C# 基础篇
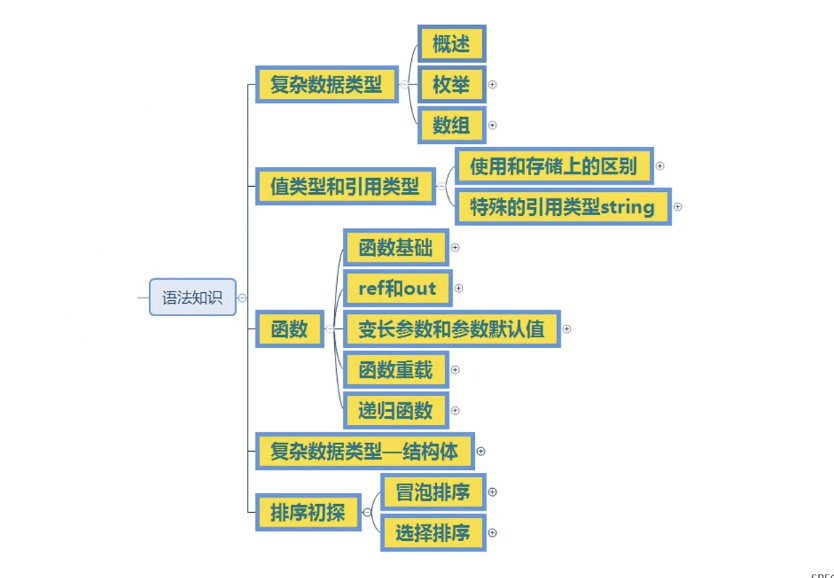
枚举(enum)
枚举是一个被命名的整形常量的集合
用于表示: 状态 类型
申明枚举:创建一个自定义的枚举类型
申明枚举变量:使用申明的自定义的枚举类型,来创建一个枚举变量
语法
csharp
//语法:枚举名 以E或E_开头,作为命名规范
enum E_自定义枚举名{
自定义枚举项名字1,//枚举中的第一个默认值是0,也可以赋值,下面依次累加。
自定义枚举项名字2,//1
自定义枚举项名字3,//2
}在哪里申明枚举
- namespace语句块中
- class语句块中
- struct语句块中
枚举不能在函数语句块中声明
csharp
#region 在哪里申明枚举
//namespace语句块中
//class语句块中
//struct语句块中
//枚举不能再函数语句块中声明
enum E_MonsterType{
Normal,
Boss,
}
enum E_PlayerType{
Main,
Other,
}
#endregion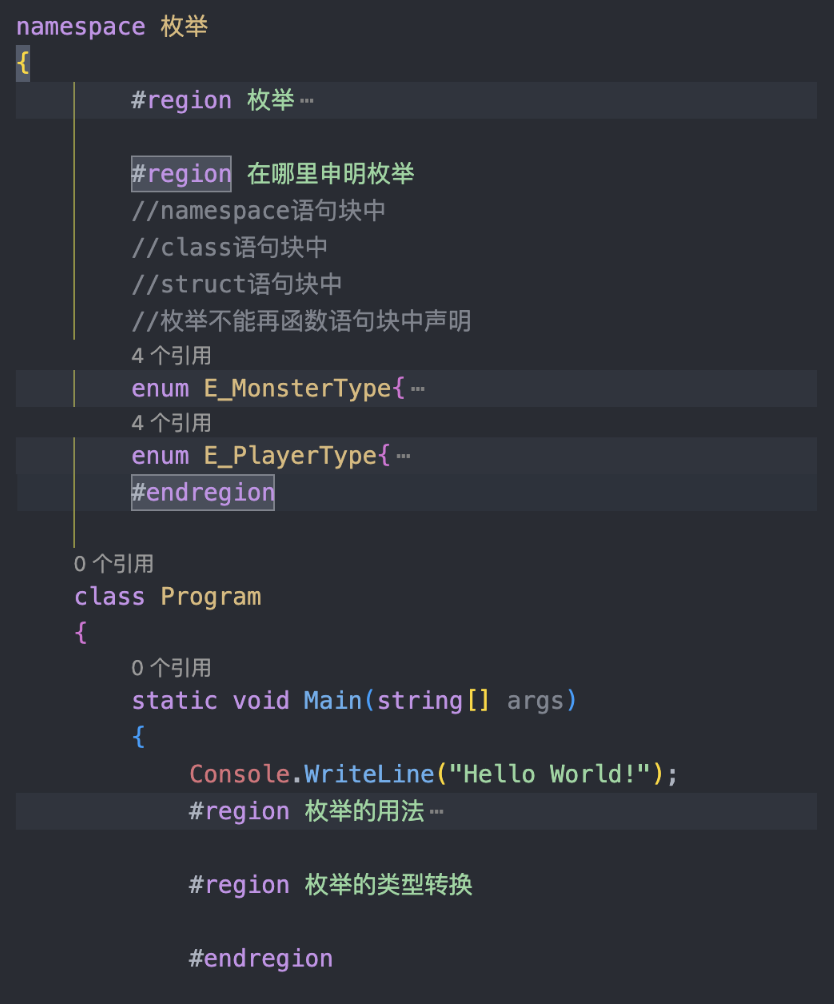
枚举的用法
- 申明枚举变量: 前面自定义的 变量名 = 默认值;
- 枚举和switch配套使用
csharp
#region 枚举的用法
//申明枚举变量
//前面自定义的 变量名 = 默认值;
// (这里的默认值的格式:自定义的枚举类型.枚举项)枚举类型
E_MonsterType monsterType = E_MonsterType.Normal;
E_PlayerType playerType = E_PlayerType.Main;
if(playerType == E_PlayerType.Main){
Console.WriteLine("主角的逻辑");
}
else if(playerType == E_PlayerType.Other){
Console.WriteLine("其他角色的逻辑");
}
//枚举很适合和switch配套使用
//也可以贯穿,两种情况使用同一个逻辑
switch (monsterType){
case E_MonsterType.Normal:
Console.WriteLine("普通怪物的逻辑");
break;
case E_MonsterType.Boss:
Console.WriteLine("BOSS的逻辑");
break;
}
#endregion枚举的类型转换
csharp
#region 枚举的类型转换
//枚举转int------括号强转
int i1 = (int)playerType;
Console.WriteLine(i1);
//int 转枚举------隐式转换
playerType = 0;
Console.WriteLine(playerType);
//枚举转string------ToString()方法
string s1 = playerType.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(s1);
//string 转枚举------Parse()方法 + 自定义枚举类型括号强转
//语法:(自定义枚举类型)Enum.Parse(typeof(自定义枚举类型), "要转换的字符串");
//注意要转换的字符串必须是枚举里有的常量
playerType = (E_PlayerType)Enum.Parse(typeof(E_PlayerType), "Main");
Console.WriteLine(playerType);
#endregion(总结)枚举的作用
在游戏开发中,对象通常会有很多状态
每个状态需要一个变量 / 标识 来表示,以便于后续使用时的判断(该对象当前处于什么状态)
不要去用int 表示他的状态 ,1走路 2空闲 3跑步 4跳跃
枚举的使用可以很好的分清楚各状态的含义,提高代码可读性
习题

csharp
/// <summary>
/// 状态
/// </summary>
enum E_StateOnlineType{
Offline,
Online,
Busy,
Invisible,
}
csharp
#region 题目1 用户状态
try
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入状态(0-3):");
E_StateOnlineType state = (E_StateOnlineType)Enum.Parse(typeof(E_StateOnlineType), Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine(state);
}
catch{
Console.WriteLine("输入错误,请输入0-3的数字!");
}
#endregion
csharp
/// <summary>
/// 咖啡类型
/// </summary>
enum E_CoffeeType{
/// <summary>
/// 中杯
M,
/// <summary>
/// 大杯
/// </summary>
L,
/// <summary>
/// 特大杯
/// </summary>
XL,
}
csharp
#region 题目2 coffee
try{
Console.WriteLine("请输入咖啡类型(M/L/XL):");
E_CoffeeType coffeeType = (E_CoffeeType)Enum.Parse(typeof(E_CoffeeType), Console.ReadLine());
switch(coffeeType){
case E_CoffeeType.M:
Console.WriteLine("中杯咖啡");
break;
case E_CoffeeType.L:
Console.WriteLine("大杯咖啡");
break;
case E_CoffeeType.XL:
Console.WriteLine("特大杯咖啡");
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("输入错误!");
break;
}
}
catch{
Console.WriteLine("输入错误,请输入M/L/XL!");
}
#endregion

csharp
数组
一维数组(数组)
一维、多维、交错数组
csharp
namespace 数组;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 数组声明
//只声明数组名,不初始化
//变量类型[] 数组名;
int[] arr1;
//声明并初始化数组的长度,元素默认值是0
//变量类型[] 数组名 = new 变量类型[数组长度];
int[] arr2 = new int[5];
//声明并初始化数组的长度和元素值
//变量类型[] 数组名 = new 变量类型[数组长度] {元素值1, 元素值2, 元素值3...};
int[] arr3 = new int[5] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
//声明并初始化数组的元素值,数组长度自动计算
//变量类型[] 数组名 = new 变量类型[] {元素值1, 元素值2, 元素值3...};
int[] arr4 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4};
//声明并初始化数组------最简单的方法
int[] arr5 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
bool[] arr6 = new bool[] { true, false, true, false };
#endregion
#region 数组使用
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
//1. 获取数组长度
//数组名.Length
Console.WriteLine("数组长度:" + arr.Length);
//2. 获取数组元素
//数组名[索引]
//注意不要越界
Console.WriteLine("数组第一个元素:" + arr[0]);
//3. 修改数组元素
//数组名[索引] = 新值;
arr[0] = 10;
Console.WriteLine("修改后的数组第一个元素:" + arr[0]);
//4. 遍历数组
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++){
Console.WriteLine("数组第" + i + "个元素:" + arr[i]);
}
//5. 增加数组元素(先拷贝数组)
int[] array2 = new int[6];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++){
array2[i] = arr[i];
}
arr = array2;
arr[5] = 6;
Console.WriteLine("增加后的数组:" + string.Join(",", arr));
//6. 删除数组元素(先拷贝数组)
int[] array3 = new int[4];
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
array3[i] = arr[i];
}
arr = array3;
Console.WriteLine("删除后的数组:" + string.Join(",", arr));
//7. 查找数组元素
int elem = 3;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++){
if(arr[i] == elem){
