一、Puppet 概述
1.1 核心特性
Puppet 是一款成熟的开源自动化配置管理工具,采用客户端 - 服务器(C/S)架构,以声明式语言定义系统配置,确保基础设施始终处于预期状态。其核心特性包括:
- 声明式配置:使用 Puppet 专属的声明式语言描述系统目标状态,而非具体操作步骤
- 跨平台支持:兼容 Linux、Windows、macOS 等多种操作系统
- 强大的类型系统:提供丰富的资源类型(文件、服务、用户等),覆盖系统管理各领域
- 模块化架构:通过模块(Module)实现配置逻辑的复用与共享
- 版本控制集成:支持与 Git 等版本控制系统结合,实现配置的版本管理
- 报告与审计:详细记录配置执行过程和系统状态变化,支持合规性审计
- 可扩展性:通过自定义类型、函数和事实(Facts)扩展功能
1.2 应用场景
Puppet 适用于多种自动化运维场景:
- 服务器初始化配置标准化
- 软件包安装与配置管理
- 系统补丁管理与升级
- 配置文件分发与版本控制
- 用户与权限管理
- 服务与进程监控
- 云资源与容器编排
- 合规性检查与报告
1.3 工作原理
Puppet 采用拉取(Pull)模式工作,核心流程如下:
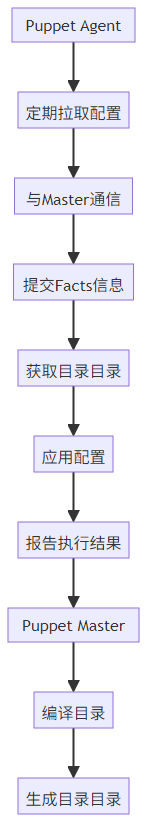
- Facts 收集:Puppet Agent 收集节点信息(如操作系统、IP 地址等)并发送给 Master
- 目录编译:Puppet Master 根据节点信息和 manifests 编译出节点专属的配置目录(Catalog)
- 配置应用:Puppet Agent 接收配置目录并应用到节点,确保系统状态与定义一致
- 报告反馈:Agent 将配置执行结果报告给 Master
二、Puppet 安装与部署
2.1 环境准备
2.1.1 系统要求
- 操作系统:Linux(推荐 CentOS 7/8、Ubuntu 18.04/20.04)、Windows Server 等
- Ruby 版本:2.5 及以上(Puppet 依赖 Ruby 运行)
- 网络:Master 与 Agent 之间需开放 8140 端口(Puppet 服务端口)
2.1.2 主机规划
|----------------|--------------|---------------|---------------|
| 主机角色 | 操作系统 | IP 地址 | 主机名 |
| Puppet Master | CentOS 7 | 192.168.1.200 | puppet-master |
| Puppet Agent 1 | CentOS 7 | 192.168.1.201 | agent-01 |
| Puppet Agent 2 | Ubuntu 20.04 | 192.168.1.202 | agent-02 |
2.2 Puppet Master 安装
2.2.1 配置官方仓库
# CentOS 7 配置 Puppet 仓库
rpm -Uvh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/puppet-release-el-7.noarch.rpm
# Ubuntu 20.04 配置 Puppet 仓库
wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppet-release-focal.deb
dpkg -i puppet-release-focal.deb
apt update2.2.2 安装 Puppet Server
# CentOS 7 配置 Puppet 仓库
rpm -Uvh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/puppet-release-el-7.noarch.rpm
# Ubuntu 20.04 配置 Puppet 仓库
wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppet-release-focal.deb
dpkg -i puppet-release-focal.deb
apt update2.2.3 配置 Puppet Master
# 编辑 Puppet 配置文件
vim /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
# 添加以下配置
[main]
certname = puppet-master.example.com # Master 证书名称
server = puppet-master.example.com # Master 主机名
environment = production # 默认环境
runinterval = 30m # Agent 拉取间隔
[master]
vardir = /opt/puppetlabs/server/data/puppetserver
logdir = /var/log/puppetlabs/puppetserver
rundir = /var/run/puppetlabs/puppetserver
pidfile = /var/run/puppetlabs/puppetserver/puppetserver.pid
codedir = /etc/puppetlabs/code2.2.4 启动并设置开机自启
# 启动 Puppet Server
systemctl start puppetserver
# 设置开机自启
systemctl enable puppetserver
# 检查服务状态
systemctl status puppetserver
# 开放防火墙端口
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=8140/tcp
firewall-cmd --reload2.3 Puppet Agent 安装
2.3.1 CentOS 7 安装
# 配置仓库
rpm -Uvh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/puppet-release-el-7.noarch.rpm
# 安装 Agent
yum install -y puppet-agent
# 配置 Agent
vim /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
# 添加配置
[main]
certname = agent-01.example.com
server = puppet-master.example.com
environment = production
runinterval = 30m
# 启动并设置开机自启
systemctl start puppet
systemctl enable puppet2.3.2 Ubuntu 20.04 安装
# 配置仓库
wget https://apt.puppetlabs.com/puppet-release-focal.deb
dpkg -i puppet-release-focal.deb
apt update
# 安装 Agent
apt install -y puppet-agent
# 配置 Agent
vim /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
# 添加配置
[main]
