案例
案例一:普通的 Spring 应用
下面的代码中使用了 @Component 注解修饰了 TestBean,表示这个类需要被 Spring 加载为一个 Bean。
使用 @Configuration 和 @Compenent 注解修饰 AppConfig 表示这是一个配置类,且需要从 com.example 包路径下去扫描加载 Bean。
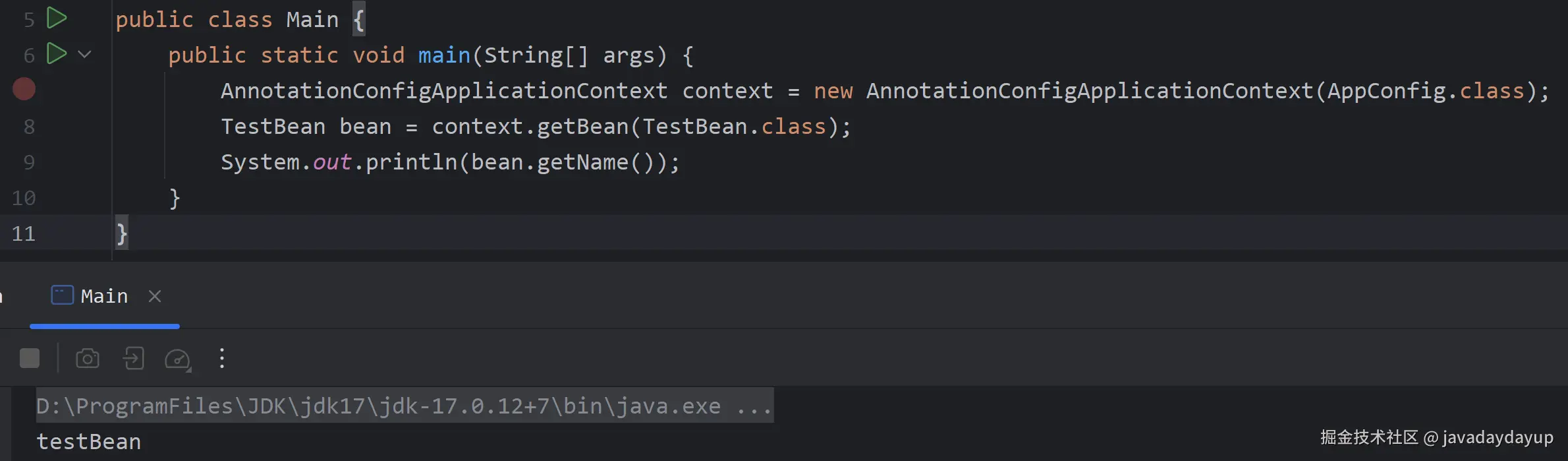
在 Main 中通过构造一个 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,并把 AppConfig 作为构造参数。然后从这个 Spring 上下文中获取 TestBean,并输出它的 name 属性。从结果看是 Spring 是可以正确扫描并加载 TestBean 到 Spring 上下文中的。代码如下:
java
@Component
public class TestBean {
private String name = "testBean";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example")
public class AppConfig {
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
TestBean bean = context.getBean(TestBean.class);
System.out.println(bean.getName());
}
}
案例二:Spring Web项目
下面的代码中的使用 @Configuration 和 @ComponentScan 注解修饰了 RootConfig,表明了它是一个配置类,且需要从 com.example 路径下扫描并加载 Bean,并且排除 @Controller 注解修饰的类。
使用 @Configuration 和 @ComponentScan 注解修饰了 WebConfig,表明了它是一个配置类,扫描 com.example.controller 路径下的 Bean。
