一、模式本质
1 策略模式:行为的选择
核心思想:定义一组算法,将每个算法封装起来,并使它们可以互相替换,让算法的变化独立于使用它的客户端。
2 适配器模式:接口的转换
核心思想:将一个类的接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口,使原本因接口不兼容而无法协同工作的类能够协同工作。
二、策略模式应用
1、策略模式模拟商品折扣算法
Vip折扣、促销折扣、满减折扣
2、策略实现
2.1定义策略接口
public interface DiscountStrategy {`` BigDecimal calculateDiscount(Order order);
}
2.2vip折扣
@Service("vipDiscount")
public class VipDiscountStrategy implements DiscountStrategy {`` @Override`` public BigDecimal calculateDiscount(Order order) {`` return order.getAmount().multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(0.9)); `` }``}
2.3促销折扣
@Service("promotionDiscount")
public class PromotionDiscountStrategy implements DiscountStrategy {`` @Override`` public BigDecimal calculateDiscount(Order order) {`` return order.getAmount().multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(0.8)); `` }``}
2.4满减折扣
@Service("fullReductionDiscount")
public class FullReductionDiscountStrategy implements DiscountStrategy {`` @Override`` public BigDecimal calculateDiscount(Order order) {`` if (order.getAmount().compareTo(BigDecimal.valueOf(100)) > 0) {`` return order.getAmount().subtract(BigDecimal.valueOf(20)); `` }`` return order.getAmount();`` }``}
2.5策略核心
@Service
public class DiscountContext { private final Map<String, DiscountStrategy> strategyMap;
@Autowired public DiscountContext(Map<String, DiscountStrategy> strategyMap) { this.strategyMap = strategyMap; }
public BigDecimal applyDiscount(String strategyName, Order order) { DiscountStrategy strategy = strategyMap.get(strategyName); if (strategy == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知折扣策略: " + strategyName); } return strategy.calculateDiscount(order); }}
2.6控制器调用
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/orders")
public class OrderController {`` @Autowired`` private DiscountContext discountContext;
@PostMapping("/calculate")`` public BigDecimal calculatePrice(@RequestParam String discountType, `` @RequestBody Order order) {`` return discountContext.applyDiscount(discountType + "Discount", order);`` }``}
3、策略模式优势
新增折扣策略只需添加新类
避免多层if-else判断
策略算法可独立测试
三、适配器模式应用
1、适配器模式模拟统一支付接口
