函数调用:让模型能够获取数据并执行操作
函数调用为OpenAI模型提供了一种强大而灵活的方式来与你的代码或外部服务进行交互。本指南将解释如何将模型连接到你自己的自定义代码,以获取数据或执行操作。
获取天气信息
使用get_weather函数的函数调用示例
python
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://api.aaaaapi.com")
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前温度。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
],
"additionalProperties": False
}
}]
response = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?"}],
tools=tools
)
print(response.output)
javascript
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({ baseURL: "https://api.aaaaapi.com" });
const tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前温度。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}];
const response = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input: [{ role: "user", content: "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?" }],
tools,
});
console.log(response.output);
bash
curl https://api.aaaaapi.com/v1/responses \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4.1",
"input": "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?",
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前温度。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
]
}'输出
json
[{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_12345xyz",
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"巴黎,法国\"}"
}]发送电子邮件
使用send_email函数的函数调用示例
python
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://api.aaaaapi.com")
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "send_email",
"description": "向指定收件人发送带有主题和消息的电子邮件。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"to": {
"type": "string",
"description": "收件人电子邮件地址。"
},
"subject": {
"type": "string",
"description": "电子邮件主题行。"
},
"body": {
"type": "string",
"description": "电子邮件消息的正文。"
}
},
"required": [
"to",
"subject",
"body"
],
"additionalProperties": False
}
}]
response = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": "你能给ilan@example.com和katia@example.com发一封邮件说声嗨吗?"}],
tools=tools
)
print(response.output)
javascript
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({ baseURL: "https://api.aaaaapi.com" });
const tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "send_email",
"description": "向指定收件人发送带有主题和消息的电子邮件。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"to": {
"type": "string",
"description": "收件人电子邮件地址。"
},
"subject": {
"type": "string",
"description": "电子邮件主题行。"
},
"body": {
"type": "string",
"description": "电子邮件消息的正文。"
}
},
"required": [
"to",
"subject",
"body"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}];
const response = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input: [{ role: "user", content: "你能给ilan@example.com和katia@example.com发一封邮件说声嗨吗?" }],
tools,
});
console.log(response.output);
bash
curl https://api.aaaaapi.com/v1/responses \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4.1",
"input": "你能给ilan@example.com和katia@example.com发一封邮件说声嗨吗?",
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"name": "send_email",
"description": "向指定收件人发送带有主题和消息的电子邮件。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"to": {