certname = agent-02.example.com
server = puppet-master.example.com
environment = production
runinterval = 30m
# 启动并设置开机自启
systemctl start puppet
systemctl enable puppet2.4 证书管理
Puppet 使用 SSL 证书确保通信安全,需要在 Master 上签署 Agent 的证书请求:
# 在 Master 上查看待签署的证书请求
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet cert list
# 输出示例:
# "agent-01.example.com" (SHA256) 1A:2B:3C:4D:5E:6F:7G:8H:9I:0J:1K:2L:3M:4N:5O:6P:7Q:8R:9S:0T
# "agent-02.example.com" (SHA256) 2A:3B:4C:5D:6E:7F:8G:9H:0I:1J:2K:3L:4M:5N:6O:7P:8Q:9R:0S:1T
# 签署单个证书
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet cert sign agent-01.example.com
# 签署所有证书
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet cert sign --all
# 列出已签署的证书
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet cert list --signed
# 吊销证书
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet cert revoke agent-01.example.com
# 清理吊销的证书
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet cert clean agent-01.example.com2.5 验证安装
# 在 Agent 上手动运行 Puppet
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test
# 输出示例(成功执行):
# Info: Caching catalog for agent-01.example.com
# Info: Applying configuration version '1620000000'
# Notice: Applied catalog in 2.34 seconds
# 在 Master 上检查节点状态
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet node status三、Puppet 核心组件与配置
3.1 目录结构
Puppet 标准目录结构如下:
/etc/puppetlabs/
├── code/ # 代码目录
│ ├── environments/ # 环境目录
│ │ ├── production/ # 生产环境
│ │ │ ├── manifests/ # 清单文件
│ │ │ │ └── site.pp # 主清单
│ │ │ └── modules/ # 环境专属模块
│ │ └── development/ # 开发环境
│ └── modules/ # 全局模块
├── puppet/
│ └── puppet.conf # 主配置文件
└── facts.d/ # 自定义事实创建标准目录结构:
mkdir -p /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/{production,development}/{manifests,modules}
mkdir -p /etc/puppetlabs/code/modules
touch /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/manifests/site.pp3.2 主配置文件(puppet.conf)
puppet.conf 是 Puppet 的核心配置文件,包含多个配置块:
[main]
# 全局配置,适用于所有组件
certname = puppet-master.example.com
server = puppet-master.example.com
environment = production
runinterval = 30m
logdir = /var/log/puppetlabs/puppet
vardir = /opt/puppetlabs/puppet/cache
ssldir = /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/ssl
[master]
# Master 特定配置
environment_timeout = 0 # 禁用环境缓存(开发环境)
# environment_timeout = 5m # 生产环境建议设置
basemodulepath = /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/$environment/modules:/etc/puppetlabs/code/modules
storeconfigs = true
storeconfigs_backend = puppetdb
[agent]
# Agent 特定配置
report = true
pluginsync = true3.3 环境配置
Puppet 支持多环境(如开发、测试、生产),通过环境隔离不同阶段的配置:
# 配置环境目录
vim /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
# 在 master 块添加
environmentpath = /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments
# 创建开发环境
cp -r /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/development
# 在 Agent 上指定环境
# 在 agent 块添加
environment = development3.4 事实(Facts)
Facts 是 Puppet 收集的节点属性信息,用于条件判断和动态配置:
# 在 Agent 上查看所有 Facts
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/facter
# 查看特定 Fact
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/facter os.family
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/facter ipaddress
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/facter memory.total
