一、启用图片文件服务
用Nginx启用图片服务,配置好映射路径。
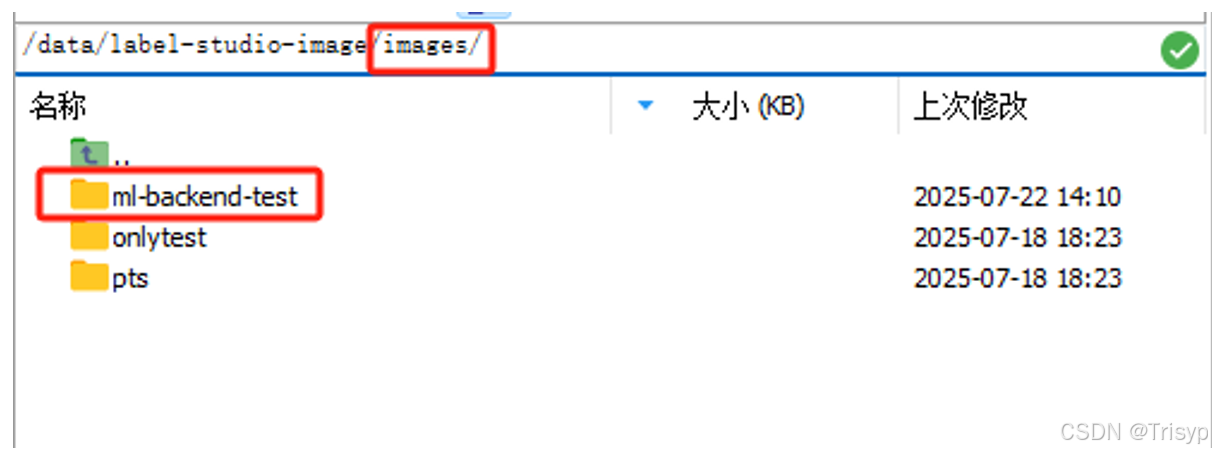
新建图片文件夹,将文件夹下的图片路径存储到txt文件中
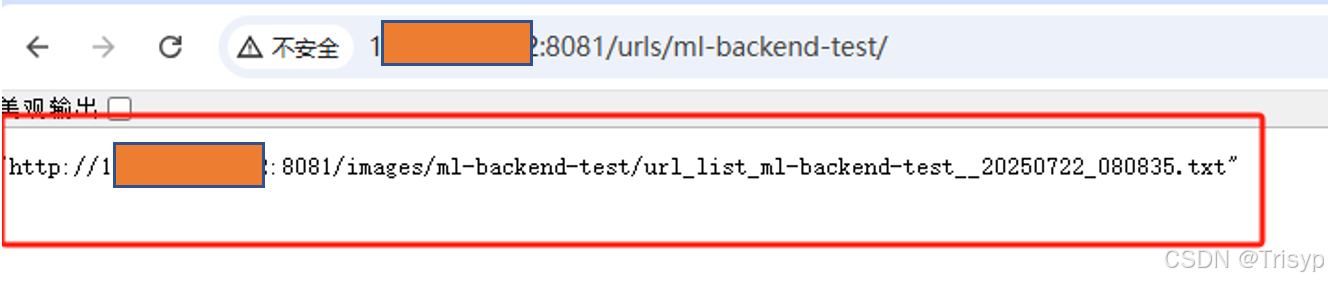
访问地址(文件夹):http://112.12.19.122:8081/urls/ml-backend-test/
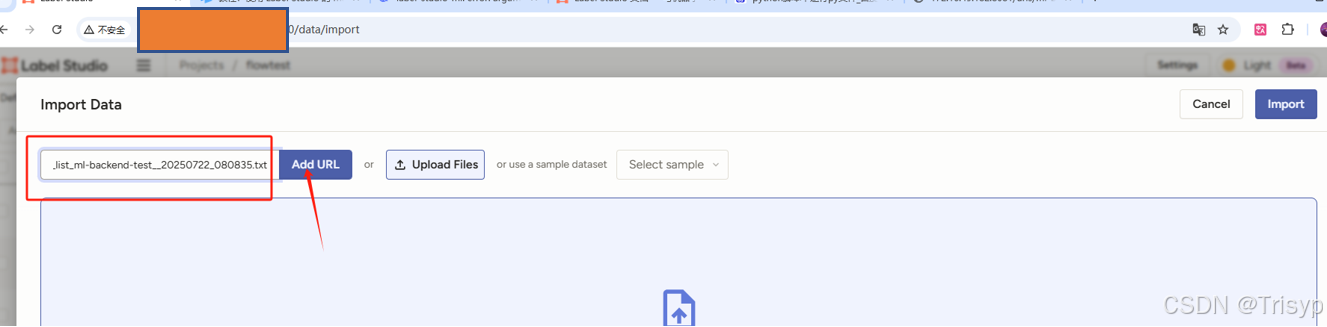
进入labelstudio将txt文件路径填入,点击Add URL将图片导入项目进行标注。
二、启用模型服务
首先pip安装label-studio-ml
进入到projects文件夹,将init_model.py放入该文件夹,然后执行命令label-studio-ml init my_backend来初始化模型文件夹。init_model.py的代码如下:
python
#!/user/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from label_studio_ml.model import LabelStudioMLBase
class DummyModel(LabelStudioMLBase):
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
# don't forget to call base class constructor
super(DummyModel, self).__init__(**kwargs)
# you can preinitialize variables with keys needed to extract info from tasks and annotations and form predictions
from_name, schema = list(self.parsed_label_config.items())[0]
self.from_name = from_name
self.to_name = schema['to_name'][0]
self.labels = schema['labels']
def predict(self, tasks, **kwargs):
""" This is where inference happens: model returns