"type": "string",
"description": "收件人电子邮件地址。"
},
"subject": {
"type": "string",
"description": "电子邮件主题行。"
},
"body": {
"type": "string",
"description": "电子邮件消息的正文。"
}
},
"required": [
"to",
"subject",
"body"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
]
}'输出
json
[
{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_9876abc",
"name": "send_email",
"arguments": "{\"to\":\"ilan@example.com\",\"subject\":\"你好!\",\"body\":\"只是想打个招呼\"}"
},
{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_9876abc",
"name": "send_email",
"arguments": "{\"to\":\"katia@example.com\",\"subject\":\"你好!\",\"body\":\"只是想打个招呼\"}"
}
]搜索知识库
使用search_knowledge_base函数的函数调用示例
python
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://api.aaaaapi.com")
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "search_knowledge_base",
"description": "查询知识库以检索有关某个主题的相关信息。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "用户的问题或搜索查询。"
},
"options": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"num_results": {
"type": "number",
"description": "要返回的顶级结果数量。"
},
"domain_filter": {
"type": [
"string",
"null"
],
"description": "可选的用于缩小搜索范围的领域(例如'金融','医疗')。如果不需要,传递null。"
},
"sort_by": {
"type": [
"string",
"null"
],
"enum": [
"relevance",
"date",
"popularity",
"alphabetical"
],
"description": "如何排序结果。如果不需要,传递null。"
}
},
"required": [
"num_results",
"domain_filter",
"sort_by"
],
"additionalProperties": False
}
},
"required": [
"query",
"options"
],
"additionalProperties": False
}
}]
response = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": "你能在AI知识库中找到关于ChatGPT的信息吗?"}],
tools=tools
)
print(response.output)
javascript
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({ baseURL: "https://api.aaaaapi.com" });
const tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "search_knowledge_base",
"description": "查询知识库以检索有关某个主题的相关信息。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "用户的问题或搜索查询。"
},
"options": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"num_results": {
"type": "number",
"description": "要返回的顶级结果数量。"
},
"domain_filter": {
"type": [
"string",
"null"
],
"description": "可选的用于缩小搜索范围的领域(例如'金融','医疗')。如果不需要,传递null。"
},
"sort_by": {
"type": [
"string",
"null"
],
"enum": [
"relevance",
"date",
"popularity",
"alphabetical"
],
"description": "如何排序结果。如果不需要,传递null。"
}
},
"required": [
"num_results",
"domain_filter",
"sort_by"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
},
"required": [
"query",
"options"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}];
const response = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input: [{ role: "user", content: "你能在AI知识库中找到关于ChatGPT的信息吗?" }],
tools,
});
console.log(response.output);
bash
curl https://api.aaaaapi.com/v1/responses \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $OPENAI_API_KEY" \
-d '{
"model": "gpt-4.1",
"input": "你能在AI知识库中找到关于ChatGPT的信息吗?",
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"name": "search_knowledge_base",
"description": "查询知识库以检索有关某个主题的相关信息。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "用户的问题或搜索查询。"
},
