更多linux系统电源管理相关的内容请看:Linux电源管理、功耗管理 和 发热管理 (CPUFreq、CPUIdle、RPM、thermal、睡眠 和 唤醒)-CSDN博客
1 简介
Linux下的空闲进程cpuidle在内核中是一个子系统。cpuidle子系统所需要做的事情就是在CPU进入idle状态后,根据一系列的决策依据判断该CPU进入什么样的C-State。
《深入Linux内核架构与底层原理》(第2版),6.4 C-State
CPU空闲态电源管理在Linux内核中称为CPUIdle⼦系统,它主要适 ⽤于CPU利⽤率在5%以下(对单个CPU核⽽⾔)动态变化的场景。
《⽤"芯"探核:基于⻰芯的Linux内核探索解析》 8.2 运⾏时电源管理
本文主要基于linux-5.4.18版本的内核代码进行分析。
2 CPUIdle子系统的整体架构
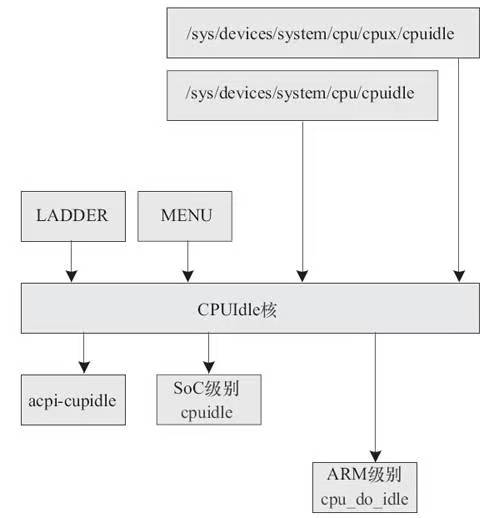
《Linux设备驱动开发详解:基于最新的Linux4.0内核》19.3 CPUIdle驱动;图19.4
3 cpuidle_state
3.1 简介
之所以C-State要定义很多种不同的暂停状态,是因为暂停的时间不同,省电的程度也不同,省电程度越深,代表恢复延迟(exit latency)的时间越长,即从暂停状态恢复到正常执行状态所需要的时间延迟不相同。
《深入Linux内核架构与底层原理》(第2版),6.4 C-State
3.2 数据结构
3.2.1 struct cpuidle_state;
cpp
//include/linux/cpuidle.h
struct cpuidle_state {
char name[CPUIDLE_NAME_LEN];
char desc[CPUIDLE_DESC_LEN];
unsigned int flags;
unsigned int exit_latency; /* in US */
int power_usage; /* in mW */
unsigned int target_residency; /* in US */
bool disabled; /* disabled on all CPUs */
int (*enter) (struct cpuidle_device *dev,
struct cpuidle_driver *drv,
int index);
int (*enter_dead) (struct cpuidle_device *dev, int index);
/*
* CPUs execute ->enter_s2idle with the local tick or entire timekeeping
* suspended, so it must not re-enable interrupts at any point (even
* temporarily) or attempt to change states of clock event devices.
*/
void (*enter_s2idle) (struct cpuidle_device *dev,
struct cpuidle_driver *drv,
int index);
};3.2.2 struct cpuidle_state_usage;
cpp
//include/linux/cpuidle.h
struct cpuidle_state_usage {
unsigned long long disable;
unsigned long long usage;
unsigned long long time; /* in US */
unsigned long long above; /* Number of times it's been too deep */
unsigned long long below; /* Number of times it's been too shallow */
#ifdef CONFIG_SUSPEND
unsigned long long s2idle_usage;
unsigned long long s2idle_time; /* in US */
#endif
};3.2.3 查看CPU每个核的cpuidle_state信息
cpp
# ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/
state0 state1 state2 state3
#
# ls /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpuidle/state0/ -l
总用量 0
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 above //cpuidle_state_usage->above
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 below //cpuidle_state_usage->below
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 16:44 default_status
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 16:44 desc //cpuidle_state->desc
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 disable //cpuidle_state_usage->disable
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 latency //cpuidle_state->exit_latency
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 16:39 name //cpuidle_state->name
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 power //cpuidle_state->power_usage
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 rejected
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 residency //cpuidle_state->target_residency
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 time //cpuidle_state_usage->time
-r--r--r-- 1 root root 4096 4月 16 22:08 usage //cpuidle_state_usage->usage3.3 支持ACPI的intel CPU的cpuidle_state
对于Intel系列笔记本计算机⽽⾔,⽀持ACPI,⼀般有4个不同的C状态 (其中C0为操作状态,C1是Halt状态,C2是Stop-Clock状态,C3是Sleep状态)
《Linux设备驱动开发详解:基于最新的Linux4.0内核》 19.3 CPUIdle驱动
Processor power states include are designated C0, C1, C2, C3, . . . Cn.