the list of predictions based on input list of tasks
"""
predictions = []
for task in tasks:
predictions.append({
'score': 0.987, # prediction overall score, visible in the data manager columns
'model_version': 'delorean-20151021', # all predictions will be differentiated by model version
'result': [{
'from_name': self.from_name,
'to_name': self.to_name,
'type': 'choices',
'score': 0.5, # per-region score, visible in the editor
'value': {
'choices': [self.labels[0]]
}
}]
})
return predictions
def fit(self, annotations, **kwargs):
""" This is where training happens: train your model given list of annotations,
then returns dict with created links and resources
"""
return {'path/to/created/model': 'my/model.bin'}进入到my_backend文件夹,可以看到下述文件:
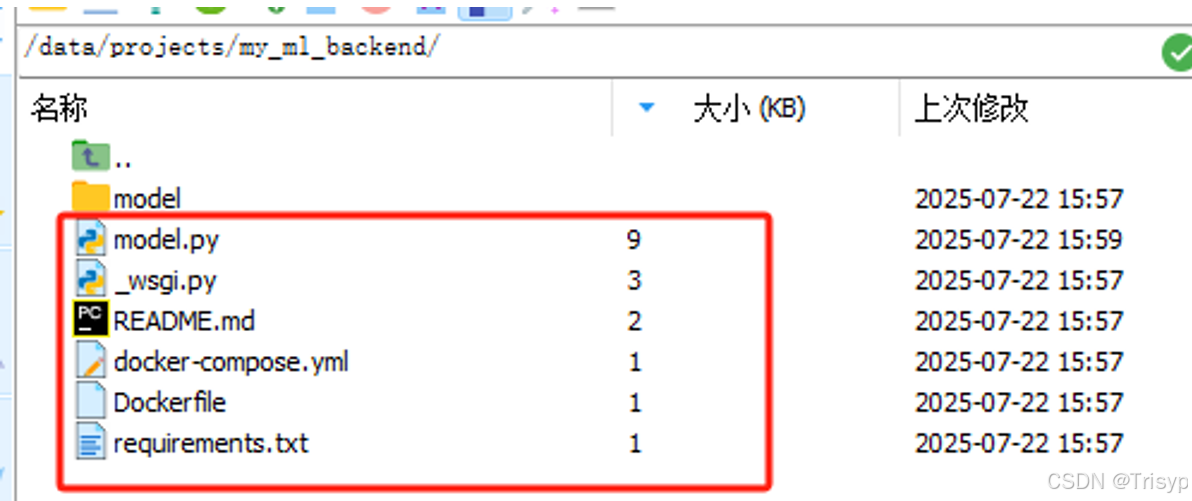
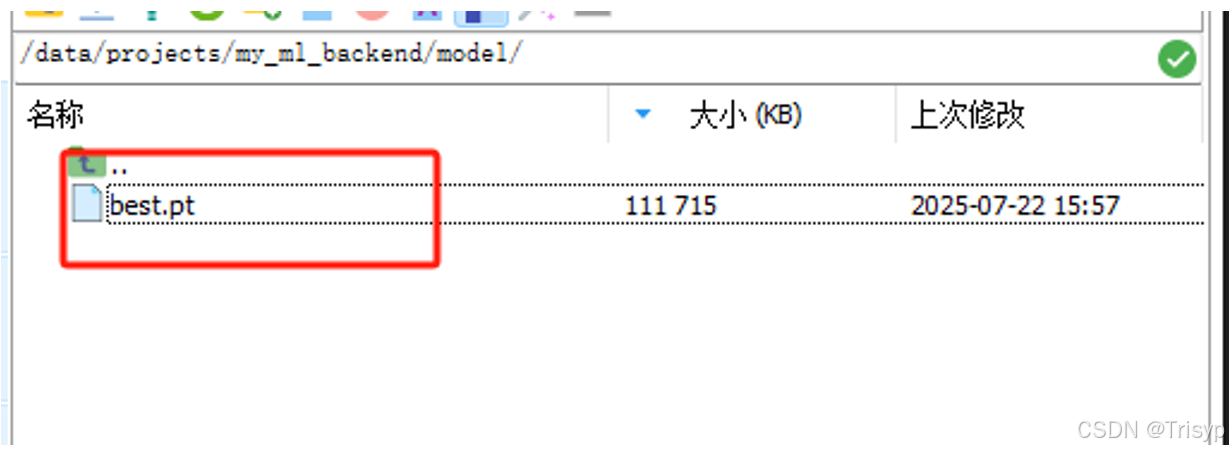
在my_backend文件夹下新建model文件夹,将训练好的YOLO模型文件放入model下:
修改my_backend文件夹下的model.py,代码如下:
python
#!/user/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
from typing import List, Dict, Optional
import torch
from label_studio_ml.model import LabelStudioMLBase
from label_studio_ml.utils import get_single_tag_keys, get_local_path
