简述
最近接了对Ticket 进行问题分类的任务,使用了prompt和机器学习两种方式来解决,这里重点介绍Longformer-base-4096 模型训练的方案
使用 Longformer-base-4096 模型实现文本分类系统,利用 Longformer 处理长序列的能力进行准确分类。该解决方案旨在实现稳健、可扩展且高效的目标,将先进的自然语言处理 (NLP) 技术与实际工程设计相结合。
Longformer-base-4096 适合文本分类任务
- 支持更长的输入(4096 tokens)
-
相比 BERT(512 tokens)、RoBERTa(512 tokens)等模型,Longformer 支持多达 4096 个 token 的输入。
-
✅ 适合处理工单系统、客户邮件、日志摘要、IT 系统输出等长文本分类任务,避免信息截断带来的语义丢失。
- 高效稀疏注意力机制
-
使用 滑动窗口 + 全局注意力机制,相比 Transformer 的全连接注意力,计算效率更高、内存占用更低。
-
✅ 可以在有限的显存下处理比普通模型长 8 倍的文本。
- 继承 RoBERTa 的语义理解能力
-
Longformer-base-4096是在 RoBERTa-base 的基础上改造的,具有优秀的语言理解能力和上下文捕捉能力。 -
✅ 不仅"长",还具备准确的语义建模能力,可用于精细分类、多维推理场景(如工单分类、多标签分类、合规判断等)。
- 更少的切分(chunking)需求
-
常规 Transformer 模型处理长文本时需要切块(chunking)并聚合结果,增加了处理复杂度且可能引入误差。
-
✅ Longformer 可以直接处理长文本整体,提高端到端分类的准确率与一致性。
- 支持全局关注(Global Attention)机制
-
可以为某些关键 token(如标题、系统名、时间、告警词等)设定全局关注,增强对关键信息的感知。
-
✅ 非常适合提示词引导、头部信息重要的 IT 工单或报告类文本的分类任务。
- 预训练模型广泛,开源生态良好
allenai/longformer-base-4096是 Hugging Face 上非常活跃的模型,有许多下游任务的使用案例(分类、QA、摘要、RAG 等)。
与其他模型比较
| 模型 | 最大输入 token | 是否适合长文本分类 | 是否开源 | 是否高效 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BERT-base | 512 | 否(需截断或chunk) | ✅ | ✅ |
| RoBERTa-base | 512 | 否 | ✅ | ✅ |
| Longformer-base | 4096 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| BigBird | 4096 | ✅(稀疏注意力) | ✅ | 一般 |
| GPT-3 / GPT-4 | 2048~32k | ✅(封闭API) | ❌ | ❌(贵) |
数据准备
使用真实生产数据,标题+描述可能超过标准如 512 tokens的任务
加载与拼接: 将标题与描述通过 [SEP] token 拼接,作为每条样本的输入文本。对缺失值进行填充(使用空字符串),以提升鲁棒性。
标签编码: 使用 scikit-learn 的 LabelEncoder 对 issue_type_name 字段进行编码,便于模型训练。
**数据集划分:**按照标签分布使用分层采样将数据集划分为训练集(80%)、验证集(10%)和测试集(10%)。
分词:
-
使用 Hugging Face 的
AutoTokenizer进行分词,最大长度设为 4096。 -
启用自动填充和截断以确保统一输入长度。
-
将分词后的数据缓存至本地磁盘,提高后续运行效率。
模型配置:
-
预训练模型:
longformer-base-4096 -
最大序列长度:4096 tokens
-
隐藏层维度:768
-
注意力头数量:12
-
Transformer 层数:12
模型训练
自定义 SingleTaskModel 类,基于 Longformer 构建:
-
基础模型 :加载
longformer-base-4096生成上下文嵌入。 -
分类头 :使用线性层将
[CLS]token 的输出(768维)映射到具体的类别数。 -
损失函数:使用交叉熵损失进行多分类训练。
使用 Hugging Face 的 Trainer API,并通过 SingleTaskTrainer 进行定制化训练以适配 Longformer:
训练参数:
-
训练轮数:10
-
批大小:2(通过梯度累积 16 步模拟更大批次,以适配显存)
-
学习率:2e-5
-
混合精度训练(fp16=True)以提升训练速度
-
评估策略:每 50 步评估一次
-
保存策略:按验证集 F1 得分保存最佳模型
**缓存机制:**将分词后的数据集缓存至磁盘,避免重复处理。
**评估指标:**准确率(Accuracy)与加权 F1 分数,用于评估在类别不均衡数据下的性能。
训练代码如下
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from datasets import Dataset, load_from_disk
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel, Trainer, TrainingArguments
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
import evaluate
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import os
import joblib
import json
from safetensors.torch import save_file
# Set random seed for reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(42)
np.random.seed(42)
# Check for CUDA
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"Using device: {device}")
# 1. Load and prepare the JSON dataset
def load_json(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df['text'] = df['title'].fillna('') + ' [SEP] ' + df['description'].fillna('')
return df
# 2. Split dataset into train, validation, and test
def split_dataset(df):
train_val, test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.1, random_state=42)
train, val = train_test_split(train_val, test_size=0.11, random_state=42)
return train, val, test
# 3. Encode string labels for single task
def encode_labels(df, label_columns=['issue_type_name']):
label_encoders = {}
for col in label_columns:
le = LabelEncoder()
df[f'labels_{col}'] = le.fit_transform(df[col].fillna('Unknown'))
label_encoders[col] = le
return df, label_encoders
# 4. Tokenize function for single-task (no chunking during tokenization)
def tokenize_function(examples):
input_ids_batch = []
attention_mask_batch = []
labels_batch = []
original_idx_batch = []
for idx, (text, label) in enumerate(zip(
examples['text'],
examples['labels_issue_type_name']
)):
if text is None or pd.isna(text) or not isinstance(text, str):
print(f"Warning: Skipping invalid text at index {idx}: {text}")
continue
try:
tokenized = tokenizer(
text,
padding='max_length',
truncation=True,
max_length=4096,
return_tensors='pt'
)
input_ids_batch.append(tokenized['input_ids'][0].tolist())
attention_mask_batch.append(tokenized['attention_mask'][0].tolist())