The C0 power state is an active power state where the CPU executes instructions. The C1 through Cn power states are
processor sleeping states where the processor consumes less power and dissipates less heat than leaving the processor in the C0 state. While in a sleeping state, the processor does not execute any instructions. Each processor sleeping state has a latency associated with entering and exiting that corresponds to the power savings. In general, the longer the entry/exit latency, the greater the power savings when in the state.
《Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification》8.1 Processor Power States
3.4 支持PSCI的ARM CPU的cpuidle_state (Power States)
3.4.1 简介
⽬前ARM SoC⼤多⽀持⼏个不同的Idle级别,CPUIdle驱动⼦系统存在的⽬的 就是对这些Idle状态进⾏管理,并根据系统的运⾏情况进⼊不同的Idle级别。
《Linux设备驱动开发详解:基于最新的Linux4.0内核》 19.3 CPUIdle驱动
Multiprocessor systems can have several different power domains to power different elements of the
system. Each power domain might contain a combination of one or more processing elements (such as
cores, coprocessors, or GPUs), memories (caches, DRAMs), and fabric (for example inter-cluster and
intra-cluster coherency fabric). PSCA [1] provides detailed descriptions of how power domains can be
constructed in systems that use Arm components.
Each component in a power domain has a set of power states that affect the components in the
domain. Although physically the power domains are not necessarily built in a hierarchical fashion, from
a software control point of view, they are arranged in a logical hierarchy. The hierarchy arises out of
ordering dependencies that are required when placing the power domains into different power states.
For example, consider a power domain that encompasses a shared cache, and power domains for the
cores that use it. In such a system, the core power domains must be powered down before the shared
cache domain, to guarantee correct operation.

《Arm Power State Coordination Interface》4.2 Power state system topologies and coordination
3.4.2 控制接口:CPU_SUSPEND
cpuidle驱动中通过下面的函数控制一个支持PSCI的CPU进入某种idle state
cpp
//drivers/firmware/psci/psci.c
static int psci_cpu_suspend(u32 state, unsigned long entry_point)
{
int err;
u32 fn;
fn = psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND];
err = invoke_psci_fn(fn, state, entry_point, 0);
return psci_to_linux_errno(err);
}psci_cpu_suspend()函数被调用的流程请看下面的"4.2.3" 小节
PSCI手册上的相关信息:
The CPU_SUSPEND API is used to move a topology node into a low-power state.
This is the only format that is supported by versions of PSCI prior to 1.0. When this format is in use,
bit[1] of the flags field returned by PSCI_FEATURES with a CPU_SUSPEND function ID is set to 0.
In this format, the power_state parameter is broken into the following fields:


PowerLevel:
• Level 0: for cores
• Level 1: for clusters
• Level 2: for system
StateType:
A value of 0 indicates a standby or retention state as defined in section 4.1.
A value of 1 indicates a powerdown state as defined in section 4.1. This also indicates that
entry_point_address and context_id fields contain valid data.
StateID:
Field to express a platform-specific state ID.