import logging
from ultralytics import YOLO
from PIL import Image
# 设置日志
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
MODEL_PATH = os.getenv('MODEL_PATH', '/data/projects/my_ml_backend/model/best.pt')
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class DummyModel(LabelStudioMLBase):
"""Custom ML Backend model
"""
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
super(DummyModel, self).__init__(**kwargs)
from_name, schema = list(self.parsed_label_config.items())[0]
self.from_name = from_name
self.to_name = schema['to_name'][0]
self.labels = schema['labels']
# 训练参数
self.train_epochs = int(os.getenv('TRAIN_EPOCHS', 150))
self.train_batch_size = int(os.getenv('TRAIN_BATCH_SIZE', 18))
def predict(self, tasks: List[Dict], context: Optional[Dict] = None, **kwargs):
task = tasks[0]
print(f'''\
Run prediction on {tasks}
Received context: {context}
Project ID: {task['id']}
Label config: {self.label_config}
Parsed JSON Label config: {self.parsed_label_config}
''')
img_url = task['data']['image']
image_path = self.get_local_path(url=img_url)
print(f'image_path: {image_path}')
# Getting URL and loading image
image = Image.open(image_path)
# Height and width of image
original_width, original_height = image.size
# Creating list for predictions and variable for scores
predictions = []
scores = 0
i = 0
# Initialize self variables
self.from_name, self.to_name, self.value, self.classes = get_single_tag_keys(
self.parsed_label_config, 'RectangleLabels', 'Image')
# 加载自己的yolov11模型
logger.info(f"加载YOLO11模型: {MODEL_PATH}")
self.model = YOLO(MODEL_PATH)
# 检查GPU可用性
logger.info(f"使用设备: {'GPU ✅' if DEVICE.type == 'cuda' else 'CPU ⚠️'}")
# 改动的地方, 增加了conf配置, 只有conf>=0.5的才会被标记出来
# 默认conf是0.25, 不改的话被标注的地方肯能会很多, 根据自己的实际情况配置
# Getting prediction using model
results = self.model.predict(image, conf=0.5)
# print(results)
# Getting mask segments, boxes from model prediction
for result in results:
for i, prediction in enumerate(result.boxes):
score = prediction.conf.item()
label_index = int(prediction.cls.item())
xyxy = prediction.xyxy[0].tolist()
# print(f"{i} prediction", prediction)
# x_center, y_center, w, h = box
predictions.append({
