视频学习:
链接1: 程序员卡尔 图论:并查集理论基础!
链接2: 并查集(Union Find)
并查集介绍
并查集(Union-Find)是一种用于处理不相交集合的合并与查询问题的树型数据结构,特别适合解决动态连通性问题。它支持两种基本操作:合并(Union) 和 查找(Find),因此得名。
并查集基本操作:
1.查找find(x) 查找x的根节点。 递归查找,路径压缩。
python中 self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x]) 是赋值语句,没有返回值。
2.union(x,y) 合并两个集合。 按秩合并。
python
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, size):
"""初始化并查集,每个元素指向自己,秩为0"""
self.parent = list(range(size))
self.rank = [0] * size
self.count = size # 连通分量计数
def find(self, x):
"""查找根节点(路径压缩优化)"""
if self.parent[x] == x
return x
else:
# 递归查找并压缩路径
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
"""合并两个集合(按秩合并优化)"""
rootX = self.find(x)
rootY = self.find(y)
# 已在同一集合中
if rootX == rootY:
return False
# 按秩合并:小树挂到大树下
if self.rank[rootX] < self.rank[rootY]:
self.parent[rootX] = rootY
elif self.rank[rootX] > self.rank[rootY]:
self.parent[rootY] = rootX
else:
# 秩相同则任意挂接,并增加秩
self.parent[rootY] = rootX
self.rank[rootX] += 1
self.count -= 1 # 连通分量减少
return True
def connected(self, x, y):
"""检查两个元素是否连通"""
return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
def components(self):
"""返回当前连通分量数量"""
return self.count使用示例
python
# 创建并查集(10个元素)
uf = UnionFind(10)
# 初始状态:10个独立集合
print("初始连通分量:", uf.components()) # 输出: 10
# 建立连接关系
uf.union(1, 2)
uf.union(2, 5)
uf.union(5, 6)
uf.union(3, 8)
# 检查连通性
print("1和6是否连通:", uf.connected(1, 6)) # 输出: True
print("3和8是否连通:", uf.connected(3, 8)) # 输出: True
print("1和8是否连通:", uf.connected(1, 8)) # 输出: False
# 合并两个连通分量
uf.union(6, 8)
print("合并后1和8是否连通:", uf.connected(1, 8)) # 输出: True
print("当前连通分量:", uf.components()) # 输出: 6#并查集在连通性问题中的应用
并查集(Union-Find)数据结构是解决连通性问题的利器,特别适合处理动态连接关系。下面我将通过几个典型应用场景展示如何使用Python实现并查集解决实际问题。
1.计算图的连通分量数量
python
def count_components(n, edges):
uf = UnionFind(n)
for a, b in edges:
uf.union(a, b)
return uf.components()
# 示例:4个节点,2条边
edges = [[0, 1], [2, 3]]
print("连通分量:", count_components(4, edges)) # 输出: 22. 网络连接检测
检测计算机网络中设备之间的连通性:
python
class Network:
def __init__(self, n):
"""初始化网络,n个设备"""
self.uf = UnionFind(n)
def connect(self, device1, device2):
"""连接两个设备"""
self.uf.union(device1, device2)
print(f"已连接设备 {device1} 和 {device2}")
def is_connected(self, device1, device2):
"""检查两个设备是否连通"""
connected = self.uf.connected(device1, device2)
print(f"设备 {device1} 和 {device2} {'连通' if connected else '不连通'}")
return connected
def network_components(self):
"""返回网络中的连通分量数量"""
count = self.uf.components()
print(f"当前网络有 {count} 个独立子网")
return count
# 使用示例
net = Network(6) # 创建6个设备的网络
net.network_components() # 输出: 当前网络有 6 个独立子网
net.connect(0, 1)
net.connect(1, 2)
net.connect(3, 4)
net.is_connected(0, 2) # 输出: 设备 0 和 2 连通
net.is_connected(0, 3) # 输出: 设备 0 和 3 不连通
net.network_components() # 输出: 当前网络有 3 个独立子网
net.connect(2, 4) # 连接两个子网
net.is_connected(0, 4) # 输出: 设备 0 和 4 连通
net.network_components() # 输出: 当前网络有 2 个独立子网3. 朋友圈关系分析
分析社交网络中的朋友圈关系:
python
class SocialNetwork:
def __init__(self, people):
"""初始化社交网络,people是人员列表"""
self.people = people
self.id_map = {name: i for i, name in enumerate(people)}
self.uf = UnionFind(len(people))
def add_friendship(self, person1, person2):
"""添加朋友关系"""
id1 = self.id_map[person1]
id2 = self.id_map[person2]
self.uf.union(id1, id2)
print(f"{person1} 和 {person2} 成为朋友")
def in_same_circle(self, person1, person2):
"""检查两人是否在同一个朋友圈"""
id1 = self.id_map[person1]
id2 = self.id_map[person2]
same_circle = self.uf.connected(id1, id2)
print(f"{person1} 和 {person2} {'在' if same_circle else '不在'}同一个朋友圈")
return same_circle
def friend_circles(self):
"""返回所有朋友圈"""
circles = {}
for i, person in enumerate(self.people):
root = self.uf.find(i)
if root not in circles:
circles[root] = []
circles[root].append(person)
print("\n当前朋友圈:")
for circle in circles.values():
print(f" - {', '.join(circle)}")
return list(circles.values())
# 使用示例
people = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie", "David", "Eve", "Frank"]
social_net = SocialNetwork(people)
social_net.add_friendship("Alice", "Bob")
social_net.add_friendship("Bob", "Charlie")
social_net.add_friendship("David", "Eve")
social_net.in_same_circle("Alice", "Charlie") # 在同一个朋友圈
social_net.in_same_circle("Alice", "David") # 不在同一个朋友圈
social_net.add_friendship("Charlie", "Eve") # 合并两个朋友圈
social_net.friend_circles()4. Kruskal最小生成树算法
在图论中使用并查集实现Kruskal算法:
python
def kruskal_mst(nodes, edges):
"""
使用Kruskal算法计算最小生成树
:param nodes: 节点列表
:param edges: 边列表,格式为[(node1, node2, weight), ...]
