less
@Bean
@Order(1)
public SecurityFilterChain authorizationServerSecurityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http)
throws Exception {
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration.applyDefaultSecurity(http);
... 忽略其他代码
return http.build();
}我们在使用授权服务器的时候,第一件事就是要注册一个 SecurityFilterChain @Bean,用来处理和授权服务器相关的请求。 SecurityFilterChain @Bean会配置很多端点 也就是endpoint,我举几个重要的例子:
为什么这些endpoint会自动生效呢?是因为OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration 会使用 OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer类去应用这些默认配置。
下面这段摘自官网:
Auth2AuthorizationServerConfigurationis a@Configurationthat provides the minimal default configuration for an OAuth2 authorization server.
也就是说Auth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration就是一个配置类,用来给授权服务器提供最小默认配置的。
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfiguration.applyDefaultSecurity(http);
这段代码就是在应用默认配置。具体做了什么呢?我们逐行分析下代码
scss
public static void applyDefaultSecurity(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer authorizationServerConfigurer =
new OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer();
RequestMatcher endpointsMatcher = authorizationServerConfigurer
.getEndpointsMatcher();
http
.securityMatcher(endpointsMatcher)
.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) ->
authorize.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.csrf((csrf) -> csrf.ignoringRequestMatchers(endpointsMatcher))
.apply(authorizationServerConfigurer);
}1.设置securityMatcher
首先是http .securityMatcher(endpointsMatcher)
🔥 http.securityMatcher(endpointsMatcher) 是 整个安全过滤器链的"守门员" ,它决定了 哪些请求会进入这个 SecurityFilterChain,哪些不会。
securityMatcher(...) 方法设置的 RequestMatcher 会在 Spring Security 的 FilterChainProxy 路由请求时 发挥作用,用于:
🔹 决定当前这个 SecurityFilterChain 是否应该处理某个 incoming request。
它就像一个"入口闸机",只有匹配的请求才能进入这条过滤器链。
而RequestMatcher是从authorizationServerConfigurer中获取的,也就是当前这个过滤器链用来匹配哪些请求是authorizationServerConfigurer来配置的
java
RequestMatcher endpointsMatcher = authorizationServerConfigurer
.getEndpointsMatcher();2 获取 getEndpointsMatcher
下面的源码选自OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer
kotlin
private RequestMatcher endpointsMatcher;
/**
* Returns a {@link RequestMatcher} for the authorization server endpoints.
* @return a {@link RequestMatcher} for the authorization server endpoints
*/
public RequestMatcher getEndpointsMatcher() {
// Return a deferred RequestMatcher
// since endpointsMatcher is constructed in init(HttpSecurity).
return (request) -> this.endpointsMatcher.matches(request);
}你发现了 getEndpointsMatcher() 返回的是一个 延迟求值的 Lambda:
也就是说OAuth2AuthorizationServerConfigurer中有endpointsMatcher属性,将来这有符合这个matcher的请求才是当前授权服务器过滤器链要处理的请求,但是目前endpointsMatcher还是null,只有将来配置完之后,才有值。
这个 Lambda 做了什么?
- 它不立即执行
matches() - 它捕获了
this引用(闭包) - 当真正需要匹配时(运行时),才去访问
this.endpointsMatcher
其实我们后面也会讲 用到lambda的原因是: endpointsMatcher 要到 init(HttpSecurity) 阶段才能构建,但 getEndpointsMatcher() 调用更早。
3.authorize.anyRequest().authenticated()
其实第三点就是确定了所有的请求都要进行认证,因为上面通过endpointsMatcher已经确定了入口,也就是说当前过滤器链只处理endpointsMatcher匹配的请求,并且这些请求都要经过登录认证。
endpointsMatcher是怎么初始化的呢?
endpointsMatcher具体配置了哪些endpoint?