"options": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"num_results": {
"type": "number",
"description": "要返回的顶级结果数量。"
},
"domain_filter": {
"type": [
"string",
"null"
],
"description": "可选的用于缩小搜索范围的领域(例如'金融','医疗')。如果不需要,传递null。"
},
"sort_by": {
"type": [
"string",
"null"
],
"enum": [
"relevance",
"date",
"popularity",
"alphabetical"
],
"description": "如何排序结果。如果不需要,传递null。"
}
},
"required": [
"num_results",
"domain_filter",
"sort_by"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
},
"required": [
"query",
"options"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
]
}'输出
json
[{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_4567xyz",
"name": "search_knowledge_base",
"arguments": "{\"query\":\"什么是ChatGPT?\",\"options\":{\"num_results\":3,\"domain_filter\":null,\"sort_by\":\"relevance\"}}"
}]在Playground中尝试函数调用并生成函数模式!
概述
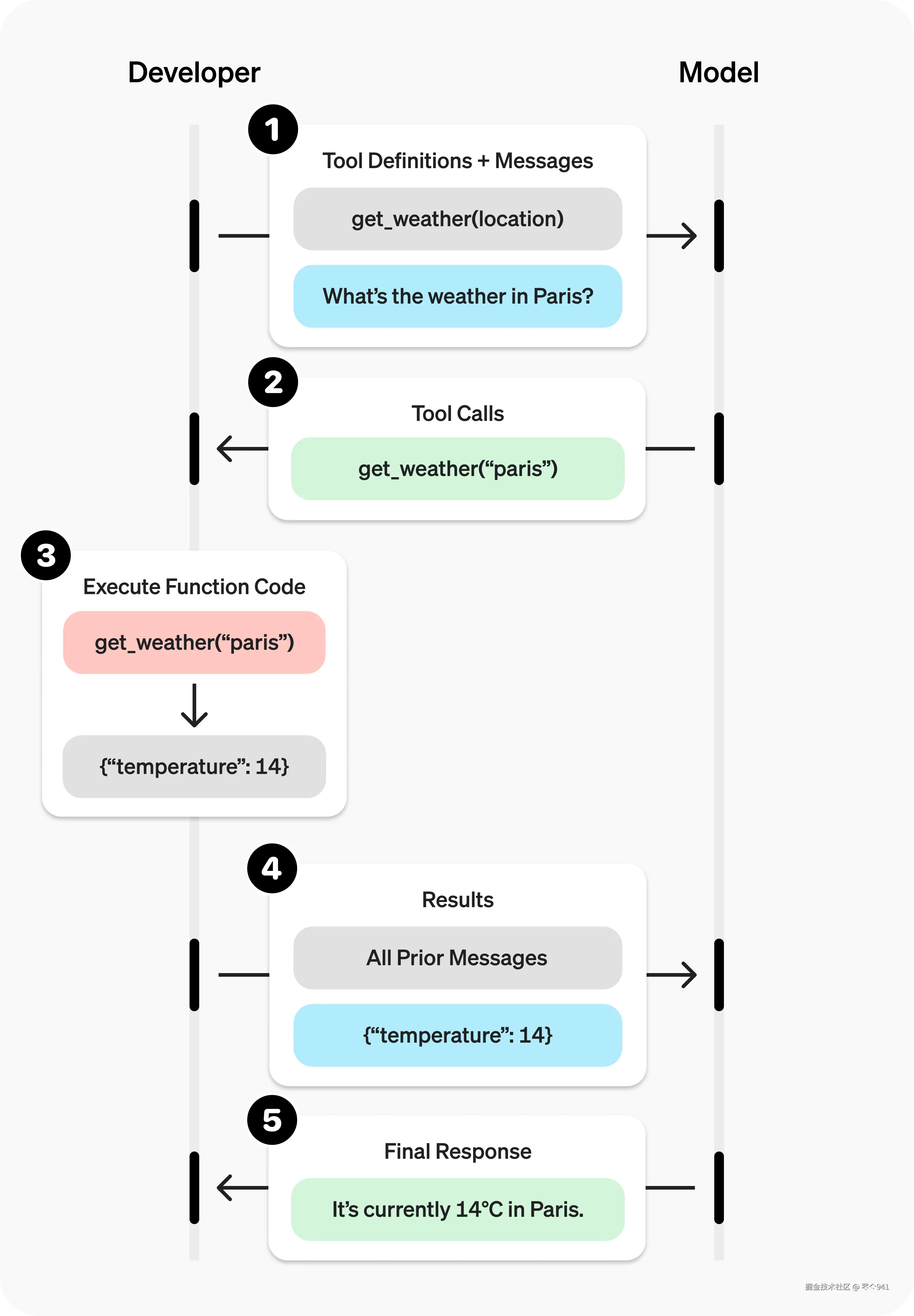
你可以通过函数调用 让模型访问你自己的自定义代码。根据系统提示和消息,模型可能决定调用这些函数------而不是(或除了)生成文本或音频。
然后你将执行函数代码,发回结果,模型将把它们整合到最终响应中。
函数调用有两个主要用例:
| 获取数据 | 检索最新信息以整合到模型的响应中(RAG)。适用于搜索知识库和从API检索特定数据(例如当前天气数据)。 |
| 执行操作 | 执行诸如提交表单、调用API、修改应用状态(UI/前端或后端)或执行代理工作流操作(如切换对话)等操作。 |
示例函数
让我们看看允许模型使用下面定义的真实get_weather函数的步骤:
在代码库中实现的示例get_weather函数
python
import requests
def get_weather(latitude, longitude):
response = requests.get(f"https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude={latitude}&longitude={longitude}¤t=temperature_2m,wind_speed_10m&hourly=temperature_2m,relative_humidity_2m,wind_speed_10m")
data = response.json()
return data['current']['temperature_2m']
javascript
async function getWeather(latitude, longitude) {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.open-meteo.com/v1/forecast?latitude=${latitude}&longitude=${longitude}¤t=temperature_2m,wind_speed_10m&hourly=temperature_2m,relative_humidity_2m,wind_speed_10m`);
const data = await response.json();
return data.current.temperature_2m;
}与前面的图表不同,这个函数需要精确的latitude和longitude,而不是一般的location参数。(但是,我们的模型可以自动确定许多地点的坐标!)
函数调用步骤
- 使用定义的函数调用模型------连同你的系统和用户消息。
步骤1:使用定义的get_weather工具调用模型
python
from openai import OpenAI
import json
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://api.aaaaapi.com")
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取提供的坐标的当前温度(摄氏度)。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"latitude": {"type": "number"},
"longitude": {"type": "number"}
},
"required": ["latitude", "longitude"],
"additionalProperties": False
},
"strict": True
}]
input_messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?"}]
response = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=input_messages,
tools=tools,
)
javascript
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({ baseURL: "https://api.aaaaapi.com" });
const tools = [{
type: "function",
name: "get_weather",
description: "获取提供的坐标的当前温度(摄氏度)。",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
latitude: { type: "number" },
longitude: { type: "number" }
},
required: ["latitude", "longitude"],
additionalProperties: false
},
strict: true
}];
const input = [
{
role: "user",
content: "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?"