:return: 最小生成树的边列表
"""
# 创建并查集
node_ids = {node: i for i, node in enumerate(nodes)}
uf = UnionFind(len(nodes))
# 按权重对边进行排序
edges.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
mst = [] # 最小生成树
total_weight = 0
for edge in edges:
node1, node2, weight = edge
id1, id2 = node_ids[node1], node_ids[node2]
# 如果两个节点不在同一个集合中,则不会形成环
if not uf.connected(id1, id2):
uf.union(id1, id2)
mst.append(edge)
total_weight += weight
# 如果已经连接所有节点,提前结束
if len(mst) == len(nodes) - 1:
break
# 检查是否形成完整生成树
if len(mst) < len(nodes) - 1:
print("图不连通,无法形成完整生成树")
return None
print(f"最小生成树权重: {total_weight}")
print("最小生成树包含边:")
for edge in mst:
print(f"{edge[0]} -- {edge[1]} (权重: {edge[2]})")
return mst
# 使用示例
nodes = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
edges = [
('A', 'B', 4),
('A', 'C', 2),
('B', 'C', 1),
('B', 'D', 5),
('C', 'D', 8),
('C', 'E', 10),
('D', 'E', 2)
]
mst = kruskal_mst(nodes, edges)4. 岛屿数量问题
解决LeetCode上的岛屿数量问题:
python
def num_islands(grid):
"""
计算二维网格中的岛屿数量
:param grid: 二维网格,'1'表示陆地,'0'表示水
:return: 岛屿数量
"""
if not grid:
return 0
rows, cols = len(grid), len(grid[0])
uf = UnionFind(rows * cols)
# 记录陆地数量
land_count = 0
# 遍历网格
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
if grid[i][j] == '1':
land_count += 1
index = i * cols + j
# 检查上方是否是陆地
if i > 0 and grid[i-1][j] == '1':
up_index = (i-1) * cols + j
if uf.union(index, up_index):
land_count -= 1
# 检查左方是否是陆地
if j > 0 and grid[i][j-1] == '1':
left_index = i * cols + (j-1)
if uf.union(index, left_index):
land_count -= 1
return land_count
# 使用示例
grid = [
['1', '1', '0', '0', '0'],
['1', '1', '0', '0', '0'],
['0', '0', '1', '0', '0'],
['0', '0', '0', '1', '1']
]
print("岛屿数量:", num_islands(grid)) # 输出: 3OD题目
【华为OD机试真题】436、5G网络建设 | 机试真题+思路参考+代码解析(最新CD卷抽中)
题目描述 :
现需要在某城市进行5G网络建设,已经选取N个地点设置5G基站,编号固定为1到N,接下来需要各个基站之间使用光纤进行连接以确保基站能互联互通,不同基站之间架设光纤的成本各不相同,且有些节点之间可能存在光纤相连,请你设计算法,计算出能联通这些基站的最小成本是多少。
注意:基站的联通具有传递性,如基站A与基站B架设了光纤,基站B与基站C也架设了光纤,则基站A与基站C视为可以互相联通。
输入输出:
输入
第一行输入表示基站的个数N,其中0<N<=20
第二行输入表示具备光纤直连条件的基站对的数目M,其中0<M<=N*(N-1)/2
第三行开始连续输入M行数据,格式为X Y Z P,其中X、Y表示基站的编号,0<X<=N, 0<Y<=N且X不等于Y,Z表示在X Y之间架设光纤的成本,其中0<Z<100,P表示是否已存在光纤连接,0表示未连接,1表示已连接
输出
如果给定条件,可以建设成功互联互通的5G网络,则输出最小的建设成本;
如果给定条件,无法建设成功互联互通的5G网络,则输出-1
输入
3
3
1 2 3 0
1 3 1 0
2 3 5 0
输出
4
python
# 并查集数据结构
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
# 初始化每个节点的父节点为其自身
self.parent = [i for i in range(n)]
def find(self, x):
# 查找节点x的根节点
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
# 合并节点x和y所在的集合
root_x = self.find(x)
root_y = self.find(y)
if root_x != root_y:
self.parent[root_y] = root_x
return True
return False
# 计算连接所有站点的最小成本
def min_cost_to_connect_stations(N, connections):
uf = UnionFind(N)
total_cost = 0
# 首先处理已经存在的连接,不增加额外成本
for x, y, cost, connected in connections:
if connected == 1:
uf.union(x - 1, y - 1) # 减1是因为并查集中节点索引是从0开始的