labels_batch.append(label)
original_idx_batch.append(idx)
print(f"Text index {idx}: input_ids len={len(tokenized['input_ids'][0])}, attention_mask len={len(tokenized['attention_mask'][0])}, label={label}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error tokenizing text at index {idx}: {e}")
continue
# Verify array lengths
lengths = {
'input_ids': len(input_ids_batch),
'attention_mask': len(attention_mask_batch),
'labels': len(labels_batch),
'original_idx': len(original_idx_batch)
}
print(f"Batch lengths: {lengths}")
if not (lengths['input_ids'] == lengths['attention_mask'] == lengths['labels'] == lengths['original_idx']):
raise ValueError(f"Array length mismatch: {lengths}")
return {
'input_ids': input_ids_batch,
'attention_mask': attention_mask_batch,
'labels': labels_batch,
'original_idx': original_idx_batch
}
# 5. Chunk long texts for inference (if needed)
def chunk_text(text, max_length=4096, stride=2048):
tokens = tokenizer(text, add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors='pt')['input_ids'][0].to(device)
chunks = []
for i in range(0, len(tokens), max_length - 2):
chunk = tokens[i:i + max_length - 2]
chunk = torch.cat([
torch.tensor([tokenizer.cls_token_id], device=device),
chunk,
torch.tensor([tokenizer.sep_token_id], device=device)
])
chunks.append(chunk)
return chunks
# 6. Aggregate predictions for chunked texts (used during inference)
def aggregate_predictions(logits, original_indices, num_original_samples):
text_logits = {}
for logit, idx in zip(logits, original_indices):
if idx not in text_logits:
text_logits[idx] = []
text_logits[idx].append(logit)
aggregated_logits = []
for idx in range(num_original_samples):
if idx in text_logits:
aggregated_logits.append(np.mean(text_logits[idx], axis=0))
else:
aggregated_logits.append(np.zeros(logits.shape[1]))
print(f"Warning: No logits for index {idx}, using zeros")
print(f"Aggregated logits length: {len(aggregated_logits)}, Expected: {num_original_samples}")
return np.array(aggregated_logits)
# 7. Cache tokenized datasets
def load_or_tokenize(dataset, cache_path, remove_columns):
if os.path.exists(cache_path):
print(f"🔁 Loading cached dataset from {cache_path}")
return load_from_disk(cache_path)
else:
print(f"🧪 Tokenizing and caching to {cache_path}")
try:
tokenized = dataset.map(tokenize_function, batched=True, batch_size=1, remove_columns=remove_columns)
tokenized.save_to_disk(cache_path)
return tokenized
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error during tokenization: {e}")
raise
# 8. Single-Task Model for Issue Type Name
class SingleTaskModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, base_model, num_labels):
super().__init__()
self.base_model = base_model
self.classifier = nn.Linear(base_model.config.hidden_size, num_labels)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask=None, labels=None, **kwargs):
outputs = self.base_model(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
hidden_state = outputs[0][:, 0, :] # CLS token
logits = self.classifier(hidden_state)
loss = None
if labels is not None:
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(logits, labels)
return {
'loss': loss,
'logits': logits
}
# 9. Custom Trainer for Single-Task
class SingleTaskTrainer(Trainer):
def __init__(self, *args, num_original_samples=None, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.num_original_samples = num_original_samples
self.chunk_indices = []
def compute_loss(self, model, inputs, return_outputs=False):
inputs.pop('original_idx', None)
outputs = model(**{k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()})
loss = outputs['loss']
return (loss, outputs) if return_outputs else loss
def prediction_step(self, model, inputs, prediction_loss_only, ignore_keys=None):
chunk_idx = inputs.pop('original_idx', None)
labels = inputs.pop('labels', None)
if chunk_idx is None:
print("Warning: chunk_idx is None, assuming no chunking for this batch")
chunk_idx = list(range(len(inputs['input_ids'])))
print(f"Chunk indices length: {len(chunk_idx)}")
print(f"Eval dataset size: {len(self.eval_dataset)}")
self.chunk_indices.extend(chunk_idx.tolist() if isinstance(chunk_idx, torch.Tensor) else chunk_idx)