# 在 Master 上查看节点 Facts
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet facts show agent-01.example.com常用 Facts:
- os.family:操作系统家族(RedHat、Debian 等)
- os.release.major:操作系统主版本
- ipaddress:主 IP 地址
- fqdn:完全限定域名
- memory.total:总内存
- processorcount:CPU 核心数
3.5 自定义 Facts
创建自定义 Facts 扩展节点信息:
# 创建 Facts 目录
mkdir -p /etc/puppetlabs/facts.d
# 创建自定义 Fact(JSON 格式)
cat > /etc/puppetlabs/facts.d/app_environment.json << 'EOF'
{
"app_environment": "production",
"app_role": "webserver"
}
EOF
# 或创建可执行脚本(返回键值对)
cat > /etc/puppetlabs/facts.d/load_average.fact << 'EOF'
#!/bin/bash
echo "load_average_1min=$(uptime | awk '{print $10}' | tr -d ',')"
echo "load_average_5min=$(uptime | awk '{print $11}' | tr -d ',')"
EOF
chmod +x /etc/puppetlabs/facts.d/load_average.fact
# 同步 Facts 到 Master
/opt/puppetlabs/bin/puppet agent --test四、Puppet 语言基础
4.1 资源(Resources)
资源是 Puppet 配置的基本单位,代表系统中的实体(文件、服务等):
# 资源基本格式
resource_type { 'title':
attribute1 => 'value1',
attribute2 => 'value2',
...
}常用资源类型示例:
4.1.1 package 资源(包管理)
# 确保安装指定版本的 Nginx
package { 'nginx':
ensure => '1.18.0',
provider => $osfamily ? {
'RedHat' => 'yum',
'Debian' => 'apt',
},
}4.1.2 file 资源(文件管理)
# 管理 Nginx 配置文件
file { '/etc/nginx/nginx.conf':
ensure => file,
source => 'puppet:///modules/nginx/nginx.conf',
owner => 'root',
group => 'root',
mode => '0644',
require => Package['nginx'], # 依赖关系
notify => Service['nginx'], # 配置变化时通知服务
}
# 确保目录存在
file { '/var/log/nginx':
ensure => directory,
owner => 'nginx',
group => 'nginx',
mode => '0755',
recurse => true, # 递归设置权限
}
# 确保文件不存在
file { '/etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf':
ensure => absent,
}4.1.3 service 资源(服务管理)
# 管理 Nginx 服务
service { 'nginx':
ensure => running, # 确保服务运行
enable => true, # 开机自启
subscribe => File['/etc/nginx/nginx.conf'], # 订阅文件变化
}4.1.4 user 和 group 资源(用户管理)
# 创建用户组
group { 'webadmin':
ensure => present,
gid => 1001,
}
# 创建用户
user { 'webadmin':
ensure => present,
uid => 1001,
gid => 1001,
home => '/home/webadmin',
shell => '/bin/bash',
comment => 'Web Administrator',
managehome => true, # 自动创建家目录
require => Group['webadmin'],
}4.2 清单(Manifests)
Manifests 是包含 Puppet 代码的文件(.pp 扩展名),用于组织资源:
# /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/manifests/site.pp
# 主清单文件,是 Puppet 执行的入口
# 节点定义
node 'agent-01.example.com' {
include nginx
include mysql
}
node 'agent-02.example.com' {
include nginx
include php
}
# 匹配所有节点
node default {
include base
}4.3 类(Classes)
类用于组织相关资源,实现代码复用:
# /etc/puppetlabs/code/modules/nginx/manifests/init.pp
class nginx {
# 安装 Nginx
package { 'nginx':
ensure => installed,
}
# 配置 Nginx
file { '/etc/nginx/nginx.conf':
ensure => file,
source => 'puppet:///modules/nginx/nginx.conf',
owner => 'root',
group => 'root',
mode => '0644',
require => Package['nginx'],
notify => Service['nginx'],
}
# 启动 Nginx 服务
service { 'nginx':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
subscribe => File['/etc/nginx/nginx.conf'],
}
}
# 在清单中使用类
include nginx
# 或
class { 'nginx': }4.4 变量与条件语句
4.4.1 变量
Puppet 支持多种类型的变量,包括字符串、数字、数组和哈希:
# 定义变量
$package_name = 'nginx'
$service_name = 'nginx'
$config_file = '/etc/nginx/nginx.conf'
$worker_processes = 4
$allowed_ips = ['192.168.1.0/24', '10.0.0.0/8']
$ports = {
http => 80,
https => 443,
}
# 使用变量
package { $package_name:
ensure => installed,
}
file { $config_file:
ensure => file,
content => template('nginx/nginx.conf.erb'),
# ...
}变量作用域:
- 顶级变量:在清单或模块顶部定义,作用域为整个文件
- 类变量:在类内部定义,仅在类中可见
- 参数变量:通过类参数传递,优先级最高
4.4.2 条件语句
Puppet 支持多种条件判断结构:
# if/else 语句
if $os['family'] == 'RedHat' {
$webserver_package = 'httpd'
$webserver_service = 'httpd'
} elsif $os['family'] == 'Debian' {
$webserver_package = 'apache2'
$webserver_service = 'apache2'
} else {
fail("Unsupported OS family: ${os['family']}")
}
# 选择语句(case)
case $os['family'] {
'RedHat': {
$package_manager = 'yum'
}
'Debian': {
$package_manager = 'apt'
}
default: {
fail("Unsupported OS family: ${os['family']}")
}
}
# 选择语句简化形式
$service_name = $os['family'] ? {
'RedHat' => 'httpd',
'Debian' => 'apache2',
default => undef,
}
# 布尔判断
if $memory['total'] > '4GB' {
$java_heap_size = '2048m'
} else {
$java_heap_size = '1024m'
}4.5 模块(Modules)
模块是 Puppet 代码组织的基本单位,用于封装相关的类、资源、文件和模板:
4.5.1 模块目录结构
nginx/ # 模块名称
├── manifests/ # 清单目录
│ ├── init.pp # 主类定义
│ ├── install.pp # 安装相关类
│ ├── config.pp # 配置相关类
│ └── service.pp # 服务相关类
├── files/ # 静态文件
│ ├── nginx.conf # Nginx 配置文件
│ └── default.conf # 默认虚拟主机配置
├── templates/ # 模板文件
│ ├── nginx.conf.erb # ERB 模板
│ └── vhost.conf.erb
├── lib/ # 自定义函数和类型
│ └── puppet/
├── facts.d/ # 模块专属 Facts
├── examples/ # 示例清单
│ └── init.pp
└── metadata.json # 模块元数据4.5.2 模块编写示例
# nginx/manifests/init.pp
class nginx (
# 类参数(带默认值)
String $package_name = 'nginx',
String $service_name = 'nginx',
Boolean $enable = true,
Integer $worker_processes = $facts['processorcount'],
) {
# 包含其他类
include nginx::install
include nginx::config
include nginx::service
# 定义类之间的依赖关系
Class['nginx::install'] -> Class['nginx::config'] ~> Class['nginx::service']
}
# nginx/manifests/install.pp
class nginx::install (
String $package_name = $nginx::package_name,
) {
package { $package_name:
ensure => installed,
}
}
# nginx/manifests/config.pp
class nginx::config (
String $package_name = $nginx::package_name,
String $service_name = $nginx::service_name,
Integer $worker_processes = $nginx::worker_processes,
) {
file { '/etc/nginx/nginx.conf':
ensure => file,
content => template('nginx/nginx.conf.erb'),
owner => 'root',
group => 'root',
mode => '0644',
require => Class['nginx::install'],
}
}
# nginx/manifests/service.pp
class nginx::service (
String $service_name = $nginx::service_name,
Boolean $enable = $nginx::enable,
) {
service { $service_name:
ensure => running,
enable => $enable,
subscribe => Class['nginx::config'],
}
}4.5.3 模块使用
# 在节点中使用模块
node 'webserver.example.com' {
# 使用默认参数
include nginx
# 或指定参数
class { 'nginx':
worker_processes => 8,
enable => true,
}
}4.6 模板系统(ERB)
Puppet 使用 ERB(Embedded Ruby)模板生成动态配置文件:
# nginx/templates/nginx.conf.erb
user nginx;
worker_processes <%= @worker_processes %>; # 使用类参数
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
<% if @facts['os']['family'] == 'RedHat' -%>
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
<% else -%>
sendfile off;
<% end -%>
keepalive_timeout 65;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
}在 Puppet 资源中使用模板:
file { '/etc/nginx/nginx.conf':