上面的案例代码中最后一步,将authorizationServerConfigurer应用到 httpSecurity上
java
http.apply(authorizationServerConfigurer);将来httpSecurity触发build的时候会先进入初始化阶段,调用 authorizationServerConfigurer的 init(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) 方法,里面有一段代码
会遍历authorizationServerConfigurer维护的所有configurers,
- 执行这些configure的init方法,
- 然后收集每个configurer的requestMatcher
swift
private final Map<Class<? extends AbstractOAuth2Configurer>, AbstractOAuth2Configurer> configurers = createConfigurers();
那到底维护了哪些AbstractOAuth2Configurer呢,下面是authorizationServerConfigurer创建时默认创建的配置类
php
private Map<Class<? extends AbstractOAuth2Configurer>, AbstractOAuth2Configurer> createConfigurers() {
Map<Class<? extends AbstractOAuth2Configurer>, AbstractOAuth2Configurer> configurers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
configurers.put(OAuth2ClientAuthenticationConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2ClientAuthenticationConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2AuthorizationServerMetadataEndpointConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2AuthorizationServerMetadataEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2AuthorizationEndpointConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2AuthorizationEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2TokenEndpointConfigurer.class, new OAuth2TokenEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2TokenIntrospectionEndpointConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2TokenIntrospectionEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2TokenRevocationEndpointConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2TokenRevocationEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2DeviceAuthorizationEndpointConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2DeviceAuthorizationEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
configurers.put(OAuth2DeviceVerificationEndpointConfigurer.class,
new OAuth2DeviceVerificationEndpointConfigurer(this::postProcess));
return configurers;
}调试代码发现这默认的9个配置类 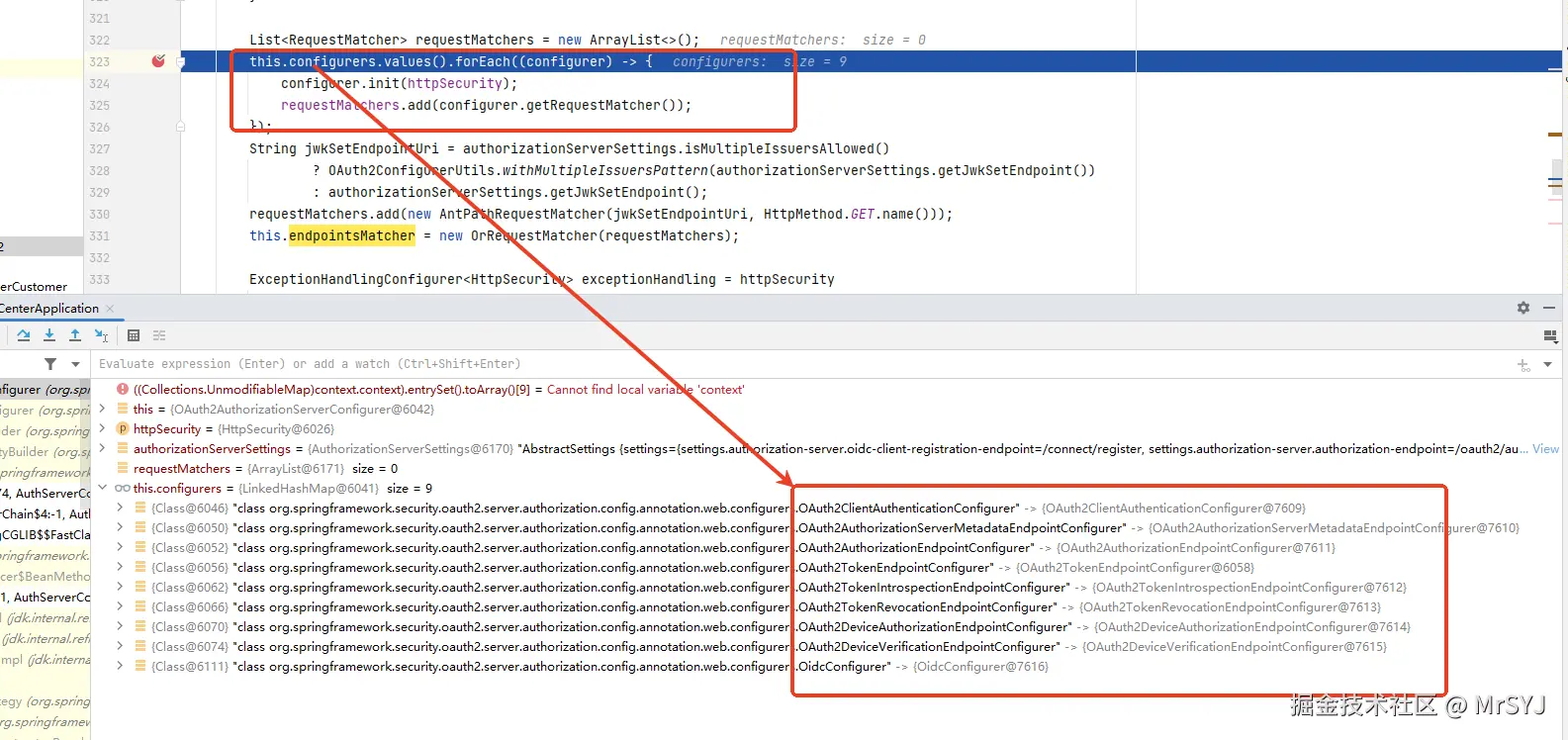
那也就是说这9个配置类,每个配置类都会维护一个RequestMatcher,这些RequestMatcher加在一起就是当前过滤器链要处理的所有请求。我们以一个为例吧:OAuth2TokenEndpointConfigurer,看看这个配置类是否配置了requestMatcher
OAuth2TokenEndpointConfigurer
首先看源码OAuth2TokenEndpointConfigurer确实维护了一个requestMatcher,接下来看看哪里对这个属性进行了初始化
scala
public final class OAuth2TokenEndpointConfigurer extends AbstractOAuth2Configurer {
private RequestMatcher requestMatcher;找到代码了 就是上面说的那个init方法 在init方法中会 this.requestMatcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher(tokenEndpointUri, HttpMethod.POST.name());
- 拦截Post请求
- 拦截路径是tokenEndpointUri(/oauth2/token),tokenEndpointUri是AuthorizationServerSettings维护的,
AuthorizationServerSettings是授权服务器的配置类,里面默认会维护很多默认的端点