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**{k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()})
logits = outputs['logits']
loss = None
if labels is not None:
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()(logits, labels.to(device))
return (loss, logits, labels)
# 10. Compute metrics for evaluation
def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
logits, labels = eval_pred
if trainer.chunk_indices:
logits = aggregate_predictions(logits, trainer.chunk_indices, num_original_samples=len(trainer.eval_dataset))
labels = np.array(labels[:len(trainer.eval_dataset)])
else:
labels = np.array(labels)
predictions = np.argmax(logits, axis=1)
return {
"accuracy_issue_type_name": accuracy_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)["accuracy"],
"f1_issue_type_name": f1_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels, average='weighted')["f1"]
}
# Main execution
if __name__ == "__main__":
# File path
file_path = "./PRD-9191.json"
# Load and preprocess dataset
df = load_json(file_path)
print(f"Loaded dataset with {len(df)} samples")
df, label_encoders = encode_labels(df, ['issue_type_name'])
num_labels = len(label_encoders['issue_type_name'].classes_)
print(f"Number of issue_type_name classes: {num_labels}")
# Load model and tokenizer
model_name = "./longformer-base-4096"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
base_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
model = SingleTaskModel(base_model, num_labels).to(device)
# Split dataset
train_df, val_df, test_df = split_dataset(df)
# Convert to Hugging Face Datasets
train_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(
train_df[['text', 'labels_issue_type_name']],
preserve_index=False)
val_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(
val_df[['text', 'labels_issue_type_name']],
preserve_index=False)
test_dataset = Dataset.from_pandas(
test_df[['text', 'labels_issue_type_name', 'issue_type_name']],
preserve_index=False)
# Print dataset sizes for debugging
print(f"Original training dataset size: {len(train_dataset)}")
print(f"Original validation dataset size: {len(val_dataset)}")
print(f"Original test dataset size: {len(test_dataset)}")
# Tokenize datasets
tokenized_train = load_or_tokenize(train_dataset, f"cache/train_issue_type", remove_columns=['text'])
tokenized_val = load_or_tokenize(val_dataset, f"cache/val_issue_type", remove_columns=['text'])
tokenized_test = load_or_tokenize(test_dataset, f"cache/test_issue_type", remove_columns=['text', 'issue_type_name'])
# Print tokenized dataset sizes for debugging
print(f"Tokenized training dataset size: {len(tokenized_train)}")
print(f"Tokenized validation dataset size: {len(tokenized_val)}")
print(f"Tokenized test dataset size: {len(tokenized_test)}")
# Training arguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir=f"./checkpoints_issue_type",
num_train_epochs=10,
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
per_device_eval_batch_size=4,
gradient_accumulation_steps=16,
learning_rate=2e-5,
fp16=True,
evaluation_strategy="steps",
eval_steps=50,
save_strategy="steps",
save_steps=1000,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
metric_for_best_model="eval_f1_issue_type_name",
save_total_limit=1,
logging_dir=f"./logs_issue_type",
logging_steps=10,
)
# Metrics
accuracy_metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
f1_metric = evaluate.load("f1")
# Initialize trainer
trainer = SingleTaskTrainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=tokenized_train,
eval_dataset=tokenized_val,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
num_original_samples=len(val_dataset),
)
# Save label encoders
output_le_path = f"./checkpoints_issue_type"
os.makedirs(output_le_path, exist_ok=True)
joblib.dump(label_encoders['issue_type_name'], f"{output_le_path}/label_encoder_issue_type_name.pkl")
# Clear chunk indices before training
trainer.chunk_indices = []
# Train
trainer.train()
# Save model in SafeTensors format
trainer.save_model(f"./final_model_issue_type")
state_dict = model.state_dict()
save_file(state_dict, f"./final_model_issue_type/model.safetensors")
# Evaluate on test set
print("\nEvaluating on Test Set...")
