大纲
1.FailoverClusterInvoker的失败重试机制
2.FailfastClusterInvoker的快速失败机制
3.FailsafeClusterInvoker的安全失败机制
4.FailbackClusterInvoker的定时重试机制
5.BroadcastClusterInvoker的多广播机制
6.ForkingClusterInvoker的并行多路调用
7.AbstractClusterInvoker多策略选择Invoker
8.基于权重随机算法的负载均衡
9.基于加权轮询算法的负载均衡
10.基于最少活跃数算法的负载均衡
11.基于一致性Hash算法的负载均衡
12.Dubbo的自动降级与Mock机制原理
13.Dubbo的Mock模拟调用原理
14.DubboInvoker的RPC调用细节
1.FailoverClusterInvoker的失败重试机制
FailoverClusterInvoker是Dubbo默认使用的集群容错策略,它会在RPC调用失败时自动切换Invoker进行重试。Dubbo中还支持其他的集群容错策略,比如Failfast、Failback、Failsafe等。
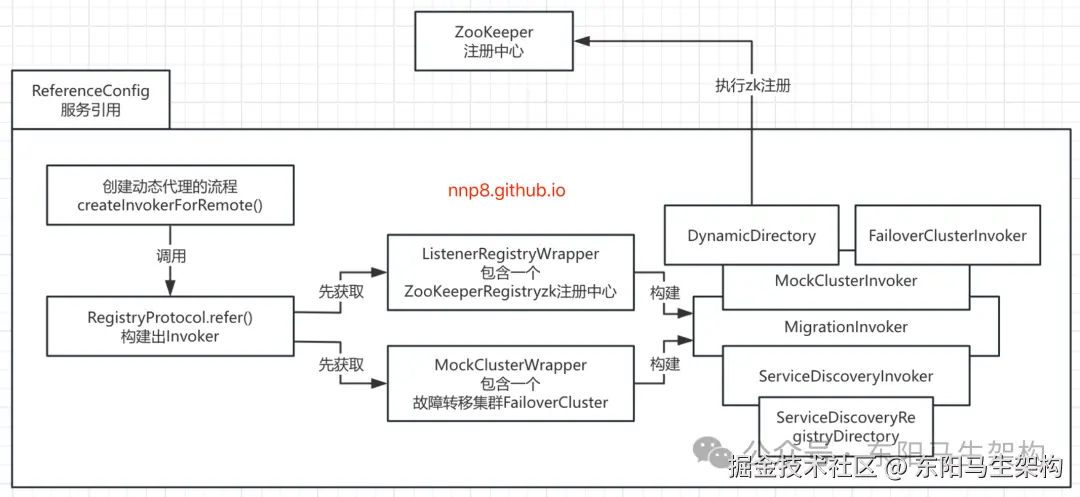
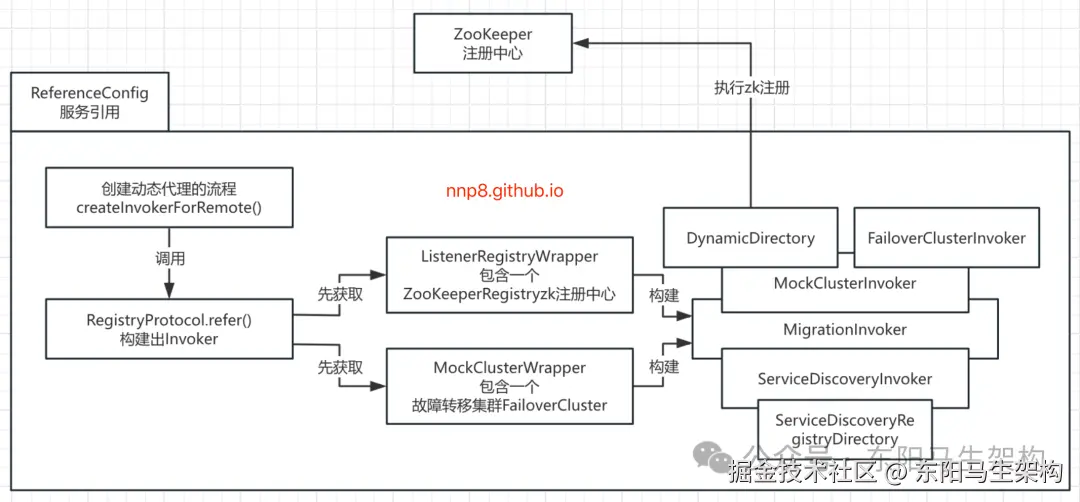
情形一:服务引用构建Invoker时
RegistryProtocol的doCreateInvoker()方法最终返回的是封装了DynamicDirectory和FailoverClusterInvoker的MockClusterInvoker。
调用链如下:
arduino
//-> RegistryProtocol.refer()
//-> getRegistry() => ZooKeeperRegistry
//-> Cluster.getCluster() => MockClusterWrapper、FailoverCluster
//-> RegistryProtocol.doRefer()
//-> RegistryProtocol.getMigrationInvoker()
//-> RegistryProtocol.interceptInvoker()
//-> MigrationRuleListener.onRefer()
//-> MigrationRuleHandler.doMigrate()
//-> MigrationRuleHandler.refreshInvoker()
//-> MigrationInvoker.refreshInterfaceInvoker() + MigrationInvoker.refreshServiceDiscoveryInvoker()
//-> InterfaceCompatibleRegistryProtocol.getInvoker() + RegistryProtocol.getServiceDiscoveryInvoker()
//-> RegistryProtocol.doCreateInvoker()情形二:负载均衡选择Invoker时
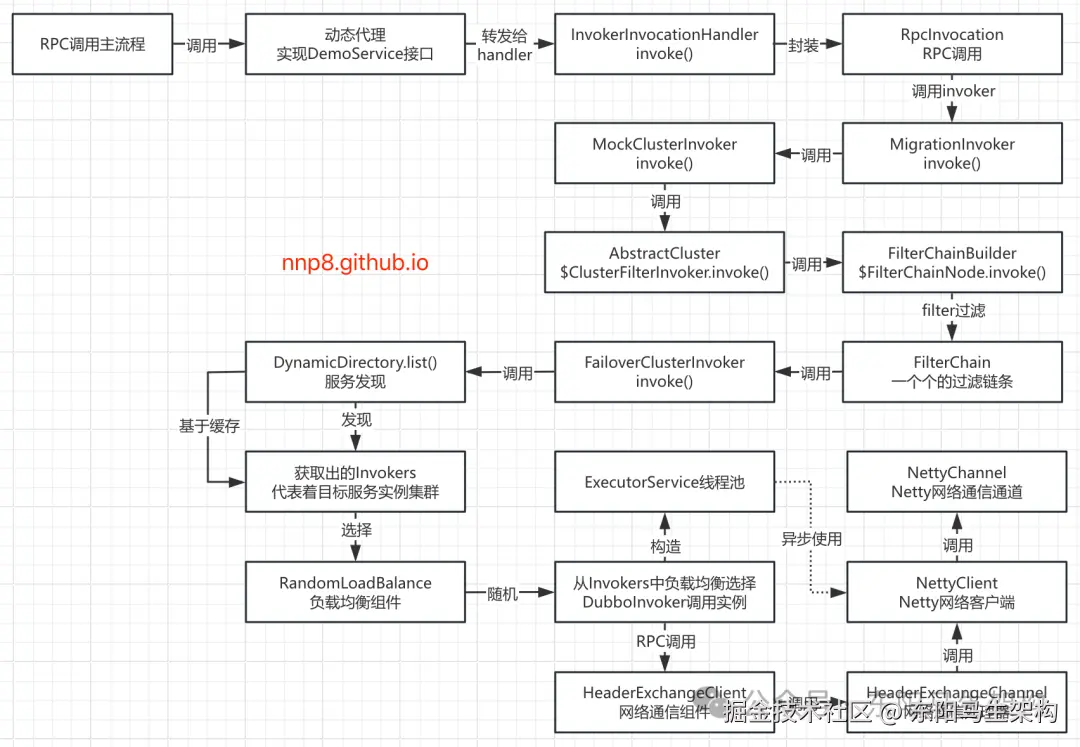
调用链如下:
arduino
//-> InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke()
//-> InvocationUtil.invoke()
// invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()
//-> MigrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> MockClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractCluster.ClusterFilterInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CallbackRegistrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> ConsumerContextFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> FutureFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> MonitorFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> RouterSnapshotFilter.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.initLoadBalance()
//-> FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.select()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect()
//-> AbstractLoadBalance.select()
//-> RandomLoadBalance.doSelect()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invokeWithContext()
//-> ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.doInvokeAndReturn()
//-> DubboInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.waitForResultIfSync()
//-> AsyncRpcResult.get()如下是FailoverClusterInvoker的源码:
scss
//Dubbo有不同的集群容错策略,通过具体的配置可以改变使用不同的策略
//还可以根据自己的需求,自定义集群容错策略,然后进行配置让Dubbo采用自定义的集群容错策略,而这使用到了策略模式
//Dubbo会针对某个环节设计出多种可替换的不同的策略,同时会提供一个默认的策略实现,然后通过配置可以使用其他策略
public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
public FailoverClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
//该方法会找出一个Invoker
//把invocation交给多个Invokers里的一个去发起RPC调用
//其中会根据传入的loadbalance来实现负载均衡
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//下面先做一个引用赋值
List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers;
//检查Invokers
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
//从RPC调用里提取一个method方法名称,从而确定需要调用的是哪个方法
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//计算最多调用次数
//因为Failover策略是:如果发现调用不成功会进行重试,但默认会最多调用3次来让调用成功
int len = calculateInvokeTimes(methodName);
//retry loop.
RpcException le = null;//last exception.
//构建了一个跟invokers数量相等的一个list
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyInvokers.size());//invoked invokers.
