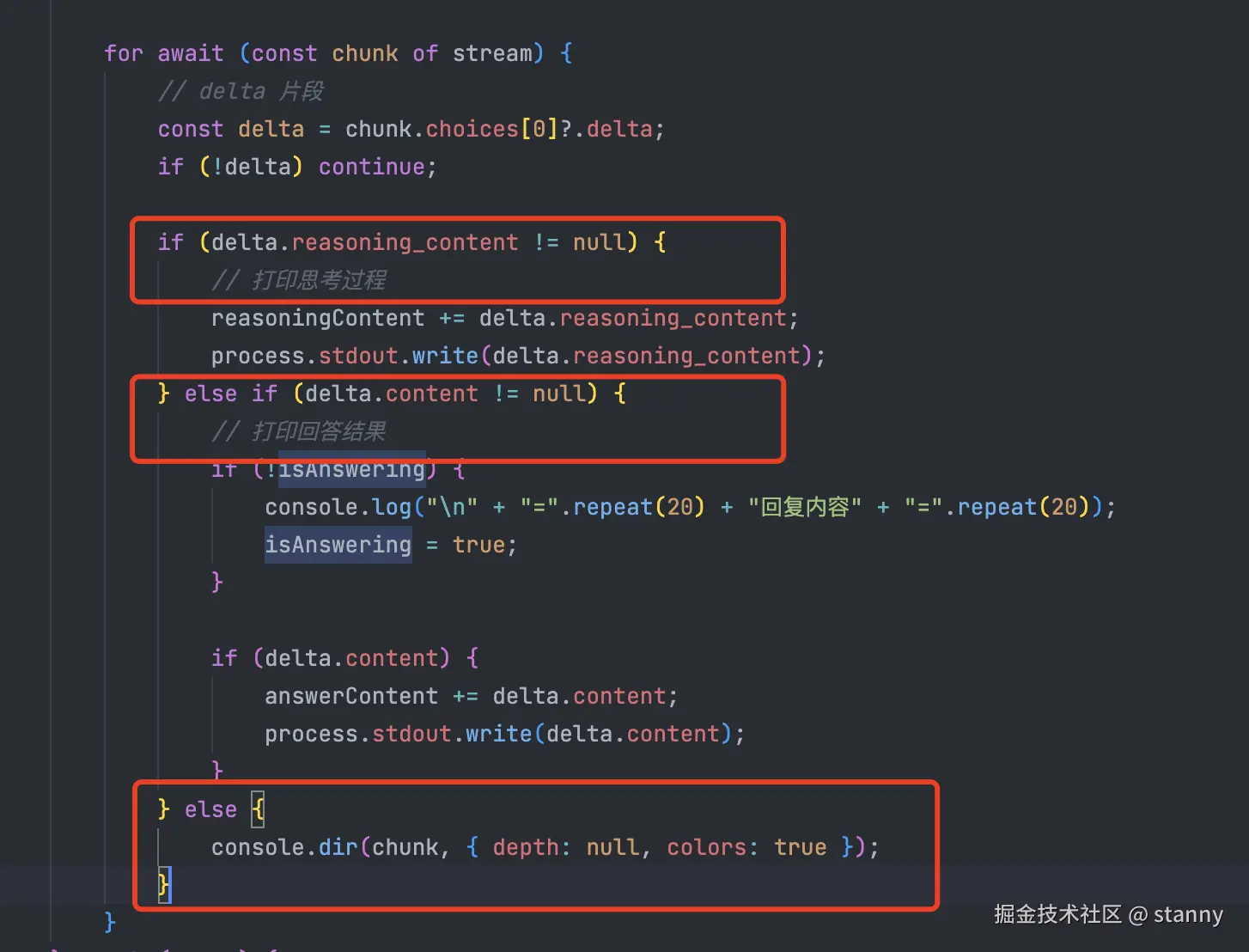
改一下代码更清晰的看到回答内容
js
async function main() {
const rl = readline.createInterface({ input, output });
const question = await rl.question("请输入您的问题:");
rl.close();
const messages = [{ role: "user", content: question }];
let reasoningContent = "";
let answerContent = "";
let isAnswering = false;
console.log("=".repeat(20) + "思考过程" + "=".repeat(20));
try {
const stream = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "qwq-plus",
messages,
stream: true,
});
for await (const chunk of stream) {
// delta 片段
const delta = chunk.choices[0]?.delta;
if (!delta) continue;
if (delta.reasoning_content !== null) {
// 打印思考过程
reasoningContent += delta.reasoning_content;
process.stdout.write(delta.reasoning_content);
} else {
// 打印回答结果
if (!isAnswering) {
console.log("\n" + "=".repeat(20) + "回复内容" + "=".repeat(20));
isAnswering = true;
}
if (delta.content) {
answerContent += delta.content;
process.stdout.write(delta.content);
}
}
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("发生错误:", error);
}
}
问题:llm 无法感知外部环境,能力受限
模型出厂之后,它的知识体系就已经被限定了,无法实时感知到最新的内容,然而在互联网时代,我们需要跟现实世界进行实时的数据交互,如果 llm 无法感知外部世界,那么它的能力就非常受限了。
还是刚刚的demo代码,我们看一个例子:

解法:function call 可以让 llm 感知外部环境;
有些模型是支持 funciton call 的,是当前问题的一个解法,我们通过一个具体的例子看看怎么回事。
当我们先按照官方的案例给他绑定tools工具试试看,观察一下 llm 是如何决策使用工具的。
api 文档里面可以看到这里:
我们提炼一下 function call 的使用方式:
js
const tools = [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "get_current_time",
description: "当你想知道现在的时间时非常有用。",
parameters: {}
}
},
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "get_current_weather",
description: "当你想查询指定城市的天气时非常有用。",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
location: {
type: "string",
description: "城市或县区,比如北京市、杭州市、余杭区等。"
}
},
required: ["location"]
}
}
}
];
const stream = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "qwq-plus",
messages,
// 绑定工具这样传即可
tools,
stream: true,
});我们看到就是调用模型的时候多传递了一个 tools,tools 的定义如下:
js
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "get_current_weather", // function name
// funciton 作用的描述,大模型根据此判断何时调用该工具
description: "当你想查询指定城市的天气时非常有用。",
// 函数入参的描述
parameters: {
// 入参通常定义为一个对象,对象内部可以结构更多的参数
type: "object",
properties: {
// 对应外层query的解构子参数定义
location: {
type: "string",
description: "城市或县区,比如北京市、杭州市、余杭区等。"
}
},
// 指定必填参数
required: ["location"]
}
}
}这么一看,tool 定义(也就是 function 定义)还是比较清晰的;
