demo_yield.py 程序主要演示了microPython中生成器(Generator)的使用,特别是通过yield语句进行双向通信的机制(既能产出值也能接收值),以及控制流的暂停和恢复机制。
常见的普通 return 函数会立即返回所有结果,而使用 yield 的函数会在每次迭代时逐步产生结果。
python
def event():
print('start yield')
# return next(task) and yield next(task.send('set_two'))
one = yield 'get_one'
assert(one == 'set_two')
print(one)
yield 'get_two' # return next(task) and yield next(task.send('set_two'))
print('exit yield')
yield # yield next() to exit or raise StopIteration
task = event()
run_one = next(task) # need next(task) init and next(task) == task.send(None)
# so next(task) => yield 'get_one' => run_one = 'get_one'
assert(run_one == 'get_one')
run_two = task.send('set_two')
assert(run_two == 'get_two')
print('run : ', run_one, ' and ', run_two)
try:
next(task)
print('run end')
next(task) # will raise StopIteration
except Exception as e:
print('yield StopIteration')
if __name__ == '__main__':
def task():
while True:
print('hello')
yield
tmp = task()
while True:
next(tmp)
while True:
print('hello')当不做任何修改,执行示例程序时,实际输出结果只有循环的 hello。
让我们来修改以下,注释掉if name == 'main':这句及以后面的程序,再运行一下:
python
def event():# event函数是一个生成器函数,因为它包含yield语句。当调用event()时,它会返回一个生成器对象,而不会立即执行函数体内的代码。
print('start yield')
# return next(task) and yield next(task.send('set_two'))
one = yield 'get_one'# 第一次暂停,返回'get_one'
assert(one == 'set_two')# 验证传入的值
print(one)# 打印接收到的值
yield 'get_two' # # 第二次暂停,返回'get_two' return next(task) and yield next(task.send('set_two'))
print('exit yield')
yield # yield next() to exit or raise StopIteration # 最后一次暂停,返回None
#这个函数包含三个yield语句,每次执行到yield时会暂停并返回一个值。
task = event()#创建生成器对象(此时函数并未执行)
run_one = next(task) ## 启动生成器,执行到第一个yield处暂停 need next(task) init and next(task) == task.send(None)
# so next(task) => yield 'get_one' => run_one = 'get_one'
assert(run_one == 'get_one')
run_two = task.send('set_two')# 发送值'set_two'到生成器,恢复执行
assert(run_two == 'get_two')
print('run : ', run_one, ' and ', run_two)
try:
next(task)
print('run end')
next(task) # will raise StopIteration
except Exception as e:
print('yield StopIteration')
#if __name__ == '__main__':