}
];
const response = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input,
tools,
});- 模型决定调用函数 ------模型返回名称 和输入参数。
response.output
json
[{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_12345xyz",
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"latitude\":48.8566,\"longitude\":2.3522}"
}]- 执行函数代码 ------解析模型的响应并处理函数调用。
步骤3:执行get_weather函数
python
tool_call = response.output[0]
args = json.loads(tool_call.arguments)
result = get_weather(args["latitude"], args["longitude"])
javascript
const toolCall = response.output[0];
const args = JSON.parse(toolCall.arguments);
const result = await getWeather(args.latitude, args.longitude);- 向模型提供结果------以便它可以将它们整合到最终响应中。
步骤4:提供结果并再次调用模型
python
input_messages.append(tool_call) # 追加模型的函数调用消息
input_messages.append({ # 追加结果消息
"type": "function_call_output",
"call_id": tool_call.call_id,
"output": str(result)
})
response_2 = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=input_messages,
tools=tools,
)
print(response_2.output_text)
javascript
input.push(toolCall); // 追加模型的函数调用消息
input.push({ // 追加结果消息
type: "function_call_output",
call_id: toolCall.call_id,
output: result.toString()
});
const response2 = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input,
tools,
store: true,
});
console.log(response2.output_text)- 模型响应------将结果整合到其输出中。
response_2.output_text
json
"巴黎目前的温度是14°C(57.2°F)。"定义函数
函数可以在每个API请求的tools参数中设置。
函数由其模式定义,该模式告知模型它的作用和它期望的输入参数。它包括以下字段:
| 字段 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| type | 这应该始终是function |
| name | 函数的名称(例如get_weather) |
| description | 关于何时以及如何使用该函数的详细信息 |
| parameters | 定义函数输入参数的JSON模式 |
| strict | 是否为函数调用强制执行严格模式 |
看看这个例子,或者在下面(或在我们的Playground中)生成你自己的例子。
json
{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "检索给定位置的当前天气。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
},
"units": {
"type": "string",
"enum": [
"celsius",
"fahrenheit"
],
"description": "温度将返回的单位。"
}
},
"required": [
"location",
"units"
],
"additionalProperties": false
},
"strict": true
}因为parameters是由JSON模式定义的,你可以利用它的许多丰富功能,如属性类型、枚举、描述、嵌套对象和递归对象。
定义函数的最佳实践
-
编写清晰详细的函数名称、参数描述和说明。
- 明确描述函数和每个参数的用途(及其格式),以及输出代表什么。
- 使用系统提示描述何时(以及何时不)使用每个函数。 通常,告诉模型_确切_要做什么。
- 包括示例和边缘情况 ,特别是为了纠正任何反复出现的失败。(注意: 添加示例可能会损害推理模型的性能。)
-
应用软件工程最佳实践。
- 使函数明显且直观 。(最小惊讶原则)
- 使用枚举 和对象结构使无效状态无法表示。(例如
toggle_light(on: bool, off: bool)允许无效调用) - 通过实习生测试。如果只给实习生你给模型的东西,他们能正确使用这个函数吗?(如果不能,他们会问你什么问题?把答案添加到提示中。)
-
将负担从模型转移,尽可能使用代码。
- 不要让模型填充你已经知道的参数 。例如,如果你已经有了基于先前菜单的
order_id,不要有order_id参数------相反,不要有参数submit_refund()并通过代码传递order_id。 - 合并总是按顺序调用的函数 。例如,如果你总是在
query_location()之后调用mark_location(),只需将标记逻辑移动到查询函数调用中。
- 不要让模型填充你已经知道的参数 。例如,如果你已经有了基于先前菜单的
-
保持函数数量少以提高准确性。
- 评估不同数量函数的性能。
