面向对象编程
JS 中的 this
js
function f() {
console.info(this.x);
}
var obj = {
f: f,
x: 1,
};
var x = 2;
f(); // 2
obj.f(); // 1
/* ************** */
let foo = function () {
var self = this;
console.info(this === obj);
f();
function f() {
console.info(this === obj);
console.info(self === obj);
console.info(self);
}
};
var obj = {
m: foo,
};
obj.m();
// true
// false
// true- this 的指向
- 全局作用域的 this 指向 window || global(node 中) 对象
- 函数中的 this 指向调用该函数的对象
- 对象方法中的 this 指向调用该方法的对象
js
const obj = {
name: "aa",
sayName: function () {
console.log(this.name);
},
};
obj.sayName(); // aa- 构造函数中的 this 指向新创建的对象
js
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const alice = new Person("Alice"); // alice.name = "Alice"
console.info(alice.name); // Alice- 箭头函数中的 this 不会创建新的 this 上下文,而是捕获外层作用域的 this
js
const obj = {
name: "Fa-ce",
sayName: () => {
console.log(this.name);
},
};
obj.sayName(); // undefined
this.name = "Fa-ce1";
obj.sayName(); // Fa-ce1- 事件处理函数中的 this 通常指向触发元素的对象
js
// DOM 事件 浏览器环境执行
const body = document.querySelector("body");
const div = document.createElement("div");
div.id = "myDiv";
body.appendChild(div);
document.getElementById("myDiv").addEventListener("click", function () {
console.info(this);
});
div.click(); // <div id="myDiv"></div>
/* ****** JS 函数 ******** */
function sayHello() {
console.log(this);
}
sayHello(); // window(非严格模式) || undefined(严格模式) || global(node 中)- 如何改变 this 的指向
call、apply、bind
js
function greet(greeting, xxx) {
console.info(greeting + ", " + this.name);
}
const person = { name: "Fa-ce" };
greet.call(person, "Hello"); // Hello, Fa-ce
greet.apply(person, ["Test"]); // Test, Fa-ce
const boundGreet = greet.bind(person);
boundGreet("Hi"); // Hi, Fa-ce面向对象的介绍
- 什么是对象
- 什么是面向对象
- 面向过程
- 对象对象(OOP)
- 面向对象编程的三大特性
- 封装
- 继承
- 多态
e.g.: 处理学生成绩表,通过面向过程的方式,需要定义很多函数,如:添加学生、删除学生、修改学生、查询学生等。而通过面向对象的方式,只需要定义一个学生类,然后通过这个类创建学生对象,就可以直接调用对象的方法来处理学生成绩表。
js
var std1 = { name: "John", age: 20 };
var std2 = { name: "Jane", age: 22 };处理学生程力可以通过函数去实现,例如:打印
js
function printScore(student) {
console.log(`${student.name} scored ${student.score}`);
}假如使用面向对象:
js
function printScore(name, score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
this.printScore = function () {
console.log(`${this.name} scored ${this.score}`);
};
}
// 根据模板创建具体实例对象
var std1 = new printScore("John", 90);
var std2 = new printScore("Jane", 80);
/* ****** class ******* */
class Student {
constructor(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
printScore() {
console.log(`${this.name} scored ${this.score}`);
}
}
var std3 = new Student("John", 90);
