一、定义
clip-path属性用于定义元素的可见区域,可将元素裁剪成任意形状的多边形。
二、简单示例
1、画圆形
css
clip-path: circle(40px)40px代表圆的半径,其实这种是circle(40px at 50% 50%)的简写,50% 50%代表圆心位置,不写默认是几何图形的中心。
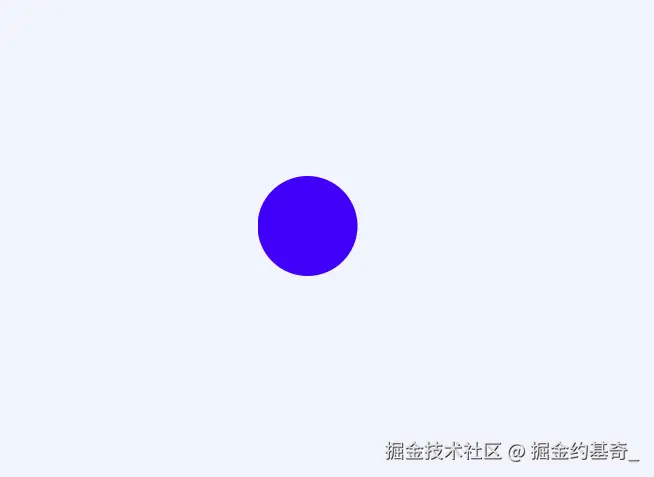


圆心稍做调整circle(40px at 10% 50%),可根据需要调整位置。

2、画椭圆形
css
clip-path: circle(40px 20px)代表主轴半径40px,侧轴半径20px,圆心在几何图形中心的椭圆。

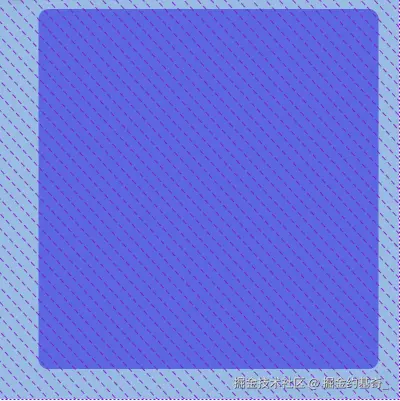
2、画矩形
css
clip-path: inset(10px 20px 30px 40px round 10px)矩形上边距顶部10排序,右边距右边20px,距底部30px,距左边40px,并且圆角是10px的矩形。
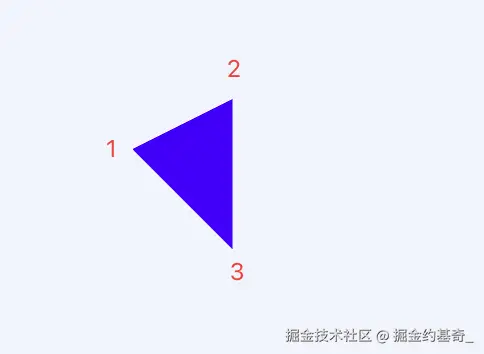
2、画多边形
(1)、三角形
css
clip-path: polygon(0 50px, 100px 0, 100px 150px)分别代表1,2,3点的坐标位置。
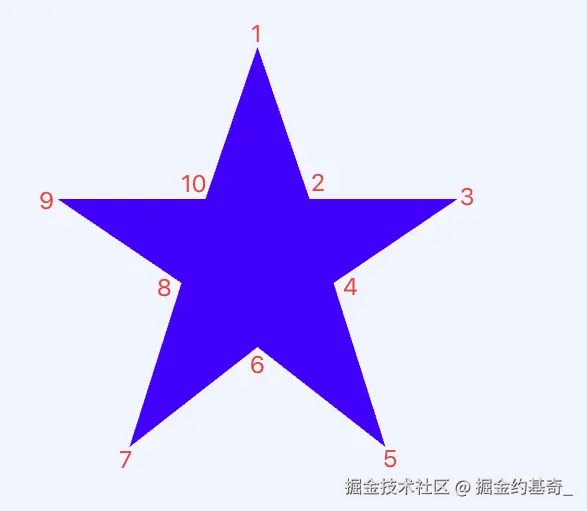
(2)、五角星
css
clip-path: polygon(
50% 0%,
63% 38%,
100% 38%,
69% 59%,
82% 100%,
50% 75%,
18% 100%,
31% 59%,
0 38%,
37% 38%
)只要坐标点足够多,可以画出任意类型的图形。
三、实战应用
开发一个调节音量大小的组件,ui稿如下: 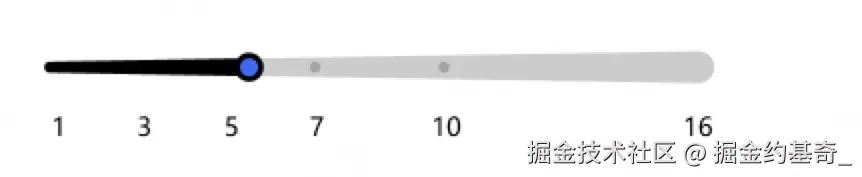
(1)、画多边形轨道
html
<div class="box">
<!-- 轨道 -->
<div class="slider"></div>
</div>使用clip-path: polygon()函数定位四个坐标点,并设置圆角。
css
.box {
width: 400px;
position: relative;
.slider {
width: 400px;
height: 24px;
background-color: #ccc;
// background: #000;
border-radius: 50px;
// polygon画四边形,需要四个点位
clip-path: polygon(0 8px, 0 16px, 100% 100%, 100% 0);
}
}
(2)、添加滑块和刻度
html
<div class="box">
<!-- 轨道 -->
<div class="slider"></div>
<!-- 滑块 -->
<div class="block"></div>
<!-- 刻度 -->
<div class="scale">
<div
v-for="(point, index) in scalePoints"
:key="index"
class="scale-point"
:style="{ left: `${(point / 16) * 100}%` }"
>
{{ point }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
js
data() {
return {
// 刻度尺
scalePoints: [0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 16],
};
},
css
.box {
width: 400px;
position: relative;
.slider {
width: 400px;
height: 24px;
background-color: #ccc;
// background: #000;
border-radius: 50px;
// polygon画四边形,需要四个点位
clip-path: polygon(0 8px, 0 16px, 100% 100%, 100% 0);
}
.block {
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
background: #409eff;
border: 2px solid #000000;
border-radius: 50%;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
cursor: grab;
&:active {
cursor: grabbing;
}
}
.scale {
position: relative;
margin-top: 10px;
height: 20px;