Console.WriteLine("元素" + elem + "在数组的索引为:" + i);
break;
}
}
#endregion
}
}用来批量存储游戏中同一类型的所有对象,比如所有的enemy和player
习题

csharp
#region 1
int[] arr1 = new int[100];
for(int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++){
arr1[i] = i;
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arr1));
#endregion
csharp
#region 2
int[] arr2 = new int[100];
for(int i = 0; i < arr2.Length; i++){
arr2[i] = arr1[i] * 2;
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arr2));
#endregion
csharp
#region 3
Random r1 = new Random();
int[] arr3 = new int[10];
for(int i = 0; i < arr3.Length; i++){
arr3[i] = r1.Next(0, 101);
}
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arr3));
#endregion
csharp
#region 4
Random r = new Random();
int[] arr = new int[10];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++){
arr[i] = r.Next(0, 101);
}
Console.WriteLine("原数组:"+string.Join(",", arr));
//MAX MIN
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1; i++){
max = (max >= arr[i])? max : arr[i];
min = (min <= arr[i])? min : arr[i];
sum += arr[i];
}
Console.WriteLine("最大值:"+max);
Console.WriteLine("最小值:"+min);
Console.WriteLine("和:"+sum);
double avg = (double)sum / arr.Length;
Console.WriteLine("平均值:"+avg);
#endregion
csharp
#region 5
Random r2 = new Random();
int[] arr4 = new int[10];
for(int i = 0; i < arr4.Length; i++){
arr4[i] = r2.Next(0, 101);
}
Console.WriteLine("原数组:"+string.Join(",", arr4));
for(int i = 0; i < arr4.Length /2; i++){
arr4[i] = arr4[i] + arr4[arr4.Length-1-i];
arr4[arr4.Length-1-i] = arr4[i] - arr4[arr4.Length-1-i];
arr4[i] = arr4[i] - arr4[arr4.Length-1-i];
}
Console.WriteLine("反转后:"+string.Join(",", arr4));
#endregion
csharp
#region 6
Random r3 = new Random();
int[] arr5 = new int[10];
for(int i = 0; i < arr5.Length; i++){
arr5[i] = r3.Next(-100, 101);
}
Console.WriteLine("原数组:"+string.Join(",", arr5));
for(int i = 0; i < arr5.Length; i++){
if(arr5[i]>0) arr5[i]++;
else if(arr5[i]<0) arr5[i]--;
}
Console.WriteLine("变化后:"+string.Join(",", arr5));
#endregion
csharp
#region 7
int[] arr6 = new int[10];
//输入
try{
for(int i = 0; i < arr6.Length; i++){
Console.Write("请输入第{0}个元素:", i+1);
arr6[i] = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
}
}
catch{
Console.WriteLine("输入有误,程序退出");
}
Console.WriteLine("原数组:"+string.Join(",", arr6));
//MAX MIN
int max = arr6[0];
int min = arr6[0];
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < arr6.Length - 1; i++){
max = (max >= arr6[i])? max : arr6[i];
min = (min <= arr6[i])? min : arr6[i];
sum += arr6[i];
}
Console.WriteLine("最大值:"+max);
Console.WriteLine("最小值:"+min);
Console.WriteLine("平均值:"+(double)sum / arr6.Length);
#endregion
csharp
#region 8
string[] arr7 = new string[25];
for(int i = 0; i < arr7.Length; i++){
arr7[i] = (i%2 == 0)? "■": "□";
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr7.Length; i++){
Console.Write(arr7[i]);
if((i+1)%5 == 0 && i!= 0){
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
#endregion二维数组
csharp
namespace 二维数组;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 二维数组的申明
//申明但不初始化:
//变量类型[,] 二维数组变量名
int[,] arr1;
//变量类型[,] 二维数组变量名 = new int[行数,列数];
int[,] arr2 = new int[3, 3];
//申明+初始化:
//变量类型[,] 二维数组变量名 = new int[行数,列数] { {元素1,元素2,元素3...}, {元素1,元素2,元素3...},... };
int[,] arr3 = new int[3, 3] { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }};
//行列自动计算
int[,] arr4 = new int[,] { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 }};
#endregion
#region 二维数组的使用
//1.二维数组的长度
int[,] array1 = new int[,]{ {1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}};
//二维数组名.GetLength(dimesion),dimesion为0表示行,为1表示列
//行
Console.WriteLine(array1.GetLength(0));
//列
Console.WriteLine(array1.GetLength(1));
//2.获取二维数组的元素
//二维数组名[行,列]
Console.WriteLine(array1[0, 0]);
//3.修改二维数组的元素
//二维数组名[行,列] = 元素值
array1[0, 0] = 10;
Console.WriteLine(array1[0, 0]);
//4.遍历二维数组
for (int i = 0; i < array1.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array1.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(array1[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("**************");
//5.增加数组元素
int[,] array2 = new int[4,3];
//先拷贝原数组元素
for (int i = 0; i < array1.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array1.GetLength(1); j++)
{
array2[i, j] = array1[i, j];
}
}
array1 = array2;
array1[3, 0] = 100;
array1[3, 1] = 101;
array1[3, 2] = 102;
