1 仿函数
在 C++ 中,仿函数(Functor)是一种特殊的对象,它可以像函数一样被调用。这种特性通过重载对象的 operator() 运算符实现,使得对象在使用时可以拥有类似函数的行为。
仿函数的基本特点
- 本质是对象:仿函数是一个类的实例,不是普通函数
- 可调用性 :通过重载
operator()实现函数调用语法 - 状态保持:可以拥有成员变量,保存状态信息
- 类型特性:作为模板参数时能提供额外的类型信息
cpp
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test.cpp
> Author: Winter
> Created Time: Thu 21 Aug 2025 08:42:31 AM EDT
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
// 仿函数
struct SortByLength {
bool operator() (const std::string& str1, const std::string& str2)
{
return str1.size() < str2.size();
}
};
struct SortByLengthDesc {
bool descending; // 可调整的状态
// 构造函数
SortByLengthDesc(bool desc) : descending(desc) {}
// 根据状态排序
bool operator() (const std::string& str1, const std::string& str2)
{
if (descending)
{
return str1.size() > str2.size();
}
else
{
return str1.size() < str2.size();
}
}
};
int main()
{
/*************************仿函数案例*************************/
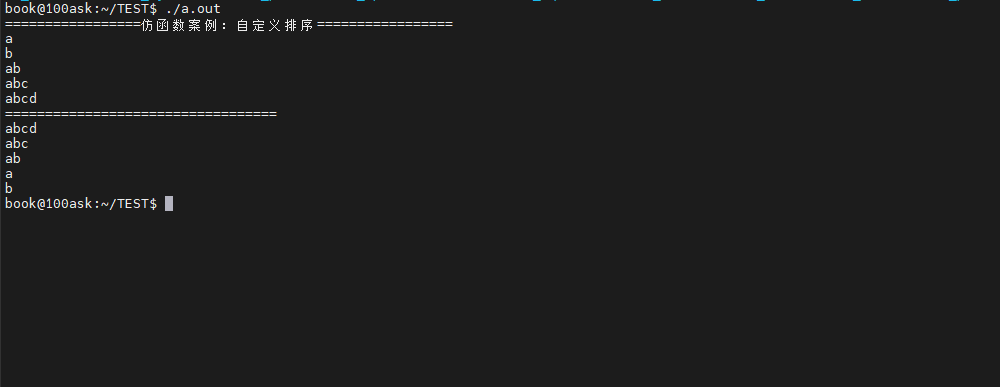
std::cout << "=================仿函数案例:自定义排序=================" << std::endl;
std::vector<std::string> words = {"a", "ab", "abc", "abcd", "b"};
std::sort(words.begin(), words.end(), SortByLength());
for (const auto& word : words)
{
std::cout << word << std::endl;
}
std::cout << "==================================" << std::endl;
std::sort(words.begin(), words.end(), SortByLengthDesc(true));
for (const auto& word : words)
{
std::cout << word << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}测试
和lambda表达式差不多
2 回调函数
在 C++ 中,回调函数(Callback Function)是一种特殊的函数,它可以作为参数传递给另一个函数,并在特定事件发生或条件满足时被调用。这种机制允许程序在运行时动态决定需要执行的代码,增强了程序的灵活性和扩展性。
回调函数的基本原理
- 函数作为参数传递:将函数的地址(函数指针)作为参数传递给另一个函数
- 延迟执行:回调函数不会立即执行,而是在被调用函数内部的合适时机执行
- 事件驱动:常用于响应特定事件(如用户操作、完成某个任务等)
c风格的回调函数
cpp
#include <iostream>
// 回调函数的原型
typedef void (*CallbackFunc)(int);
// 接受回调函数作为参数的函数
void process(int data, CallbackFunc callback)
{
std::cout << "处理数据: " << data << std::endl;
// 在合适的时机调用回调函数
callback(data);
}
// 具体的回调函数实现
void printResult(int result)
{
std::cout << "回调函数: 处理结果为 " << result << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
// 将函数名作为参数传递(函数名即函数地址)
process(100, printResult);
return 0;
}测试

C++风格的回调,使用function
cpp
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test.cpp
> Author: Winter