# 对所有未连接的边按成本从低到高排序
remaining_connections = [c for c in connections if c[3] == 0]
remaining_connections.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
# 使用克鲁斯卡尔算法逐条检查未连接的边
for x, y, cost, connected in remaining_connections:
# 如果添加这条边不会造成循环,则添加到MST中
if uf.union(x - 1, y - 1):
total_cost += cost
# 检查是否所有节点都已经连接在同一棵树上
root = uf.find(0)
for i in range(1, N):
if uf.find(i) != root:
return -1 # 如果有节点未连接,返回-1
return total_cost
# 读取输入数据
N = int(input())
M = int(input())
connections = []
for _ in range(M):
x, y, z, p = map(int, input().split())
connections.append((x, y, z, p))
# 计算最小成本并输出
min_cost = min_cost_to_connect_stations(N, connections)
print(min_cost)【华为OD机试真题】287、图像物体的边界 | 机试真题+思路参考+代码分析
项目描述:
给定一个二维数组M行N列,二维数组里的数字代表图片的像素,为了简化问题,仅包含像素1和5两种像素,每种像素代表一个物体,2个物体相邻的格子为边界,求像素1代表的物体的边界的个数。
像素1代表的物体的边界指与像素5相邻的像素1的格子,边界相邻的属于同一个边界,相邻需要考虑8个方向(上,下,左,右,左上,左下,右上,右下)。
其他约束:
地图规格约束为:
0 < M = 100
0 < N = 100
1.如下图,与像素5的格子相邻的像素1的格子(0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(1,0),(1,2),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2),(4,4),(4,5),(5,4)为边界,另(0,0),(0,1),(0,2),(1,0),(1,2),(2,0),(2,1),(2,2)相邻,为1个边界;(4,4),(4,5),(5,4)相邻,为1个边界,所以下图边界个数为2。
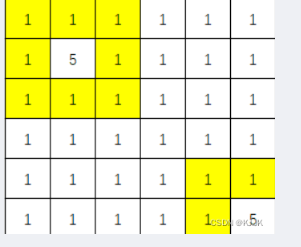
输入
6 6
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 5 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 5
输出
2
python
# 并查集数据结构
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
# 初始化每个节点的父节点为其自身
self.parent = [i for i in range(n)]
def find(self, x):
# 查找节点x的根节点
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
# 合并节点x和y所在的集合
root_x = self.find(x)
root_y = self.find(y)
if root_x != root_y:
self.parent[root_y] = root_x
return True
return False
# 计算连接所有站点的最小成本
def min_cost_to_connect_stations(N, connections):
uf = UnionFind(N)
total_cost = 0
# 首先处理已经存在的连接,不增加额外成本
for x, y, cost, connected in connections:
if connected == 1:
uf.union(x - 1, y - 1) # 减1是因为并查集中节点索引是从0开始的
# 对所有未连接的边按成本从低到高排序
remaining_connections = [c for c in connections if c[3] == 0]
remaining_connections.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
# 使用克鲁斯卡尔算法逐条检查未连接的边
for x, y, cost, connected in remaining_connections:
# 如果添加这条边不会造成循环,则添加到MST中
if uf.union(x - 1, y - 1):
total_cost += cost
# 检查是否所有节点都已经连接在同一棵树上
root = uf.find(0)
for i in range(1, N):
if uf.find(i) != root:
return -1 # 如果有节点未连接,返回-1
return total_cost
# 读取输入数据
N = int(input())
M = int(input())
connections = []
for _ in range(M):
x, y, z, p = map(int, input().split())
connections.append((x, y, z, p))
# 计算最小成本并输出
min_cost = min_cost_to_connect_stations(N, connections)
print(min_cost)并查集的优势
- 高效处理动态连通性问题:在添加新连接时能够快速更新连通状态
- 时间复杂度优异:路径压缩和按秩合并使操作接近常数时间
- 空间复杂度低:仅需O(n)额外空间
- 实现简洁:核心代码只需几十行,易于理解和实现
这些示例展示了并查集在各种连通性问题中的强大应用能力,从网络连接到社交关系分析,再到图论算法和二维网格问题。通过并查集,我们可以高效解决许多看似复杂的连通性问题。