ensure => file,
content => template('nginx/nginx.conf.erb'), # 引用模板
# ...
}五、Hiera 数据管理
5.1 Hiera 概述
Hiera 是 Puppet 的分层数据存储工具,用于分离代码与数据,支持:
- 按环境、角色、节点等层级存储数据
- 数据与代码分离,便于维护
- 支持多种数据格式(YAML、JSON 等)
- 可用于存储敏感信息
5.2 Hiera 配置
# /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/hiera.yaml
---
version: 5
defaults:
datadir: data
data_hash: yaml_data
hierarchy:
- name: "节点特定数据"
path: "nodes/%{trusted.certname}.yaml"
- name: "角色特定数据"
path: "roles/%{facts.app_role}.yaml"
- name: "环境特定数据"
path: "environments/%{environment}.yaml"
- name: "操作系统家族数据"
path: "os/%{facts.os.family}.yaml"
- name: "全局数据"
path: "common.yaml"创建 Hiera 数据目录:
mkdir -p /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/data/{nodes,roles,environments,os}
touch /etc/puppetlabs/code/environments/production/data/common.yaml5.3 Hiera 数据文件示例
# data/common.yaml
nginx::worker_processes: 4
mysql::root_password: 'default_root_pass'
# data/roles/webserver.yaml
nginx::enable: true
nginx::vhosts:
- name: 'example.com'
port: 80
docroot: '/var/www/example.com'
# data/os/RedHat.yaml
nginx::package_name: 'nginx'
apache::package_name: 'httpd'
# data/os/Debian.yaml
nginx::package_name: 'nginx'
apache::package_name: 'apache2'
# data/nodes/agent-01.example.com.yaml
mysql::root_password: 'agent01_specific_pass'5.4 在 Puppet 中使用 Hiera 数据
# 使用 lookup 函数获取数据
$nginx_worker_processes = lookup('nginx::worker_processes', Integer, 'first', 2)
# 在类参数中自动查找
class nginx (
Integer $worker_processes = lookup('nginx::worker_processes'),
String $root_password = lookup('mysql::root_password'),
) {
# ...
}
# 使用自动数据绑定(需在模块中启用)
# 在 metadata.json 中添加
# "data_provider": "hiera"六、Puppet 实战案例
6.1 服务器初始化配置
# modules/base/manifests/init.pp
class base {
include base::packages
include base::network
include base::security
include base::time
Class['base::packages'] -> Class['base::security']
Class['base::network'] -> Class['base::security']
}
# modules/base/manifests/packages.pp
class base::packages {
$packages = $facts['os']['family'] ? {
'RedHat' => ['vim', 'wget', 'curl', 'net-tools', 'chrony'],
'Debian' => ['vim', 'wget', 'curl', 'net-tools', 'chrony'],
}
package { $packages:
ensure => installed,
}
}
# modules/base/manifests/security.pp
class base::security {
# 配置防火墙
firewall { '000 accept all input on loopback':
proto => 'all',
iniface => 'lo',
action => 'accept',
}
firewall { '001 accept related established':
proto => 'all',
state => ['RELATED', 'ESTABLISHED'],
action => 'accept',
}
# 禁用密码登录
file_line { 'ssh disable password auth':
path => '/etc/ssh/sshd_config',
line => 'PasswordAuthentication no',
match => '^PasswordAuthentication',
notify => Service['sshd'],
}
service { 'sshd':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
}
}6.2 部署 LAMP 堆栈
# manifests/site.pp
node 'webserver.example.com' {
include base
include apache
include mysql
include php
# 配置虚拟主机
apache::vhost { 'example.com':
port => 80,
docroot => '/var/www/example.com',
require => Class['apache'],
}
# 创建数据库
mysql::db { 'webapp':
user => 'webuser',
password => lookup('webapp::db_password'),
host => 'localhost',
grant => ['ALL'],
require => Class['mysql'],
}
}
# modules/apache/manifests/init.pp
class apache {
package { 'apache2':