# def task():
# while True:
# print('hello')
# yield
# tmp = task()
# while True:
# next(tmp)
# while True:
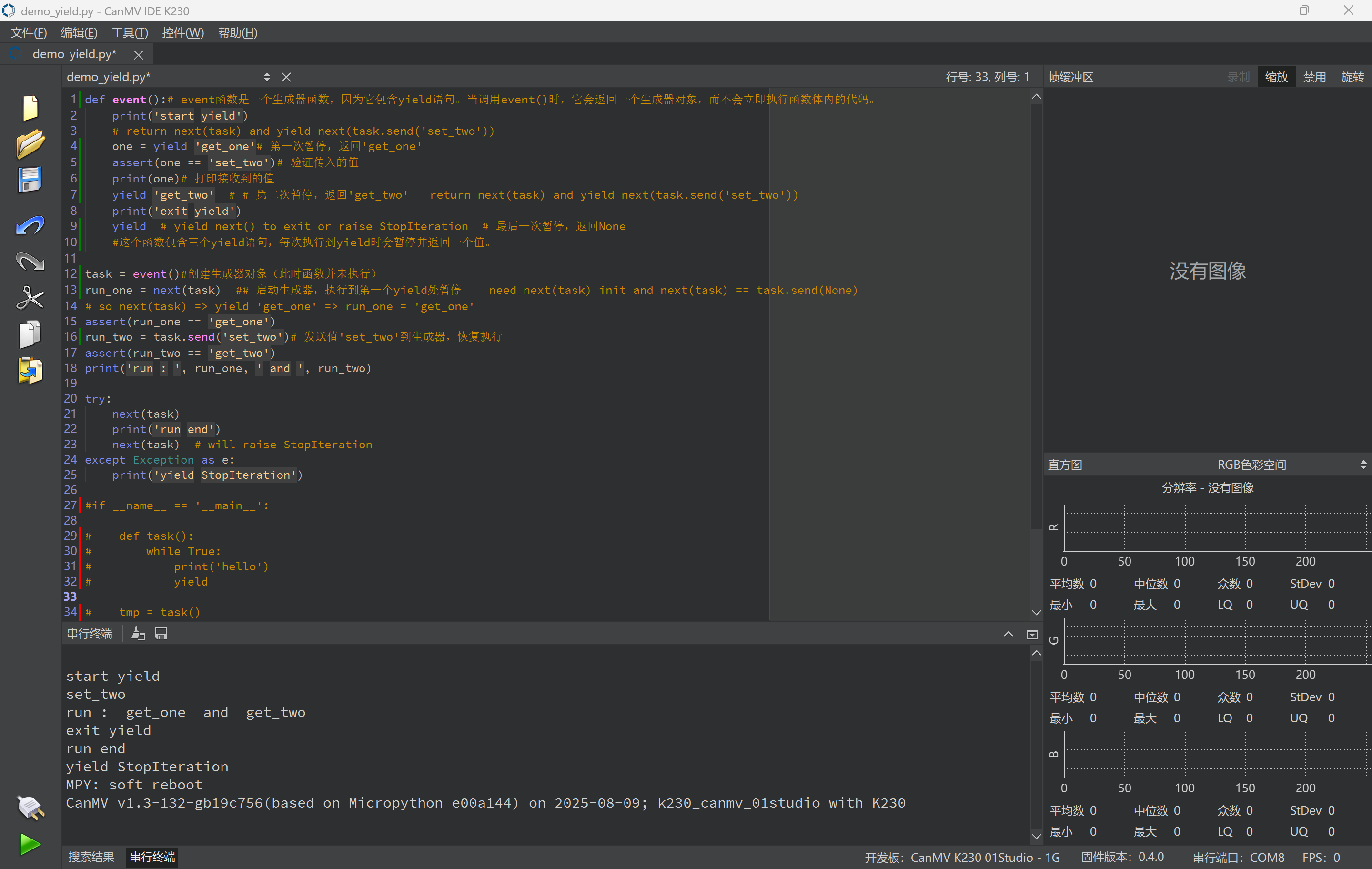
# print('hello')修改后的程序运行结果如下:
yield 是定义 生成器函数(generator function) 的关键字。通过以上程序也可以看出来:yield 的作用就是把一个函数变成一个 生成器 generator,带有 yield 的函数Python 解释器会将其认为是一个生成器 generator,函数内部的代码执行到 yield时,函数就返回一个迭代值,下次迭代时,代码从 yield 的下一条语句继续执行,直到再次遇到 yield。
-
调用生成器函数不会立即执行,而是返回一个生成器对象。
-
必须使用
next()或send(参数)启动生成器。 -
当需要逐个返回大量数据项时,优先使用
yield,可以很好的节约内存使用量。 -
在构建数据处理流水线时,结合
yield和函数组合可进行高效的处理。
python
start yield
set_two
run : get_one and get_two
exit yield
run end
yield StopIteration
MPY: soft reboot
CanMV v1.3-132-gb19c756(based on Micropython e00a144) on 2025-08-09; k230_canmv_01studio with K230结合每步的输出,加详细注释如下:
python
def event():# event函数是一个生成器函数,因为它包含yield语句。当调用event()时,它会返回一个生成器对象,而不会立即执行函数体内的代码。
print('start yield')
# return next(task) and yield next(task.send('set_two'))
one = yield 'get_one'# 第一次暂停,返回'get_one'
assert(one == 'set_two')# 验证传入的值
print(one)# 打印接收到的值
yield 'get_two' # # 第二次暂停,返回'get_two' return next(task) and yield next(task.send('set_two'))
print('exit yield')
yield # yield next() to exit or raise StopIteration # 最后一次暂停,返回None
#这个函数包含三个yield语句,每次执行到yield时会暂停并返回一个值。
task = event()#创建生成器对象(此时函数并未执行)
run_one = next(task) # 实际输出:start yield (启动生成器,执行到第一个yield处暂停 need next(task) init and next(task) == task.send(None))
print(run_one)#实际输出:get_one
## so next(task) => yield 'get_one' => run_one = 'get_one'
assert(run_one == 'get_one')
run_two = task.send('set_two')# 发送值'set_two'到生成器,恢复执行
print(run_two)#实际输出:get_two
assert(run_two == 'get_two')
print('run : ', run_one, ' and ', run_two)
try:
next(task)
print('run end')
next(task) # will raise StopIteration
except Exception as e:
print('yield StopIteration')
#====================================================
实际输出结果::
start yield
get_one
set_two
get_two
run : get_one and get_two
exit yield
run end
yield StopIteration
MPY: soft reboot
CanMV v1.3-132-gb19c756(based on Micropython e00a144) on 2025-08-09; k230_canmv_01studio with K230