> Created Time: Thu 21 Aug 2025 08:42:31 AM EDT
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
// 定义回调函数类型
using EventCallBack = std::function<void(const std::string& eventType, const std::string& messge)>;
// 时间管理器:负责触发事件并调用回调
class EventManager {
private:
EventCallBack callback; // 存储回调函数
public:
// 注册回调函数
void setCallBack(EventCallBack cb)
{
callback = cb;
}
// 模拟触发事件
void triggerEvent(const std::string& eventType, const std::string& messge)
{
// 检查回调是否有效
if (callback)
{
callback(eventType, messge); // 调用回调函数
}
}
};
void functionTest(const std::string& eventType, const std::string& messge)
{
std::cout << eventType << " + " << messge << std::endl;
}
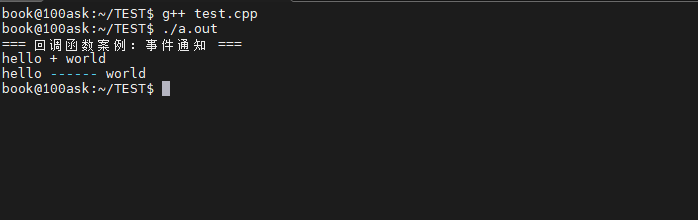
int main()
{
std::cout << "=== 回调函数案例:事件通知 ===" << std::endl;
EventManager eventManager;
// 注册回调
eventManager.setCallBack(functionTest);
// 触发回调
eventManager.triggerEvent("hello", "world");
// 使用lambda表达式
eventManager.setCallBack([](const std::string& eventType, const std::string& messge) {
std::cout << eventType << " ------ " << messge << std::endl;
});
eventManager.triggerEvent("hello", "world");
return 0;
}
注意对比结果
3 回调函数和仿函数结合的案例
cpp
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: test.cpp
> Author: Winter
> Created Time: Thu 21 Aug 2025 08:42:31 AM EDT
************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
// 仿函数:过滤数字
struct NumberFilter
{
int threshold; // 过滤值
NumberFilter(int thresh) : threshold(thresh) {}
// 重载()
bool operator() (int num) const {
return num > threshold;
}
};
using Callback = std::function<void(int)>;
// 回调函数:处理过滤后的结果
void processNumbers(const std::vector<int>& nums, const NumberFilter& numberFilter, Callback callBack)
{
for (int num :nums)
{
if (numberFilter(num))
{
callBack(num);
}
}
}
void functionTest(int a)
{
std::cout << "----" << a << "----"<< std::endl;
}
int main()
{
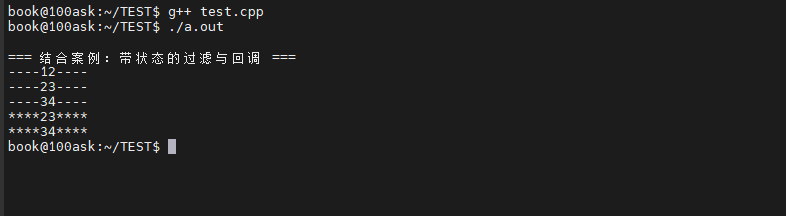
std::cout << "\n=== 结合案例:带状态的过滤与回调 ===" << std::endl;
std::vector<int> nums = {12, 5, 23, 8, 34, 1};
// 创建带状态的仿函数(阈值为10)
NumberFilter filter1(10);
processNumbers(nums, filter1, functionTest);
// 使用lambda表达式
NumberFilter filter2(15);
processNumbers(nums, filter2, [] (int num) {
std::cout << "****" << num << "****"<< std::endl;
});
return 0;
}测试