FPGA生成随机数的方法,目前有以下几种:
1、震荡采样法
实现方式一:通过低频时钟作为D触发器的时钟输入端,高频时钟作为D触发器的数据输入端,使用高频采样低频,利用亚稳态输出随机数。
实现方式二:使用三个或以上反相器首尾互联,形成环路振荡器。使用时钟采集,得到不稳定的数据,以形成随机数(其实此种方式与方式一相类似,反相器的组合逻辑相当于高频时钟,时钟信号相当于低频时钟,同样利用亚稳态生成随机数)。
(直接按照实现方式二,上具体实现代码)
//反相器环形级联,组合为振荡器,利用亚稳态状态,得到随机数
module random_gen
(
input clk,
input start, //开始命令
output reg random_valid = 0,
output reg [7:0] random_data = 0
);
reg state = 1'b0; //0空闲态 1随机态
(*dont_touch = "true" *)reg a = 1'b0;
(*dont_touch = "true" *)reg b = 1'b0;
(*dont_touch = "true" *)reg c = 1'b0;
reg [2:0] bit_cnt = 0;
//3个取反器,环形震荡
//取反器
always@(state)
begin
b <= !a;
end
//取反器
always@(state)
begin
c <= !b;
end
//取反器
always@(state)
begin
a <= !c;
end
always@(posedge clk)
begin
if(state == 1'b0) begin //state == 0
bit_cnt <= 3'd0;
random_valid <= 1'b0;
if(start) begin
state <= 1'b1;
end
else begin
state <= 1'b0;
end
end
else begin //state == 1
bit_cnt <= bit_cnt + 1'b1;
if(bit_cnt == 3'b111) begin
state <= 1'b1;
random_valid <= 1'b1;
end
else begin
random_valid <= 1'b0;
end
random_data <= {random_data[6:0],c};
end
end
endmodule2、LFSR伪随机数
LFSR(Linear-feedback shift register)是一种特殊的的移位寄存器,他的输入取决于其先前状态,其生成的随机数是一种伪随机数。其架构如下图所示:
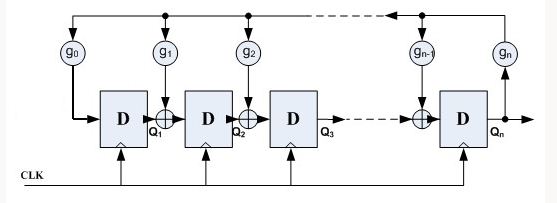
上图中,gn为反馈系数,取值只能是1或者0,N个D触发器,可以提供2^(N-1)个输出状态,为了保证随机性,gn的选择必须满足一定的条件,不能全部为0,且gn必须等于1。
假设输出的随机数的位宽为8bits,且取值g0g1g2g3g4g5g6g7g8=101110001,则可以实现如下代码:
module LFSR #
( parameter [7:0] SEED = 8'h11)
(
input rstn,
input clk,
output reg [7:0] rand_data //随机数
);
always@(posedge clk or negedge rstn)
begin
if(!rstn)
rand_data <=SEED;
else begin
rand_data[0] <= rand_data[7];
rand_data[1] <= rand_data[0];
rand_data[2] <= rand_data[1];
rand_data[3] <= rand_data[2];
rand_data[4] <= rand_data[3]^rand_data[7];
rand_data[5] <= rand_data[4]^rand_data[7];
rand_data[6] <= rand_data[5]^rand_data[7];
rand_data[7] <= rand_data[6];
end
end
endmodule3、使用FLASH或EEPROM生成随机数
读取FLASH中预存的seed,然后进行相关逻辑运算,得到伪随机数。同时按照既定的逻辑生成新的seed,写入到FLASH或者EEPROM中,这样就可以保证每次输出的随机数不同。(此种方式较为复杂,不推荐)
此处不进行具体实现。