《Arm Power State Coordination Interface》5.4 CPU_SUSPEND
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》16.4.3 CPU_SUSPEND函数
上面提到的"power_state parameter"可以通过设备树中的"arm,psci-suspend-param"属性来指定,例如:
cpp
idle-states {
entry-method = "psci";
CPU_SLEEP: cpu-sleep {
compatible = "arm,idle-state";
local-timer-stop;
arm,psci-suspend-param = <0x0010000>;
entry-latency-us = <700>;
exit-latency-us = <250>;
min-residency-us = <1000>;
};
CLUSTER_SLEEP: cluster-sleep {
compatible = "arm,idle-state";
local-timer-stop;
arm,psci-suspend-param = <0x1010000>;
entry-latency-us = <1000>;
exit-latency-us = <700>;
min-residency-us = <2700>;
wakeup-latency-us = <1500>;
};
};
cpu0: cpu@0 {
......
enable-method = "psci";
cpu-idle-states = <&CPU_SLEEP &CLUSTER_SLEEP>;
......
};cpuidle驱动中获取设备树中"power_state parameter"值的流程请看下面的"4.2.2"小节
更多设备树中PSCI相关的设置请看Documentation/devicetree/bindings/arm/idle-states.txt
3.4.3 CPU_SUSPEND和RESUME流程示意图
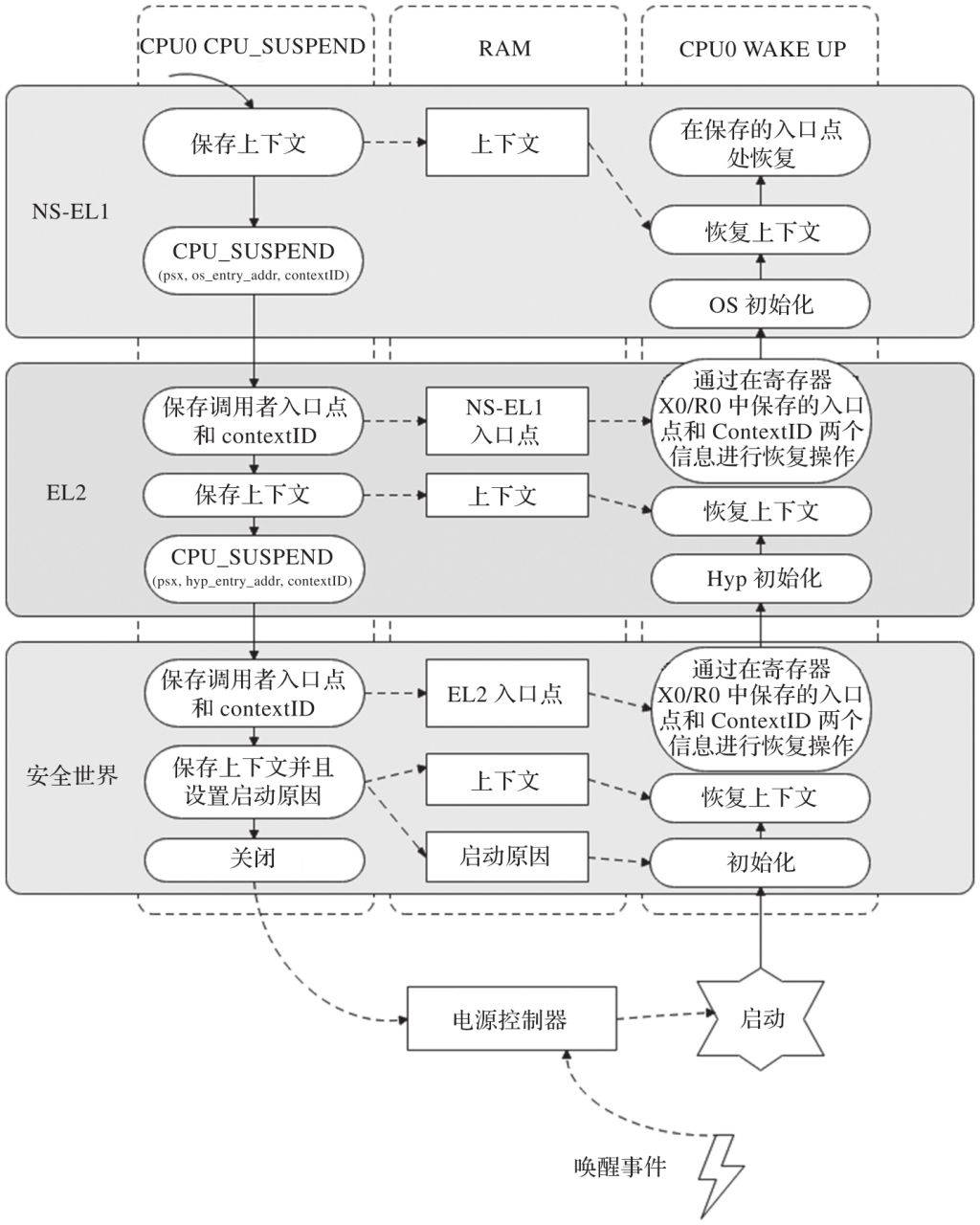
《SoC底层软件低功耗系统设计与实现》16.5.1 CPU_SUSPEND、SYSTEM_SUSPEND调用流程
4 struct cpuidle_driver 和 struct cpuidle_device
4.1 简介
CPUIdle驱动必须针对每个CPU注册相应的cpuidle_device。
struct cpuidle_driver结构体关键成员是1个cpuidle_state表,其实该表就是用于存储各种不同Idle级别的信息
《Linux设备驱动开发详解:基于最新的Linux4.0内核》19.3 CPUIdle驱动
4.2 psci_idle_driver驱动分析
4.2.1 数据结构
cpp
//drivers/cpuidle/cpuidle-psci.c
static struct cpuidle_driver psci_idle_driver __initdata = {
.name = "psci_idle",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
/*
* PSCI idle states relies on architectural WFI to
* be represented as state index 0.
*/
.states[0] = {
.enter = psci_enter_idle_state,
.exit_latency = 1,
.target_residency = 1,
.power_usage = UINT_MAX,
.name = "WFI",
.desc = "ARM WFI",
}
};4.2.2 初始化大致流程
cpp
psci_idle_init(); //device_initcall(psci_idle_init);
-> psci_idle_init_cpu(cpu);
-> drv = kmemdup(&psci_idle_driver, sizeof(*drv), GFP_KERNEL);
-> dt_init_idle_driver(drv, psci_idle_state_match, 1);
-> idle_state = &drv->states[state_idx++];
-> init_state_node(idle_state, match_id, state_node); //从设备树中读取state的值,并设置cpuidle_state的成员
-> idle_state->enter = match_id->data; //psci_enter_idle_state();
-> idle_state->enter_s2idle = match_id->data;
-> of_property_read_u32(state_node, "wakeup-latency-us", &idle_state->exit_latency);
