文章目录
1.输出自己的命令行
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SIZE 256
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if (name == NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if (hostname == NULL) return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if (cwd == NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
char line[SIZE];
const char* username = GetUserName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]> ", username, hostname, cwd);
printf("%s", line);
fflush(stdout);
}
int main()
{
//1.输出自己的命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
sleep(5); //用来测试 MakeCommandLinePrint函数中fflush刷新缓冲区的作用
return 0;
}
2.获取用户命令字符串
- 使用
char *fgets(char *s, int size, FILE *stream);库函数
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define SIZE 256
#define ZERO '\0'
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if (name == NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if (hostname == NULL) return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if (cwd == NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
char line[SIZE];
const char* username = GetUserName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]> ", username, hostname, cwd);
printf("%s", line);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin);
if (s == NULL) return -1;
//目的是为了解决 "\n"被都进来的情况
command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO;
return strlen(command);
}
int main()
{
//1.输出自己的命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//2.获取用户输入的命令字符串
char usercommand[SIZE];
int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
printf("%s\n", usercommand);
return 0;
}3.分割命令行字符串
》》 strtok() 分割的使用
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define SIZE 512
#define ZERO '\0'
#define SEP " "
#define NUM 32
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if (name == NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if (hostname == NULL) return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if (cwd == NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
char line[SIZE];
const char* username = GetUserName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]> ", username, hostname, cwd);
printf("%s", line);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin);
if (s == NULL) return -1;
//目的是为了解决 "\n"被都进来的情况
command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO;
return strlen(command);
}
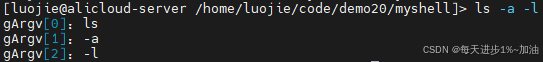
char* gArgv[NUM];
void SplitCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP);
int index = 1;
while(gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP));
}
int main()
{
//1.输出自己的命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//2.获取用户输入的命令字符串
char usercommand[SIZE];
int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
//3.命令行字符串分割
SplitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
for (int i = 0; gArgv[i]; i ++)
printf("gArgv[%d]:%s\n",i, gArgv[i]);
return 0;
}4.开始执行,第一版本Shell
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define SIZE 512
#define ZERO '\0'
#define SEP " "
#define NUM 32
void Die()
{
exit(1);
}
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if (name == NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if (hostname == NULL) return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if (cwd == NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
char line[SIZE];
const char* username = GetUserName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]> ", username, hostname, cwd);
printf("%s", line);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin);
if (s == NULL) return -1;
//目的是为了解决 "\n"被都进来的情况
command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO;
return strlen(command);
}
char* gArgv[NUM];
void SplitCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP);
int index = 1;
while(gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP));
}
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0) Die();
//child
if (id == 0)
{
execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
}
}
int main()
{
int quit = 0;
while (!quit)
{
//1.输出自己的命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//2.获取用户输入的命令字符串
char usercommand[SIZE];
int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
//3.命令行字符串分割
SplitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
//4.执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
}
return 0;
}5.检查内键命令
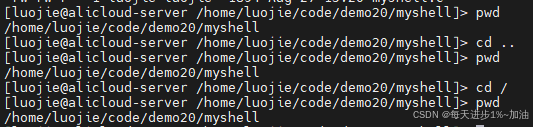
- 第一版本Shell存在的问题,cd 无效,工作的路径根本没有改变,原因是由于
cd属于内建命令,而内建命令是要由父进程Bash来执行的,下面出现Bug的原因就是由于子进程执行的cd命令;
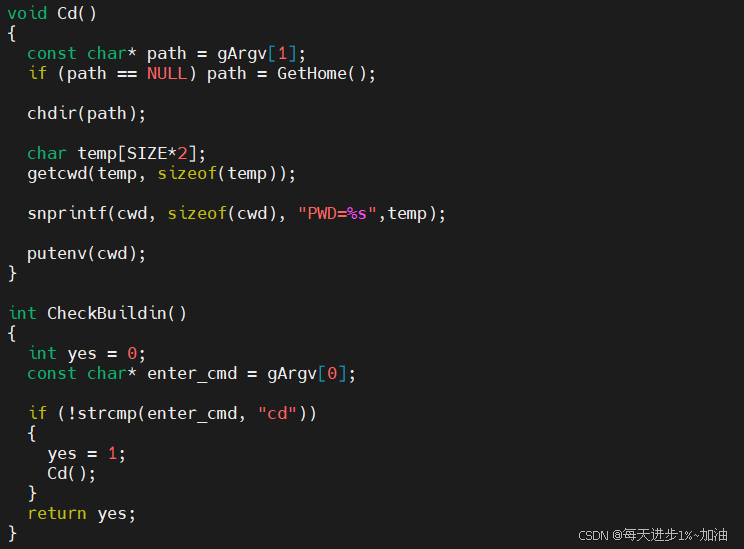
- 🍊处理内建命令
cd的主要核心代码如下图:
代码解释:char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);获取当前的工作目录
cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <errno.h>
#define SIZE 512
#define ZERO '\0'
#define SEP " "
#define NUM 32
char cwd[SIZE*4];
void Die()
{
exit(1);
}
const char* GetHome()
{
const char* home = getenv("HOME");
if (home == NULL) return "/";
return home;
}
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
if (name == NULL) return "None";
return name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
if (hostname == NULL) return "None";
return hostname;
}
const char* GetCwd()
{
const char* cwd = getenv("PWD");
if (cwd == NULL) return "None";
return cwd;
}
void MakeCommandLineAndPrint()
{
char line[SIZE];
const char* username = GetUserName();
const char* hostname = GetHostName();
const char* cwd = GetCwd();
snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]> ", username, hostname, cwd);
printf("%s", line);
fflush(stdout);
}
int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin);
if (s == NULL) return -1;
//目的是为了解决 "\n"被都进来的情况
command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO;
return strlen(command);
}
char* gArgv[NUM];
void SplitCommand(char command[], size_t n)
{
gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP);
int index = 1;
while(gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP));
}
void ExecuteCommand()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if (id < 0) Die();
//child
if (id == 0)
{
execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv);
exit(errno);
}
else
{
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
}
}
void Cd()
{
const char* path = gArgv[1];
if (path == NULL) path = GetHome();
chdir(path);
char temp[SIZE*2];
getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp));
snprintf(cwd, sizeof(cwd), "PWD=%s",temp);
putenv(cwd);
}
int CheckBuildin()
{
int yes = 0;
const char* enter_cmd = gArgv[0];
if (!strcmp(enter_cmd, "cd"))
{
yes = 1;
Cd();
}
return yes;
}
int main()
{
int quit = 0;
while (!quit)
{
//1.输出自己的命令行
MakeCommandLineAndPrint();
//2.获取用户输入的命令字符串
char usercommand[SIZE];
int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
if (n <= 0) return 1;
//3.命令行字符串分割
SplitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand));
//4.检测命令是否是内键命令
n = CheckBuildin();
if (n) continue;
//5.执行命令
ExecuteCommand();
}
return 0;
}