ini
@Override
void init(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) {
AuthorizationServerSettings authorizationServerSettings = OAuth2ConfigurerUtils
.getAuthorizationServerSettings(httpSecurity);
String tokenEndpointUri = authorizationServerSettings.isMultipleIssuersAllowed()
? OAuth2ConfigurerUtils.withMultipleIssuersPattern(authorizationServerSettings.getTokenEndpoint())
: authorizationServerSettings.getTokenEndpoint();
this.requestMatcher = new AntPathRequestMatcher(tokenEndpointUri, HttpMethod.POST.name());
.... 省略本次不讨论的代码
}AuthorizationServerSettings默认维护的端点如下,也是可以手动配置的。
vbscript
public static Builder builder() {
return new Builder().multipleIssuersAllowed(false)
.authorizationEndpoint("/oauth2/authorize")
.deviceAuthorizationEndpoint("/oauth2/device_authorization")
.deviceVerificationEndpoint("/oauth2/device_verification")
.tokenEndpoint("/oauth2/token")
.jwkSetEndpoint("/oauth2/jwks")
.tokenRevocationEndpoint("/oauth2/revoke")
.tokenIntrospectionEndpoint("/oauth2/introspect")
.oidcClientRegistrationEndpoint("/connect/register")
.oidcUserInfoEndpoint("/userinfo")
.oidcLogoutEndpoint("/connect/logout");
}最后所有的requestMatcher,会被传入到OrRequestMatcher 看名称也知道这个是
ini
this.endpointsMatcher = new OrRequestMatcher(requestMatchers);OrRequestMatcher 看名称也知道它维护了所有的requestMatcher,里面的任何一个requestMatcher匹配通过就返回true,代表当前请求
kotlin
public final class OrRequestMatcher implements RequestMatcher {
private final List<RequestMatcher> requestMatchers;
/**
* Creates a new instance
* @param requestMatchers the {@link RequestMatcher} instances to try
*/
public OrRequestMatcher(List<RequestMatcher> requestMatchers) {
Assert.notEmpty(requestMatchers, "requestMatchers must contain a value");
Assert.noNullElements(requestMatchers, "requestMatchers cannot contain null values");
this.requestMatchers = requestMatchers;
}
/**
* Creates a new instance
* @param requestMatchers the {@link RequestMatcher} instances to try
*/
public OrRequestMatcher(RequestMatcher... requestMatchers) {
this(Arrays.asList(requestMatchers));
}
@Override
public boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request) {
for (RequestMatcher matcher : this.requestMatchers) {
if (matcher.matches(request)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}✅ 最终结论
经过上面的分析我们终于知道了:Spring Authorization Server如何做到只处理oauth相关请求,因为AuthorizationServerConfigurer维护了很多端点的配置类,每个端点的配置类负责定义和维护要处理的请求(requestMatcher),这些请求结合在一起就是最终构成过滤器链的入口。
说的更直白些就是这条过滤器链只处理AuthorizationServerSettings中设置的端点,因为AuthorizationServerSettings配置的端点都会被各个configure使用。
🔥
http.securityMatcher(endpointsMatcher)是 Spring Security 多 Filter Chain 架构的基石。它确保:
- OAuth 2.0 的 endpoints 由专门的链处理(Chain 1)
- 普通应用请求(如
/login,/user,/api)由另一条链处理(Chain 2)这种设计实现了 关注点分离 ,是 Spring Authorization Server 官方配置的核心设计思想。