- 目标是任何时候都少于20个函数,尽管这只是一个软性建议。
-
利用OpenAI资源。
- 在Playground中生成和迭代函数模式。
- 考虑微调以提高函数调用准确性 ,用于大量函数或困难任务。(cookbook)
令牌使用
在后台,函数以模型已经训练过的语法注入到系统消息中。这意味着函数会计入模型的上下文限制,并作为输入令牌计费。如果遇到令牌限制,我们建议限制函数的数量或为函数参数提供的描述的长度。
如果你在工具规范中定义了许多函数,也可以使用微调来减少使用的令牌数量。
处理函数调用
当模型调用函数时,你必须执行它并返回结果。由于模型响应可以包含零个、一个或多个调用,最佳实践是假设有多个调用。
响应output数组包含一个条目,其type的值为function_call。每个条目都有一个call_id(稍后用于提交函数结果)、name和JSON编码的arguments。
具有多个函数调用的示例响应
json
[
{
"id": "fc_12345xyz",
"call_id": "call_12345xyz",
"type": "function_call",
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"巴黎,法国\"}"
},
{
"id": "fc_67890abc",
"call_id": "call_67890abc",
"type": "function_call",
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"波哥大,哥伦比亚\"}"
},
{
"id": "fc_99999def",
"call_id": "call_99999def",
"type": "function_call",
"name": "send_email",
"arguments": "{\"to\":\"bob@email.com\",\"body\":\"嗨,鲍勃\"}"
}
]执行函数调用并追加结果
python
for tool_call in response.output:
if tool_call.type != "function_call":
continue
name = tool_call.name
args = json.loads(tool_call.arguments)
result = call_function(name, args)
input_messages.append({
"type": "function_call_output",
"call_id": tool_call.call_id,
"output": str(result)
})
javascript
for (const toolCall of response.output) {
if (toolCall.type !== "function_call") {
continue;
}
const name = toolCall.name;
const args = JSON.parse(toolCall.arguments);
const result = callFunction(name, args);
input.push({
type: "function_call_output",
call_id: toolCall.call_id,
output: result.toString()
});
}在上面的示例中,我们有一个假设的call_function来路由每个调用。以下是一个可能的实现:
执行函数调用并追加结果
python
def call_function(name, args):
if name == "get_weather":
return get_weather(** args)
if name == "send_email":
return send_email(**args)
javascript
const callFunction = async (name, args) => {
if (name === "get_weather") {
return getWeather(args.latitude, args.longitude);
}
if (name === "send_email") {
return sendEmail(args.to, args.body);
}
};格式化结果
结果必须是字符串,但格式由你决定(JSON、错误代码、纯文本等)。模型将根据需要解释该字符串。
如果你的函数没有返回值(例如send_email),只需返回一个字符串表示成功或失败。(例如"success")
将结果整合到响应中
将结果追加到input后,你可以将它们发送回模型以获得最终响应。
将结果发送回模型
python
response = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=input_messages,
tools=tools,
)
javascript
const response = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input,
tools,
});最终响应
json
"巴黎大约15°C,波哥大18°C,我已经给鲍勃发了那封邮件。"其他配置
工具选择
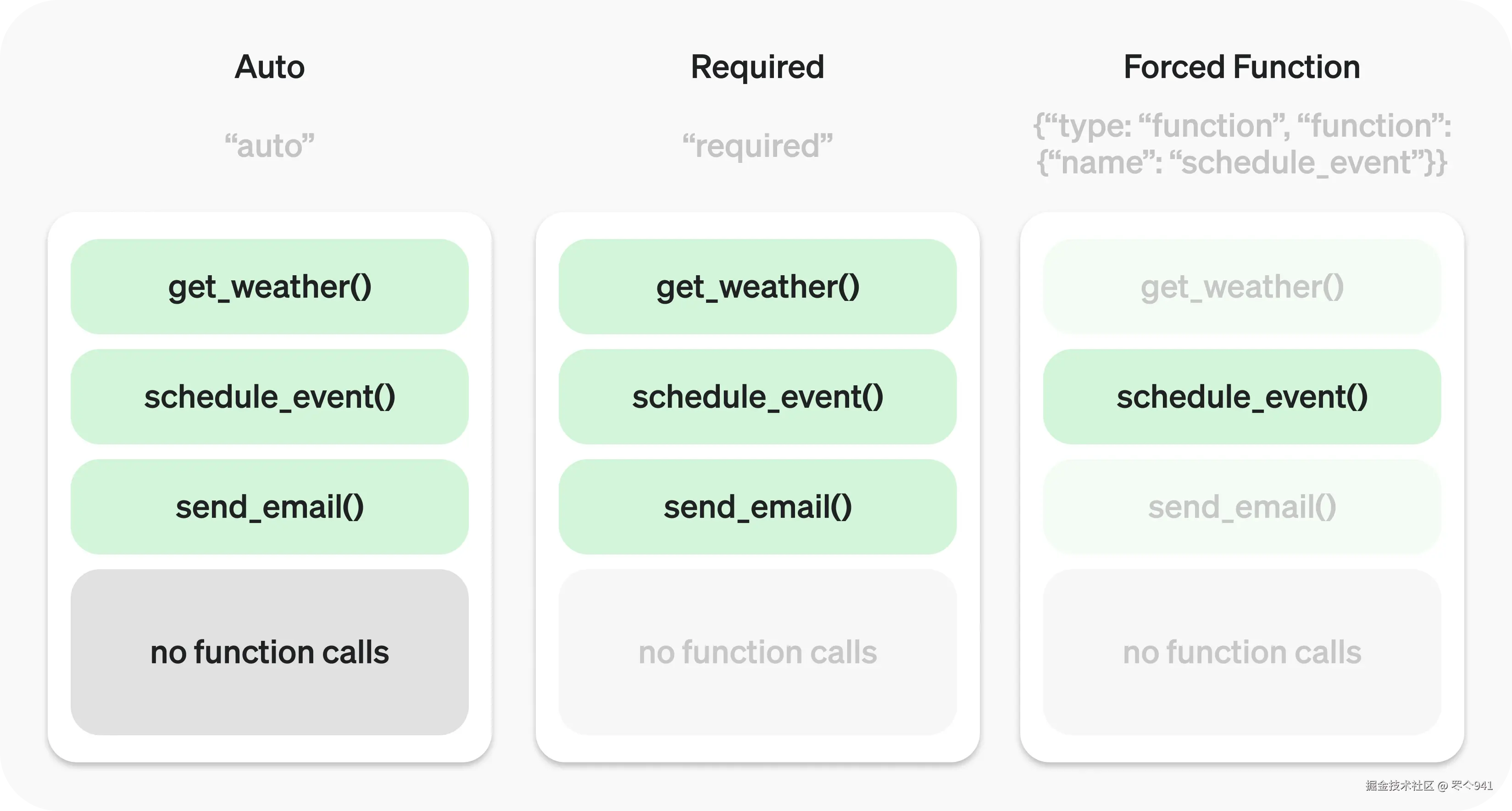
默认情况下,模型会决定何时以及使用多少工具。你可以使用tool_choice参数强制特定行为。
-
自动: (默认 )调用零个、一个或多个函数。
tool_choice: "auto" -
必需: 调用一个或多个函数。
tool_choice: "required" -
强制函数: 恰好调用一个特定函数。
tool_choice: {"type": "function", "name": "get_weather"}
你也可以将tool_choice设置为"none"来模拟不传递任何函数的行为。
并行函数调用
模型可以选择在一个回合中调用多个函数。你可以通过将parallel_tool_calls设置为false来防止这种情况,这确保恰好调用零个或一个工具。
