目录
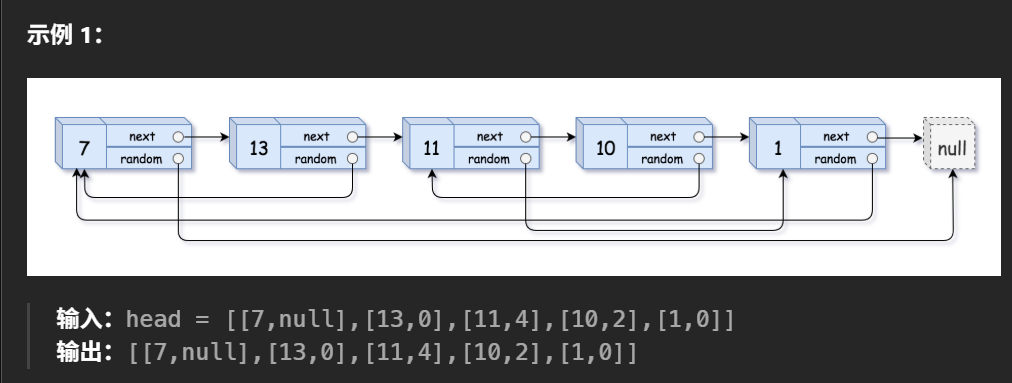
问题描述
问题解读分析
这里我们要注意深拷贝和随机指针 ,首先就是深拷贝对应的浅拷贝是和原链表用一个结点,而深拷贝则对应的不和原链表一个结点,也就是说需要我们自己开辟空间去创建一个结点和原链表一模一样。而这里随机指针,是链表中一个指针,他随机但是又固定,固定是因为我们不需要随机给他寻找结点,而是实例给,但是随机又不能琢磨他只能在相对结点的右边,而还有相对于这个结点的左边。所以这里最为复杂的是该如何处理random指针,这里很难寻找到相对结点靠左的结点和random对应,我们这里选择在原链表基础上进行拷贝,通过原链表上的random指针的next(这个表示在原链表上的下一个指针,这个指针就是复制的链表)与我们拷贝对应 。很抽象上图: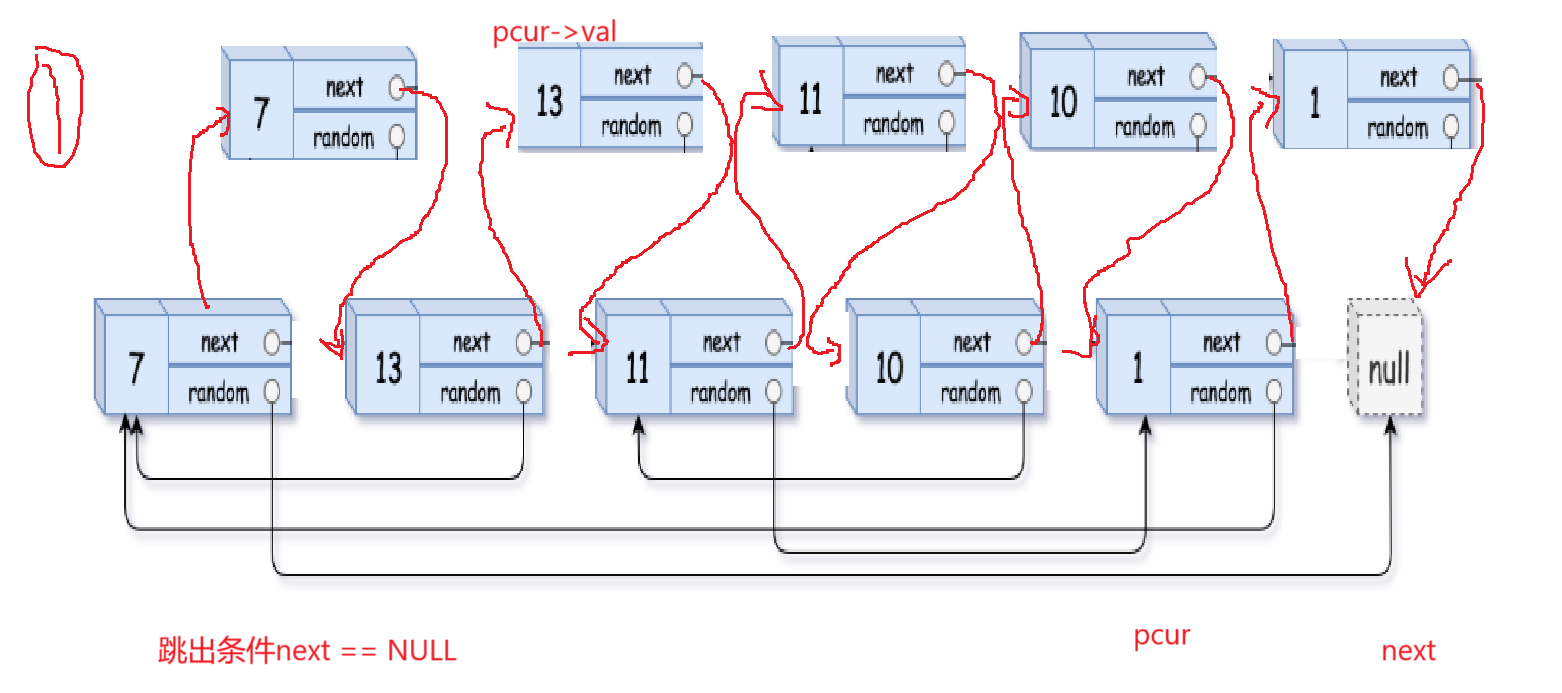
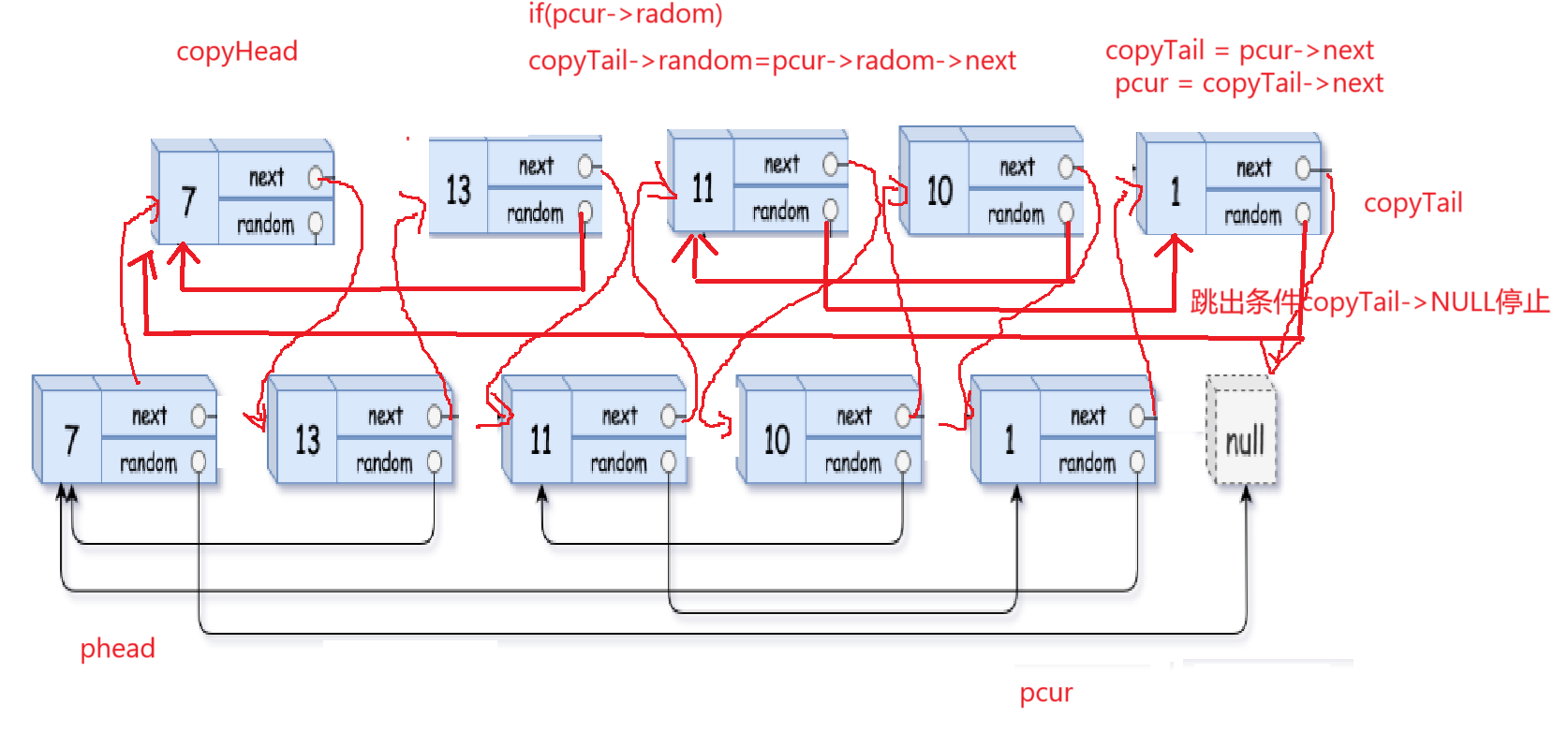 最后一步就是将原链表和复制好的链表断开
最后一步就是将原链表和复制好的链表断开
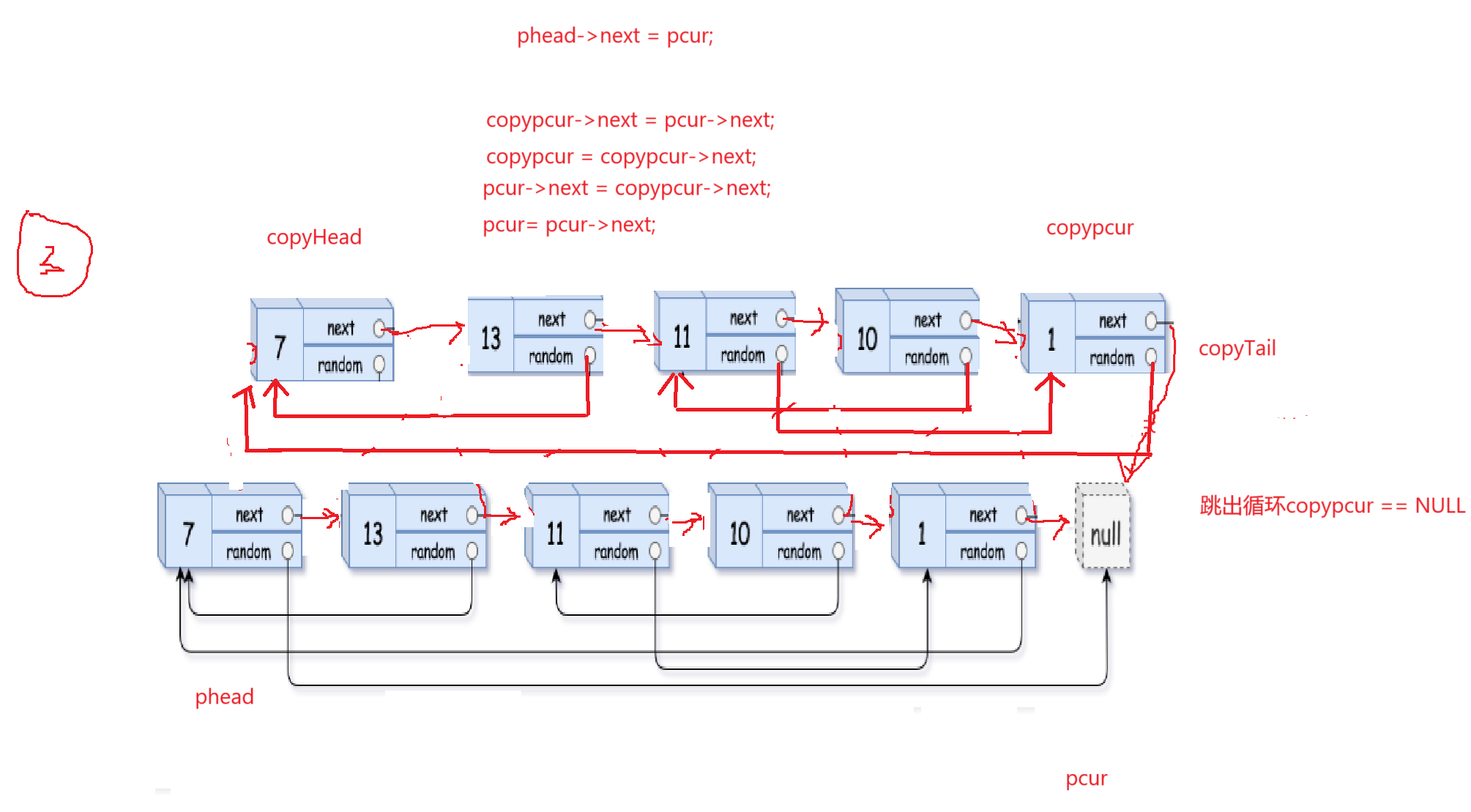
解决代码
cpp
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* buyNode(int x)
{
struct Node* newnode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if(newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
newnode->val = x;
newnode->random= newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void AddNode(struct Node* phead)
{
struct Node* pcur = phead;
while(pcur)
{
struct Node* next = pcur->next;
struct Node* newnode =buyNode(pcur->val);
pcur->next = newnode;
newnode->next = next;
pcur = next;
}
}
void setRandom(struct Node* phead)
{
struct Node* pcur = phead;
//根据newnode->random = pcur->random->next
while(pcur)
{
struct Node* copy = pcur->next;
if(pcur->random)//防止为空时解引用
{
copy->random = pcur->random->next;
}
pcur = copy->next;
}
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
if(head == NULL)//防止没意义空指针的发生
{
return head;
}
//复制原链表
AddNode(head);
//复制random
setRandom(head);
//将原链表上的复制链表拆除
struct Node* pcur = head;
struct Node* copyHead=pcur->next;
struct Node* copyTail = pcur->next;
head->next = copyTail->next;//原链表链接
while(pcur->next)
{
//copyTail --- pcur->next
pcur = copyTail->next;
copyTail->next = pcur->next;
copyTail = copyTail->next;
//pcur ----- pcur->next
pcur->next = copyTail->next;
}
return copyHead;
}