需要接入支付宝、微信支付和PayPal,但三家接口完全不同
2、适配器实现
2.1定义统一支付接口
public interface PaymentGateway {`` PaymentResult pay(BigDecimal amount, String orderId);
}
2.2支付宝适配器
2.2.1原生接口
public class AlipayService { public AlipayResponse createPayment(AlipayRequest request) { // 支付宝原生逻辑 }
}
2.2.2支付宝适配器
@Service
public class AlipayAdapter implements PaymentGateway {`` private final AlipayService alipayService;
@Override`` public PaymentResult pay(BigDecimal amount, String orderId) {`` // 转换参数`` AlipayRequest request = new AlipayRequest(amount, orderId);
// 调用原生接口`` AlipayResponse response = alipayService.createPayment(request);
// 转换结果`` return new PaymentResult(`` response.isSuccess(), `` response.getTransactionId()`` );`` }
}
2.3微信支付适配器
@Service
public class WechatPayAdapter implements PaymentGateway {`` private final WechatPayService wechatService;
@Override`` public PaymentResult pay(BigDecimal amount, String orderId) {`` // 转换并调用微信接口`` }
}
2.4Paypal支付适配器
@Service
public class PayPalAdapter implements PaymentGateway {`` private final PayPalClient paypalClient;
@Override`` public PaymentResult pay(BigDecimal amount, String orderId) {`` // 转换并调用PayPal接口`` }
}
2.5统一支付实现
@Service
public class PaymentService {`` private final Map<String, PaymentGateway> gateways;
@Autowired`` public PaymentService(List<PaymentGateway> gatewayList) {`` this.gateways = gatewayList.stream()`` .collect(Collectors.toMap(`` g -> g.getClass().getSimpleName().replace("Adapter", "").toLowerCase(),`` Function.identity()`` ));`` }
public PaymentResult processPayment(String gatewayType, `` BigDecimal amount, String orderId) {`` PaymentGateway gateway = gateways.get(gatewayType);`` if (gateway == null) {`` throw new IllegalArgumentException("不支持的支付方式: " + gatewayType);`` }`` return gateway.pay(amount, orderId);`` }
}
3适配器模式优势
无需修改三方支付SDK
统一支付接口简化调用
新增支付渠道只需添加适配器
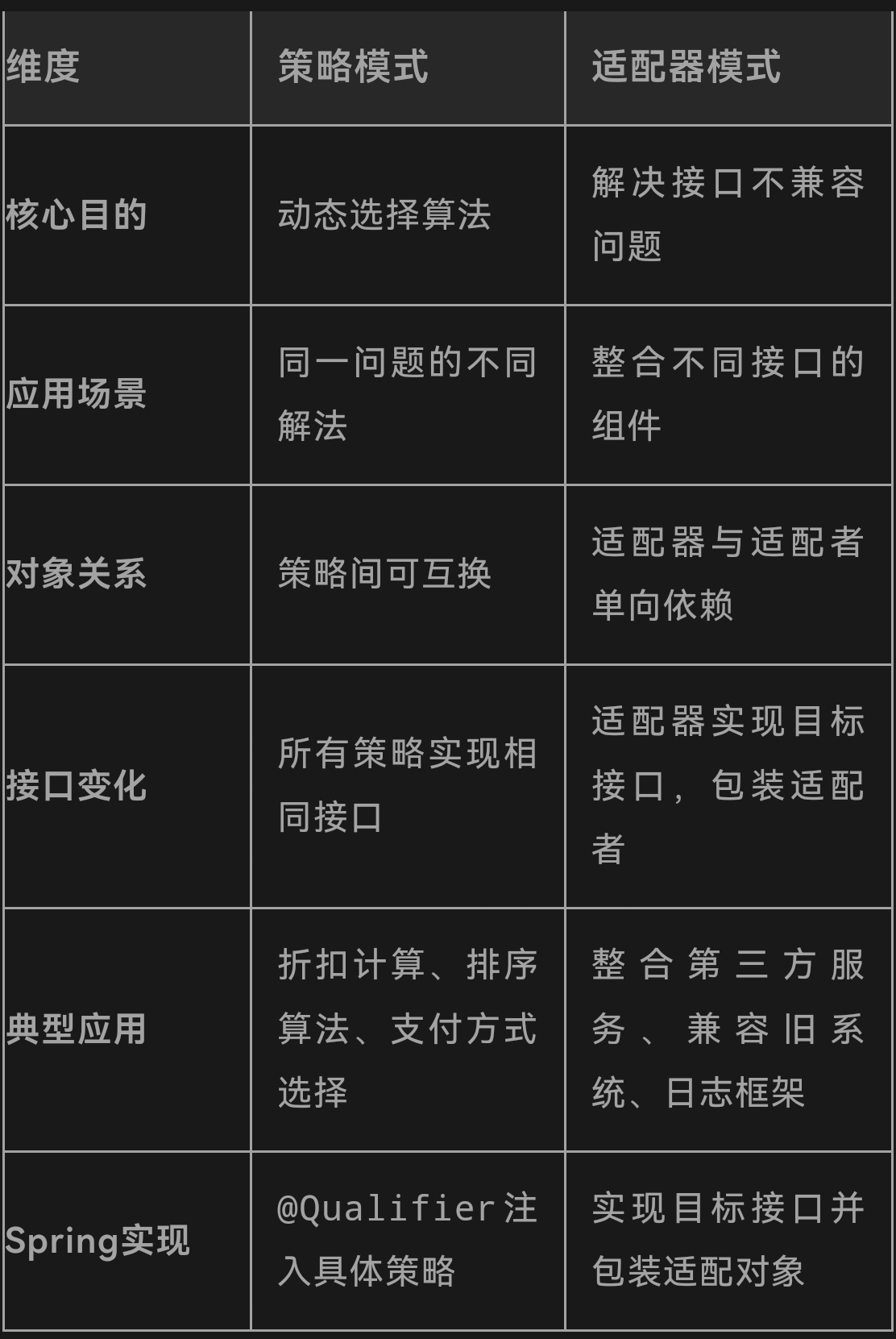
四、对比
五、如何正确选择何种模式
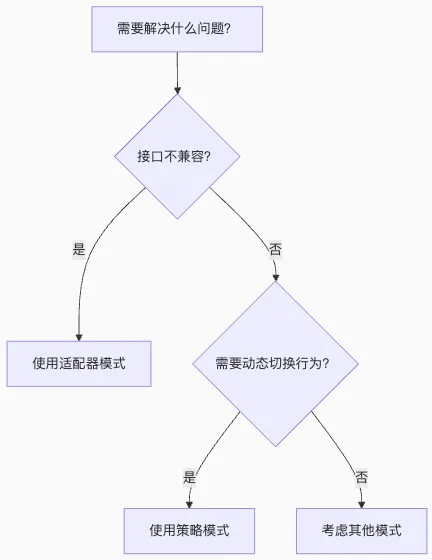
1 选择策略模式
需要动态选择算法或行为
有多个相似类仅在行为上
有差异需要消除复杂的件语句
希望算法能够独立于客户端变化
2 选择适配器模式
需要使用现有类但其接口不符合要求
需要创建可复用的类与不兼容接口协同工作
需要统一多个独立开发的模块接口
需要兼容旧系统或第三方库
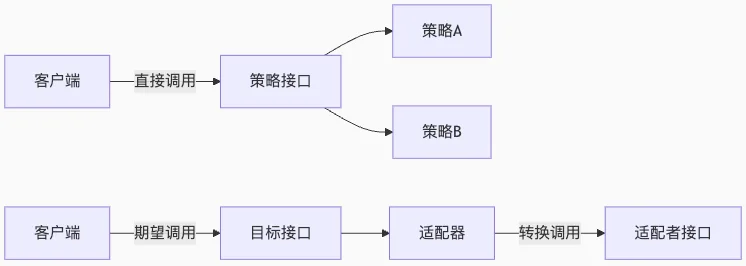
3流程示意图