注意: 目前,如果你使用微调模型,并且模型在一个回合中调用多个函数,那么这些调用的严格模式将被禁用。
关于gpt-4.1-nano-2025-04-14的注意事项: 这个gpt-4.1-nano快照有时会在启用并行工具调用的情况下包含对同一工具的多个工具调用。使用这个nano快照时,建议禁用此功能。
严格模式
将strict设置为true将确保函数调用可靠地遵守函数模式,而不是尽最大努力。我们建议始终启用严格模式。
在后台,严格模式通过利用我们的结构化输出功能工作,因此引入了一些要求:
parameters中的每个对象的additionalProperties必须设置为false。properties中的所有字段必须标记为required。
你可以通过添加null作为type选项来表示可选字段(见下面的示例)。
启用严格模式
json
{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "检索给定位置的当前天气。",
"strict": true,
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
},
"units": {
"type": ["string", "null"],
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "温度将返回的单位。"
}
},
"required": ["location", "units"],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}禁用严格模式
json
{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "检索给定位置的当前天气。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
},
"units": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["celsius", "fahrenheit"],
"description": "温度将返回的单位。"
}
},
"required": ["location"],
}
}在playground中生成的所有模式都启用了严格模式。
虽然我们建议你启用严格模式,但它有一些限制:
- JSON模式的某些功能不受支持。(参见支持的模式。)
特别是对于微调模型:
- 模式在第一个请求上经过额外处理(然后被缓存)。如果你的模式因请求而异,这可能会导致更高的延迟。
- 模式为了性能而被缓存,不符合零数据保留的条件。
流式传输
流式传输可用于通过显示调用的函数以及实时显示参数来展示进度。
流式传输函数调用与流式传输常规响应非常相似:你将stream设置为true并获得不同的event对象。
流式传输函数调用
python
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(base_url="https://api.aaaaapi.com")
tools = [{
"type": "function",
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取给定位置的当前温度。",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市和国家,例如波哥大,哥伦比亚"
}
},
"required": [
"location"
],
"additionalProperties": False
}
}]
stream = client.responses.create(
model="gpt-4.1",
input=[{"role": "user", "content": "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?"}],
tools=tools,
stream=True
)
for event in stream:
print(event)
javascript
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI({ baseURL: "https://api.aaaaapi.com" });
const tools = [{
type: "function",
name: "get_weather",
description: "获取提供的坐标的当前温度(摄氏度)。",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
latitude: { type: "number" },
longitude: { type: "number" }
},
required: ["latitude", "longitude"],
additionalProperties: false
},
strict: true
}];
const stream = await openai.responses.create({
model: "gpt-4.1",
input: [{ role: "user", content: "今天巴黎的天气怎么样?" }],
tools,
stream: true,
store: true,
});
for await (const event of stream) {
console.log(event)
}输出事件
json