test_results = trainer.evaluate(tokenized_test)
print("Test Results:", test_results)**高效性:**通过滑动窗口注意力机制将复杂度从 O(n²) 降至 O(n),显著降低内存占用,使得在消费级 GPU 上也可训练。
**鲁棒的数据处理流程:**处理缺失值、不合法输入以及极长文本,提高模型在实际场景中的稳定性。
**可扩展性:**数据缓存机制和混合精度训练优化了计算资源,为大规模训练做好准备。
**平衡评估:**加权 F1 得分衡量所有类别表现,尤其适用于类别不均的实际数据。
测试集自测结果
Aggregated logits length: 5772, Expected: 5772
Test Results: {
'eval_loss': 0.5606201887130737,
'eval_accuracy_issue_type_name': 0.02442827442827443,
'eval_f1_issue_type_name': 0.0028243325750626426,
'eval_runtime': 234.714,
'eval_samples_per_second': 24.839,
'eval_steps_per_second': 1.555,
'epoch': 9.98
}接口测试
封装 fastapi接口
import torch
import numpy as np
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException
from pydantic import BaseModel
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
import joblib
from safetensors.torch import load_file
import torch.nn as nn
import uvicorn
import os
# Initialize FastAPI app
app = FastAPI()
# Check for CUDA
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Define input data model
class InputData(BaseModel):
title: str
description: str
# Single-Task Model for Issue Type Name (same as in training)
class SingleTaskModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, base_model, num_labels):
super().__init__()
self.base_model = base_model
self.classifier = nn.Linear(base_model.config.hidden_size, num_labels)
def forward(self, input_ids, attention_mask=None):
outputs = self.base_model(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
hidden_state = outputs[0][:, 0, :] # CLS token
logits = self.classifier(hidden_state)
return logits
# Load model, tokenizer, and label encoder
model_path = "./final_model_issue_type"
tokenizer_path = "./longformer-base-4096"
label_encoder_path = f"{model_path}/label_encoder_issue_type_name.pkl"
try:
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tokenizer_path)
base_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(tokenizer_path)
num_labels = len(joblib.load(label_encoder_path).classes_)
model = SingleTaskModel(base_model, num_labels).to(device)
state_dict = load_file(f"{model_path}/model.safetensors")
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
model.eval()
label_encoder = joblib.load(label_encoder_path)
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"Error loading model or tokenizer: {e}")
# Function to chunk text if needed
def chunk_text(text, max_length=4096, stride=2048):
tokens = tokenizer(text, add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors='pt')['input_ids'][0].to(device)
chunks = []