//基于计算出的调用次数,构建一个set
//如果调用次数为3,那么意味着最多会调用3个provider服务实例
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
//对len次数进行循环
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
//到i>0时,表示的是第一次调用失败,要开始进行重试了
if (i > 0) {
//检查当前服务实例是否被销毁
checkWhetherDestroyed();
//此时要调用DynamicDirectory进行一次invokers列表刷新
//因为第一次调用都失败了,所以有可能invokers列表出现了变化,因而需要刷新一下invokers列表
copyInvokers = list(invocation);
//再次check一下invokers是否为空
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
}
//1.下面会调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法
//select()方法会选择一个Invoker出来,具体逻辑是:
//首先尝试用负载均衡算法去选
//如果选出的Invoker是选过的或者不可用的,那么就直接reselect
//也就是对选过的找一个可用的,对选不出的直接挑选下一个
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getServiceContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
boolean success = false;
try {
//2.调用AbstractClusterInvoker的invokeWithContext()方法
//基于该Invoker发起RPC调用,并拿到一个result
Result result = invokeWithContext(invoker, invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("...");
}
success = true;
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
//如果本次RPC调用失败了,那么就会有异常抛出来
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
//下面会把出现RPC调用异常的进行设置,把本次调用失败的invoker地址添加到providers
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
}
//如果最后抛出如下这个异常,则说明本次RPC调用彻底失败了
throw new RpcException("...");
}
//计算调用Invoker的最多次数
private int calculateInvokeTimes(String methodName) {
//len默认是3,也就是如果第一次调用失败了,那么最多会发起两次重试
int len = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, RETRIES_KEY, DEFAULT_RETRIES) + 1;
RpcContext rpcContext = RpcContext.getClientAttachment();
//如果有配置的retry次数,就按照配置的来生效
Object retry = rpcContext.getObjectAttachment(RETRIES_KEY);
if (retry instanceof Number) {
len = ((Number) retry).intValue() + 1;
rpcContext.removeAttachment(RETRIES_KEY);
}
if (len <= 0) {
len = 1;
}
return len;
}
}2.FailfastClusterInvoker的快速失败机制
Failfast就是一旦RPC调用失败时,就直接抛出异常,不再进行重试了。
Failover是支持支持失败重试的,适用于读接口,比如多查几次也不影响的查询接口、或者是支持幂等的写接口。
Failfast适用于不支持幂等的写接口,比如万一重试几次可能会导致数据重复的接口。
FailfastClusterInvoker只会进行一次请求,请求失败后会立即抛出异常,这种策略适合非幂等的接口。
java
//Failfast,就是一旦RPC调用时遇到了异常,就直接抛出异常,不再进行重试了
//Failover,则是支持故障转移,支持重试的,适用于读接口,比如多查几次也不影响的查询接口、或者是支持幂等的写接口
//Failfast,适用于不支持幂等的写接口,比如万一重试几次可能会导致数据重复的接口
public class FailfastClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
public FailfastClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//先是对invokers进行检查
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
//在进行负载均衡策略实现,选择目标Invoker时,用到的代码是一样的
//调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法得到此次要调用的Invoker对象
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
try {
return invokeWithContext(invoker, invocation);//发起请求
} catch (Throwable e) {
//请求失败,直接抛出异常
if (e instanceof RpcException && ((RpcException) e).isBiz()) { // biz exception.
throw (RpcException) e;
}
//封装一个异常往外抛
throw new RpcException("...");
}
}
}
//如果要对一个目标服务实例进行RPC调用,那么负责调用的这个组件就可以叫做Invoker
//Dubbo大量使用了模板方法设计模式:
//首先抽象出一个抽象的父类,把一些基础的方法和骨架,都放在父类里面
//然后定义一些抽象方法,各个子类来具体实现自己的逻辑,可以复用的代码逻辑都会由父类实现
//比如父类有一个invoke()方法、一个doInvoke()抽象方法由子类实现
//外部调用时就调用invoke()方法,doInvoke()方法则由各策略子类实现
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
...
@Override
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//检测当前Invoker是否已销毁
checkWhetherDestroyed();
InvocationProfilerUtils.enterDetailProfiler(invocation, () -> "Router route.");
//下面会根据invocation信息列出所有的Invoker
//也就是通过DynamicDirectory.list()方法进行服务发现
//由于通过Directory获取Invoker对象列表
//通过了解RegistryDirectory可知,其中已经调用了Router进行过滤
//从而可以知道有哪些服务实例、有哪些Invoker
//由于一个服务实例会对应一个Invoker,所以目标服务实例集群已变成invokers了
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
InvocationProfilerUtils.releaseDetailProfiler(invocation);
//通过SPI加载LoadBalance实例,也就是在这里选择出对应的负载均衡策略
//比如下面默认会获取到一个RandomLoadBalance
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
InvocationProfilerUtils.enterDetailProfiler(invocation, () -> "Cluster " + this.getClass().getName() + " invoke.");
try {
//调用由子类实现的抽象方法doInvoke()
//下面会由子类FailoverClusterInvoker执行doInvoke()方法
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
} finally {
InvocationProfilerUtils.releaseDetailProfiler(invocation);
}
}
protected abstract Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException;
...
}3.FailsafeClusterInvoker的安全失败机制
Failsafe就是如果调用失败,则不用抛出错误,而是直接打印一个异常log日志即可。
对于要写一些类似于远程日志数据,比如审计数据或者是可有可无的可以丢失的数据,此时就可以用Failsafe。
FailsafeClusterInvoker只会进行一次请求,请求失败之后会返回一个空结果。
scala
public class FailsafeClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
public FailsafeClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
}
@Override
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
//检测Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
//调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法得到此次要调用的Invoker对象
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
//发起请求
return invokeWithContext(invoker, invocation);
} catch (Throwable e) {
//请求失败之后,会打印一行日志并返回空结果
logger.error("Failsafe ignore exception: " + e.getMessage(), e);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, null, invocation);
}
}
}4.FailbackClusterInvoker的定时重试机制
Failback就是如果调用失败了,则会把这次调用记录存储起来,后续根据一定的策略,隔一段时间后再去进行重试。
如果重试次数已经达到上限,则只输出警告日志。如果重试次数未达到上限,则重新添加定时任务等待重试。默认重试次数的上限为3。
java
public class FailbackClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
//多线程的DoubleCheck检查机制,一般是会配合volatile关键字去使用
private volatile Timer failTimer;
...
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
Invoker<T> invoker = null;
URL consumerUrl = RpcContext.getServiceContext().getConsumerUrl();
try {
//检测Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
//调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法得到此次尝试的Invoker对象
invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, null);
//调用invoke()方法完成远程调用
return invokeWithContextAsync(invoker, invocation, consumerUrl);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Failback to invoke method " + invocation.getMethodName() + ", wait for retry in background. Ignored exception: " + e.getMessage() + ", ", e);
//如果不出意外,默认也是3次,调用addFailed之后,就会返回一个空结果
if (retries > 0) {
//请求失败之后,会添加一个定时任务进行重试
addFailed(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, invoker, consumerUrl);
}
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(null, null, invocation); // ignore
}
}
private void addFailed(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invoker<T> lastInvoker, URL consumerUrl) {
//为了保证多线程并发安全问题,这里用了一个DoubleCheck
if (failTimer == null) {
synchronized (this) {
//DoubleCheck防止并发问题
if (failTimer == null) {
//初始化时间轮
failTimer = new HashedWheelTimer(
new NamedThreadFactory("failback-cluster-timer", true),
1,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
32,
failbackTasks
);
}
}
}
//创建一个定时任务
RetryTimerTask retryTimerTask = new RetryTimerTask(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, lastInvoker, retries, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, consumerUrl);
try {
//将定时任务添加到时间轮中
failTimer.newTimeout(retryTimerTask, RETRY_FAILED_PERIOD, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Failback background works error, invocation->" + invocation + ", exception: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private class RetryTimerTask implements TimerTask {
...
public void run(Timeout timeout) {
try {
//到了一定的间隔时间后,就会重新通过select算法选择一个新的Invoker对象
//注意:这里会将上次重试失败的Invoker作为selected集合传入
Invoker<T> retryInvoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, Collections.singletonList(lastInvoker));
lastInvoker = retryInvoker;
//请求对应的Provider节点
invokeWithContextAsync(retryInvoker, invocation, consumerUrl);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if ((++retriedTimes) >= retries) {
//重试次数达到上限,输出警告日志
logger.error("Failed retry times exceed threshold (" + retries + "), We have to abandon, invocation->" + invocation);
} else {
//重试次数未达到上限,则重新添加定时任务等待重试,默认次数为3
rePut(timeout);
}
}
}
private void rePut(Timeout timeout) {
//边界检查
if (timeout == null) {
return;
}
Timer timer = timeout.timer();
//检查时间轮状态、检查定时任务状态
if (timer.isStop() || timeout.isCancelled()) {
return;
}
//重新添加定时任务,每隔tick=5秒重试一次
timer.newTimeout(timeout.task(), tick, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
...
}
...