"id": str(i),
"from_name": self.from_name,
"to_name": self.to_name,
"type": "rectanglelabels",
"score": score,
"original_width": original_width,
"original_height": original_height,
"image_rotation": 0,
"value": {
"rotation": 0,
# 坐标转换, 只有转换后才能标注在正确的位置
"x": xyxy[0] / original_width * 100,
"y": xyxy[1] / original_height * 100,
"width": (xyxy[2] - xyxy[0]) / original_width * 100,
"height": (xyxy[3] - xyxy[1]) / original_height * 100,
"rectanglelabels": [self.labels[label_index]]
}})
scores += score
logger.info(f"预测完成: 检测到 {len(predictions)} 个对象")
# Dict with final dicts with predictions
final_prediction = [{
"result": predictions,
"score": scores / (i + 1),
"model_version": "11x"
}]
return final_prediction
def fit(self, event, data, **kwargs):
"""
使用新标注数据训练模型
参数:
event: 事件类型 ('ANNOTATION_CREATED', 'ANNOTATION_UPDATED')
data: 包含标注数据的字典
**kwargs: 额外参数
"""
# 检查是否有训练数据
if not self.train_output:
logger.info("初始化训练数据存储")
self.train_output = {
'image_paths': [],
'labels': []
}
# 获取标注信息
annotation = data['annotation']
image_url = annotation['task']['data']['image']
image_path = self.get_local_path(image_url)