for i in range(0, len(tokens), max_length - 2):
chunk = tokens[i:i + max_length - 2]
chunk = torch.cat([
torch.tensor([tokenizer.cls_token_id], device=device),
chunk,
torch.tensor([tokenizer.sep_token_id], device=device)
])
chunks.append(chunk)
return chunks
# Function to aggregate predictions
def aggregate_predictions(logits):
return np.mean(logits, axis=0)
# Prediction endpoint
@app.post("/predict")
async def predict(data: InputData):
try:
# Combine title and description
text = f"{data.title} [SEP] {data.description}"
# Tokenize input
chunks = chunk_text(text)
all_logits = []
for chunk in chunks:
inputs = {
'input_ids': chunk.unsqueeze(0),
'attention_mask': torch.ones_like(chunk).unsqueeze(0)
}
inputs = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
# Get model predictions
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(**inputs)
all_logits.append(logits.cpu().numpy())
# Aggregate logits if multiple chunks
aggregated_logits = aggregate_predictions(np.vstack(all_logits))
probabilities = torch.softmax(torch.tensor(aggregated_logits), dim=-1).numpy()
# Get top 5 predictions
top_5_indices = np.argsort(probabilities)[-5:][::-1]
top_5_labels = label_encoder.inverse_transform(top_5_indices)
top_5_probs = probabilities[top_5_indices]
# Prepare response
result = [
{"label": label, "confidence": float(prob)}
for label, prob in zip(top_5_labels, top_5_probs)
]
return {"predictions": result}
except Exception as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=f"Prediction error: {str(e)}")
# Run the app
if __name__ == "__main__":
uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=5000)使用postman 调用测试
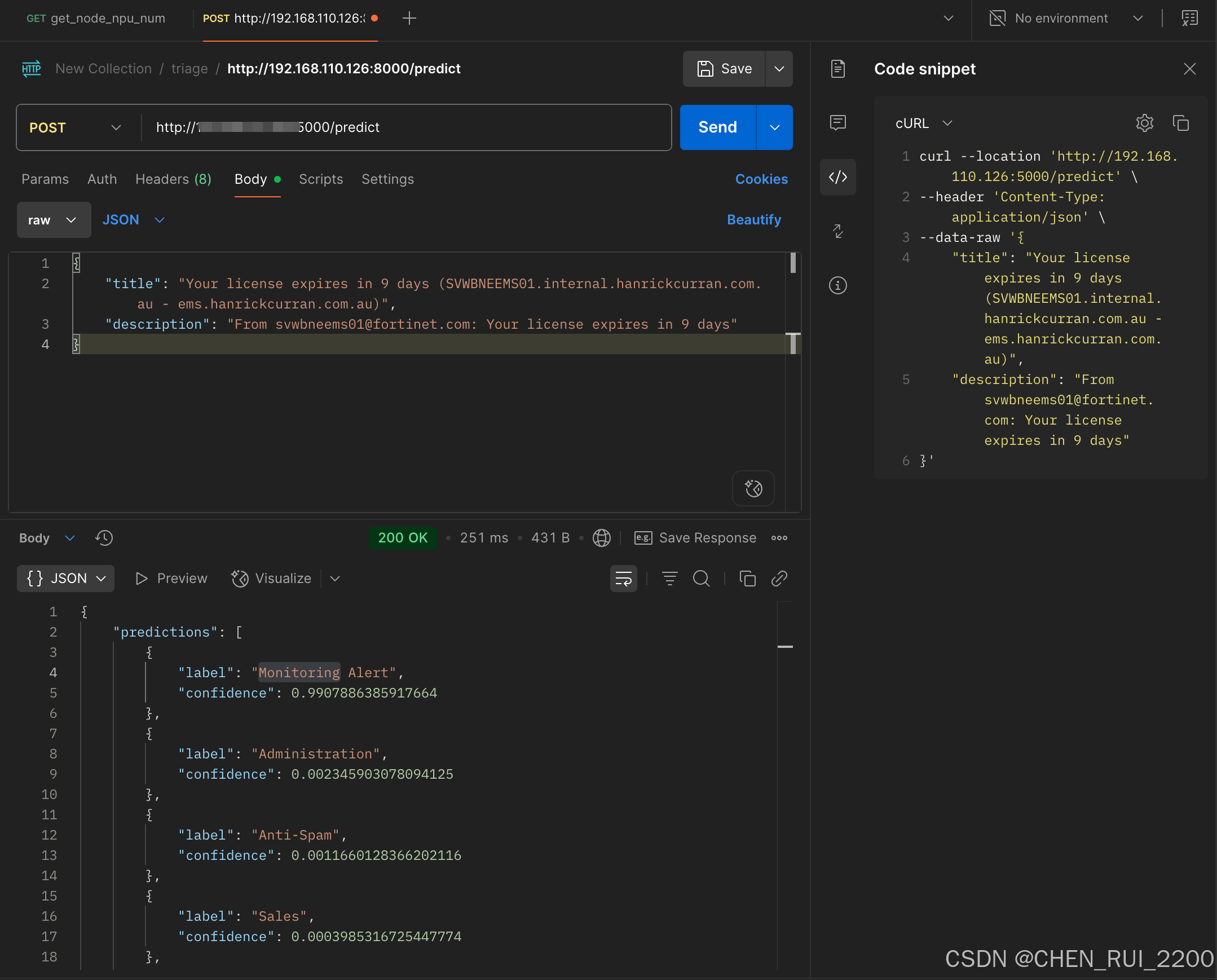
在验证数据集上进行覆盖测试
def get_prediction(title, description):
payload = {
"title": title,
"description": description
}
try:
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload, headers={'Content-Type': 'application/json'})
response.raise_for_status()
predictions = response.json().get("predictions", [])
if not predictions:
print(f"Warning: No predictions returned for title: {title}")
return None
# Get the top prediction (highest confidence)
top_prediction = max(predictions, key=lambda x: x['confidence'])
return top_prediction['label']
except requests.RequestException as e:
print(f"Error calling API for title: {title}: {e}")
return None
# Main accuracy test
def main():
# Load dataset
df = load_json(JSON_FILE_PATH)
print(f"Loaded dataset with {len(df)} samples")
# Initialize variables for accuracy tracking
correct = 0
total = 0
print("Starting accuracy test...")