}5.BroadcastClusterInvoker的多广播机制
如果目标服务实例集群有3个实例,那么广播的话就是对3个实例都做一次调用。
在BroadcastClusterInvoker中,会逐个调用每个Provider节点,其中任意一个Provider节点报错,都会在全部调用结束之后抛出异常。
BroadcastClusterInvoker通常用于通知类的操作,例如通知所有Provider节点更新本地缓存。
ini
//如果目标服务实例集群有3个实例,那么广播就是对3个实例的某种比例都做一次调用,实践中很少使用
public class BroadcastClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
...
public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//检测Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
RpcContext.getServiceContext().setInvokers((List) invokers);
//用于记录失败请求的相关异常信息
RpcException exception = null;
Result result = null;
URL url = getUrl();
//广播失败的容忍度/百分比
int broadcastFailPercent = url.getParameter(BROADCAST_FAIL_PERCENT_KEY, MAX_BROADCAST_FAIL_PERCENT);
...
int failThresholdIndex = invokers.size() * broadcastFailPercent / MAX_BROADCAST_FAIL_PERCENT;
int failIndex = 0;
//遍历所有Invoker对象
//因为是广播,所以会遍历所有的Invoker进行逐个调用
for (int i = 0, invokersSize = invokers.size(); i < invokersSize; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
RpcContext.RestoreContext restoreContext = new RpcContext.RestoreContext();
try {
RpcInvocation subInvocation = new RpcInvocation(invocation.getTargetServiceUniqueName(),
invocation.getServiceModel(), invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getServiceName(), invocation.getProtocolServiceKey(),
invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments(), invocation.copyObjectAttachments(),
invocation.getInvoker(), Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>(invocation.getAttributes())),
invocation instanceof RpcInvocation ? ((RpcInvocation) invocation).getInvokeMode() : null);
//发起请求
result = invokeWithContext(invoker, subInvocation);
if (null != result && result.hasException()) {
Throwable resultException = result.getException();
if (null != resultException) {
exception = getRpcException(result.getException());
logger.warn(exception.getMessage(), exception);
failIndex++;
//广播过程中,达到一定比例的Invoker所有都失败了,就中断,表示这次invoke都失败了
if (failIndex == failThresholdIndex) {
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
exception = getRpcException(e);
logger.warn(exception.getMessage(), exception);
failIndex++;
if (failIndex == failThresholdIndex) {
break;
}
} finally {
if (i != invokersSize - 1) {
restoreContext.restore();
}
}
}
//出现任何异常,都会在这里抛出
if (exception != null) {
if (failIndex == failThresholdIndex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(String.format("The number of BroadcastCluster call failures has reached the threshold %s", failThresholdIndex));
}
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(String.format("The number of BroadcastCluster call failures has not reached the threshold %s, fail size is %s", failThresholdIndex, failIndex));
}
}
throw exception;
}
return result;
}
...
}6.ForkingClusterInvoker的并行多路调用
ForkingClusterInvoker就是会并行地调用几个服务,如果谁先返回结果就用谁的结果。这种模式可能会耗费比较多的资源,可能导致CPU飙高、但是延迟可能会降低。
ForkingClusterInvoker中会维护一个线程池(executor字段),这个线程池是通过Executors的newCachedThreadPool()方法创建的线程池。
并发调用多个Provider节点,只要有一个Provider节点成功返回了结果,ForkingClusterInvoker的doInvoke()方法就会立即结束运行。
ForkingClusterInvoker主要是为了应对一些实时性要求较高的读操作,因为没有并发控制的多线程写入,可能会导致数据不一致。
ForkingClusterInvoker的doInvoke()方法首先从Invoker集合中选出指定个数(forks参数决定)的Invoker对象,然后通过executor线程池并发调用这些Invoker,并将请求结果存储在ref阻塞队列中,则当前线程会阻塞在ref队列上,等待第一个请求结果返回。
scss
public class ForkingClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
private final ExecutorService executor;
public ForkingClusterInvoker(Directory<T> directory) {
super(directory);
executor = directory.getUrl().getOrDefaultFrameworkModel().getBeanFactory()
.getBean(FrameworkExecutorRepository.class).getSharedExecutor();
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
try {
//检查Invoker集合是否为空
checkInvokers(invokers, invocation);
final List<Invoker<T>> selected;
//从URL中获取forks参数,作为并发请求的上限,默认值为2
final int forks = getUrl().getParameter(FORKS_KEY, DEFAULT_FORKS);
final int timeout = getUrl().getParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
if (forks <= 0 || forks >= invokers.size()) {
//如果forks为负数或是大于Invoker集合的长度,会直接并发调用全部Invoker
selected = invokers;
} else {
//按照forks指定的并发度,选择此次并发调用的Invoker对象
selected = new ArrayList<>(forks);
while (selected.size() < forks) {
//调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
if (!selected.contains(invoker)) {
//Avoid add the same invoker several times.
//避免重复选择
selected.add(invoker);
}
}
}
RpcContext.getServiceContext().setInvokers((List) selected);
//记录失败的请求个数
final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
//用于记录请求结果
final BlockingQueue<Object> ref = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1);
//遍历selected列表,遍历Invoker,跑并行去调用,谁调用完了,就把结果放到queue里去
for (final Invoker<T> invoker : selected) {
URL consumerUrl = RpcContext.getServiceContext().getConsumerUrl();
//提交一个异步化的任务给线程池
executor.execute(() -> {
try {
if (ref.size() > 0) {
return;
}
//发起请求
Result result = invokeWithContextAsync(invoker, invocation, consumerUrl);
//将请求结果写到ref队列中
ref.offer(result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
int value = count.incrementAndGet();
if (value >= selected.size()) {
//如果失败的请求个数超过的并发请求的个数,则向ref队列中写入异常
ref.offer(e);
}
}
});
}
try {
//当前线程会阻塞等待任意一个请求结果的出现,阻塞等待最多就是等待一秒钟
Object ret = ref.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//如果结果类型为Throwable,则抛出异常
if (ret instanceof Throwable) {
Throwable e = (Throwable) ret;
throw new RpcException("...");
}
//返回结果
return (Result) ret;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RpcException("...");
}
} finally {
//clear attachments which is binding to current thread.
//清除上下文信息
RpcContext.getClientAttachment().clearAttachments();
}
}
}7.AbstractClusterInvoker多策略选择Invoker
AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法会对invokers进行多种策略选择:先尝试用负载均衡算法去选,如果选出来的Invoker是选过的或者不可用的,那么就直接reselect。对选过的找一个可用的,对选不出的直接挑选下一个。
scss
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.select()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.reselect()
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
...
//第一个参数是此次使用的LoadBalance实现
//第二个参数Invocation是此次服务调用的上下文信息
//第三个参数是待选择的Invoker集合
//第四个参数用来记录负载均衡已经选出来、尝试过的Invoker集合
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
//invokers不能为空,为空的话就直接返回
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
}
//获取调用方法名,调用的方法名称处理逻辑是:
//如果RPC调用是null,则method方法名就是一个空字符串,否则就是RPC调用里的方法名称
String methodName = invocation == null ? StringUtils.EMPTY_STRING : invocation.getMethodName();
//下面会获取sticky的配置,其中sticky表示粘滞连接
//所谓粘滞连接是指Consumer会尽可能的调用同一个Provider节点,除非这个Provider无法提供服务
//invokers代表了服务集群地址,首先会根据invokers获取第一个invoker
//然后拿到这个invoker的URL,接着去获取URL中对应的sticky,其默认值是false
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY);
//ignore overloaded method
//检测invokers列表是否包含stickyInvoker
//如果不包含则说明stickyInvoker代表的服务提供者挂了,此时需要将其置空
if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) {
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore concurrency problem
//如果开启了粘滞连接特性,则需要先判断这个Provider节点是否已经重试过了
//下面的判断前半部分表示粘滞连接,后半部分表示stickyInvoker未重试过
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) {
//检测当前stickyInvoker是否可用,如果可用,直接返回stickyInvoker
if (availableCheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
//执行到这里,说明前面的stickyInvoker为空,或者不可用
//这里会继续调用doSelect选择新的Invoker对象
//也就是基于LoadBalance去进行负载均衡选择一个Invoker出来
Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
//是否开启粘滞,更新stickyInvoker为选择出来的invoker
//sticky表示粘滞连接(粘滞调用)
//所谓粘滞连接(粘滞调用)是指Consumer会尽可能的调用同一个Provider节点,除非这个Provider无法提供服务
//也就是把一个Consumer端和一个Provider端粘在一起
if (sticky) {
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
//判断是否需要进行负载均衡,Invoker集合为空,直接返回null
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
}
//只有一个Invoker对象,直接返回即可
//如果invokers的数量就1个,那么目标Provider服务实例就一个
//所以直接返回invokers里的第一个即可
if (invokers.size() == 1) {
Invoker<T> tInvoker = invokers.get(0);
checkShouldInvalidateInvoker(tInvoker);
return tInvoker;
}
//通过LoadBalance实现选择Invoker对象
//即基于负载均衡的策略和算法选择出一个Invoker
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
//Invoke是否已经尝试调用过但是失败了
boolean isSelected = selected != null && selected.contains(invoker);
//Invoker是否不可用
boolean isUnavailable = availableCheck && !invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null;
if (isUnavailable) {
invalidateInvoker(invoker);
}
//如果LoadBalance选出的Invoker对象,已经尝试请求过了或不可用,则需要调用reselect()方法进行重选
if (isSelected || isUnavailable) {
try {
//调用reselect()方法重选
Invoker<T> rInvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availableCheck);
if (rInvoker != null) {
//如果重选的Invoker对象不为空,则直接返回这个rInvoker
invoker = rInvoker;
} else {
//Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1.
//如果选来选去都是空,那么对当前Invoker就直接选择它的下一个invoker即可
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try {
//Avoid collision
//如果重选的Invoker对象为空,则返回该Invoker的下一个Invoker对象
invoker = invokers.get((index + 1) % invokers.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("...");
}
}
return invoker;
}
private Invoker<T> reselect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected, boolean availableCheck) throws RpcException {
//Allocating one in advance, this list is certain to be used.
//构建一个重新选择的invokers列表,也就是用于记录要重新进行负载均衡的Invoker集合
List<Invoker<T>> reselectInvokers = new ArrayList<>(Math.min(invokers.size(), reselectCount));
//1.Try picking some invokers not in `selected`.
//1.1.If all selectable invokers' size is smaller than reselectCount, just add all
//1.2.If all selectable invokers' size is greater than reselectCount, randomly select reselectCount.
// The result size of invokers might smaller than reselectCount due to disAvailable or de-duplication (might be zero).
// This means there is probable that reselectInvokers is empty however all invoker list may contain available invokers.
// Use reselectCount can reduce retry times if invokers' size is huge, which may lead to long time hang up.
//下面会把不可用的invokers挑出来,以及选择过的invoker也挑出来,以形成一个新的可用于选择的invokers列表
if (reselectCount >= invokers.size()) {
//将不在selected集合中的Invoker过滤出来进行负载均衡
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
//check if available
if (availableCheck && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
//add to invalidate invoker
invalidateInvoker(invoker);
continue;
}
if (selected == null || !selected.contains(invoker)) {
reselectInvokers.add(invoker);
}
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < reselectCount; i++) {
//select one randomly
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(invokers.size()));
//check if available
if (availableCheck && !invoker.isAvailable()) {
//add to invalidate invoker
invalidateInvoker(invoker);
continue;
}
//de-duplication
if (selected == null || !selected.contains(invoker) || !reselectInvokers.contains(invoker)) {
reselectInvokers.add(invoker);
}
}
}
//2.Use loadBalance to select one (all the reselectInvokers are available)
//reselectInvokers不为空时,才需要再次通过负载均衡组件进行选择一个Invoker
if (!reselectInvokers.isEmpty()) {
return loadbalance.select(reselectInvokers, getUrl(), invocation);
}
//3.reselectInvokers is empty. Unable to find at least one available invoker.
//Re-check all the selected invokers.
//If some in the selected list are available, add to reselectInvokers.
//只能对selected集合中可用的Invoker再次进行负载均衡
if (selected != null) {
//如果上面的reselect列表是空的,选无可选,只能从选择过的invokers里面进行选择
for (Invoker<T> invoker : selected) {
//如果之前选择过的Invoker此时是可用的
if ((invoker.isAvailable()) //available first
&& !reselectInvokers.contains(invoker)) {
//那么再次把选择过的但是此时可用了的Invoker放到reselect列表里去
reselectInvokers.add(invoker);
}
}
}
//4.If reselectInvokers is not empty after re-check.
//Pick an available invoker using loadBalance policy
if (!reselectInvokers.isEmpty()) {
//如果把选择过的Invoker再次选一遍后也可以选出可用的
//那么就放到reselect里面去,再次进行负载均衡选择
return loadbalance.select(reselectInvokers, getUrl(), invocation);
}
//5.No invoker match, return null.
return null;
}
...
}8.基于权重随机算法的负载均衡
(1)加权随机算法的原理
(2)加权随机算法的实现
(1)加权随机算法的原理
RandomLoadBalance使用的负载均衡算法是加权随机算法,它是一个简单、高效的负载均衡实现,也是Dubbo默认使用的LoadBalance实现。
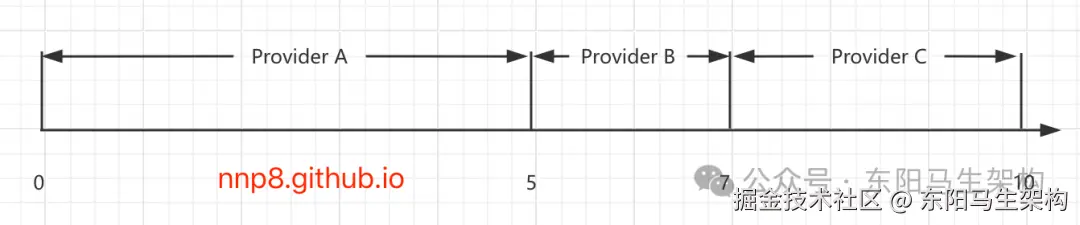
假设有三个Provider节点A、B、C,它们对应的权重分别为5、2、3,权重总和为10。把这些权重值放到一维坐标轴上,[0, 5)区间属于节点A,[5, 7)区间属于节点B,[7, 10)区间属于节点C。
可以通过随机数生成器在[0, 10)这个范围内生成一个随机数,然后计算这个随机数会落到哪个区间中。例如随机生成4,就会落到节点A对应的区间中,此时RandomLoadBalance就会返回节点A。
(2)加权随机算法的实现
RandomLoadBalance的doSelect()方法实现中,首先会计算每个Invoker对应的权重值以及总权重值。如果各个Invoker权重值不相等,则计算随机数应该落在哪个Invoker区间中,返回对应的Invoker对象。如果各个Invoker权重值相同,则随机返回一个Invoker。
RandomLoadBalance经过多次请求后,便能将调用请求按权重值均匀分配到各个Provider节点上。
scss
//-> InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke()
//-> InvocationUtil.invoke()
// invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()
//-> MigrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> MockClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractCluster.ClusterFilterInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CallbackRegistrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> ConsumerContextFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> FutureFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> MonitorFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> RouterSnapshotFilter.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.initLoadBalance()
//-> FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.select()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect()
//-> AbstractLoadBalance.select()
//-> RandomLoadBalance.doSelect()
//This class select one provider from multiple providers randomly.
//You can define weights for each provider:
//If the weights are all the same then it will use random.nextInt(number of invokers).
//If the weights are different then it will use random.nextInt(w1 + w2 + ... + wn)
//Note that if the performance of the machine is better than others, you can set a larger weight.
//If the performance is not so good, you can set a smaller weight.
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "random";
//Select one invoker between a list using a random criteria
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
int length = invokers.size();
boolean sameWeight = true;
//计算每个Invoker对象对应的权重,并填充到weights[]数组中
int[] weights = new int[length];
//计算第一个Invoker的权重
int firstWeight = getWeight(invokers.get(0), invocation);
weights[0] = firstWeight;
//totalWeight用于记录总权重值
int totalWeight = firstWeight;
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
//计算每个Invoker的权重,以及总权重totalWeight
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
weights[i] = weight;
totalWeight += weight;
//检测每个Provider的权重是否相同
if (sameWeight && weight != firstWeight) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
//各个Invoker权重值不相等时,计算随机数落在哪个区间上
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
//随机获取一个[0, totalWeight) 区间内的数字
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
//循环让offset数减去Invoker的权重值,当offset小于0时,返回相应的Invoker
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
offset -= weights[i];
if (offset < 0) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
//各个Invoker权重值相同时,随机返回一个Invoker即可
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
}
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
...
protected int getWeight(Invoker<?> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
int weight;
URL url = invoker.getUrl();
if (invoker instanceof ClusterInvoker) {
url = ((ClusterInvoker<?>) invoker).getRegistryUrl();
}
//Multiple registry scenario, load balance among multiple registries.
if (REGISTRY_SERVICE_REFERENCE_PATH.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) {
//注册中心的的话,直接获取权重即可
weight = url.getParameter(WEIGHT_KEY, DEFAULT_WEIGHT);
} else {
weight = url.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), WEIGHT_KEY, DEFAULT_WEIGHT);
if (weight > 0) {
//获取服务提供者启动时间戳
long timestamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(TIMESTAMP_KEY, 0L);
if (timestamp > 0L) {
//计算Provider运行时长
long uptime = System.currentTimeMillis() - timestamp;
if (uptime < 0) {
return 1;
}
//计算Provider预热时长
int warmup = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(WARMUP_KEY, DEFAULT_WARMUP);
//如果Provider运行时间小于预热时间,则该Provider节点可能还在预热阶段,需要重新计算服务权重(降低其权重)
if (uptime > 0 && uptime < warmup) {
weight = calculateWarmupWeight((int)uptime, warmup, weight);
}
}
}
}
return Math.max(weight, 0);
}
...
}9.基于加权轮询算法的负载均衡
(1)加权轮询算法的原理
(2)加权轮询算法的执行流程
(3)加权轮询算法的实现
(1)加权轮询算法的原理
RoundRobinLoadBalance使用的负载均衡算法是加权轮询算法,该算法会将请求轮流分配给每个Provider。
例如有A、B、C三个Provider节点,按照普通轮询的方式,会将第一个请求分配给Provider A,将第二个请求分配给 Provider B,第三个请求分配给Provider C,第四个请求再次分配给Provider A,如此循环往复。
轮询是一种无状态负载均衡算法,实现简单,适用于集群中所有Provider节点性能相近的场景。但现实中就很难保证这一点,因为很容易出现集群中性能最好和最差的Provider节点处理同样流量的情况。这就可能导致性能差的Provider节点各方面资源非常紧张,甚至无法及时响应了,但是性能好的Provider节点的各方面资源使用还较为空闲。
这时我们可以通过加权轮询的方式,降低分配到性能较差的Provider节点的流量。加权之后,分配给每个Provider节点的流量比会接近或等于它们的权重比。
例如Provider节点A、B、C权重比为5:1:1。那么在7次请求中,节点A将收到5次请求,节点B会收到1次请求,节点C则会收到1次请求。
二.加权轮询算法的执行流程
每个Provider节点有两个权重:一个权重是配置的weight,该值在负载均衡的过程中不会变化。另一个权重是currentWeight,该值会在负载均衡的过程中动态调整,初始值为0。
当有新的请求进来时,RoundRobinLoadBalance会遍历Invoker列表,并用对应的currentWeight加上其配置的权重。遍历完成后,再找到最大的currentWeight,将其减去权重总和,然后返回相应的Invoker对象。
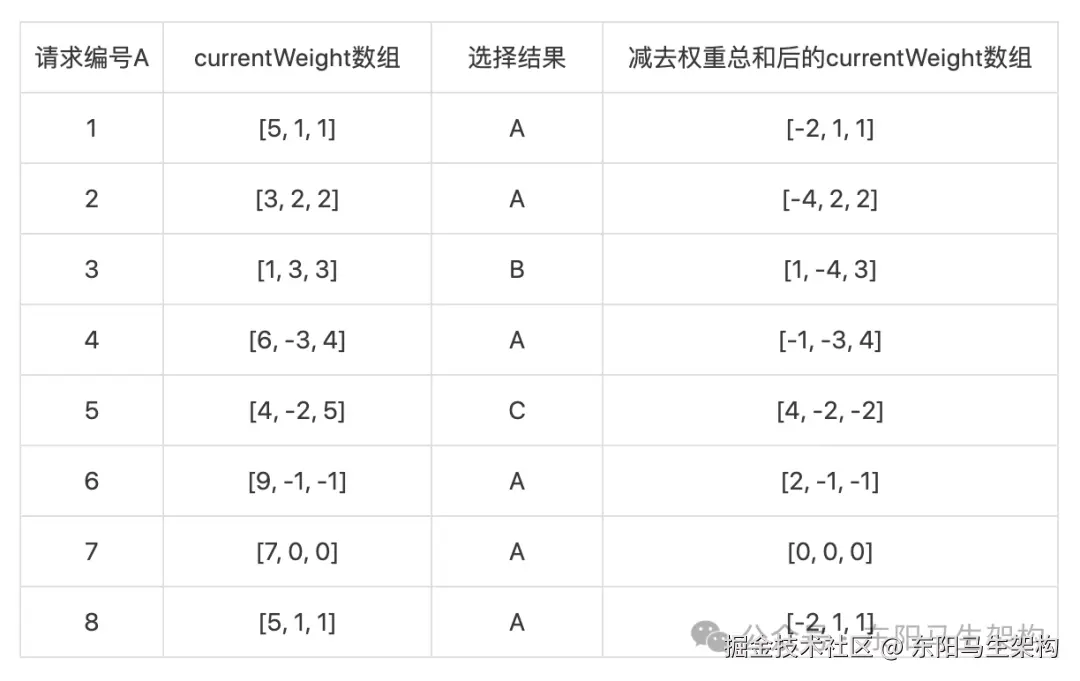
假设A、B、C三个节点的权重比例为5:1:1。
说明一: 处理第一个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[0, 0, 0]变为[5, 1, 1]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点A。最后,将节点A的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为[-2, 1, 1]。
说明二: 处理第二个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[-2, 1, 1]变为[3, 2, 2]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点A。最后,将节点A的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为[-4, 2, 2]。
说明三: 处理第三个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[-4, 2, 2]变为[1, 3, 3]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点B。最后,将节点B的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为[1, -4, 3]。
说明四: 处理第四个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[1, -4, 3]变为[6, -3, 4]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点A。最后,将节点A的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为[-1, -3, 4]。
说明五: 处理第五个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[-1, -3, 4]变为[4, -2, 5]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点C。最后,将节点C的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为[4, -2, -2]。
说明六: 处理第六个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[4, -2, -2]变为[9, -1, -1]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点A。最后,将节点A的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为 [2, -1, -1]。
说明七: 处理第七个请求,currentWeight数组中的权重与配置的weight相加,即从[2, -1, -1]变为[7, 0, 0]。接下来,从中选择权重最大的Invoker作为结果,即节点A。最后,将节点A的currentWeight值减去totalWeight值,最终得到currentWeight数组为[0, 0, 0]。
到此为止,一个轮询的周期就结束了。
三.加权轮询算法的实现
RoundRobinLoadBalance会为每个Invoker对象创建对应的WeightedRoundRobin对象,用来记录配置的权重(weight字段)以及随着每次负载均衡算法执行变化的current权重(current字段)。
java
public class RoundRobinLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "roundrobin";
private static final int RECYCLE_PERIOD = 60000;
protected static class WeightedRoundRobin {
//配置的Invoker权重,该权重不会变化
private int weight;
//当前的权重值,随着RoundRobin过程而改变
private AtomicLong current = new AtomicLong(0);
//最后一次更新时间
private long lastUpdate;
public int getWeight() {
return weight;
}
public void setWeight(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
//初始current为0
current.set(0);
}
public long increaseCurrent() {
return current.addAndGet(weight);
}
public void sel(int total) {
current.addAndGet(-1 * total);
}
public long getLastUpdate() {
return lastUpdate;
}
public void setLastUpdate(long lastUpdate) {
this.lastUpdate = lastUpdate;
}
}
private ConcurrentMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>> methodWeightMap =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin>>();
//get invoker addr list cached for specified invocation
protected <T> Collection<String> getInvokerAddrList(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
Map<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.get(key);
if (map != null) {
return map.keySet();
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + invocation.getMethodName();
//获取整个Invoker列表对应的WeightedRoundRobin映射表
//如果为空,则创建一个新的WeightedRoundRobin映射表
ConcurrentMap<String, WeightedRoundRobin> map = methodWeightMap.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
int totalWeight = 0;
long maxCurrent = Long.MIN_VALUE;
//获取当前时间
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
Invoker<T> selectedInvoker = null;
WeightedRoundRobin selectedWRR = null;
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String identifyString = invoker.getUrl().toIdentityString();
int weight = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
//检测当前Invoker是否有相应的WeightedRoundRobin对象,没有则进行创建
WeightedRoundRobin weightedRoundRobin = map.computeIfAbsent(identifyString, k -> {
WeightedRoundRobin wrr = new WeightedRoundRobin();
wrr.setWeight(weight);
return wrr;
});
//检测Invoker权重是否发生了变化,若发生变化,则更新WeightedRoundRobin的weight字段
if (weight != weightedRoundRobin.getWeight()) {
weightedRoundRobin.setWeight(weight);
}
//让currentWeight加上配置的Weight
long cur = weightedRoundRobin.increaseCurrent();
//设置lastUpdate字段
weightedRoundRobin.setLastUpdate(now);
//寻找具有最大currentWeight的Invoker,以及Invoker对应的WeightedRoundRobin
if (cur > maxCurrent) {
maxCurrent = cur;
selectedInvoker = invoker;
selectedWRR = weightedRoundRobin;
}
//计算权重总和
totalWeight += weight;
}
if (invokers.size() != map.size()) {
map.entrySet().removeIf(item -> now - item.getValue().getLastUpdate() > RECYCLE_PERIOD);
}
if (selectedInvoker != null) {
//用currentWeight减去totalWeight
selectedWRR.sel(totalWeight);
//返回选中的Invoker对象
return selectedInvoker;
}
//should not happen here
return invokers.get(0);
}
}10.基于最少活跃数算法的负载均衡
(1)最小活跃数算法的原理
(2)最小活跃数算法的实现
(1)最小活跃数算法的原理
LeastActiveLoadBalance使用的负载均衡算法是最小活跃数算法。该算法认为当前活跃请求数越小的Provider节点,剩余的处理能力越多,处理请求的效率也就越高,那么该Provider在单位时间内就可以处理更多的请求,所以我们应该优先将请求分配给该Provider节点。
LeastActiveLoadBalance需要配合ActiveLimitFilter使用。ActiveLimitFilter会记录每个接口方法的活跃请求数,在LeastActiveLoadBalance进行负载均衡时,只会从活跃请求数最少的Invoker集合里挑选Invoker。
二.最小活跃数算法的实现
在LeastActiveLoadBalance的doSelect()方法中,首先会选出所有活跃请求数最小的Invoker对象,然后会按照这些Invoker对象的权重挑选最终的Invoker对象。
ini
//Filter the number of invokers with the least number of active calls and count the weights and quantities of these invokers.
//If there is only one invoker, use the invoker directly;
//if there are multiple invokers and the weights are not the same, then random according to the total weight;
//if there are multiple invokers and the same weight, then randomly called.
public class LeastActiveLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "leastactive";
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
//初始化Invoker数量
int length = invokers.size();
//记录最小的活跃请求数
int leastActive = -1;
//记录活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合的个数
int leastCount = 0;
//记录活跃请求数最小的Invoker在invokers数组中的下标位置
int[] leastIndexes = new int[length];
//记录活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合中,每个Invoker的权重值
int[] weights = new int[length];
//记录活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合中,所有Invoker的权重值之和
int totalWeight = 0;
//记录活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合中,第一个Invoker的权重值
int firstWeight = 0;
//是否活跃请求数最小的集合中,所有Invoker的权重值是否相同
boolean sameWeight = true;
//遍历所有Invoker,获取活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Invoker<T> invoker = invokers.get(i);
//获取该Invoker的活跃请求数
int active = RpcStatus.getStatus(invoker.getUrl(), invocation.getMethodName()).getActive();
//获取该Invoker的权重
int afterWarmup = getWeight(invoker, invocation);
weights[i] = afterWarmup;
//比较活跃请求数
if (leastActive == -1 || active < leastActive) {
//当前的Invoker是第一个活跃请求数最小的Invoker,则记录如下信息
//重新记录最小的活跃请求数
leastActive = active;
//重新记录活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合个数
leastCount = 1;
//重新记录Invoker
leastIndexes[0] = i;
//重新记录总权重值
totalWeight = afterWarmup;
//该Invoker作为第一个Invoker,记录其权重值
firstWeight = afterWarmup;
//重新记录是否权重值相等
sameWeight = true;
} else if (active == leastActive) {
//当前Invoker属于活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合
//记录该Invoker的下标
leastIndexes[leastCount++] = i;
//更新总权重
totalWeight += afterWarmup;
if (sameWeight && afterWarmup != firstWeight) {
//更新权重值是否相等
sameWeight = false;
}
}
}
//如果只有一个活跃请求数最小的Invoker对象,直接返回即可
if (leastCount == 1) {
return invokers.get(leastIndexes[0]);
}
//下面按照RandomLoadBalance的逻辑,从活跃请求数最小的Invoker集合中,随机选择一个Invoker对象返回
if (!sameWeight && totalWeight > 0) {
int offsetWeight = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
for (int i = 0; i < leastCount; i++) {
int leastIndex = leastIndexes[i];
offsetWeight -= weights[leastIndex];
if (offsetWeight < 0) {
return invokers.get(leastIndex);
}
}
}
return invokers.get(leastIndexes[ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(leastCount)]);
}
}11.基于一致性Hash算法的负载均衡
(1)一致性Hash算法的原理
(2)ConsistentHashSelector的实现
(1)一致性Hash算法的原理
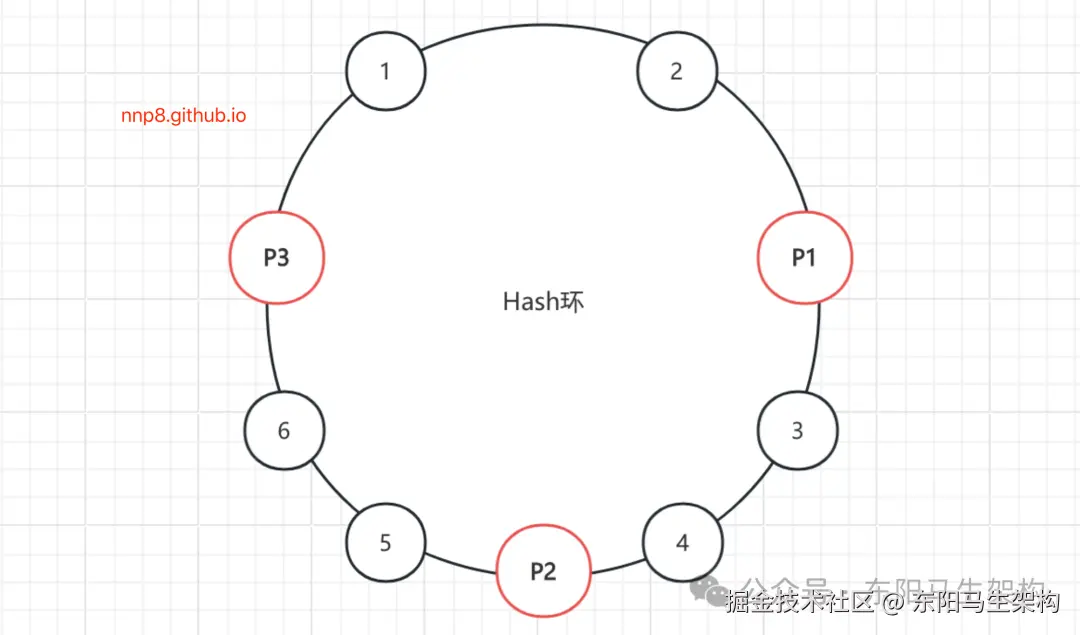
ConsistentHashLoadBalance是基于一致性Hash算法来实现负载均衡的。一致性Hash负载均衡可以让参数相同的请求每次都路由到相同的服务节点上,该负载均衡策略在某些Provider节点下线时,可让这些节点上的流量平摊到其他Provider上,不会引起所有节点流量的剧烈波动。
假设现在有1、2、3三个Provider节点对外提供服务,有100个请求同时到达。如果想让请求尽可能均匀地分布到这三个Provider节点上,最简单的方法就是Hash取模,即hash(请求参数) % 3。如果参与Hash计算的是请求的全部参数,那么参数相同的请求将会落到同一个Provider节点上。不过此时如果突然有一个Provider节点出现宕机,那就需要对2取模,即请求会重新分配到相应的Provider之上。在极端情况下,甚至会出现所有请求的处理节点都发生了变化,这就会造成比较大的波动。
为了避免因为一个Provider节点宕机,而导致大量请求的处理节点发生变化,可以考虑使用一致性Hash算法。一致性Hash算法的原理也是取模算法,与Hash取模的不同之处在于:Hash取模是对Provider节点数量取模,而一致性Hash算法是对2^32取模。
一致性Hash算法需要同时对Provider地址以及请求参数的hash值进行取模:
bash
# 确定Provider节点在Hash环上的位置
hash(Provider地址) % 2^32
# 确定请求在Hash环上的位置
# 靠近哪个Provider节点,就将请求发送给哪个Provider节点
hash(请求参数) % 2^32Provider地址和请求参数的hash值经过对2^32取模后,得到的结果值都会落到一个Hash环上,如下一致性Hash节点均匀分布图所示:
假设按顺时针方向,依次将请求分发到对应的Provider。这样,当某台Provider节点宕机或增加新的Provider节点时,只会影响这个Provider节点对应的请求。
在理想情况下,一致性Hash算法会将这三个Provider节点均匀地分布到Hash环上,请求也可以均匀地分发给这三个Provider节点。
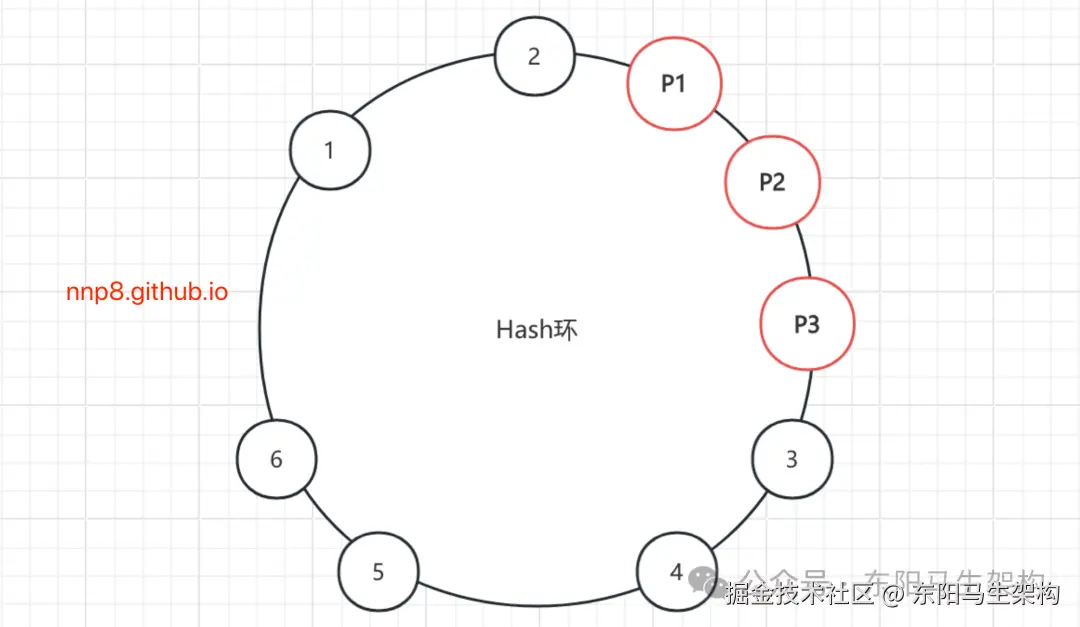
但在实际情况中,这三个Provider节点地址取模之后的值,可能差距不大,这样会导致大量的请求落到一个Provider节点上。如下一致性Hash节点非均匀分布图所示:
这就出现了数据倾斜的问题。所谓数据倾斜是指由于节点不够分散,导致大量请求落到同一个节点上,而其他节点只收到少量请求的情况。
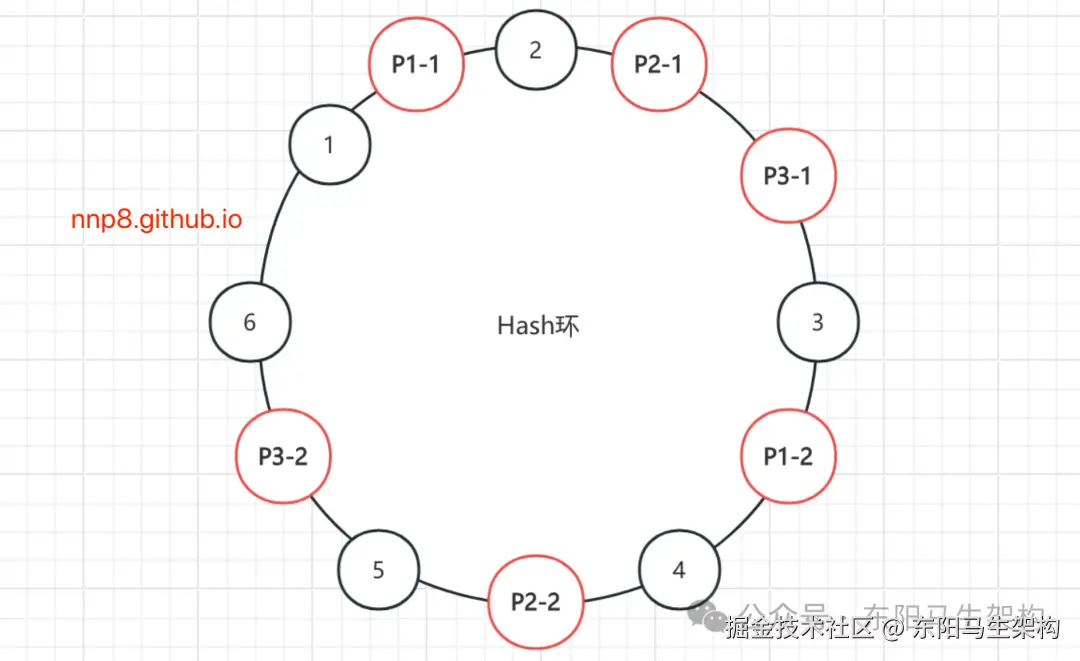
为了解决一致性Hash算法中出现的数据倾斜问题,又引入了Hash槽。Hash槽解决数据倾斜的思路是:既然问题是由Provider节点在Hash环上分布不均匀造成的,那么可以虚拟出n组P1、P2、P3的Provider节点,让多组Provider节点相对均匀地分布在Hash环上。
如下数据倾斜解决示意图所示,相同前缀的节点均为同一个Provider节点,比如P1-1、P1-2、P1-99表示的都是P1这个Provider节点。引入Provider虚拟节点之后,便可以让Provider节点在圆环上分散开,从而有效避免数据倾斜。
(2)ConsistentHashSelector的实现
ConsistentHashLoadBalance的doSelect()方法会根据ServiceKey和methodName选择一个ConsistentHashSelector对象,核心算法会委托给ConsistentHashSelector对象来完成。
ConsistentHashSelector构造方法的主要任务是:构建Hash槽和确认参与一致性Hash计算的参数(默认是第一个参数),这些操作的目的就是为了让Invoker尽可能均匀地分布在Hash环上。
ConsistentHashSelector的select()方法会选择合适的Invoker对象来处理请求。其中会先对请求参数进行md5以及Hash运算,得到一个Hash值,然后再通过这个Hash值到TreeMap中查找目标Invoker。
ini
public class ConsistentHashLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "consistenthash";
public static final String HASH_NODES = "hash.nodes";
public static final String HASH_ARGUMENTS = "hash.arguments";
private final ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>> selectors = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector<?>>();
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
//获取调用的方法名称
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//将ServiceKey和方法拼接起来,构成一个key
String key = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getServiceKey() + "." + methodName;
//using the hashcode of list to compute the hash only pay attention to the elements in the list
int invokersHashCode = invokers.hashCode();
//根据key获取对应的ConsistentHashSelector对象
//selectors是一个ConcurrentMap<String, ConsistentHashSelector>集合
ConsistentHashSelector<T> selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
if (selector == null || selector.identityHashCode != invokersHashCode) {
//未查找到ConsistentHashSelector对象,则进行创建
selectors.put(key, new ConsistentHashSelector<T>(invokers, methodName, invokersHashCode));
selector = (ConsistentHashSelector<T>) selectors.get(key);
}
//通过ConsistentHashSelector对象选择一个Invoker对象
return selector.select(invocation);
}
private static final class ConsistentHashSelector<T> {
//字段一:用于记录虚拟Invoker对象的Hash环
//使用TreeMap实现Hash环,并将虚拟的Invoker对象分布在Hash环上
private final TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>> virtualInvokers;
//字段二:虚拟Invoker个数
private final int replicaNumber;
//字段三:Invoker集合的HashCode值
private final int identityHashCode;
//字段四:需要参与Hash计算的参数索引
private final int[] argumentIndex;
ConsistentHashSelector(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, String methodName, int identityHashCode) {
//初始化virtualInvokers字段,也就是虚拟Hash槽
this.virtualInvokers = new TreeMap<Long, Invoker<T>>();
//记录Invoker集合的hashCode,用该hashCode值来判断Provider列表是否发生了变化
this.identityHashCode = identityHashCode;
//从hash.nodes参数中获取虚拟节点的个数
URL url = invokers.get(0).getUrl();
this.replicaNumber = url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_NODES, 160);
//获取参与hash计算的参数下标值,默认对第一个参数进行hash运算
String[] index = COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url.getMethodParameter(methodName, HASH_ARGUMENTS, "0"));
argumentIndex = new int[index.length];
for (int i = 0; i < index.length; i++) {
argumentIndex[i] = Integer.parseInt(index[i]);
}
//构建虚拟Hash槽,默认replicaNumber=160,相当于在Hash槽上放160个槽位
//外层轮询40次,内层轮询4次,共40*4=160次,也就是同一节点虚拟出160个槽位
for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) {
String address = invoker.getUrl().getAddress();
for (int i = 0; i < replicaNumber / 4; i++) {
//对address + i进行md5运算,得到一个长度为16的字节数组
byte[] digest = md5(address + i);
//对digest部分字节进行4次Hash运算,得到四个不同的long型正整数
for (int h = 0; h < 4; h++) {
//h = 0时,取 igest中下标为0 ~ 3的4个字节进行位运算
//h = 1时,取 digest 中下标为4 ~ 7的4个字节进行位运算
//h = 2, h = 3时过程同上
long m = hash(digest, h);
virtualInvokers.put(m, invoker);
}
}
}
}
public Invoker<T> select(Invocation invocation) {
//将参与一致性Hash的参数拼接到一起
String key = toKey(invocation.getArguments());
//计算key的Hash值
byte[] digest = md5(key);
//匹配Invoker对象
return selectForKey(hash(digest, 0));
}
private String toKey(Object[] args) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder();
for (int i : argumentIndex) {
if (i >= 0 && i < args.length) {
buf.append(args[i]);
}
}
return buf.toString();
}
private Invoker<T> selectForKey(long hash) {
//从virtualInvokers集合(TreeMap是按照Key排序的)中
//查找第一个节点值大于或等于传入Hash值的Invoker对象
Map.Entry<Long, Invoker<T>> entry = virtualInvokers.ceilingEntry(hash);
//如果Hash大于Hash环中的所有Invoker
//则回到Hash环的开头,返回第一个Invoker对象
if (entry == null) {
entry = virtualInvokers.firstEntry();
}
return entry.getValue();
}
private long hash(byte[] digest, int number) {
return (((long) (digest[3 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 24)
| ((long) (digest[2 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 16)
| ((long) (digest[1 + number * 4] & 0xFF) << 8)
| (digest[number * 4] & 0xFF))
& 0xFFFFFFFFL;
}
private byte[] md5(String value) {
MessageDigest md5;
try {
md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
md5.reset();
byte[] bytes = value.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
md5.update(bytes);
return md5.digest();
}
}
}12.Dubbo的自动降级与Mock机制原理
(1)Mock机制和Mock模拟调用
(2)MockClusterInvoker的创建
(3)MockClusterInvoker实现Mock机制
(1)Mock机制和Mock模拟调用
Mock机制是RPC框架中非常常见、也非常有用的功能。Mock机制不仅可以用来实现服务降级,还可以用来在测试中模拟调用的各种异常情况。
Dubbo中的Mock机制是在Consumer这一端实现的,具体来说就是在Cluster这一层实现的。
Mock模拟调用,指的是如果目标Provider服务实例突然故障了,这时Consumer端可以进行降级调用。也就是本地进行mock,Consumer端就不再发起远程调用了,直接在本地调用一个mock()方法。而本地调用一个mock()方法,其实就是在mock()方法里写死一个结果,直接返回。
(2)MockClusterInvoker的创建
Cluster接口的实现类MockClusterWrapper负责创建MockClusterInvoker对象,是Dubbo Mock机制的入口。
MockClusterWrapper是Cluster对象的包装类,MockClusterWrapper类会对Cluster进行包装。
下面是MockClusterWrapper的实现,它会在Cluster Invoker对象的基础上使用MockClusterInvoker进行包装。
java
public class MockClusterWrapper implements Cluster {
private Cluster cluster;
public MockClusterWrapper(Cluster cluster) {
//Wrapper类都会有一个拷贝构造函数
this.cluster = cluster;
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException {
//用MockClusterInvoker进行包装,将DynamicDirectory和FailoverClusterInvoker包装在里面
return new MockClusterInvoker<T>(directory, this.cluster.join(directory));
}
}(3)MockClusterInvoker实现Mock机制
MockClusterInvoker是Dubbo Mock机制的核心,它主要是通过invoke()、doMockInvoke()和selectMockInvoker()这三个核心方法来实现Mock机制。
一.invoke()方法的具体实现
它会先判断是否需要开启Mock机制。如果在mock参数中配置force模式,则会直接调用doMockInvoke()方法进行mock。如果在mock参数中配置fail模式,则会正常调用Invoker发起请求,在请求失败时会调动doMockInvoke()进行mock。
二.doMockInvoke()方法的具体实现
会调用selectMockInvoker()方法获取MockInvoker对象,并调用其invoke()方法进行mock操作。
三.selectMockInvoker()方法的具体实现
它并没有进行MockInvoker的选择或是创建,仅仅将Invocation附属信息中的invocation.need.mock属性设置为true,然后交给Directory中的Router集合进行处理。
java
public class MockClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
Result result;
//从URL中获取方法对应的mock配置
String value = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), MOCK_KEY, Boolean.FALSE.toString()).trim();
if (ConfigUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
//no mock
//若mock参数未配置或是配置为false,则不会开启Mock机制,直接调用底层的Invoker
//这里会直接发起正常的调用
//每一层Invoker都会去负责自己的事情,对Invoker的调用使用了严格的责任链模式,运用了责任链模式的思想
//A Invoker->B Invoker->C Invoker->D Invoker
//在发起RPC调用时,由于会涉及到很多的机制,比如降级调用机制(mock),集群容错机制,负载均衡机制等
//此时如果只有一个Invoker,那么它里面的代码就会很多很复杂,所以才用上了责任链模式
//下面会调用AbstractCluster内部类ClusterFilterInvoker的invoke()方法,进行正常的RPC调用
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
} else if (value.startsWith(FORCE_KEY)) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("force-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " force-mock enabled , url : " + getUrl());
}
//force:direct mock
//若mock参数配置为force,则表示强制开始mock,直接调用doMockInvoke()方法
//也就是对这个服务实例的调用使用了force-mock,强制性进行mock,根本就不会发起真正的RPC调用
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, null);
} else {
//fail-mock
//如果mock配置的不是force,则配置的是fail,则会继续调用Invoker对象的invoke()方法进行请求
try {
//下面会调用AbstractCluster内部类ClusterFilterInvoker的invoke()方法,进行正常的RPC调用
result = this.invoker.invoke(invocation);
//fix:#4585
if (result.getException() != null && result.getException() instanceof RpcException) {
RpcException rpcException = (RpcException) result.getException();
if (rpcException.isBiz()) {
throw rpcException;
} else {
//如果RPC调用出现异常,那么会在这里直接进行mock调用
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, rpcException);
}
}
} catch (RpcException e) {
//如果是业务异常,会直接抛出
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
}
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("fail-mock: " + invocation.getMethodName() + " fail-mock enabled , url : " + getUrl(), e);
}
//如果是非业务异常,会调用doMockInvoke()方法直接进行mock调用
result = doMockInvoke(invocation, e);
}
}
return result;
}
private Result doMockInvoke(Invocation invocation, RpcException e) {
Result result;
Invoker<T> mockInvoker;
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = (RpcInvocation)invocation;
rpcInvocation.setInvokeMode(RpcUtils.getInvokeMode(getUrl(),invocation));
//调用selectMockInvoker()方法过滤得到MockInvoker
List<Invoker<T>> mockInvokers = selectMockInvoker(invocation);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(mockInvokers)) {
//如果selectMockInvoker()方法未返回MockInvoker对象,则创建一个MockInvoker
mockInvoker = (Invoker<T>) new MockInvoker(getUrl(), directory.getInterface());
} else {
mockInvoker = mockInvokers.get(0);
}
//调用MockInvoker.invoke()方法进行mock
result = mockInvoker.invoke(invocation);
...
return result;
}
private List<Invoker<T>> selectMockInvoker(Invocation invocation) {
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = null;
if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
//将Invocation附属信息中的invocation.need.mock属性设置为true
invocation.setAttachment(INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK, Boolean.TRUE.toString());
//directory will return a list of normal invokers if Constants.INVOCATION_NEED_MOCK is absent or not true in invocation
//otherwise, a list of mock invokers will return.
RpcContext.getServiceContext().setConsumerUrl(getUrl());
invokers = directory.list(invocation);
...
}
return invokers;
}
...
}13.Dubbo的Mock模拟调用原理
(1)mock参数以return开头
(2)mock参数以throw开头
(3)mock参数为true或default时
在MockInvoker中会解析各类Mock配置,并根据不同Mock配置进行不同的Mock操作。MockInvoker的invoke()方法会针对mock参数的分类进行不同情况的处理:
(1)mock参数以return开头
直接返回mock参数指定的固定值,例如empty、null、true、false、json等。mock参数中指定的固定返回值将会由parseMockValue()方法进行解析。
(2)mock参数以throw开头
直接抛出异常,如果在mock参数中没有指定异常类型,则抛出RpcException,否则抛出指定的Exception类型。
(3)mock参数为true或default时
会查找服务接口对应的Mock实现。如果是其他值,则直接作为服务接口的Mock实现;拿到Mock实现之后,转换成Invoker进行调用。
MockInvoker的invoke()方法如下所示:
java
//位于dubbo-rpc下的dubbo-rpc-api下
final public class MockInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
((RpcInvocation) invocation).setInvoker(this);
}
//获取mock值(会从URL中的methodName.mock参数或mock参数获取)
String mock = getUrl().getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), MOCK_KEY);
//没有配置mock值,直接抛出异常
if (StringUtils.isBlank(mock)) {
throw new RpcException(new IllegalAccessException("mock can not be null. url :" + url));
}
//mock值进行处理,去除"force:"、"fail:"前缀等
mock = normalizeMock(URL.decode(mock));
if (mock.startsWith(RETURN_PREFIX)) {
//mock值以return开头
mock = mock.substring(RETURN_PREFIX.length()).trim();
try {
//获取响应结果的类型,也就是针对这个RPC调用看一下本次调用要返回的类型是什么
Type[] returnTypes = RpcUtils.getReturnTypes(invocation);
//根据结果类型,对mock值中结果值进行转换,返回的可能是null、object、map、list、字符串
Object value = parseMockValue(mock, returnTypes);
//将固定的mock值设置到Result中
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(value, invocation);
} catch (Exception ew) {
throw new RpcException("mock return invoke error. method :" + invocation.getMethodName() + ", mock:" + mock + ", url: " + url, ew);
}
} else if (mock.startsWith(THROW_PREFIX)) {
//mock值以throw开头
mock = mock.substring(THROW_PREFIX.length()).trim();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(mock)) {
//未指定异常类型,直接抛出RpcException
throw new RpcException("mocked exception for service degradation.");
} else {//user customized class
//抛出自定义异常
Throwable t = getThrowable(mock);
throw new RpcException(RpcException.BIZ_EXCEPTION, t);
}
} else {//impl mock
//执行mockService得到mock结果
try {
Invoker<T> invoker = getInvoker(mock);
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to create mock implementation class " + mock, t);
}
}
}
...
}针对return和throw的处理逻辑比较简单,但getInvoker()方法略微复杂些。其中会处理MOCK_MAP缓存的读写、Mock实现类的查找、生成和调用Invoker,具体实现如下:
scss
final public class MockInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
private Invoker<T> getInvoker(String mock) {
Class<T> serviceType = (Class<T>) ReflectUtils.forName(url.getServiceInterface());
String mockService = ConfigUtils.isDefault(mock) ? serviceType.getName() + "Mock" : mock;
//尝试从MOCK_MAP集合中获取对应的Invoker对象
Invoker<T> invoker = (Invoker<T>) MOCK_MAP.get(mockService);
if (invoker != null) {
return invoker;
}
//根据serviceType查找mock的实现类
T mockObject = (T) getMockObject(url.getOrDefaultApplicationModel().getExtensionDirector(), mock, serviceType);
//创建Invoker对象
invoker = proxyFactory.getInvoker(mockObject, serviceType, url);
if (MOCK_MAP.size() < 10000) {
//写入缓存
MOCK_MAP.put(mockService, invoker);
}
return invoker;
}
...
}在getMockObject()方法中会检查mockService参数是否为true或default。如果是的话,则在服务接口后添加Mock字符串,作为服务接口的Mock实现。如果不是的话,则直接将mockService实现作为服务接口的Mock实现。
vbnet
final public class MockInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public static Object getMockObject(String mockService, Class serviceType) {
if (ConfigUtils.isDefault(mockService)) {
//如果mock为true或default值,会在服务接口后添加Mock字符串走位实现类进行实例化
mockService = serviceType.getName() + "Mock";
}
Class<?> mockClass = ReflectUtils.forName(mockService);
if (!serviceType.isAssignableFrom(mockClass)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("...");
}
try {
return mockClass.newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No default constructor from mock class " + mockClass.getName(), e);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
...
}14.DubboInvoker的RPC调用细节
(1)DubboInvoker构建时的调用链
(2)DubboInvoker被调用时的调用链
(3)DubboInvoker的RPC调用细节
(1)DubboInvoker构建时的调用链
scala
//-> ReferenceConfig.get()
//...
//-> RegistryProtocol.doCreateInvoker()
// directory.subscribe(toSubscribeUrl(urlToRegistry))
//-> RegistryDirectory.subscribe()
//-> DynamicDirectory.subscribe()
//-> ListenerRegistryWrapper.subscribe()
//-> FailbackRegistry.subscribe()
//-> AbstractRegistry.subscribe() + FailbackRegistry.doSubscribe()
//-> ZookeeperRegistry.doSubscribe() + create()/notify()
//-> FailbackRegistry.notify()
//-> AbstractRegistry.notify()
//-> RegistryDirectory.notify()
//-> RegistryDirectory.toInvokers()
//-> DubboProtocol.refer()
//-> DubboProtocol.protocolBindingRefer()
//-> new DubboInvoker()
// protocolBindingRefer()方法中会先通过getClients(url)进行网络连接,然后才封装一个DubboInvoker返回
public class DubboProtocol extends AbstractProtocol {
...
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
checkDestroyed();
return protocolBindingRefer(type, url);
}
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> protocolBindingRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
checkDestroyed();
//进行序列化优化,注册需要优化的类
optimizeSerialization(url);
//create rpc invoker,创建DubboInvoker对象
//首先将url传入getClients()方法中,针对目标服务实例进行网络连接
//然后再根据这个目标服务实例的url,构建一个DubboInvoker
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
//将上面创建的DubboInvoker对象添加到invoker集合中
invokers.add(invoker);
return invoker;
}
...
}(2)DubboInvoker被调用时的调用链
arduino
//-> InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke()
//-> InvocationUtil.invoke()
// invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()
//-> MigrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> MockClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractCluster.ClusterFilterInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CallbackRegistrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> ConsumerContextFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> FutureFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> MonitorFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> RouterSnapshotFilter.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.initLoadBalance()
//-> FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.select()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect()
//-> AbstractLoadBalance.select()
//-> RandomLoadBalance.doSelect()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invokeWithContext()
//-> ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.doInvokeAndReturn()
//-> DubboInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.getCallbackExecutor()
//-> 配合线程池使用currentClient.request()发起RPC请求
//-> ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request()
//-> HeaderExchangeClient.request()
//-> HeaderExchangeChannel.request()
//-> DefaultFuture.newFuture()
//-> NettyClient.send() => AbstractPeer.send() => AbstractClient.send()
//-> NettyChannel.send() => channel.writeAndFlush()(3)DubboInvoker的RPC调用细节
scss
public class DubboInvoker<T> extends AbstractInvoker<T> {
//ExchangeClient底层封装的就是NettyClient
private final ExchangeClient[] clients;
...
public DubboInvoker(Class<T> serviceType, URL url, ExchangeClient[] clients, Set<Invoker<?>> invokers) {
super(serviceType, url, new String[]{INTERFACE_KEY, GROUP_KEY, TOKEN_KEY});
//DubboProtocol的protocolBindingRefer()方法在构建DubboInvoker时
//会先通过DubboProtocol的getClients()方法获取ReferenceCountExchangeClient
//然后再将这些ReferenceCountExchangeClient传入这里去构建DubboInvoker
this.clients = clients;
// get version.
this.version = url.getVersion(DEFAULT_VERSION);
this.invokers = invokers;
this.serverShutdownTimeout = ConfigurationUtils.getServerShutdownTimeout(getUrl().getScopeModel());
}
@Override
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
//此次调用的方法名称
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//向Invocation中添加附加信息
//这里将URL的path和version添加到附加信息中
inv.setAttachment(PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(VERSION_KEY, version);
//ExchangeClient和Exchange都是跟网络相关的
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
//选择一个ExchangeClient实例
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
//如果有多个用于网络通信的client,就会逐个去使用,这会是一个循环使用的过程
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
//根据调用的方法名称和配置计算此次调用的超时时间,默认是1秒
int timeout = calculateTimeout(invocation, methodName);
invocation.setAttachment(TIMEOUT_KEY, timeout);
if (isOneway) {
//不需要关注返回值的请求
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
} else {
//需要关注返回值的请求
//1.获取处理响应的线程池
//下面会调用AbstractInvoker的getCallbackExecutor()方法
//对于同步请求,会使用ThreadlessExecutor
//对于异步请求,则会使用共享的线程池;
ExecutorService executor = getCallbackExecutor(getUrl(), inv);
//2.发起网络请求
//currentClient.request()会使用上面选出的ExchangeClient执行request()方法将请求发送出去
//下面其实会调用ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request()方法
//而thenApply()会将AppResponse封装成AsyncRpcResult返回
CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture = currentClient.request(inv, timeout, executor)
.thenApply(obj -> (AppResponse) obj);
//3.处理请求的响应结果
//save for 2.6.x compatibility, for example, TraceFilter in Zipkin uses com.alibaba.xxx.FutureAdapter
FutureContext.getContext().setCompatibleFuture(appResponseFuture);
AsyncRpcResult result = new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, inv);
result.setExecutor(executor);
//要想拿到AppResponse结果,就需要基于CompletableFuture进行同步等待
//只要Provider返回响应结果,就必然会写入到CompletableFuture里
//此时就可以通过CompletableFuture取出AppResponse结果了
//比如InvocationUtil的invoke()方法在执行"invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()"时
//就会调用AsyncRpcResult的recreate()方法来获取Provider返回的响应结果
//也就是会调用到CompletableFuture的get()方法获取Provider返回的响应结果
return result;
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
throw new RpcException("...");
} catch (RemotingException e) {
throw new RpcException("...");
}
}
...
}