一:背景
1. 讲故事
前面文章所介绍的一些注入技术都是以方法为原子单位,但在一些罕见的场合中,这种方法粒度又太大了,能不能以语句为单位,那这个就是我们这篇介绍的 Transpiler,它可以修改方法的 IL 代码,甚至重构,所以这就非常考验你的 IL 功底,个人建议在写的时候要多借助如下三个工具:
- ILSpy:观察原生代码
- 日志: 多看harmony日志,即方法上加盖 HarmonyDebug 特性。
- DeepSeek:大模型是一个非常好的助手,合理利用定会效率加倍。
否则遇到稍微复杂一点的,真的难搞。。。
二:有趣的IL编织案例
1. 如何将Sub中的加法改成减法
为了方便演示,我们先上一段代码,实现一个简单的 a+b 操作,代码如下:
C#
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var num = MyMath.Sub(40, 30);
Console.WriteLine($"Result: {num}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public class MyMath
{
public static int Sub(object a, object b)
{
var num1 = Convert.ToInt32(a);
var num2 = Convert.ToInt32(b);
var num = num1 + num2;
return num;
}
}上面卦中的 Sub 方法的 IL 代码如下:
C#
.method public hidebysig static
int32 Sub (
object a,
object b
) cil managed
{
.custom instance void [System.Runtime]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.NullableContextAttribute::.ctor(uint8) = (
01 00 01 00 00
)
// Method begins at RVA 0x20b0
// Header size: 12
// Code size: 25 (0x19)
.maxstack 2
.locals init (
[0] int32 num1,
[1] int32 num2,
[2] int32 sum,
[3] int32
)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldarg.0
IL_0002: call int32 [System.Runtime]System.Convert::ToInt32(object)
IL_0007: stloc.0
IL_0008: ldarg.1
IL_0009: call int32 [System.Runtime]System.Convert::ToInt32(object)
IL_000e: stloc.1
IL_000f: ldloc.0
IL_0010: ldloc.1
IL_0011: add
IL_0012: stloc.2
IL_0013: ldloc.2
IL_0014: stloc.3
IL_0015: br.s IL_0017
IL_0017: ldloc.3
IL_0018: ret
} // end of method MyMath::Sub因为Sub怎么可能是a+b,所以现在我的需求就是将 num1 + num2 改成 num1 - num2,从 il 的角度就是将 IL_0011: add 改成 IL_0011: sub 即可,如何做到呢?用 harmony 的 CodeMatcher 类去替换IL代码即可,完整的代码如下:
C#
namespace Example_20_1_1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 应用Harmony补丁
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.patch");
harmony.PatchAll();
var num = MyMath.Sub(40, 30);
Console.WriteLine($"Result: {num}"); // 原应输出70,补丁后输出10
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public class MyMath
{
public static int Sub(object a, object b)
{
var num1 = Convert.ToInt32(a);
var num2 = Convert.ToInt32(b);
var num = num1 + num2; // 此行将被Transpiler修改为减法
return num;
}
}
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(MyMath), "Sub")]
[HarmonyDebug]
public static class MyMathPatch
{
static IEnumerable<CodeInstruction> Transpiler(IEnumerable<CodeInstruction> instructions)
{
var codeMatcher = new CodeMatcher(instructions);
codeMatcher.MatchStartForward(new CodeMatch(OpCodes.Add)) // 匹配加法操作 (add 指令)
.ThrowIfInvalid("Could not find add instruction")
.SetOpcodeAndAdvance(OpCodes.Sub); // 将 add 指令替换为 sub 指令
return codeMatcher.Instructions();
}
}
}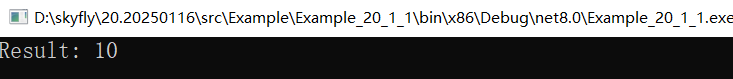
从卦中的输出看,我们修改成功了,这里稍微说一下 CodeMatcher 的方法。
- MatchStartForward:这个就是游标,定位到
OpCodes.Add行。 - ThrowIfInvalid: 如果没有定位到就抛出异常。
- SetOpcodeAndAdvance:替换 IL中的add为sub,并向下移动一行,可以理解成 i++。
由于在 MyMathPatch 上加了一个 [HarmonyDebug] 特性,打开 harmony.log.txt 的输出结果,成功看到了替换后的sub,参考如下:
C#
### Patch: static System.Int32 Example_20_1_1.MyMath::Sub(System.Object a, System.Object b)
### Replacement: static System.Int32 Example_20_1_1.MyMath::Example_20_1_1.MyMath.Sub_Patch0(System.Object a, System.Object b)
IL_0000: Local var 0: System.Int32
IL_0000: Local var 1: System.Int32
IL_0000: Local var 2: System.Int32
IL_0000: Local var 3: System.Int32
IL_0000: // start original
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldarg.0
IL_0002: call static System.Int32 System.Convert::ToInt32(System.Object value)
IL_0007: stloc.0
IL_0008: ldarg.1
IL_0009: call static System.Int32 System.Convert::ToInt32(System.Object value)
IL_000E: stloc.1
IL_000F: ldloc.0
IL_0010: ldloc.1
IL_0011: sub
IL_0012: stloc.2
IL_0013: ldloc.2
IL_0014: stloc.3
IL_0015: br => Label0
IL_001A: Label0
IL_001A: ldloc.3
IL_001B: // end original
IL_001B: ret
DONE2. 如何给Sub加业务逻辑
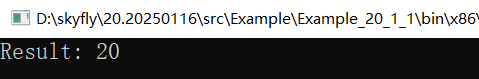
上面的例子本质上是IL代码的原地替换,接下来我们看下如何对IL代码进行删增操作,我的业务需求是这样的,想将 num1 + num2 改成 num1 - num2 - num3,我想要最终的 C# 代码变为这样:
C#
public class MyMath
{
public static int Sub(object a, object b)
{
var num1 = Convert.ToInt32(a);
var num2 = Convert.ToInt32(b);
var num3 = Convert.ToInt32("20"); // 新增的代码
var num = num1 - num2 - num3;
return num;
}
}接下来用Transpiler进行编织,代码如下:
C#