var std4 = new Student("Jane", 80);
/* 打印成绩 */
std1.printScore();
std2.printScore();
std3.printScore();
std4.printScore();基于函数的面向对象实现
- 创建对象
new Object()
js
const person = new Object();
person.name = "Fa-ce";
person.age = 18;- 字面量
js
const person = {
name: "Fa-ce",
age: 18,
sayName: function () {},
};- 工厂函数 => 构造函数
- 引入工厂函数
js
function createPerson(name, age) {
return {
name: name,
age: age,
sayName: function () {
console.log(this.name);
},
};
}
const person_0 = createPerson("Fa-ce", 18);- 构造函数的问题:构造函数中的方法每次实例化都会重复创建,浪费内存;不利于代码维护与优化
js
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
}
const person_1 = new Person("Fa-ce", 18);
const person_2 = new Person("Fa-ce1", 19);
// 每次调用 new Person(...) 时,this.sayName = function () {...} 都会生成一个新的函数实例。
// person_1.sayName !== person_2.sayName,这两个是不同的函数对象,即使它们内容完全一样。- new 做了哪些事情
- 创建一个空对象
- 将构造函数的作用域付给新对象(this 指向新对象)
- 执行构造函数中的代码(为新对象添加属性)
- 返回新对象
js
function Person(name, age) {
// 使用 new 调用 Person() 时, 会创建一个对象
// var instance = {}
// 让内部的 this 指向 instance 对象
// this = instance
// 接下来所有针对 this 的操作, 都会针对 instance 对象
return this;
}
console.info(p1.constructor === Person); // true
console.info(p2.constructor === Person); // true
console.info(p1.constructor === p2.constructor); // true
console.info(p1 instanceof Person); // true- 构造函数的问题:通过构造函数创建的实例,每个实例都有自己的一份方法
js
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
}
const person_1 = new Person("Fa-ce", 18);
const person_2 = new Person("Fa-ce1", 19);
// 每次调用 new Person(...) 时,this.sayName = function () {...} 都会生成一个新的函数实例。
console.info(person_1.sayName === person_2.sayName); // false
/* ******* 将 sayName 函数写在外部 ******* */
function sayName() {
console.log(this.name);
}
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sayName = sayName;
}
const person_1 = new Person("Fa-ce", 18);
const person_2 = new Person("Fa-ce1", 19);
// 每次构造不会生成新的函数实例,而是指向同一个函数
console.info(person_1.sayName === person_2.sayName); // true- 原型 和 原型链
js
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
Person.prototype.type = "human";
Person.prototype.sayName = function () {
console.info(this.name);
};
const person_1 = new Person("Fa-ce", 18);
const person_2 = new Person("Fa-ce1", 19);
console.info(person_1.type); // human
console.info(person_2.type); // human
console.info(person_1.sayName === person_2.sayName); // true
/* **** 原型链 **** */
function F() {
const sayHi = function () {};
}
console.info(F.prototype); // {constructor: ƒ}
console.info(F.prototype.constructor === F); // true
var instance = new F();
console.info(instance.__proto__ === F.prototype); // true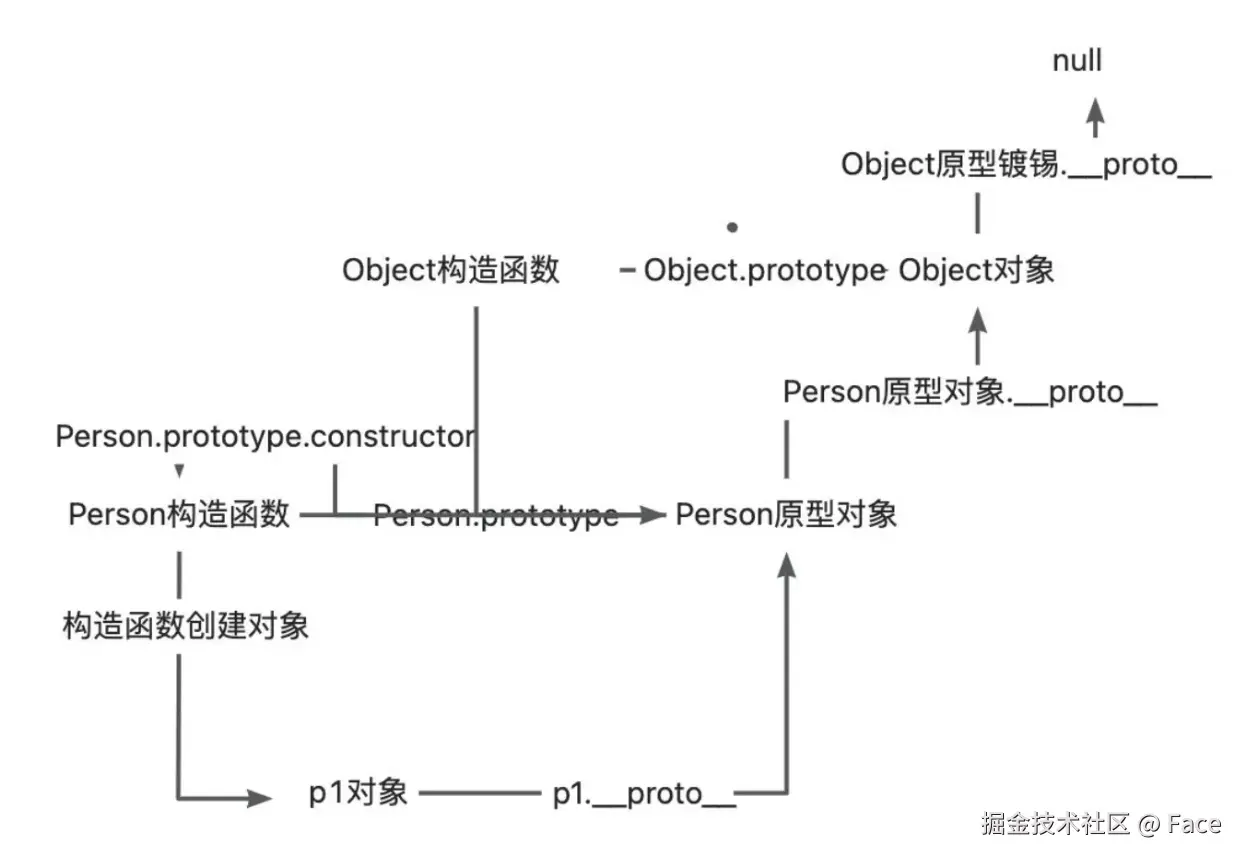
es6 面向对象
- Class(类) 和 Object(对象)
- 类是一种特定对象中方法和变量的模板定义
- 对象是类的具体示例,并且在内存中分配
js
// 定义类
class Form {
submit() {
console.info(this.name + "" + this.roll + "submitted");
}
cancel() {
console.info(this.name + "" + this.roll + "cancelled");
}
fill(give_name, give_roll) {
this.name = give_name;
this.roll = give_roll;
}
}
// 创建对象
var student = new Form();
student.fill("Fa-ce", 123);
student.submit();
student.cancel();- Constructor (构造函数)
js
class Form {
constructor() {
// 构造函数,初始化默认的 name 、roll
this.name = "Fa-ce";
this.roll = "admin";
}
submit() {
console.info(this.name + "" + this.roll + "submitted");
}
cancel() {
console.info(this.name + "" + this.roll + "cancelled");
}
fill(give_name, give_roll) {
this.name = give_name;
this.roll = give_roll;
}
}
// 创建对象
const student1 = new Form();
const student2 = new Form();
student1.fill("Fa-ce", 123);
student1.submit();
student2.fill("Fa-ce1", 124);
student2.cancel();- 无参数构造函数:构造函数没有参数,不需要在构造函数中添加参数
js
class Example {
constructor() {
this.name = "test";
}
}- 有参数构造函数:构造函数有参数,需要在构造函数中添加参数
js
class Example {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
}分割线 ,未写完......
- 继承
js
class Student extends Form {
constructor() {
super();
this.name = "test";
}
}- Inheritance 继承
js
class Animal {
constructor(name, age, color) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.color = color;
}
run() {
console.info(this.name + " is running");
}
shout() {
console.info(this.name + " is shouting");
}
sleep() {
console.info(this.name + " is sleeping");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
constructor(name, age, color, breed) {
super(name, age, color);
this.breed = breed;
}
run() {
console.info(this.name + " is running");
}
shout() {
console.info(this.name + " is shouting");
}
sleep() {
console.info(this.name + " is sleeping");
}
}
const dog = new Dog("Fa-ce", 18, "red", "Bulldog");
dog.run();
dog.shout();
dog.sleep();- 多态
js
class Animal {
}-
访问修饰符
-
Public:可以从其他任何类中访问 -
Protected:受保护的成员,可以在同一类及其子类中访问 -
Private:私有成员,只能在同一个类中访问
-
-
静态方法
static:给类定义一个静态方法或字段,静态方法是属于类本身的方法,而不是类的具体实例方法- 静态方法:静态方法属于类本身,而不是类的实例。静态方法不能通过类的实例调用,只能通过类本身调用。静态方法可以访问类的静态属性和方法,但不能访问类的实例属性和方法。
- 静态方法:静态方法可以用于实现一些与类本身相关的功能,而不需要创建类的实例。例如,可以定义一个静态方法来计算类的实例数量,或者定义一个静态方法来生成类的实例。
-
Getter 和 Setter
- getter 不应该加
(),应该直接访问属性,例如:console.log(person_0.getName); - setter 不能当作函数调用,而应该直接赋值,例如:
person_0.setName = "newName"; - 如果想要用
()方式调用,就应该 不用get和set关键字,直接创建普通方法
- getter 不应该加
-
instanceOf
- 检查一个对象是否是某个类或者接口的实例
-
封装
- 一种限制,对对象某些组件或属性直接访问的方式
-
多态
-
抽象