提供了 MyWebAppInitializer 继承自 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 并在它的 getRootConfigClasses() 和 getServletConfigClasses() 分别指定了 RootConfig 和 WebConfig 配置类。
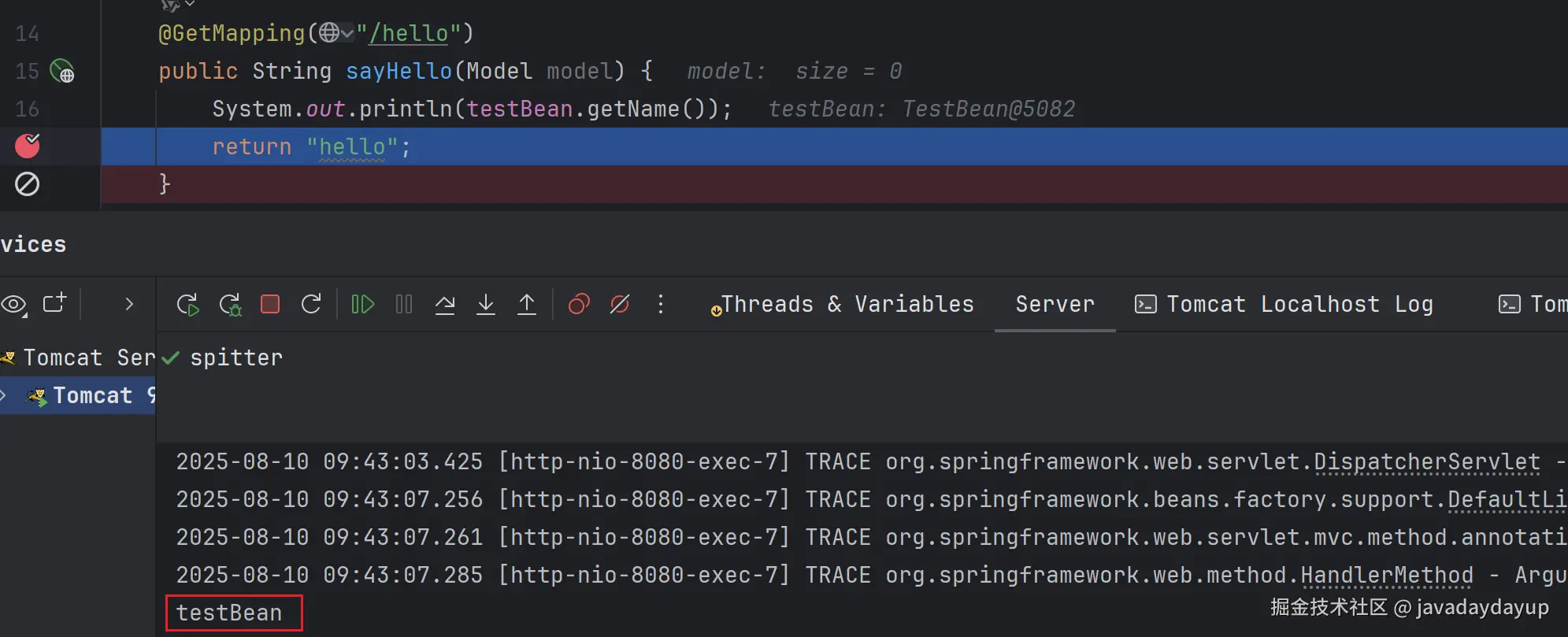
然后在 HelloController 中注入了 TestBean 这个 Bean,并在请求的时候并输出它的 name 属性。从结果看 Spring 是可以正确扫描并加载 TestBean 这个 Bean 到 Spring 上下文中的。
java
@Component
public class TestBean {
private String name = "testBean";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] { RootConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class<?>[] { WebConfig.class };
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] { "/" };
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(
basePackages = "com.example",
excludeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, value = Controller.class)
}
)
public class RootConfig {
}
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.example.controller")
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
}
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private TestBean testBean;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(Model model) {
System.out.println(testBean.getName());
return "hello";
}
}
案例三:Spring Boot 应用
下面的代码中少了 RootConfig 和 WebConfig 两个配置类,取而代之的是 @SpringBootApplication 注解修饰的 SpringBootTestApplication。
@SpringBootApplication 这个注解实际上是个复合注解,它被 @Configuration 和 @ComponentScan 注解修饰,那等效的效果就是 @Configuration 和 @ComponentScan 注解修饰了 SpringBootTestApplication。
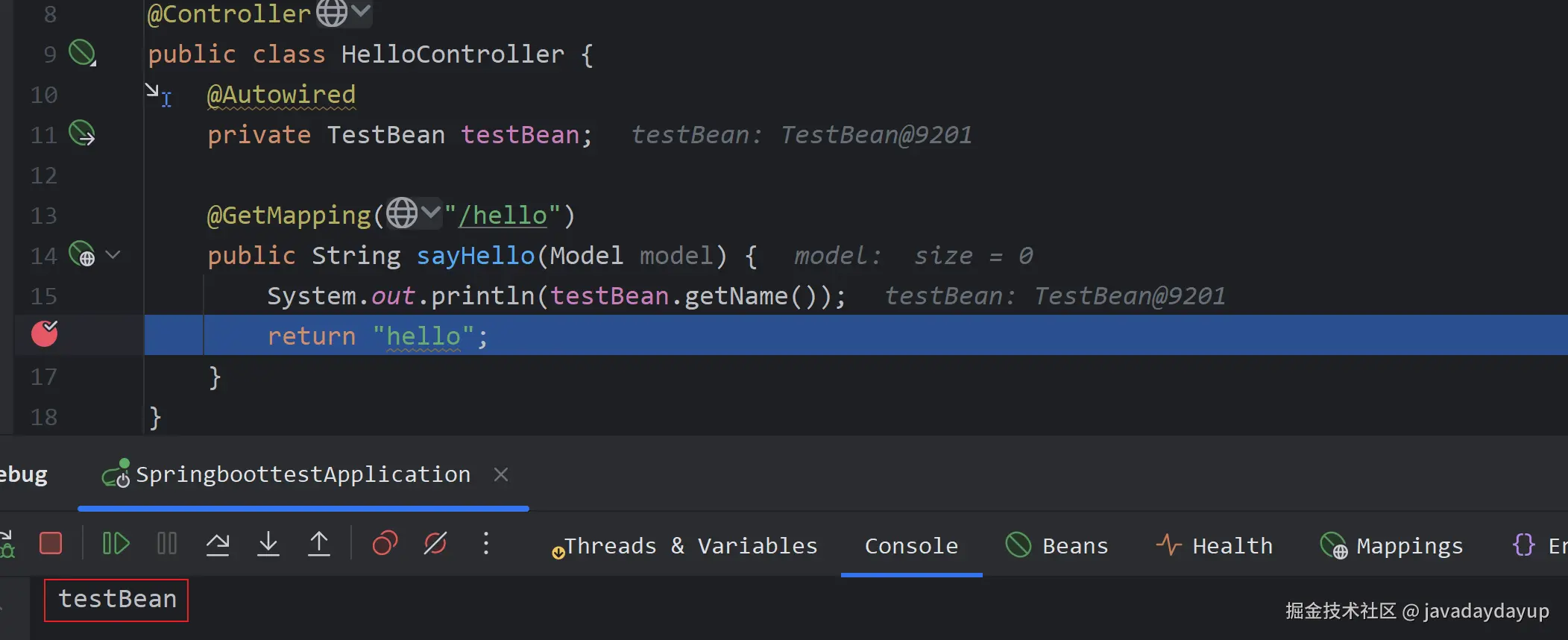
然后在 HelloController 中注入了 TestBean 这个 Bean,并在请求的时候并输出它的 name 属性。从结果看 Spring 是可以正确扫描并加载 TestBean 这个 Bean 到 Spring 上下文中的。
java
@Component
public class TestBean {
private String name = "testBean";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@Autowired
private TestBean testBean;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(Model model) {
System.out.println(testBean.getName());
return "hello";
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootTestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
@Indexed
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}
从上面的三个案例可以看出这几种案例下 Spring 都能够正确地扫描到 @Component 注解修饰的 Bean,那在 Spring 内部是如何实现的呢?
先说结论: Spring 在创建了上下文之后,会把 @Configuration 注解修饰的配置类的 Bean 定义注册到上下文中。然后在 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法中,解析配置类上面的 @ComponentScan 注解上定义 basePackages 信息,然后从这些路径下去读取 class 文件,判断它是否有 @Component 注解修饰,如果有则将其解析为一个 Bean 定义,然后注册到 Spring 上下文中,从而完成对 @Component 注解定义的 Bean 的扫描。
接下来将从源码的角度来分析一下。
源码分析
在 Spring 中提供了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,它有一个 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法,扩展这个方法可以向 Spring 中注册额外的 Bean 定义。而对于 @Component 注解修饰的 Bean 的定义就是通过这个扩展方法注册到 Spring 中的。
java
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
@Override
default void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}案例一
先看下案例一 中的 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 构造函数的实现。当传入一个配置类时,它会把这个配置类在 Spring 中注册一个 Bean 定义,注册是委托给 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 进行注册的,其实后面的案例二和案例三最终也是委托给该类进行注册的。代码如下:
java
ublic class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
this();
register(componentClasses);
refresh();
}
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
// 调用reader的register()方法进行注册
this.reader.register(componentClasses);
registerComponentClass.end();
}
}
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
for (Class<?> componentClass : componentClasses) {
registerBean(componentClass);
}
}
}Spring 提供了一个 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,然后在它的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 方法中会查找所有的 Bean 定义中带有 @Configuration 注解修饰的 Bean 定义,然后委托 ConfigurationClassParser 去解析这些配置类配置的要扫描的 Bean 定义。 代码如下:
java
public class ConfigurationClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,
BeanRegistrationAotProcessor, BeanFactoryInitializationAotProcessor, PriorityOrdered,
ResourceLoaderAware, ApplicationStartupAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 省略代码
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (beanDef.getAttribute(ConfigurationClassUtils.CONFIGURATION_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
// 省略代码
}
// 这里判断是否有@Configuration注解修饰,如果有就加入到configCandidates中
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
}
// 省略代码
// 构造ConfigurationClassParser对象
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set<ConfigurationClass> alreadyParsed = CollectionUtils.newHashSet(configCandidates.size());
do {
// 调用ConfigurationClassParser的parse()方法解析Bean定义
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
// 获取到解析的Bean定义
Set<ConfigurationClass> configClasses = new LinkedHashSet<>(parser.getConfigurationClasses());
// 省略代码
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
alreadyParsed.addAll(configClasses);
// 省略代码
candidates.clear();
}
while (!candidates.isEmpty());
}
}在 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 的 parse() 方法中,对每一个有 @Configuration 注解的 Bean 定义进行解析,最终的解析逻辑是在 doProcessConfigurationClass() 方法中实现的。代码如下:
java
class ConfigurationClassParser {
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) {
BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition();
if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition annotatedBeanDef) {
// 对每一个有@Configuration注解的Bean定义进行解析
parse(annotatedBeanDef.getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
// 省略代码
}
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(configClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.PARSE_CONFIGURATION)) {
return;
}
SourceClass sourceClass = null;
sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass, filter);
do {
// 在doProcessConfigurationClass()方法执行真正的解析
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}
}在 doProcessConfigurationClass() 方法中又获取 @ConponentScan 注解的属性信息,然后委托 ComponentScanAnnotationParser 进行 Bean 定义的解析。代码如下:
java
class ConfigurationClassParser {
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// 省略代码
// 获取@ComponentScan注解的属性信息
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScan.class, ComponentScans.class,
MergedAnnotation::isDirectlyPresent);
// 省略代码
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// 调用componentScanParser的parse()方法进行解析
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// 省略代码
}
}
}
}在 ComponentScanAnnotationParser 的 parse() 方法中获取 @ComponentScan 的 basePackages 属性,然后委托给 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 进行扫描。代码如下:
java
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> parse(AnnotationAttributes componentScan, String declaringClass) {
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this.registry,
componentScan.getBoolean("useDefaultFilters"), this.environment, this.resourceLoader);
// 省略代码
Set<String> basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 获取 `basePackages` 属性
String[] basePackagesArray = componentScan.getStringArray("basePackages");
for (String pkg : basePackagesArray) {
String[] tokenized = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(pkg),
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
Collections.addAll(basePackages, tokenized);
}
// 省略代码
// 调用scanner的doScan()方法进行扫描
return scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages));
}在 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 的 doScan() 方法中实际上往下调用到 scanCandidateComponents() 方法,在该方法中会从设置的 basePackages 路径下读取所有的 class 文件,然后判断它上面是否有 @Component 注解修饰,如果有,则把它加载到返回结果中 ,然后在 doScan() 方法中将返回的 Bean 定义注册到 Spring 中,这样在后面就可以基于这些 Bean 定义创建 Bean 了。
java
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
// 省略代码
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 注册Bean定义
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
if (this.componentsIndex != null && indexSupportsIncludeFilters()) {
return addCandidateComponentsFromIndex(this.componentsIndex, basePackage);
}
else {
return scanCandidateComponents(basePackage);
}
}
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
for (Resource resource : resources) { // 每一个 class文件对应一个Resource
String filename = resource.getFilename();
if (filename != null && filename.contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
// Ignore CGLIB-generated classes in the classpath
continue;
}
// 从class文件中读取元数据
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
// 判断是否有@Component注解修饰
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
candidates.add(sbd);
}
}
}
return candidates;
}
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return false;
}
}
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
// 这里通过includeFilter来判断
if (tf.match(metadataReader, getMetadataReaderFactory())) {
return isConditionMatch(metadataReader);
}
}
return false;
}
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
// 默认会加一个AnnotationTypeFilter,它会判断是否有@Component注解
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
// 省略代码
}案例二
对于案例二的加载原理是类似的。在 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer 内部的 createRootApplicationContext() 和 createServletApplicationContext() 方法中实际上分别创建了一个 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 上下文对象,并将 @Configuration 注解修饰的配置类注册到它内部的变量中。代码如下:
java
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
public abstract class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
// 创建AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext上下文对象
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
// 注册对应的配置类
context.register(configClasses);
return context;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
// 创建AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext上下文对象
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) {
// 注册对应的配置类
context.register(configClasses);
}
return context;
}
}在 AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext 的 loadBeanDefinitions() 方法中和 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类似,也向 Spring 中注册了 @Configuration 注解修饰的配置类的 Bean 定义。代码如下:
java
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 可以看到这里也是AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader对象
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader = getAnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = getClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(beanFactory);
// 省略代码
if (!this.componentClasses.isEmpty()) {
// 和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类似这里
// 也向Spring中注册了@Configuration注解修饰的配置类的Bean定义
reader.register(ClassUtils.toClassArray(this.componentClasses));
}
// 省略代码
}而在 Spring 上下文启动过程中,在 AbstractApplicationContext 中的 refresh() 方法中调用了 obtainFreshBeanFactory() 方法,在其子类 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext 中的 obtainFreshBeanFactory() 方法调用了 loadBeanDefinitions() 方法,也就将配置类的 Bean 定义注册到 Spring 中了。代码如下:
java
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
this.startupShutdownLock.lock();
try {
this.startupShutdownThread = Thread.currentThread();
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// 这里获取BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 省略代码
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex ) {
// 省略代码
}
finally {
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
finally {
this.startupShutdownThread = null;
this.startupShutdownLock.unlock();
}
}
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
}
public abstract class AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext {
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
beanFactory.setApplicationStartup(getApplicationStartup());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 这里调用了loadBeanDefinitions()方法
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
// 省略代码
}
}
}案例三
对于案例三,在 SpringApplication 的 run() 方法中会创建一个 AnnotationConfigServletWebApplicationContext 类型的 Spring 上下文,然后调用 prepareContext() 方法准备上下文,然后调用 load() 方法,在该方法中委托给 BeanDefinitionLoader 进行加载。代码如下:
java
public class SpringApplication {
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 省略代码
// 创建一个AnnotationConfigServletWebApplicationContext类型Spring上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
// 省略代码
return context;
}
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext,
ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 省略代码
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) {
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 这里会注册Bean定义
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
}
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
public Set<Object> getAllSources() {
Set<Object> allSources = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.primarySources)) {
allSources.addAll(this.primarySources);
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.getSources())) {
allSources.addAll(this.properties.getSources());
}
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(allSources);
}
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
// 这里进行加载
loader.load();
}
}在 BeanDefinitionLoader 的 load() 方法中又调用了 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 的 register() 方法实现了配置类 Bean 定义的注册,到这里就和案例一的达到的效果是相同的了。代码如下:
java
class BeanDefinitionLoader {
void load() {
for (Object source : this.sources) {
load(source);
}
}
private void load(Object source) {
Assert.notNull(source, "Source must not be null");
if (source instanceof Class<?> type) {
load(type);
return;
}
// 省略代码
}
private void load(Class<?> source) {
// 省略代码
if (isEligible(source)) {
// 这里同样是通过AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader的register()方法注册的Bean定义
this.annotatedReader.register(source);
}
}
}
public class AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader {
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
for (Class<?> componentClass : componentClasses) {
registerBean(componentClass);
}
}
}后续
假设现在在 lib 目录下有两个 jar 包的不同版本,里面有一个 TestBean 的类,其中一个 jar 包中该类没有 @Component 注解修饰,另外一个有 @Component 注解修饰,且按照 jar 包在 CLASSPATH 中的顺序,没有 @Component 注解修饰的类所在的 jar 包在前面。那么 Spring 会创建一个 TestBean 类型的 Bean 么?
想知道这个问题的答案,可以看另外的这篇文章一次 Spring 扫描 @Component 注解修饰的类坑。