除了刚刚提到的思考过程和回答结果(两种chunk),调用工具应该会返回新的chunk,我们来打印一下看看具体是怎么返回的。
当我们提问的内容需要调用工具时,看看 llm 的返回:
js
请输入您的问题:今天是几号
====================思考过程====================
好的,用户问"今天是几号",我需要知道当前的日期。
提供的工具里有get_current_time函数,这个函数可以获取当前时间。
用户没有提到城市或天气,所以不需要用到get_current_weather。
接下来我应该调用get_current_time函数来获取当前日期信息。
这个函数不需要参数,直接调用即可。
确认一下函数描述是否正确,是的,确实用于获取时间。
所以正确的工具调用应该是使用get_current_time,参数为空对象。
然后返回的结果应该包含当前日期,用户的问题就能解决了
{
choices: [
{
delta: {
content: null,
reasoning_content: null,
tool_calls: [
{
function: { name: 'get_current_time', arguments: '{}' },
index: 0,
id: 'call_c5ecd978c0f34343a8c20a',
type: 'function'
}
]
},
finish_reason: null,
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}
{
choices: [
{
delta: {
tool_calls: [
{
function: { arguments: null },
index: 0,
id: '',
type: 'function'
}
]
},
index: 0
}
],
// ...
}
{
choices: [
{
finish_reason: 'tool_calls',
delta: {},
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}当我们调用 llm 时,如果传入了tools,它就会在需要的场景下"意识"到可以调用哪些工具;这就是大模型的魅力所在,感觉它真的具备像人一样的思考能力。
首先它的思考很清晰:
好的,用户问"今天是几号",我需要知道当前的日期。
提供的工具里有get_current_time函数,这个函数可以获取当前时间。
用户没有提到城市或天气,所以不需要用到get_current_weather。
接下来我应该调用get_current_time函数来获取当前日期信息。
这个函数不需要参数,直接调用即可。
确认一下函数描述是否正确,是的,确实用于获取时间。
所以正确的工具调用应该是使用get_current_time,参数为空对象。
然后返回的结果应该包含当前日期,用户的问题就能解决了紧接着,它返回的 chunk 核心信息入下:
js
{
content: null,
reasoning_content: null,
tool_calls: [
{
function: { name: 'get_current_time', arguments: '{}' },
index: 0,
id: 'call_c5ecd978c0f34343a8c20a',
type: 'function'
}
]
}可以关注一下 tool_calls 里面的内容:
js
function: { name: 'get_current_time', arguments: '{}' },name 就是 llm 想调用函数的名称,arguments 就是它要传的入参;入参的格式是根据tool的描述,llm 会自动构建出来;
我们看到后面还返回了两条 chunk 信息
js
{
choices: [
{
delta: {
tool_calls: [
{
function: { arguments: null },
index: 0,
id: '',
type: 'function'
}
]
},
index: 0
}
],
// ...
}这里的 tool_calls 内容里面没有返回实际的 function name,是可忽略的信息。
猜测这里 tool 相关的 chunks 数量和我们传入的 tool 数量是一致的:
我们传入两个工具:
- 查时间:get_current_time
- 查天气:get_current_weather
当我们的提问是:今天是几号?
llm 的返回tools的调用情况
- 我需要查时间,请调用 get_current_time
- 我不要查天气
最后一个chunk 如下:
js
{
choices: [
{
finish_reason: 'tool_calls',
delta: {},
index: 0,
logprobs: null
}
],
// ...
}finish_reason: 'tool_calls', 这是 llm 在告诉我们,它停下来了,因为它需要知道这些工具调用的结果,才能进一步给出问题的答案;
至于如何调用工具,llm 已经告诉了我们要调用的function 以及 arguments,function 也是我们自己定义的,所以这一步需要我们用写代码的方式自己完成,最终按固定格式返回 tool_calls 结果,然后再进步调用 llm 拿到最终结果;
下一节我们继续探究:如何自动化的执行大模型返回的 tools,拿到整个流程的回答结果。