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(MyMath), "Sub")]
[HarmonyDebug]
public static class MyMathPatch
{
public static IEnumerable<CodeInstruction> Transpiler(IEnumerable<CodeInstruction> instructions, ILGenerator generator)
{
var codeMatcher = new CodeMatcher(instructions, generator)
.MatchStartForward( // 匹配模式:ldloc.0, ldloc.1, add
new CodeMatch(OpCodes.Ldloc_0),
new CodeMatch(OpCodes.Ldloc_1),
new CodeMatch(OpCodes.Add)
)
.ThrowIfInvalid("Could not find add operation pattern")
// 移除原来的三条指令
.RemoveInstructions(3)
// 插入新的指令序列
.InsertAndAdvance(
new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ldloc_0),
new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ldloc_1),
new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Sub),
new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ldstr, "20"),
new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Call, typeof(Convert).GetMethod(
nameof(Convert.ToInt32),
new[] { typeof(string) })),
new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Sub)
);
return codeMatcher.InstructionEnumeration();
}
}代码的逻辑非常简单,先在IL代码中定位到 num1 + num2,然后删除再写入 num1 - num2 - num3。
3. 如何添加try catch
最后我们来一个比较实用的修改,即在 Sub 中增加try catch,理想的代码如下:
C#
public class MyMath
{
public static int Sub(object a, object b)
{
try
{
var num1 = Convert.ToInt32(a);
var num2 = Convert.ToInt32(b);
var num = num1 - num2;
return num;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
return 0;
}
}
}接下来就要开始编织了,这是从0开始的代码段,完整代码如下:
C#
namespace Example_20_1_1
{
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// 应用Harmony补丁
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.patch");
harmony.PatchAll();
// 测试原始方法
var num = MyMath.Sub("a", 30);
Console.WriteLine($"异常: {num}");
var num2 = MyMath.Sub(50, 30);
Console.WriteLine($"正常: {num2}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
public class MyMath
{
public static int Sub(object a, object b)
{
try
{
var num1 = Convert.ToInt32(a);
var num2 = Convert.ToInt32(b);
var num = num1 - num2;
return num;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
return 0;
}
}
}
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(MyMath), "Sub")]
[HarmonyDebug]
public static class MyMathPatch
{
static IEnumerable<CodeInstruction> Transpiler(IEnumerable<CodeInstruction> originalInstructions, ILGenerator generator)
{
// 定义标签
Label tryStart = generator.DefineLabel();
Label tryEnd = generator.DefineLabel();
Label catchStart = generator.DefineLabel();
Label endLabel = generator.DefineLabel();
// 声明局部变量
var exVar = generator.DeclareLocal(typeof(Exception)); // 用于存储异常的变量
var resultVar = generator.DeclareLocal(typeof(int)); // 用于存储返回值的变量
var newInstructions = new List<CodeInstruction>();
// 1. try 块开始
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Nop).WithLabels(tryStart));
// 2. 添加原始方法体(保持不变)
newInstructions.AddRange(originalInstructions);
// 3. 存储结果并离开 try 块
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Stloc, resultVar));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Leave, endLabel).WithLabels(tryEnd));
// 4. catch 块
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Stloc, exVar).WithLabels(catchStart));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Nop));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ldloc, exVar));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Callvirt,
typeof(Exception).GetProperty("Message").GetGetMethod()));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Call,
typeof(Console).GetMethod("WriteLine", new[] { typeof(string) })));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ldc_I4_0)); // 返回0
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Stloc, resultVar));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Leave, endLabel));
// 5. 方法结束(加载结果并返回)
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ldloc, resultVar).WithLabels(endLabel));
newInstructions.Add(new CodeInstruction(OpCodes.Ret));
// 添加异常处理
generator.BeginExceptionBlock();
generator.BeginCatchBlock(typeof(Exception));
generator.EndExceptionBlock();
return newInstructions;
}
}
}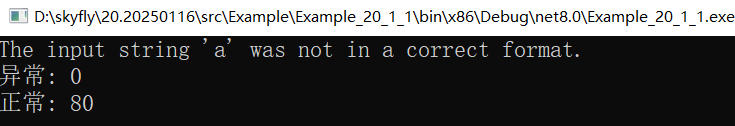
哈哈,上面的代码正如我们所料。。。如果不借助 ILSpy 和 DeepSeek,不敢想象得要浪费多少时间。。。门槛太高了。。。
三:总结
这个系列总计8篇,已经全部写完啦!希望对同行们在解决.NET程序疑难杂症相关问题时提供一些资料和灵感,同时也是对.NET调试训练营 的学员们功力提升添砖加瓦!