-> idle_state->exit_latency = entry_latency + exit_latency;
-> of_property_read_u32(state_node, "min-residency-us", &idle_state->target_residency);
-> psci_cpu_init_idle();
-> psci_dt_cpu_init_idle();
-> of_parse_phandle(cpu_node, "cpu-idle-states", i);
-> psci_dt_parse_state_node();
-> of_property_read_u32(np, "arm,psci-suspend-param", state);
-> cpuidle_register(drv, NULL);
-> cpuidle_register_driver();
-> cpuidle_register_device();4.2.3 进入某个idle state的大致流程
cpp
do_idle(); //kernel/sched/idle.c
-> cpuidle_idle_call();
-> cpuidle_select(); //choose an idle state
-> cpuidle_curr_governor->select(drv, dev, stop_tick);
-> call_cpuidle();
-> cpuidle_enter(); //drivers/cpuidle/cpuidle.c
-> cpuidle_enter_state();
-> trace_cpu_idle_rcuidle();
-> entered_state = target_state->enter(dev, drv, index);
-> trace_cpu_idle_rcuidle();
-> cpuidle_reflect();
-> cpuidle_curr_governor->reflect(dev, index);psci_idle_driver中的target_state->enter()是psci_enter_idle_state()
cpp
psci_enter_idle_state();
-> psci_cpu_suspend_enter();
-> cpu_suspend();
-> __cpu_suspend_enter();
-> psci_suspend_finisher();
-> psci_ops.cpu_suspend();
-> psci_cpu_suspend(); //drivers/firmware/psci/psci.c
-> fn = psci_function_id[PSCI_FN_CPU_SUSPEND];
-> invoke_psci_fn(fn, state, entry_point, 0);4.3 查看系统当前使用的cpuidle_driver
cpp
# cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_driver
intel_idle5 governor
5.1 简介
与CPUFreq类似,在CPUIdle子系统中也有对应的governor来抉择何时进入何种Idle级别的策略。
5.2 数据结构
cpp
//include/linux/cpuidle.h
struct cpuidle_governor {
char name[CPUIDLE_NAME_LEN];
struct list_head governor_list;
unsigned int rating;
int (*enable) (struct cpuidle_driver *drv,
struct cpuidle_device *dev);
void (*disable) (struct cpuidle_driver *drv,
struct cpuidle_device *dev);
int (*select) (struct cpuidle_driver *drv, //决策要进入的下一个State
struct cpuidle_device *dev,
bool *stop_tick);
void (*reflect) (struct cpuidle_device *dev, int index); //从State退出的时候调用的回调函数
};register接口
cpp
int cpuidle_register_governor(struct cpuidle_governor *gov);5.3 现有的governor
5.3.1 ladder 和 menu
LADDER在进入和退出Idle级别的时候是步进的,它以过去的Idle时间作为参考,而MENU总是根据预期的空闲时间直接进入目标Idle级别。前者适用于没有采用动态时间节拍的系统(即没有选择NO_HZ的系统),不依赖于NO_HZ配置选项,而后者依赖于内核的NO_HZ选项。