ensure => installed,
}
service { 'apache2':
ensure => running,
enable => true,
require => Package['apache2'],
}
}
# modules/apache/manifests/vhost.pp
define apache::vhost (
Integer $port,
String $docroot,
) {
file { $docroot:
ensure => directory,
owner => 'www-data',
group => 'www-data',
mode => '0755',
}
file { "/etc/apache2/sites-available/${title}.conf":
ensure => file,
content => template('apache/vhost.conf.erb'),
require => Package['apache2'],
notify => Service['apache2'],
}
exec { "a2ensite ${title}":
command => "/usr/sbin/a2ensite ${title}",
creates => "/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/${title}.conf",
require => File["/etc/apache2/sites-available/${title}.conf"],
notify => Service['apache2'],
}
}七、Puppet 高级特性
7.1 导出资源与收集
导出资源允许一个节点导出资源,其他节点收集使用,适用于服务发现:
# 在数据库节点导出资源
@@mysql::db { 'shared_db':
user => 'appuser',
password => 'secret',
host => '%',
grant => ['SELECT', 'INSERT', 'UPDATE'],
tag => 'shared',
}
# 在应用节点收集资源
Mysql::Db <<| tag == 'shared' |>> {
# 可以覆盖部分属性
host => $facts['ipaddress'],
}7.2 自定义函数
创建自定义函数扩展 Puppet 功能:
# modules/custom/lib/puppet/functions/custom/validate_ip.rb
Puppet::Functions.create_function(:'custom::validate_ip') do
dispatch :validate_ip do
param 'String', :ip_address
end
def validate_ip(ip_address)
require 'ipaddr'
IPAddr.new(ip_address)
rescue ArgumentError
raise Puppet::Error, "#{ip_address} is not a valid IP address"
end
end在 Puppet 中使用自定义函数:
$ip = '192.168.1.1'
custom::validate_ip($ip)7.3 PuppetDB 与报告
PuppetDB 用于存储 Puppet 目录、 Facts 和报告数据:
# 安装 PuppetDB
yum install -y puppetdb puppetdb-termini # CentOS
# 或
apt install -y puppetdb puppetdb-termini # Ubuntu
# 配置 PuppetDB
vim /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppetdb.conf
# 添加
[main]
server_urls = https://puppet-master.example.com:8081
# 配置 Puppet 使用 PuppetDB
vim /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf
# 在 master 块添加
storeconfigs = true
storeconfigs_backend = puppetdb
reports = puppetdb
# 启动 PuppetDB
systemctl start puppetdb
systemctl enable puppetdb查询 PuppetDB 数据:
# 安装 PuppetDB 命令行工具
yum install -y puppetdb-cli
# 查询节点 Facts
pdb query 'facts[value] { name = "osfamily" and certname = "agent-01.example.com" }'
# 查询资源状态
pdb query 'resources { type = "Package" and title = "nginx" }'八、最佳实践与总结
8.1 最佳实践
- 代码组织:
-
- 遵循模块化设计原则,每个模块专注于单一功能
-
- 使用 Hiera 分离代码与数据,特别是环境特定配置
-
- 为模块编写文档和示例,提高可维护性
2. 版本控制:
-
- 将所有 Puppet 代码纳入版本控制(Git)
-
- 采用语义化版本管理模块
-
- 实施代码审查流程
3. 测试策略:
-
- 使用 puppet parser validate 检查语法错误
-
- 采用 puppet-lint 确保代码风格一致
-
- 使用 rspec-puppet 编写单元测试
-
- 在测试环境验证配置后再推广到生产
4. 安全实践:
-
- 加密存储敏感数据(使用 Hiera 与加密后端)
-
- 定期轮换 SSL 证书
-
- 限制 Puppet Master 访问权限
-
- 审查模块内容,避免恶意代码
5. 性能优化:
-
- 合理设置 Agent 拉取间隔(runinterval)
-
- 对大规模部署使用 PuppetDB 缓存
-
- 减少目录编译时间,避免复杂条件判断
-
- 使用 --noop 模式测试配置变更
8.2 总结
Puppet 作为一款成熟的配置管理工具,通过声明式语言和强大的类型系统,帮助运维团队实现基础设施的自动化管理和标准化配置。其核心优势在于:
-
声明式语言使配置更直观,只需描述目标状态而非具体步骤
-
强大的模块化设计促进代码复用和团队协作
-
Hiera 数据分层机制实现代码与数据的分离
-
丰富的生态系统提供大量现成模块,加速部署流程
-
完善的报告和审计功能满足合规性要求
-
对于需要管理大规模、多环境基础设施的组织,Puppet 提供了可靠的自动化解决方案。通过遵循最佳实践,运维团队可以构建可扩展、可维护的自动化体系,减少人为错误,提高系统一致性和稳定性。
随着云计算和容器技术的发展,Puppet 也在不断进化,增加了对云资源和容器编排平台的支持,使其能够适应现代 IT 基础设施的管理需求。无论是传统数据中心还是混合云环境,Puppet 都能提供一致的配置管理体验,帮助组织实现 IT 自动化的全面落地。