for(int i = 0; i < array1.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < array1.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(array1[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("***************");
//6.删除数组元素
//先拷贝原数组元素
int[,] array3 = new int[2, 3];
for (int i = 0; i < array3.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array3.GetLength(1); j++)
{
array3[i, j] = array1[i, j];
}
}
array1 = array3;
for(int i = 0; i < array1.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < array1.GetLength(1); j++)
{
Console.Write(array1[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
//7.查找数组元素
for(int i = 0; i < array1.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < array1.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if(array1[i,j] == 6)
{
Console.WriteLine("元素6的位置为:{0},{1}", i, j);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
}习题
csharp
#region 1
int[,] arr1 = new int[100, 100];
int count = 1;
Console.WriteLine("1到10000的二维数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr1.GetLength(1); j++){
arr1[i, j] = count;
count++;
Console.Write(arr1[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 2
int[,] arr2 = new int[4, 4];
Random r = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("随机生成的4x4二维数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr2.GetLength(1); j++){
arr2[i, j] = r.Next(1, 101);
Console.Write(arr2[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("将数组的右上角区域清零:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr2.GetLength(1); j++){
if(i < arr2.GetLength(0) / 2 && j >= arr2.GetLength(1) / 2){
arr2[i, j] = 0;
}
Console.Write(arr2[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 3
int[,] arr3 = new int[3, 3];
Random r = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("随机生成的3x3二维数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr3.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr3.GetLength(1); j++){
arr3[i, j] = r.Next(1, 11);
Console.Write(arr3[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("对角线:");
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr3.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr3.GetLength(1); j++){
if(i == j || i+j == 3-1){
sum += arr3[i, j];
Console.Write(arr3[i, j] + " ");
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("对角线的和为:" + sum);
#endregion
csharp
#region 4
int[,] arr4 = new int[5, 5];
Random r = new Random();
//记录最大值的位置
int maxRow = 0, maxCol = 0;
Console.WriteLine("随机生成的5x5二维数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr4.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr4.GetLength(1); j++){
arr4[i, j] = r.Next(1, 11);
Console.Write(arr4[i, j] + " ");
if(arr4[maxRow, maxCol] < arr4[i, j]){
maxRow = i;
maxCol = j;
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("最大值{0}的位置:({1},{2})" , arr4[maxRow, maxCol], maxRow, maxCol);
Console.WriteLine("****所有最大值元素{0}的位置****");
for(int i = 0; i < arr4.GetLength(0); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < arr4.GetLength(1); j++){
if(arr4[i,j] == arr4[maxRow, maxCol]){
Console.WriteLine("最大值{0}的位置:({1},{2})" , arr4[maxRow, maxCol], i, j);
}
}
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 5
int[,] arr5 = new int[5, 5] { { 0,0,0,0,0},
{ 0,0,0,0,0},
{ 0,0,1,1,0},
{ 0,0,0,0,0},
{ 0,0,0,0,0}};
void transArray(int[,] arr){
//用来记录行和列是否有1的真值数组
bool[] boolRow = new bool[arr.GetLength(0)];
bool[] boolCol = new bool[arr.GetLength(1)];
//标记行和列
for(int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < arr.GetLength(1); j++){
if(arr[i,j] == 1){
boolRow[i] = true;
boolCol[j] = true;
}
}
}
//转置
for(int i = 0; i < arr.GetLength(0); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < arr.GetLength(1); j++){
if(boolRow[i] == true || boolCol[j] == true){
arr[i,j] = 1;
}
}
}
}
transArray(arr5);
Console.WriteLine("转置后的数组:");
for (int i = 0; i < arr5.GetLength(0); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < arr5.GetLength(1); j++){
Console.Write(arr5[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
#endregion交错数组
数组的数组
特点:存储 确定行数,不确定列数的数据
csharp
namespace 交错数组;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 交错数组的申明
//只申明
//变量类型[][] 交错数组名;
int[][] arr1;
//申明+初始化
//变量类型[][] 交错数组名 = new int[行数][];
int[][] arr2 = new int[3][];
//变量类型[][] 交错数组名 = new int[行数][] { 一维数组1, 一维数组2, 一维数组3 };
//注意:{一维数组的数据类型要和交错数组的类型一致}
int[][] arr3 = new int[3][] { new int[] { 1, 2 },
new int[] { 3, 4},
new int[] { 5 } };
//变量类型[][] 交错数组名 = new int[][] { 一维数组1, 一维数组2, 一维数组3 };
int[][] arr4 = new int[][] { new int[] { 1, 2 },
new int[] { 3, 4},
new int[] { 5 } };
//最常用:
//变量类型[][] 交错数组名 = { 一维数组1, 一维数组2, 一维数组3 };
int[][] arr5 = {new int[] {1, 2, 3},
new int[] {4, 5},
new int[] {6, 7, 8, 9}};
#endregion
#region 交错数组的使用
int[][] array1 = { new int[] {1, 2, 3},
new int[] {4, 5} };
//1.数组的长度
//行
//交错数组名.Length
//交错数组名.GetLength(0)
Console.WriteLine(array1.Length);
Console.WriteLine(array1.GetLength(0));
//列
//交错数组名[行].Length
//其实就是找到交错数组中的某个一维数组的长度
Console.WriteLine(array1[0].Length);
Console.WriteLine(array1[1].Length);
//2.获取交错数组的元素
//交错数组名[行][列]
Console.WriteLine(array1[0][0]);
//3.修改交错数组的元素
//交错数组名[行][列] = 值;
array1[0][0] = 10;
Console.WriteLine(array1[0][0]);
//4.遍历交错数组
//和二维数组一样,只不过是遍历每一个一维数组
for (int i = 0; i < array1.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array1[i].Length; j++)
{
Console.Write(array1[i][j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
//5.增加交错数组的元素
//6.删除交错数组的元素
//7.查找交错数组的元素
//***都和二维数组一样***
#endregion
}
}值类型和引用类型
引用类型:string、数组、(class)类
值类型:其他数据类型,结构体
区别:
值类型:在相互赋值的时候把内容拷贝给对方,一个变另一个不会变
引用类型:两者指向同一个值,一个变另一个也变
csharp
namespace 值类型和引用类型;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//值类型
int a = 1;
//引用类型
int[] arr = new int[] {1,2,3,4 };
//赋值给另一个变量
int b = a;
int[] arr2 = arr;
Console.WriteLine("a={0},b={1}\narr[0]={2},arr2[0]={3}",a,b,arr[0],arr2[0]);
//修改新的变量
b = 2;
arr2[0] = 99;
Console.WriteLine("a={0},b={1}\narr[0]={2},arr2[0]={3}",a,b,arr[0],arr2[0]);
}
}WHY?
值类型存储在栈空间------系统分配,自动回收,小而快
引用类型存储在堆空间------手动申请释放,大而慢
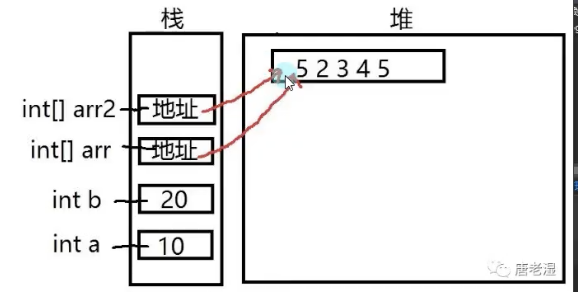
值类型每次申明相当于开了一个栈空间,赋值的时候互不影响。
引用类型申明的时候开的栈空间存放的是一个指针(地址),指向一块堆内存,赋值的时候其实赋的是地址。
习题

- 10
- 20
- "123"
string------特殊的引用类型
每次重新赋值的时候在堆内存重新分配空间,地址也会重新分配
csharp
#region string------特殊的引用类型
string str1 = "123";
string str2 = str1;//这一步两个变量指向的地址相同
str2 = "456";//str2重新赋值,地址改变
Console.WriteLine("str1={0},str2={1}",str1,str2);
#endregion习题
csharp
#region 习题
int[] arr3 = new int[]{1};
int[] arr4 = arr3;
int[] arr5 = arr3;
arr4[0] = 99;//arr4修改单个元素,地址不变
arr5 = new int[5];//arr5重新赋值,地址改变,指向新的堆内存
Console.WriteLine("arr3[0]={0},arr4[0]={1},arr5[0]={2}",arr3[0],arr4[0],arr5[0]);
#endregion总结
只要是整体重新赋值(像new int[])地址就会改变
而单独改一个元素,地址不会改变
函数(方法)
函数基础
作用:
- 封装代码
- 提高代码复用率
- 抽象行为
写在哪儿?
- class(类)语句块中
- struct(结构体)语句块中
语法
csharp
namespace 函数;
class Program
{
#region 函数的语法
// static 返回类型 函数名(参数类型 参数名){
// // 函数体
// return 返回值;
// }
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}- 在学习类和结构体之前,static必须写
- 函数名用帕斯卡命名法,比如:MyName()
- 参数名用驼峰命名法
- 即使函数返回类型是void,也可以选择性使用return
使用
csharp
namespace 函数;
class Program
{
//有参有返回值的函数
static int[] sum_avg(int a, int b)
{
int sum = a + b;
int avg = sum / 2;
// int[] result = { sum, avg };
return new int[] { sum, avg };
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int[] result = sum_avg(a, b);
Console.WriteLine("The sum is: " + result[0]);
Console.WriteLine("The average is: " + result[1]);
}
}关于return
csharp
static void Say(string str){
//void也是可以写return的,return后面的语句不会执行
if(str == "Fuck") return;
Console.WriteLine(str);
}习题

csharp
#region 1
static int Max(int a, int b){
return (a > b)? a : b;
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 2
static float[] Circle(float r){
//1
// float area = 3.14f * r * r;
// float perimeter = 2 * 3.14f * r;
// float[] result = {area, perimeter};
// return result;
//2
return new float[] { 3.14f * r * r, 2 * 3.14f * r };
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 3
static int[] CalculateArr(int[] arr){
if( arr.Length == 0 )
{
Console.WriteLine("数组不能为空");
return new int[0];
}
int sum = 0, max = arr[0], min = arr[0], average = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
sum += arr[i];
max = (max >= arr[i]) ? max : arr[i];
min = (min <= arr[i]) ? min : arr[i];
}
average = sum / arr.Length;
int[] result = { sum, max, min, average };
return result;
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 4
static bool IsPrime(int num){
for(int i = 2; i <= num; i++){
if(num%i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
#endregion
csharp
#region 5
static bool IsLeapYear(int year){
if(year%4 == 0 && year%100!= 0 || year%400 == 0) return true;
//默认返回false
return false;
}
#endregionref和out
为什么要学这个?
csharp
namespace ref和out;
class Program
{
#region 为什么要学习ref和out?
//正常来说,我们在调用函数的时候,传递的是值,函数内部修改这个值,并不会影响到外部的变量。
//只有当传入参数是引用类型且引用类型没有被重新赋值时,才会影响到外部的变量。
static void ChangeValue(int value){
value = 1;
}
static void ChangeArrValue(int[] arr){
arr[0] = 1;
}
static void ChangeArr(int[] arr){
arr = new int[]{1};
}
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int value = 0;
//传入函数的只是这个变量,没有返回,所以值不变
ChangeValue(value);
Console.WriteLine(value); // Output: 0
int[] arr1 = new int[1];
//传入函数的是arr的地址,arr和arr1都指向arr1的地址,所以值会变
ChangeArrValue(arr1);
Console.WriteLine(arr1[0]); // Output: 1
int[] arr2 = new int[1];
//因为函数ChangeArr中arr新开辟了一个地址,与传入的数组的地址不再有关联,所以值不变
ChangeArr(arr2);
Console.WriteLine(arr2[0]); // Output: 0
}
}正常来说,我们在调用函数的时候,传递的是值,函数内部修改这个值,并不会影响到外部的变量。
只有当传入参数是引用类型且引用类型没有被重新赋值时,才会影响到外部的变量。
ref和out用来实现: 当传入参数在函数内修改时,外部也发生变化
使用
函数参数的修饰符,比如 ChangeValueRef( ref int value )
csharp
namespace ref和out;
class Program
{
#region 为什么要学习ref和out?
//正常来说,我们在调用函数的时候,传递的是值,函数内部修改这个值,并不会影响到外部的变量。
//只有当传入参数是引用类型且引用类型没有被重新赋值时,才会影响到外部的变量。
static void ChangeValue(int value){
value = 1;
}
static void ChangeArrValue(int[] arr){
arr[0] = 1;
}
static void ChangeArr(int[] arr){
arr = new int[]{1};
}
#endregion
#region ref和out的使用
//ref
static void ChangeValueRef(ref int value){
value = 1;
}
static void ChangeArrRef(ref int[] arr){
arr = new int[]{1};
}
//out
static void ChangeValueOut(out int value){
value = 2;
}
static void ChangeArrOut(out int[] arr){
arr = new int[]{2};
}
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int value = 0;
//传入函数的只是这个变量,没有返回,所以值不变
ChangeValue(value);
Console.WriteLine("正常传入参数,值不变: "+value); // Output: 0
ChangeValueRef(ref value);
Console.WriteLine("加了ref关键字,值变了: "+value); // Output: 1
ChangeValueOut(out value);
Console.WriteLine("加了out关键字,值变了: "+value); // Output: 2
int[] arr1 = new int[1];
//传入函数的是arr的地址,arr和arr1都指向arr1的地址,所以值会变
ChangeArrValue(arr1);
Console.WriteLine(arr1[0]); // Output: 1
int[] arr2 = new int[1];
//因为函数ChangeArr中arr新开辟了一个地址,与传入的数组的地址不再有关联,所以值不变
ChangeArr(arr2);
Console.WriteLine("正常传入参数,值不变: "+arr2[0]); // Output: 0
ChangeArrRef(ref arr2);
Console.WriteLine("加了ref关键字,值变了: "+arr2[0]); // Output: 1
ChangeArrOut(out arr2);
Console.WriteLine("加了out关键字,值变了: "+arr2[0]); // Output: 2
}
}区别
ref传入的变量必须初始化,所以在函数内部就可以不赋值
out传入的变量可以不初始化,所以在函数内部必须赋值
csharp
namespace ref和out;
class Program
{
#region ref和out的使用
//ref
static void ChangeValueRef(ref int value){
value = 1;
}
static void ChangeArrRef(ref int[] arr){
arr = new int[]{1};
}
static void ChangeValueRef2(ref int value){
// value = 1;
}
//out
static void ChangeValueOut(out int value){
value = 2;
}
static void ChangeArrOut(out int[] arr){
arr = new int[]{2};
}
// 报错,因为out修饰的传入变量必须在函数内部赋值,ref不需要
// static void ChangeValueOut2(out int value){
// // value = 2;
// }
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region ref和out的区别
//ref修饰的传入变量必须初始化,out不需要
//out修饰的传入变量必须在函数内部赋值,ref不需要
int value;
// ChangeValueRef(ref value); 报错
ChangeValueOut(out value);
//其实总的来看,
// ref传入的变量必须初始化,所以在函数内部就可以不赋值
// out传入的变量可以不初始化,所以在函数内部必须赋值
#endregion
}
}习题

csharp
// See https://aka.ms/new-console-template for more information
static bool CheckLogin(string username, string password, out string message)
{
message = "";
if (username == "eano")
{
if(password == "666"){
message = "Login successful";
return true;
}
else{
message = "Invalid password";
return false;
}
}
else
{
message = "Invalid username";
return false;
}
}
string message;
Console.WriteLine("请输入正确的用户名:");
string adminUsername = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("请输入正确的密码:");
string adminPassword = Console.ReadLine();
while(CheckLogin(adminUsername, adminPassword, out message)== false){
// 输出上一次的错误信息
Console.WriteLine(message);
Console.WriteLine("请输入正确的用户名:");
adminUsername = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("请输入正确的密码:");
adminPassword = Console.ReadLine();
}
Console.WriteLine(message);变长参数和参数默认值
变长参数不能和ref/out 一起用
变长参数
csharp
#region 变长参数
//修饰参数关键字 params
//params后面必须是数组,所以只能是同一类型的可变参数
//参数最多只能出现一个params关键字,且一定是最后一组参数
static int Sum(params int[] numbers){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++){
sum += numbers[i];
}
return sum;
}
#endregion
Console.WriteLine(Sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); // 15参数默认值
ref和out不能有参数默认值
csharp
#region 参数默认值(可选参数)
//每个参数都可以有一个默认值
//混用的时候,可选参数要写在必选参数后面
static void Say(string str = "Hello"){
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
static void Say2(string str, string name = "World"){
Console.WriteLine(str + " " + name);
}
#endregion
//不传入参数时,默认使用参数默认值
Say(); // Hello
//传入参数时,使用传入的参数值
Say("World"); // World
Say2("Hello"); // Hello World习题

csharp
#region 1
static int[] Calculate(params int[] numbers){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++){
sum += numbers[i];
}
int average = sum / numbers.Length;
return new int[] {sum, average};
}
#endregion
#region 2
static int[] Sum_Odd_Even(params int[] numbers){
int sum_odd = 0;
int sum_even = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++){
if(numbers[i] % 2 == 0){
sum_even += numbers[i];
}
else{
sum_odd += numbers[i];
}
}
return new int[] {sum_odd, sum_even};
}
#endregion
int[] result = Calculate(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Console.WriteLine("Sum: " + result[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Average: " + result[1]);
int[] result2 = Sum_Odd_Even(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
Console.WriteLine("Sum of odd numbers: " + result2[0]);
Console.WriteLine("Sum of even numbers: " + result2[1]);函数重载
函数名相同、参数的数量不同 (或 参数的数量相同,但参数的类型、顺序不同)的一组函数
作用:
- 用来命名一组功能相似的函数(不同参数的同一逻辑处理),减少函数名的数量,避免命名空间的污染
- 提高程序可读性
csharp
namespace 函数重载;
class Program
{
static int Sum(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
//参数的数量不同
static int Sum(int a, int b, int c)
{
return a + b + c;
}
//参数的类型不同
static double Sum(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
}
//参数的顺序不同(其实也是类型不同)
static float Sum(float a, int b){
return a + b;
}
//参数用ref out 修饰
//out传入的参数必须要在函数内部赋值
static int Sum(ref int a,out int b)
{
b = 1;
return a + b;
}
//参数是可变参数
static int Sum(params int[] nums)
{
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++)
{
sum += nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Sum(1, 2);
Sum(1, 2, 3);
Sum(1.0, 2.0);
Sum(1.0f, 2);
int a = 1;
int b;
Sum(ref a, out b);
}
}习题

csharp
namespace 函数重载习题;
public class Program{
#region 1
static int Max(int a, int b){
return a > b? a : b;
}
static double Max(double a, double b){
return a > b? a : b;
}
#endregion
#region 2
static int Max(params int[] numbers){
int max = numbers[0];
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++){
max = (numbers[i] > max)? numbers[i] : max;
}
return max;
}
static double Max(params double[] numbers){
double max = numbers[0];
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.Length; i++){
max = (numbers[i] > max)? numbers[i] : max;
}
return max;
}
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine(Max(1, 2));
Console.WriteLine(Max(1.0, 2.0));
Console.WriteLine(Max(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
Console.WriteLine(Max(1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0));
}
}递归
必须有结束掉用的条件
csharp
static void Fun(int n0 = 1,int n1 = 10){
if(n1 < n0)return;
Console.WriteLine(n1);
n1--;
Fun(n0,n1);
}
Fun(1,10);习题

csharp
#region 1
static void PrintNum(int n0, int n1){
if(n1 < n0){
return;
}
Console.WriteLine(n1);
// n1--;
//这里要用前缀--n1,先减后用,不然会出现无限递归导致栈溢出
PrintNum(n0, --n1);
}
#endregion
#region 2
static int Factorial(int n){
if(n == 1) return n;
return n * Factorial(n-1);
// 5 * Fun2(4) = 5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1
// 4 * Fun2(3) = 4 * 3 * 2 * 1
// 3 * Fun2(2) = 3 * 2 * 1
// 2 * Fun2(1) = 2 * 1
// 1
}
#endregion
#region 3
static int SumOfFactorial(int n){
if(n == 1) return Factorial(n);
return Factorial(n) + SumOfFactorial(n-1);
}
#endregion
#region 4
static float getFinalLength(float length,int days){
//从第0天开始,所以days要+1
if(days+1 == 0) return length;
//这里要用前缀--days,先减后用,不然会出现无限递归导致栈溢出
return getFinalLength(length/2.0f,--days);
}
#endregion
#region 5
static bool PrintNum2(int n0, int n1){
// if(n1 < n0){
// return;
// }
Console.WriteLine(n1);
// n1--;
//这里要用前缀--n1,先减后用,不然会出现无限递归导致栈溢出
return n1 < n0 || PrintNum2(n0, --n1);
}
#endregion
PrintNum(0, 10);
Console.WriteLine("阶乘5= "+Factorial(5));
Console.WriteLine("!1 + ... + !10 = "+SumOfFactorial(10));
Console.WriteLine("100 的最终长度为: "+getFinalLength(100, 10));
PrintNum(0, 200);结构体
结构体相当于一个人,他的变量相当于人的各个属性,方法相当于人的各个功能函数
语法
- 写在namespace语句块中
- 关键字struct
- 帕斯卡命名法
csharp
struct 结构体名{
//1. 变量
int 变量名;
//2. 构造函数
结构体名(int 变量名){
this.变量名 = 变量名;
}
//3. 方法
void 方法名(){
//...
}
}访问修饰符
修饰结构体中的变量和方法 是否能被外部使用
public 可以被外部访问
private 只能在内部使用
默认不写,就是private
结构体的构造函数
- 没有返回值
- 函数名和结构体名相同
- 必须有参数
- 如果申明了构造函数,那就必须在其中对所有变量数据初始化
使用
csharp
namespace 结构体;
class Program
{
#region 语法
// struct 结构体名{
// //1. 变量
// int 变量名;
// //2. 构造函数
// 结构体名(int 变量名){
// this.变量名 = 变量名;
// }
// //3. 方法
// void 方法名(){
// //...
// }
// }
#endregion
#region 示例
struct Student{
//1. 变量
//结构体申明的变量 不能直接在结构体里面初始化
//变量类型任意,包括结构体类型,但是只能是其他结构体类型,不能是自身结构体类型
public int age;
public bool sex; //true表示男性,false表示女性
public string name;
public Teacher teacher1;
// Student student1; //错误,不能是自身结构体类型
//2. 构造函数
//用于在外部初始化结构体变量
public Student(int age, bool sex, string name, Teacher teacher1){
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
this.name = name;
this.teacher1 = teacher1;
}
//3. 方法
//用来表现这个数据结构的行为,在结构体中不需要加static关键字
//函数中可以直接使用结构体申明的变量
public void Speak(){
Console.WriteLine("Hi, my name is {0}, I am {1} years old.", name, age);
}
}
struct Teacher{
}
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#region 结构体的使用
Student s1;
s1.age = 20;
s1.sex = true;
s1.name = "Tom";
s1.Speak();
//用构造函数的方式初始化结构体变量
Student s2 = new Student(25, false, "Jerry", new Teacher());
s2.Speak();
#endregion
}
}习题

csharp
namespace 结构体习题
{
class Program
{
#region 1
struct Student{
public string name;
public int age;
public bool isMale;
public int classNum;
public string subject;
public Student(string name, int age, bool isMale, int classNum, string subject){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.isMale = isMale;
this.classNum = classNum;
this.subject = subject;
}
public void PrintInfo(){
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}, Age:{1}, Gender:{2}, Class:{3}, Subject:{4}", name, age, isMale? "Male" : "Female", classNum, subject);
}
}
#endregion
#region 3
struct Rectangle{
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(int height, int width){
this.height = height;
this.width = width;
}
public void PrintInfo(){
Console.WriteLine("Rectangle length: {0}, width: {1}, area: {2}, perimeter: {3}", height, width, height * width, 2 * (height + width));
}
}
#endregion
#region 4
enum Occupation{
/// <summary>
/// 战士
/// </summary>
warrior,
/// <summary>
/// 法师
/// </summary>
mage,
/// <summary>
/// 猎人
/// </summary>
hunter,
}
struct Player{
public string playerName;
public Occupation playerOccupation;
public Player(string playerName, Occupation playerOccupation){
this.playerName = playerName;
this.playerOccupation = playerOccupation;
}
public void PrintAtkInfo(){
string occupation = "";
string skill = "";
switch(playerOccupation){
case Occupation.warrior:
occupation = "战士";
skill = "冲锋";
break;
case Occupation.mage:
occupation = "法师";
skill = "奥术攻击";
break;
case Occupation.hunter:
occupation = "猎人";
skill = "假死";
break;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0}{1}释放了{2}", occupation, playerName,skill);
}
}
#endregion
#region 5
struct Monster{
public string name;
public int attack;
public Monster(string name, int attack){
this.name = name;
this.attack = attack;
}
public void PrintInfo(){
Console.WriteLine("{0}的攻击力为{1}", name, attack);
}
}
#endregion
#region 7
struct OutMan{
public string name;
public int attack;
public int hp;
public int defence;
public OutMan(string name, int attack, int hp, int defence){
this.name = name;
this.attack = attack;
this.hp = hp;
this.defence = defence;
}
public void PrintInfo(){
Console.WriteLine("{0}的攻击力为{1}", name, attack);
}
public void Attack(ref Boss boss) {
if (boss.attack > defence) {
boss.hp -= (attack - boss.defence);
Console.WriteLine("{0}攻击了{1}, 造成{2}点伤害, {3}剩余{4}点血量", name, boss.name, attack - boss.defence, boss.name, boss.hp);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("{0}闪避了{1}的攻击", name, boss.name);
}
}
}
struct Boss{
public string name;
public int attack;
public int hp;
public int defence;
public Boss(string name, int attack, int hp, int defence){
this.name = name;
this.attack = attack;
this.hp = hp;
this.defence = defence;
}
public void PrintInfo(){
Console.WriteLine("{0}的攻击力为{1}", name, attack);
}
public void Attack(ref OutMan outman) {
if (outman.attack > defence) {
outman.hp -= (attack - outman.defence);
Console.WriteLine("{0}攻击了{1}, 造成{2}点伤害, {3}剩余{4}点血量", name, outman.name, attack - outman.defence, outman.name, outman.hp);
}
else {
Console.WriteLine("{0}闪避了{1}的攻击", name, outman.name);
}
}
}
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{ //1
Student s1 = new Student("John", 18, true, 101, "Math");
s1.PrintInfo();
//2
// private只能在类内部访问
// public可以在类外部访问
//3
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle(5, 10);
r1.PrintInfo();
//4
Player p1 = new Player("唐老师", Occupation.hunter);
p1.PrintAtkInfo();
//6
Monster[] monstersName = new Monster[10];
Random r = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
//用结构体构造函数初始化每个怪物的名字:
// monstersName[i].name 、 monstersName[i].attack
monstersName[i] = new Monster("怪物" + i, r.Next(100));
monstersName[i].PrintInfo();
}
//7
OutMan outMan = new OutMan("路飞", 50, 100, 55);
Boss boss = new Boss("索隆", 60, 200, 30);
while(outMan.hp > 0 && boss.hp > 0){
outMan.Attack(ref boss);
boss.Attack(ref outMan);
}
}
}
}排序
冒泡排序
csharp
//冒泡排序
static int[] BubbleSort(int[] arr){
// 数组几个数就需要进行n轮冒泡
for(int n=0;n<arr.Length;n++){
//每轮冒泡
// 数组长度减去第n轮,因为每轮冒泡都会将最大的数冒泡到最后面,所以不需要再比较后面的数
for(int i=0;i<arr.Length-1 - n;i++){
if(arr[i]>arr[i+1]){
arr[i] = arr[i] + arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = arr[i] - arr[i+1];
arr[i] = arr[i] - arr[i+1];
}
}
}
return arr;
}
int[] arr = { 3, 5, 8, 6, 2, 7, 1, 4};
BubbleSort(arr);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arr));
csharp
//优化后的冒泡排序
static int[] BubbleSort2(int[] arr){
// 数组几个数就需要进行n轮冒泡
for(int n=0;n<arr.Length;n++){
//每轮冒泡开始前,标志位isSwap置为false
bool isSwap = false;
//每轮冒泡
// 数组长度减去第n轮,因为每轮冒泡都会将最大的数冒泡到最后面,所以不需要再比较后面的数
for(int i=0;i<arr.Length-1 - n;i++){
if(arr[i]>arr[i+1]){
int tmp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = tmp;
//每次交换后,isSwap置为true
isSwap = true;
}
}
//如果本轮没有发生交换,说明已经排序好了,即刻退出循环
if(!isSwap)break;
}
return arr;
}
int[] arr2 = { 3, 5, 8, 6, 2, 7, 1, 4};
BubbleSort2(arr2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(",", arr2));习题

csharp
#region 1
static void BubbleSortUp(int[] arr){
for(int n = 0; n < arr.Length; n++){
bool isSwap = false;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1 - n; i++){
//大于后面的就换位置,也就是大的放后面
if(arr[i] > arr[i+1]){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = temp;
isSwap = true;
}
}
if(!isSwap) break;
}
}
static void BubbleSortDown(int[] arr){
for(int n = 0; n < arr.Length; n++){
bool isSwap = false;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1 - n; i++){
//小于后面的就换位置,也就是小的放后面
if(arr[i] < arr[i+1]){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = temp;
isSwap = true;
}
}
if(!isSwap) break;
}
}
int[] arr1 = new int[20];
Random r1 = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++){
arr1[i] = r1.Next(0, 101);
}
Console.WriteLine("Before Sort:"+string.Join(",", arr1));
BubbleSortUp(arr1);
Console.WriteLine("After Sort Up:"+string.Join(",", arr1));
BubbleSortDown(arr1);
Console.WriteLine("After Sort Down:"+string.Join(",", arr1));
#endregion
csharp
#region 2
static void BubbleSort_UpOrDown(int[] arr,bool isUp){
for(int n = 0; n < arr.Length; n++){
bool isSwap = false;
for(int i = 0; i < arr.Length - 1 - n; i++){
if(isUp){
//大于后面的就换位置,也就是大的放后面
if(arr[i] > arr[i+1]){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = temp;
isSwap = true;
}
}
else{
//小于后面的就换位置,也就是小的放后面
if(arr[i] < arr[i+1]){
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[i+1];
arr[i+1] = temp;
isSwap = true;
}
}
}
if(!isSwap) break;
}
}
int[] arr2 = new int[20];
Random r2 = new Random();
for(int i = 0; i < arr2.Length; i++){
arr2[i] = r2.Next(0, 101);
}
BubbleSort_UpOrDown(arr2,true);
Console.WriteLine("After Sort Up:"+string.Join(",", arr2));
BubbleSort_UpOrDown(arr2,false);
Console.WriteLine("After Sort Down:"+string.Join(",", arr2));
#endregion选择排序
步骤:
- 新建中间商
- 每轮依次比较,更新中间商
- 找出极值
- 中间商与目标位置互换位置
- n轮比较
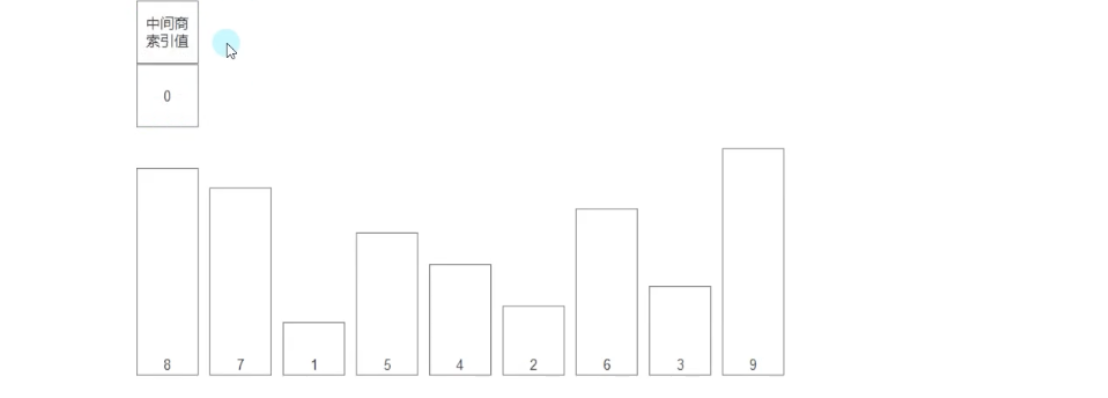
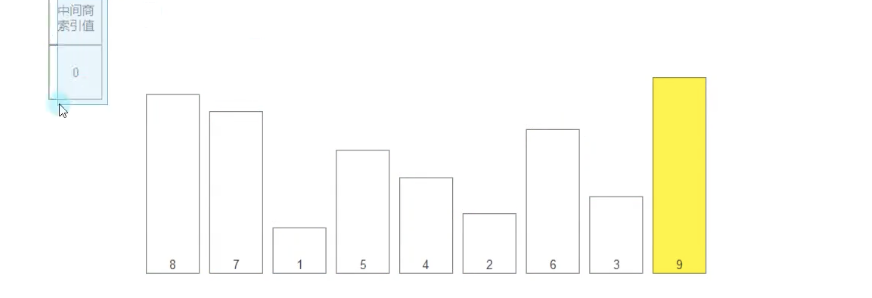
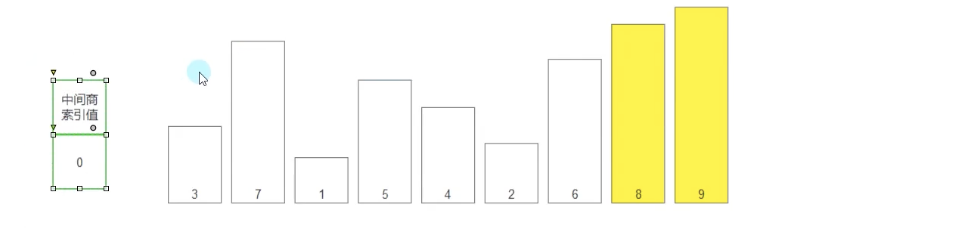
详细步骤:
- 新建一个中间商,索引为0
- 中间商与数组的值比较,从索引0开始向后依次比较,每次比较后更新中间商的索引为较大值(或较小值)的索引,找到极值(MAX/min),把极值与目标位置(arr.Length-n-1)互换位置(如果是升序排列,就把MAX放在末尾)
- 这样比较n轮,每轮比较完重置中间商的索引为0,再继续比较,后续每轮的比较只需i从1遍历到数组长度-n即可(第0个不需要和自己比较,末尾的已经排序完不需要再比较)
csharp
// 选择排序
//升序, 中间商:maxIndex,目标位置:arr[arr.Length - 1 - n]
static void SelectionSort(int[] arr){
//n轮
for(int n = 0; n < arr.Length - 1; n++){
int maxIndex = 0;
//用中间商找出每轮的最优元素maxIndex
//只需要从1到arr.Length - n - 1遍历
// 不需要和第0个比较(因为中间商就是索引0),不需要和末尾的元素比较,因为arr[arr.Length - 1 - n]后面的元素在前面n轮已经排好序了
for(int i = 1; i < arr.Length - n; i++){
//更新中间商的索引为较大值的索引
if(arr[i] > arr[maxIndex]){
maxIndex = i;
}
}
//交换极值和目标位置(末尾)的元素
//交换条件:中间商不是目标位置
if(maxIndex!= arr.Length - 1 - n){
int tmp = arr[arr.Length - 1 - n];
arr[arr.Length - 1 - n] = arr[maxIndex];
arr[maxIndex] = tmp;
}
}
}
int[] arr = {5, 3, 8, 6, 2, 7, 1, 4};
SelectionSort(arr);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", arr));习题

csharp
static void SelectionSort(int[] arr,bool isUp){
for(int n = 0; n < arr.Length - 1; n++){
int bestIndex = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < arr.Length - n; i++){
if(isUp){
if(arr[i] > arr[bestIndex]){
bestIndex = i;
}
}else{
if(arr[i] < arr[bestIndex]){
bestIndex = i;
}
}
}
if(bestIndex!=arr.Length-n-1){
int temp = arr[arr.Length-n-1];
arr[arr.Length-n-1] = arr[bestIndex];
arr[bestIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
int[] arr = new int[20];
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
arr[i] = r.Next(0, 101);
}
Console.WriteLine("Before Sort:"+string.Join(",",arr));
SelectionSort(arr,true);
Console.WriteLine("After Sort Up:"+string.Join(",",arr));
SelectionSort(arr,false);
Console.WriteLine("After Sort Down:"+string.Join(",",arr));