下图演示了LADDER步进从C0进入C3,而MENU则可能直接从C0跳入C3。
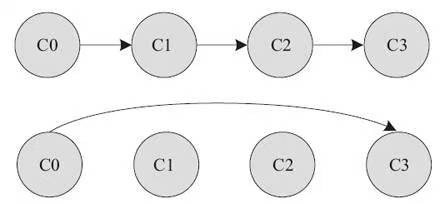
《Linux设备驱动开发详解:基于最新的Linux4.0内核》 19.3 CPUIdle驱动
数据结构
cpp
//drivers/cpuidle/governors/ladder.c
static struct cpuidle_governor ladder_governor = {
.name = "ladder",
.rating = 10,
.enable = ladder_enable_device,
.select = ladder_select_state,
.reflect = ladder_reflect,
};
cpp
//drivers/cpuidle/governors/menu.c
static struct cpuidle_governor menu_governor = {
.name = "menu",
.rating = 20,
.enable = menu_enable_device,
.select = menu_select,
.reflect = menu_reflect,
};5.3.2 teo
The Timer Events Oriented (TEO) Governor
========================================
The timer events oriented (TEO) governor is an alternative ``CPUIdle`` governor
for tickless systems. It follows the same basic strategy as the ``menu`` `one
<menu-gov_>`_: it always tries to find the deepest idle state suitable for the
given conditions. However, it applies a different approach to that problem.
Documentation/admin-guide/pm/cpuidle.rst
数据结构
cpp
//drivers/cpuidle/governors/teo.c
static struct cpuidle_governor teo_governor = {
.name = "teo",
.rating = 19,
.enable = teo_enable_device,
.select = teo_select,
.reflect = teo_reflect,
};5.3.3 haltpoll (虚拟机)
Guest halt polling
==================
The cpuidle_haltpoll driver, with the haltpoll governor, allows
the guest vcpus to poll for a specified amount of time before
halting.
This provides the following benefits to host side polling:
- The POLL flag is set while polling is performed, which allows
a remote vCPU to avoid sending an IPI (and the associated
cost of handling the IPI) when performing a wakeup.
- The VM-exit cost can be avoided.
Documentation/virtual/guest-halt-polling.txt
数据结构
cpp
//drivers/cpuidle/governors/haltpoll.c
static struct cpuidle_governor haltpoll_governor = {
.name = "haltpoll",
.rating = 9,
.enable = haltpoll_enable_device,
.select = haltpoll_select,
.reflect = haltpoll_reflect,
};5.4 查看 和 设置系统当前使用的governor
查看当前系统支持的governor
cpp
# cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/available_governors
ladder menu teo 设置当前系统使用的governor
cpp
echo menu > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuidle/current_governor