# 解析标注结果
bboxes = []
for result in annotation['result']:
if result['from_name'] == self.from_name:
value = result['value']
label = value['rectanglelabels'][0]
# 获取图像尺寸
image = Image.open(image_path)
img_width, img_height = image.size
# 转换为绝对坐标
x = value['x'] * img_width / 100
y = value['y'] * img_height / 100
width = value['width'] * img_width / 100
height = value['height'] * img_height / 100
# YOLO格式: [class_idx, x_center, y_center, width, height] (归一化)
x_center = (x + width / 2) / img_width
y_center = (y + height / 2) / img_height
norm_width = width / img_width
norm_height = height / img_height
class_idx = self.labels.index(label)
bboxes.append([class_idx, x_center, y_center, norm_width, norm_height])
# 保存训练数据
self.train_output['image_paths'].append(image_path)
self.train_output['labels'].append(bboxes)
logger.info(f"收到新标注: 图像={image_path}, 标注数={len(bboxes)}")
logger.info(f"当前训练集大小: {len(self.train_output['image_paths'])}")
# 当有足够数据时开始训练
if len(self.train_output['image_paths']) >= 10:
logger.info("达到最小训练集大小,开始训练...")
self.train_model()
# 重置训练数据
self.train_output = {
'image_paths': [],
'labels': []
}
# 返回新模型信息
return {
'model_path': MODEL_PATH,
'model_version': f"retrained-{len(self.train_output['image_paths'])}"
}
return {}
def train_model(self):
"""使用收集的标注数据训练模型"""
logger.info("准备训练数据...")
# 创建YOLO格式的训练数据目录结构
train_dir = 'yolo_train_data'
images_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'images')
labels_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'labels')
os.makedirs(images_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(labels_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 创建数据集描述文件
with open(os.path.join(train_dir, 'dataset.yaml'), 'w') as f:
f.write(f"train: {os.path.abspath(images_dir)}\n")
f.write(f"nc: {len(self.labels)}\n")
f.write(f"names: {self.labels}\n")
# 准备训练数据
for i, (image_path, bboxes) in enumerate(zip(
self.train_output['image_paths'],
self.train_output['labels']
)):
# 复制图像
img = Image.open(image_path)
img_filename = f'train_{i}.jpg'
img.save(os.path.join(images_dir, img_filename))
# 创建标签文件
label_filename = f'train_{i}.txt'
with open(os.path.join(labels_dir, label_filename), 'w') as f:
for bbox in bboxes:
class_idx, x_center, y_center, width, height = bbox
f.write(f"{class_idx} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}\n")
logger.info(f"训练数据准备完成: {len(self.train_output['image_paths'])} 张图像")
# 训练模型 (这里简化了实际训练过程)
logger.info(f"开始训练模型 (模拟) - 周期={self.train_epochs}, 批次大小={self.train_batch_size}")
# 调用YOLO的训练脚本:
# import subprocess
# subprocess.run(['python', 'train.py'])
# 参数配置: --img 640 --batch {self.train_batch_size} --epochs {self.train_epochs}
# --data {os.path.join(train_dir, 'dataset.yaml')} --weights {MODEL_PATH}
logger.info("训练完成! 模型已更新")
# 重新加载训练后的模型
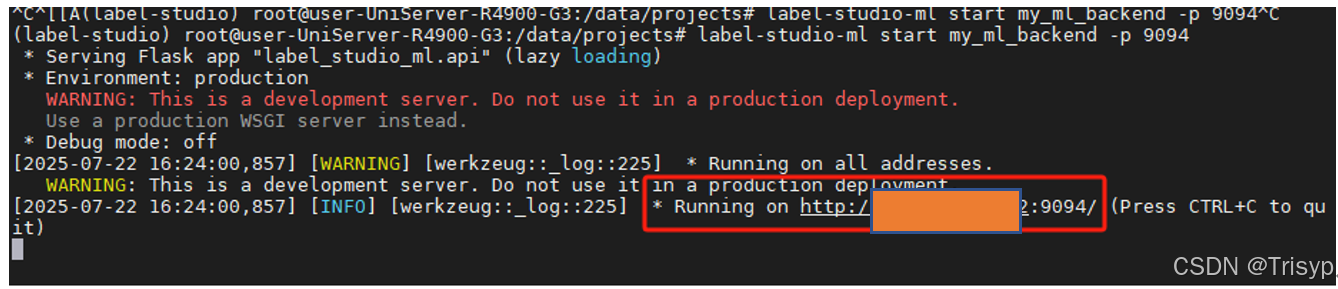
# self.model = YOLO(MODEL_PATH)最后执行命令label-studio-ml start my_ml_backend -p 9094来启动模型后端服务
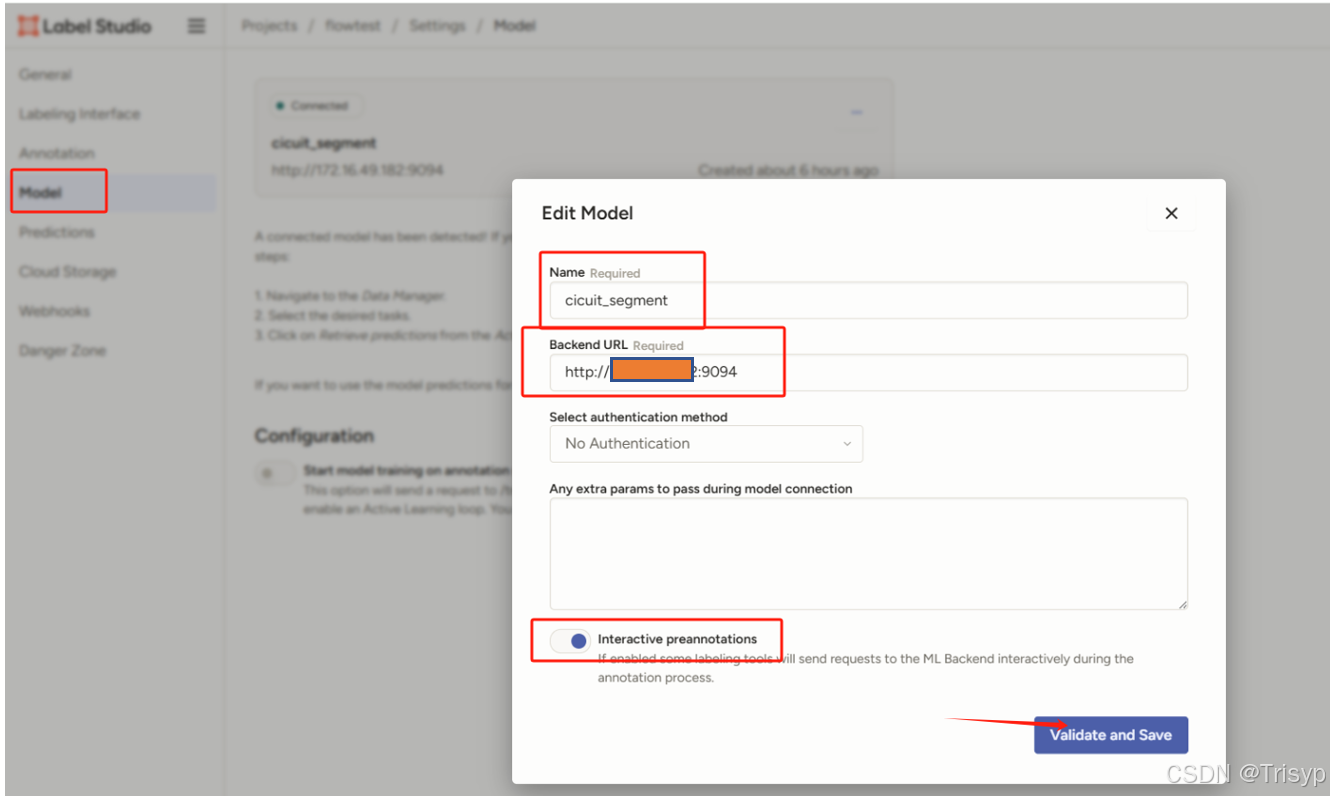
三、labelstudio中配置后端模型服务
进入到项目中点击Model菜单,然后点击connect model,弹框填写配置好服务地址,点击保存即可。
|---|
| |
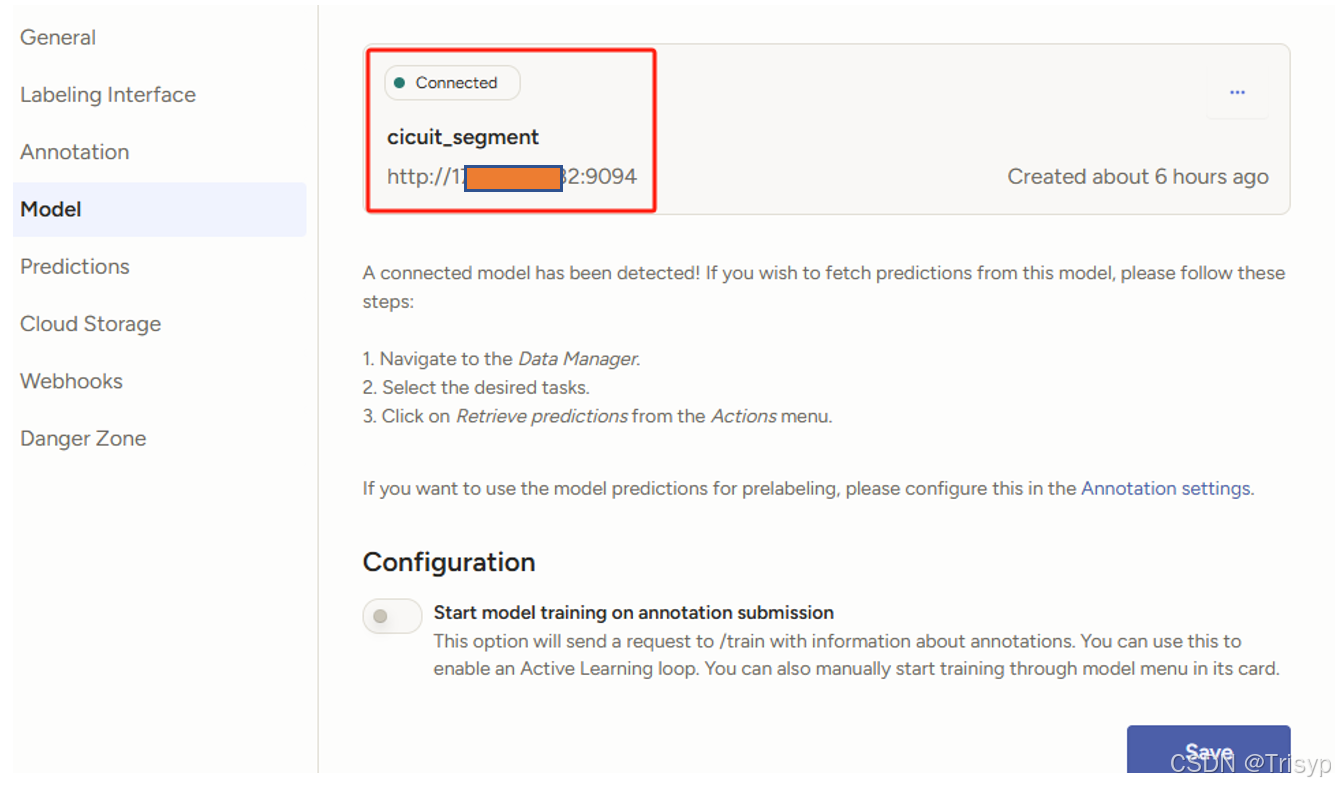
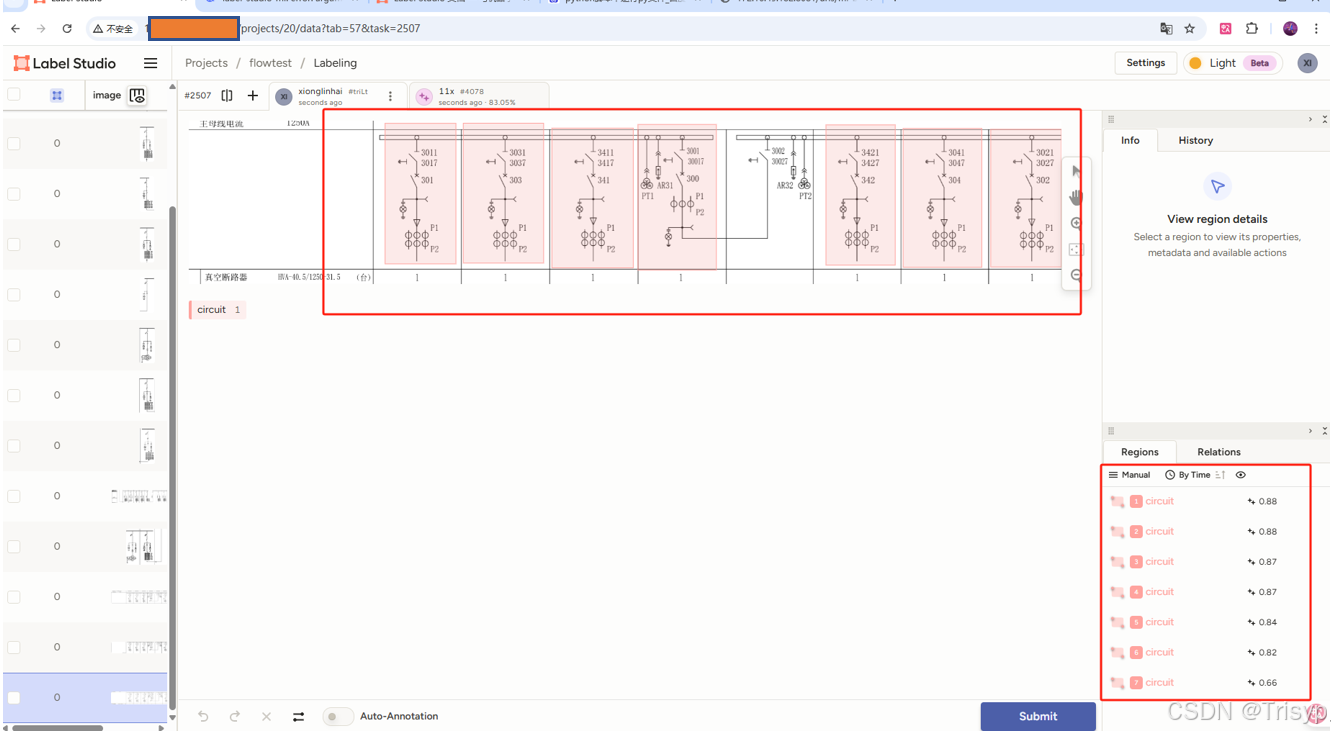
四、逐个点击任务即可完成自动化标注
点击任务后自动加载模型推理,片刻后得到自动化标注结果,基于该标注结果可继续修改标注。
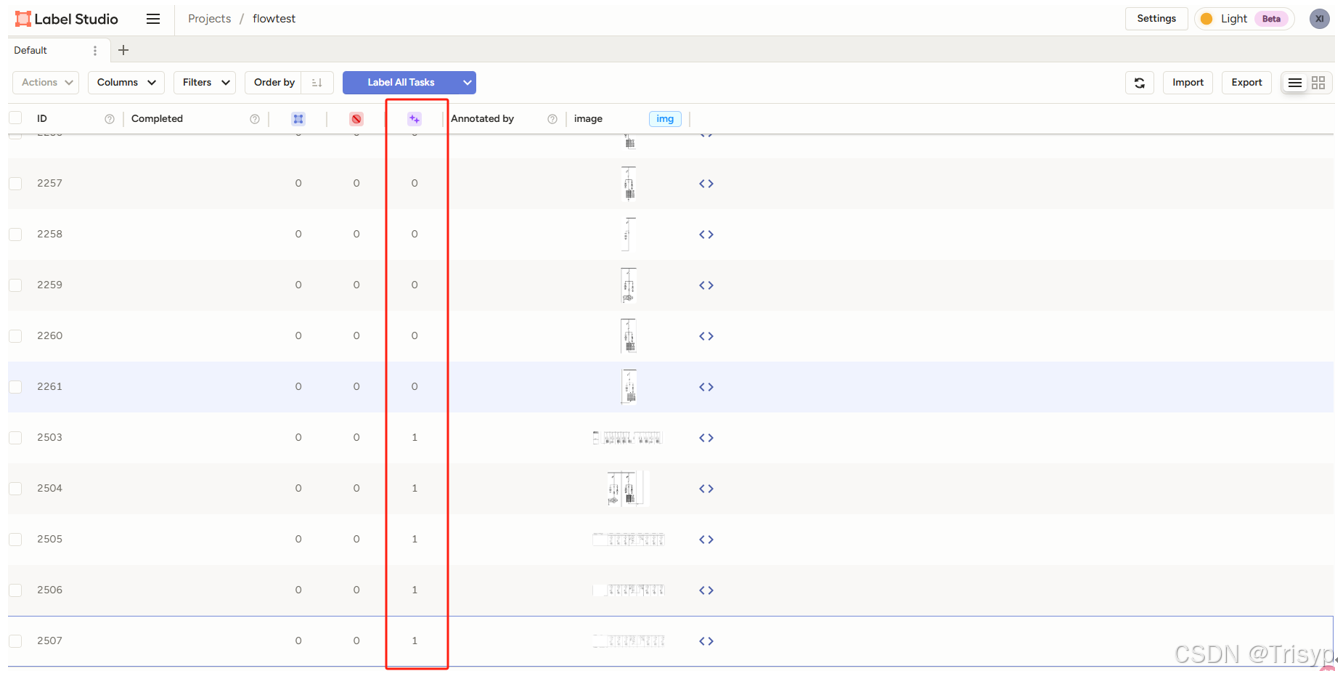
可以看到,预测列为1的表明已经推理完毕。
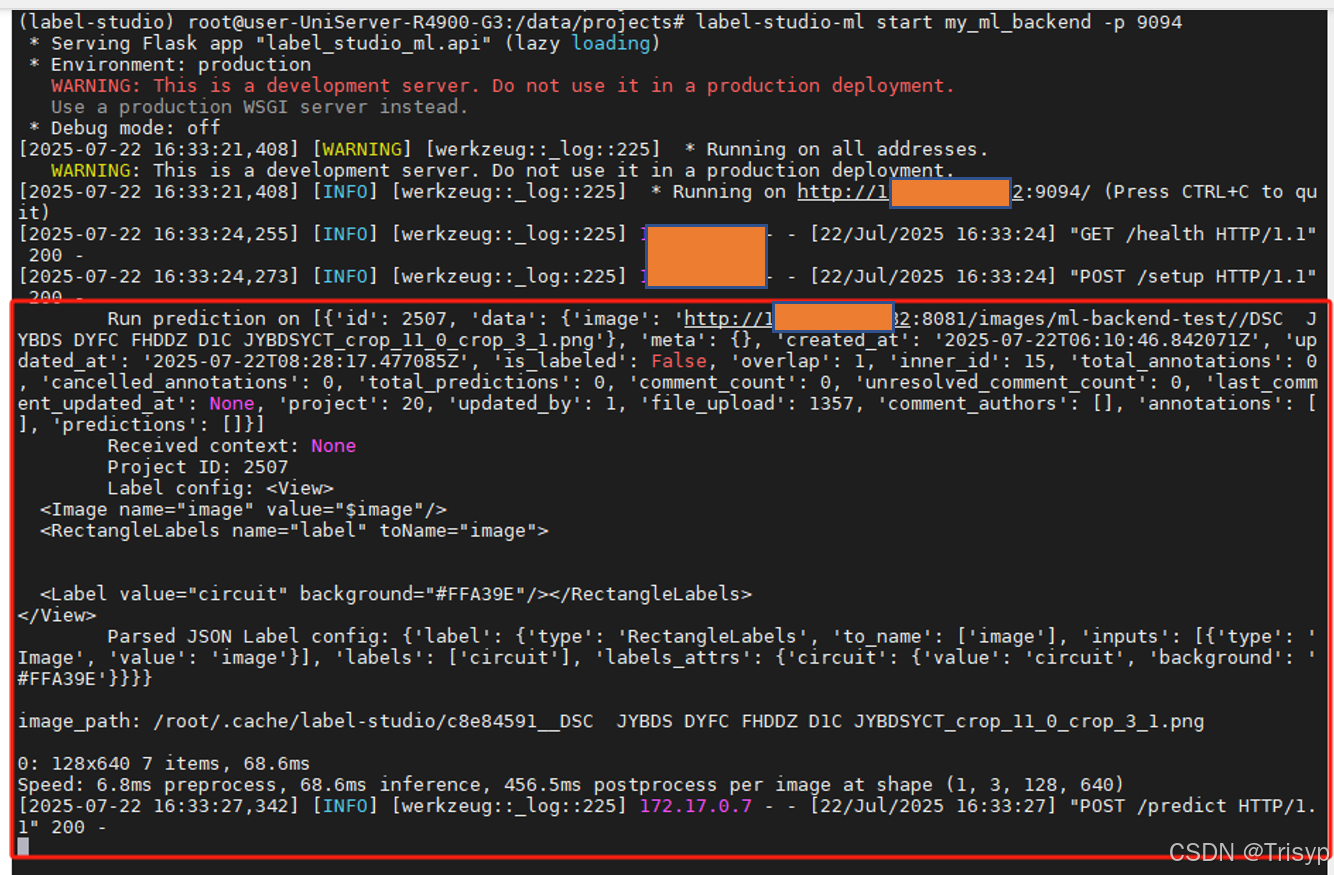
对应的脚本打印信息如下: