逻辑回归是一种广泛使用的统计学习方法,主要用于处理二分类问题。它基于线性回归模型,通过Sigmoid函数将输出映射到[0, 1]范围内,表示实例属于正类别的概率。尽管逻辑回归适用于二分类任务,但在多分类问题中常使用Softmax函数,它将多个类别的概率输出为和为1的正值,允许模型进行多类别预测。PyTorch是一个灵活且强大的深度学习框架,以其动态计算图和易用性受到广泛欢迎,适用于研究和生产环境中的各种机器学习任务。
一、sigmoid激活函数
1.1、输入散点
python
import numpy as np
class1_points = np.array([[1.9, 1.2],
[1.5, 2.1],
[1.9, 0.5],
[1.5, 0.9],
[0.9, 1.2],
[1.1, 1.7],
[1.4, 1.1]])
class2_points = np.array([[3.2, 3.2],
[3.7, 2.9],
[3.2, 2.6],
[1.7, 3.3],
[3.4, 2.6],
[4.1, 2.3],
[3.0, 2.9]])
x_train = np.concatenate((class1_points, class2_points))
y_train = np.concatenate((np.zeros(len(class1_points)), np.ones(len(class2_points))))1.2、转换为Tensor张量
python
import torch
inputs=torch.tensor(x_train,dtype=torch.float32)
labels=torch.tensor(y_train,dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)1.3、定义模型
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.manual_seed(42)
class LogisticRegreModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inputsizes):
super().__init__()
self.linear=nn.Linear(inputsizes,1)
def forward(self,x):
return torch.sigmoid(self.linear(x))
model=LogisticRegreModel(x_train.shape[1])1.4、定义损失函数和优化器
python
from torch.optim import SGD
cri=torch.nn.BCELoss()
optimizer=SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.05)1.5、开始迭代
python
for i in range(1,1001):
output=model(inputs)
loss=cri(output,labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if i%100==0 or i==1:
print(i,loss.item()) 1.6、可视化
python
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
fig,(ax1,ax2)=plt.subplots(1,2)
epoch_list=[]
loss_list=[]
for i in range(1,1001):
inputs=torch.tensor(x_train,dtype=torch.float32)
labels=torch.tensor(y_train,dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
output=model(inputs)
loss=cri(output,labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if i%100==0 or i==1:
print(i,loss.item())
w1,w2=model.linear.weight.data.flatten()
b=model.linear.bias.data[0]
slope=-w1/w2
intercept=-b/w2
x_min,x_max=0,5
x=np.array([x_min,x_max])
y=slope*x+intercept
ax1.clear()
ax1.scatter(class1_points[:,0],class1_points[:,1])
ax1.scatter(class2_points[:,0],class2_points[:,1])
ax1.plot(x,y)
ax2.clear()
epoch_list.append(i)
loss_list.append(loss.item())
ax2.plot(epoch_list,loss_list)
plt.show()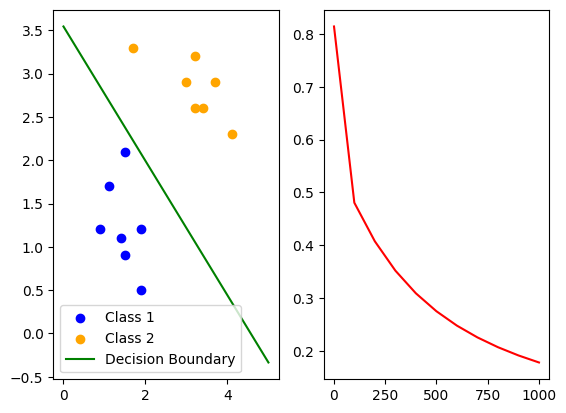
1.7、完整代码
python
import numpy as np # 导入 NumPy 库以进行数组和数学运算
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt # 导入 Matplotlib 库以绘制图形
import torch # 导入 PyTorch 库
import torch.nn as nn # 导入 PyTorch 的神经网络模块
from torch.optim import SGD # 导入随机梯度下降优化器
# 定义类1的数据点
class1_points = np.array([[1.9, 1.2],
[1.5, 2.1],
[1.9, 0.5],
[1.5, 0.9],
[0.9, 1.2],
[1.1, 1.7],
[1.4, 1.1]])
# 定义类2的数据点
class2_points = np.array([[3.2, 3.2],
[3.7, 2.9],
[3.2, 2.6],
[1.7, 3.3],
[3.4, 2.6],
[4.1, 2.3],
[3.0, 2.9]])
# 合并类1和类2的数据点,作为训练特征
x_train = np.concatenate((class1_points, class2_points))
# 合并类1和类2的标签,类1为 0,类2为 1
y_train = np.concatenate((np.zeros(len(class1_points)), np.ones(len(class2_points))))
# 将训练特征和标签转换为 PyTorch 张量
inputs = torch.tensor(x_train, dtype=torch.float32)
labels = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1)
# 设置随机种子以便复现结果
torch.manual_seed(42)
# 定义逻辑回归模型类
class LogisticRegreModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_sizes):
super().__init__() # 继承父类的初始化方法
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_sizes, 1) # 定义线性层,输入大小为 input_sizes,输出为 1
def forward(self, x):
return torch.sigmoid(self.linear(x)) # 前向传播,应用 Sigmoid 函数
# 实例化逻辑回归模型,输入特征的维度为 x_train 的列数
model = LogisticRegreModel(x_train.shape[1])
# 定义二元交叉熵损失函数
cri = torch.nn.BCELoss()
# 使用随机梯度下降算法作为优化器
optimizer = SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.05)
# 创建子图用于展示
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
epoch_list = [] # 存储每次训练的epoch数
loss_list = [] # 存储每次训练的损失值
# 训练模型,进行 1000 次迭代
for i in range(1, 1001):
inputs = torch.tensor(x_train, dtype=torch.float32) # 再次定义输入张量
labels = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.float32).unsqueeze(1) # 再次定义标签张量
output = model(inputs) # 前向传播计算模型输出
loss = cri(output, labels) # 计算损失值
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空之前的梯度
loss.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
optimizer.step() # 更新参数
# 每 100 次迭代打印损失并更新图形
if i % 100 == 0 or i == 1:
print(i, loss.item()) # 打印当前epoch和损失值
# 获取当前模型参数
w1, w2 = model.linear.weight.data.flatten() # 权重参数
b = model.linear.bias.data[0] # 偏置参数
# 计算决策边界的斜率和截距
slope = -w1 / w2
intercept = -b / w2
x_min, x_max = 0, 5 # 决定x轴的范围
x = np.array([x_min, x_max]) # 创建x值的数组
y = slope * x + intercept # 根据斜率和截
# 根据斜率和截距计算决策边界的y值
y = slope * x + intercept
ax1.clear() # 清空第一张子图
# 绘制类1和类2的数据点
ax1.scatter(class1_points[:, 0], class1_points[:, 1], color='blue', label='Class 1')
ax1.scatter(class2_points[:, 0], class2_points[:, 1], color='orange', label='Class 2')
# 绘制当前的决策边界
ax1.plot(x, y, color='green', label='Decision Boundary')
ax1.legend() # 显示图例
ax2.clear() # 清空第二张子图
epoch_list.append(i) # 将当前epoch添加到列表
loss_list.append(loss.item()) # 将当前损失值添加到列表
ax2.plot(epoch_list, loss_list, color='red') # 绘制损失变化曲线
# 显示绘制的图形
plt.show() 二、Softmax激活函数
2.1、输入散点
python
import numpy as np
class1_points = np.array([[1.9, 1.2],
[1.5, 2.1],
[1.9, 0.5],
[1.5, 0.9],
[0.9, 1.2],
[1.1, 1.7],
[1.4, 1.1]])
class2_points = np.array([[3.2, 3.2],
[3.7, 2.9],
[3.2, 2.6],
[1.7, 3.3],
[3.4, 2.6],
[4.1, 2.3],
[3.0, 2.9]])
x_train = np.concatenate((class1_points, class2_points))
y_train = np.concatenate((np.zeros(len(class1_points)), np.ones(len(class2_points))))2.2、转换为Tensor张量
python
import torch
inputs=torch.tensor(x_train,dtype=torch.float32)
labels=torch.tensor(y_train,dtype=torch.long)2.3、定义模型
python
class LogisticRegreModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LogisticRegreModel, self).__init__()
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(2, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc(x)
# dim 指定了softmax在哪个维度上进行
# dim = 1第二个维度上进行,列
# example:x (sample, num_classes)
# torch.softmax(x, dim=1), pytorch在每个样本上的类别进行softmax,保证每个样本的所有类别的概率和为1。
return torch.softmax(x, dim=1)
model = LogisticRegreModel()2.4、定义损失函数和优化器
python
cri = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.05)2.5、开始迭代
python
for epoch in range(1, 1001):
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = cri(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 50 == 0 or epoch == 1:
print(f"epoch: {epoch}, loss: {loss}")2.6、可视化
python
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, 6, 0.1), np.arange(0, 6, 0.1))
grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]
epoches = 1000
for epoch in range(1, epoches + 1):
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = cri(outputs, labels)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 50 == 0 or epoch == 1:
print(f"epoch: {epoch}, loss: {loss}")
grid_tensor = torch.tensor(grid_points, dtype=torch.float32)
Z = model(grid_tensor).detach().numpy()
Z = Z[:, 1]
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(class1_points[:, 0], class1_points[:, 1])
plt.scatter(class2_points[:, 0], class2_points[:, 1])
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0.5])
plt.pause(1)
plt.show()
2.7、完整代码
python
import numpy as np # 导入 NumPy 库进行数组和数学运算
import torch # 导入 PyTorch 库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 导入 Matplotlib 用于绘图
# 定义类1的数据点
class1_points = np.array([[1.9, 1.2],
[1.5, 2.1],
[1.9, 0.5],
[1.5, 0.9],
[0.9, 1.2],
[1.1, 1.7],
[1.4, 1.1]])
# 定义类2的数据点
class2_points = np.array([[3.2, 3.2],
[3.7, 2.9],
[3.2, 2.6],
[1.7, 3.3],
[3.4, 2.6],
[4.1, 2.3],
[3.0, 2.9]])
# 合并类1和类2的数据点,作为训练特征
x_train = np.concatenate((class1_points, class2_points))
# 合并类1和类2的标签,类1为 0,类2为 1
y_train = np.concatenate((np.zeros(len(class1_points)), np.ones(len(class2_points))))
# 将训练特征和标签转换为 PyTorch 张量
inputs = torch.tensor(x_train, dtype=torch.float32) # 输入特征
labels = torch.tensor(y_train, dtype=torch.long) # 标签应为长整型
# 定义逻辑回归模型类
class LogisticRegreModel(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LogisticRegreModel, self).__init__() # 继承父类的初始化方法
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(2, 2) # 定义线性层,输入大小为 2,输出类别数为 2
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc(x) # 进行前向传播,计算线性层输出
# 使用 softmax 函数将输出转换为概率
return torch.softmax(x, dim=1) # dim=1 表示在列上进行 softmax 操作
# 实例化逻辑回归模型
model = LogisticRegreModel()
# 定义交叉熵损失函数,适用于多分类问题
cri = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义优化器为随机梯度下降
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.05)
# 创建绘图窗口
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
# 创建网格点用于绘制决策边界
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, 6, 0.1), np.arange(0, 6, 0.1)) # 生成网格坐标
grid_points = np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()] # 将网格点展平为 (样本数, 特征数) 的形式
epoches = 1000 # 定义训练的轮数
for epoch in range(1, epoches + 1):
outputs = model(inputs) # 前向传播获得模型输出
loss = cri(outputs, labels) # 计算损失
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空之前的梯度
loss.backward() # 反向传播计算梯度
optimizer.step() # 更新模型参数
# 每 50 个 epoch 更新绘图
if epoch % 50 == 0 or epoch == 1:
print(f"epoch: {epoch}, loss: {loss.item()}") # 打印当前 epoch 和损失值
grid_tensor = torch.tensor(grid_points, dtype=torch.float32) # 将网格点转换为张量
Z = model(grid_tensor).detach().numpy() # 前向传播获得每个网格点的输出
Z = Z[:, 1] # 取出第二类的概率,用于绘制决策边界
Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) # 重塑为网格形状
plt.cla() # 清除当前图形
plt.scatter(class1_points[:, 0], class1_points[:, 1], label='Class 1') # 绘制类1数据点
plt.scatter(class2_points[:, 0], class2_points[:, 1], label='Class 2')
plt.contour(xx, yy, Z, levels=[0.5])
plt.legend()
plt.pause(1)
plt.show()