# Iterate through dataset with progress bar
for idx, row in tqdm(df.iterrows(), total=len(df), desc="Testing Progress"):
title = row['title']
description = row['description']
true_label = row['issue_type_name']
# Get prediction
predicted_label = get_prediction(title, description)
if predicted_label is None:
print(f"Skipping sample {idx + 1} due to API error")
continue
# Update accuracy metrics
total += 1
if predicted_label == true_label:
correct += 1
# Calculate and display current accuracy
current_accuracy = (correct / total) * 100 if total > 0 else 0
print(f"Sample {total}/{len(df)}: True Label: {true_label}, Predicted Label: {predicted_label}, "
f"Correct: {correct}, Current Accuracy: {current_accuracy:.2f}%")
# Final accuracy
final_accuracy = (correct / total) * 100 if total > 0 else 0
print(f"\nTest Completed!")
print(f"Total Samples Processed: {total}")
print(f"Correct Predictions: {correct}")
print(f"Final Accuracy: {final_accuracy:.2f}%")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()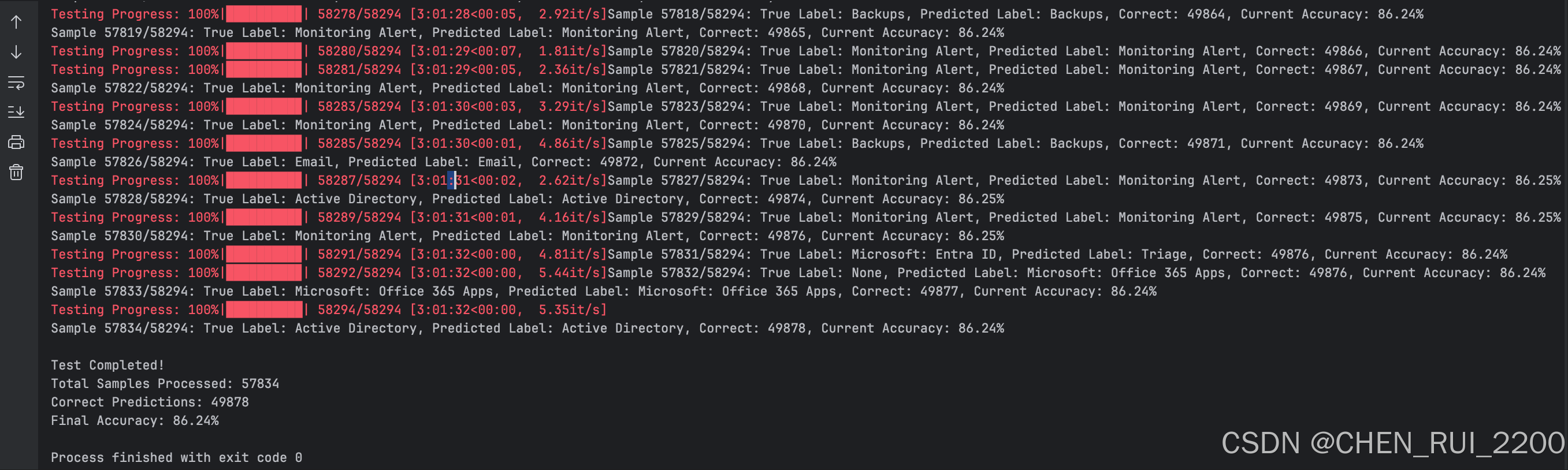
总记58294 个ticket, issue type 预测准确率Final Accuracy: 86.24%