&-point {
position: absolute;
}
}
}(3)、事件绑定
这里面的背景色不能写死,需根据滑动过的轨迹的百分比动态计算,使用linear-gradient css渐变函数实现。
js
methods: {
handleSliderClick(e) {
const slider = this.$el.querySelector(".slider");
const block = this.$el.querySelector(".block");
const sliderRect = slider.getBoundingClientRect();
const maxLeft = slider.offsetWidth - block.offsetWidth;
// 计算点击位置相对轨道的水平坐标
const clickX = e.clientX - sliderRect.left - block.offsetWidth / 2;
const newLeft = Math.max(0, Math.min(clickX, maxLeft));
// 更新滑块位置
block.style.left = `${newLeft}px`;
// 同步更新背景渐变
const progress = (newLeft / maxLeft) * 100;
slider.style.background = `linear-gradient(to right, #000 ${progress}%, #ccc ${progress}%)`;
},
startDrag(e) {
const box = this.$el;
const block = this.$el.querySelector(".block");
const slider = this.$el.querySelector(".slider");
// 计算滑块最大移动距离=(轨道宽度-滑块宽度)
const maxLeft = slider.offsetWidth - block.offsetWidth;
// 开始滑动
const handleMove = (e) => {
console.log(e.clientX, "e.clientX");
// 计算滑块距左边位置的距离
let newLeft =
e.clientX - box.getBoundingClientRect().left - block.offsetWidth / 2;
newLeft = Math.max(0, Math.min(newLeft, maxLeft));
block.style.left = `${newLeft}px`;
// 动态改变进度条背景色
const progress = (newLeft / maxLeft) * 100;
slider.style.background = `linear-gradient(to right, #000 ${progress}%, #ccc ${progress}%)`;
};
// 滑动结束
const handleUp = () => {
document.removeEventListener("mousemove", handleMove);
document.removeEventListener("mouseup", handleUp);
};
document.addEventListener("mousemove", handleMove);
document.addEventListener("mouseup", handleUp);
},
},效果图:

完整代码:
vue
<template>
<!-- <div class="container"> -->
<div class="box">
<!-- 轨道 -->
<div class="slider" @click="handleSliderClick"></div>
<!-- 滑块 -->
<div class="block" @mousedown="startDrag"></div>
<!-- 刻度 -->
<div class="scale">
<div
v-for="(point, index) in scalePoints"
:key="index"
class="scale-point"
:style="{ left: `${(point / 16) * 100}%` }"
>
{{ point }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- </div> -->
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
// 刻度尺
scalePoints: [0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 16],
};
},
methods: {