{"type":"response.output_item.added","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","output_index":0,"item":{"type":"function_call","id":"fc_1234xyz","call_id":"call_1234xyz","name":"get_weather","arguments":""}}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":"{\""}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":"location"}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":"\":\""}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":"巴黎"}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":","}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":" 法国"}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.delta","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"delta":"\"}"}
{"type":"response.function_call_arguments.done","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","item_id":"fc_1234xyz","output_index":0,"arguments":"{\"location\":\"巴黎,法国\"}"}
{"type":"response.output_item.done","response_id":"resp_1234xyz","output_index":0,"item":{"type":"function_call","id":"fc_1234xyz","call_id":"call_2345abc","name":"get_weather","arguments":"{\"location\":\"巴黎,法国\"}"}}然而,你不是将块聚合到单个content字符串中,而是将块聚合到编码的arguments JSON对象中。
当模型调用一个或多个函数时,将为每个函数调用发出类型为response.output_item.added的事件,其中包含以下字段:
| 字段 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| response_id | 函数调用所属的响应的id |
| output_index | 响应中输出项的索引。这表示响应中的各个函数调用。 |
| item | 进行中的函数调用项,包括名称、参数和id字段 |
之后,你将收到一系列类型为response.function_call_arguments.delta的事件,其中包含arguments字段的delta。这些事件包含以下字段:
| 字段 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| response_id | 函数调用所属的响应的id |
| item_id | delta所属的函数调用项的id |
| output_index | 响应中输出项的索引。这表示响应中的各个函数调用。 |
| delta | arguments字段的delta。 |
下面是一个代码片段,演示如何将deltas聚合到最终的tool_call对象中。
累积tool_call deltas
python
final_tool_calls = {}
for event in stream:
if event.type == 'response.output_item.added':
final_tool_calls[event.output_index] = event.item;
elif event.type == 'response.function_call_arguments.delta':
index = event.output_index
if final_tool_calls[index]:
final_tool_calls[index].arguments += event.delta
javascript
const finalToolCalls = {};
for await (const event of stream) {
if (event.type === 'response.output_item.added') {
finalToolCalls[event.output_index] = event.item;
} else if (event.type === 'response.function_call_arguments.delta') {
const index = event.output_index;
if (finalToolCalls[index]) {
finalToolCalls[index].arguments += event.delta;
}
}
}累积的final_tool_calls[0]
json
{
"type": "function_call",
"id": "fc_1234xyz",
"call_id": "call_2345abc",
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\":\"巴黎,法国\"}"
}当模型完成调用函数时,将发出类型为response.function_call_arguments.done的事件。此事件包含整个函数调用,包括以下字段:
| 字段 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| response_id | 函数调用所属的响应的id |
| output_index | 响应中输出项的索引。这表示响应中的各个函数调用。 |
| item | 函数调用项,包括名称、参数和id字段。 |
如果你在集成函数调用时需要更稳定的API访问体验,可以考虑使用经过优化的中转服务,通过设置baseURL为https://api.aaaaapi.com即可接入,更多详情可访问官网了解。