handleSliderClick(e) {
const slider = this.$el.querySelector(".slider");
const block = this.$el.querySelector(".block");
const sliderRect = slider.getBoundingClientRect();
const maxLeft = slider.offsetWidth - block.offsetWidth;
// 计算点击位置相对轨道的水平坐标
const clickX = e.clientX - sliderRect.left - block.offsetWidth / 2;
const newLeft = Math.max(0, Math.min(clickX, maxLeft));
// 更新滑块位置
block.style.left = `${newLeft}px`;
// 同步更新背景渐变
const progress = (newLeft / maxLeft) * 100;
slider.style.background = `linear-gradient(to right, #000 ${progress}%, #ccc ${progress}%)`;
},
startDrag(e) {
const box = this.$el;
const block = this.$el.querySelector(".block");
const slider = this.$el.querySelector(".slider");
// 计算滑块最大移动距离=(轨道宽度-滑块宽度)
const maxLeft = slider.offsetWidth - block.offsetWidth;
// 开始滑动
const handleMove = (e) => {
console.log(e.clientX, "e.clientX");
// 计算滑块距左边位置的距离
let newLeft =
e.clientX - box.getBoundingClientRect().left - block.offsetWidth / 2;
newLeft = Math.max(0, Math.min(newLeft, maxLeft));
block.style.left = `${newLeft}px`;
// 动态改变进度条背景色
const progress = (newLeft / maxLeft) * 100;
slider.style.background = `linear-gradient(to right, #000 ${progress}%, #ccc ${progress}%)`;
};
// 滑动结束
const handleUp = () => {
document.removeEventListener("mousemove", handleMove);
document.removeEventListener("mouseup", handleUp);
};
document.addEventListener("mousemove", handleMove);
document.addEventListener("mouseup", handleUp);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped lang="scss">
.container {
width: 100%;
height: 100vh;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.box {
width: 400px;
position: relative;
.slider {
width: 400px;
height: 24px;
background-color: #ccc;
// background: #000;
border-radius: 50px;
// polygon画四边形,需要四个点位
clip-path: polygon(0 8px, 0 16px, 100% 100%, 100% 0);
}
.block {
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
background: #409eff;
border: 2px solid #000000;
border-radius: 50%;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
cursor: grab;
&:active {
cursor: grabbing;
}
}
.scale {
position: relative;
margin-top: 10px;
height: 20px;
&-point {
position: absolute;
}
}
}
</style>