基本概念
定义
RPC(Remote Procedure Call)即远程过程调用,是一种计算机通信协议,它允许程序在不同的计算机之间进行通信和交互,就像本地调用一样。
为什么需要RPC
- 微服务、分布式应用的开发越来越常见,RPC可以解决各个节点之间的服务调用以及通信问题。
- 治理功能,比如连接管理、健康检测、负载均衡、优雅启停机、异常重试、业务分组以及熔断限流等等。
- 看起来就跟调用自己项目的方法没有任何区别
RPC 框架实现思路
基本设计
代理对象 :为了简化消费者发请求的代码,实现类似本地调用的体验。可以基于代理模式,为消费者要调用的接口生成一个代理对象,由代理对象完成请求和响应的过程。
本地服务注册器 ,记录服务和对应实现类的映射
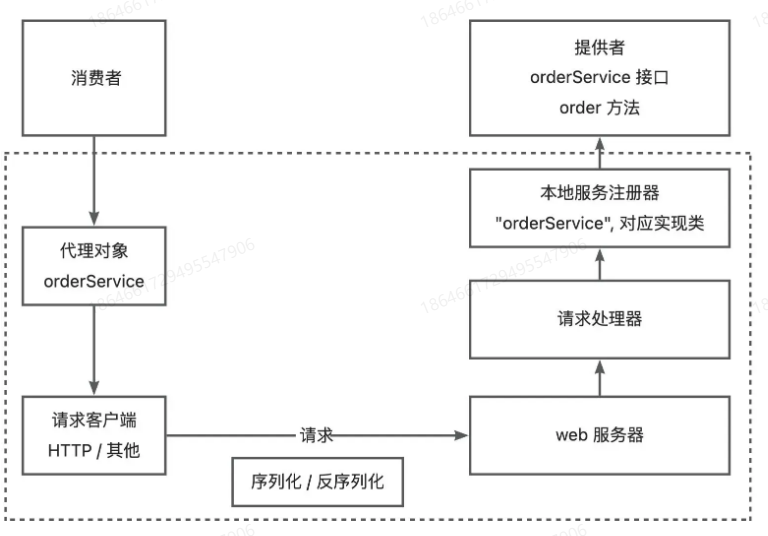
扩展设计
服务注册发现
消费者如何知道提供者的调用地址呢?
需要一个 注册中心,来保存服务提供者的地址。消费者要调用服务时,只需从注册中心获取对应服务的提供者地址即可。
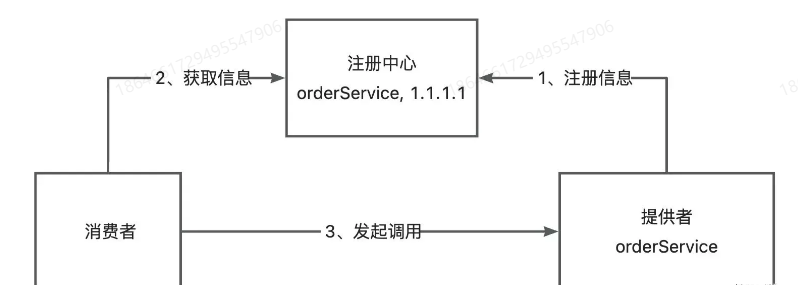
负载均衡
如果有多个服务提供者,消费者应该调用哪个服务提供者呢?
我们可以给服务调用方增加负载均衡能力,通过指定不同的算法来决定调用哪一个服务提供者,比如轮询、随机、根据性能动态调用等。
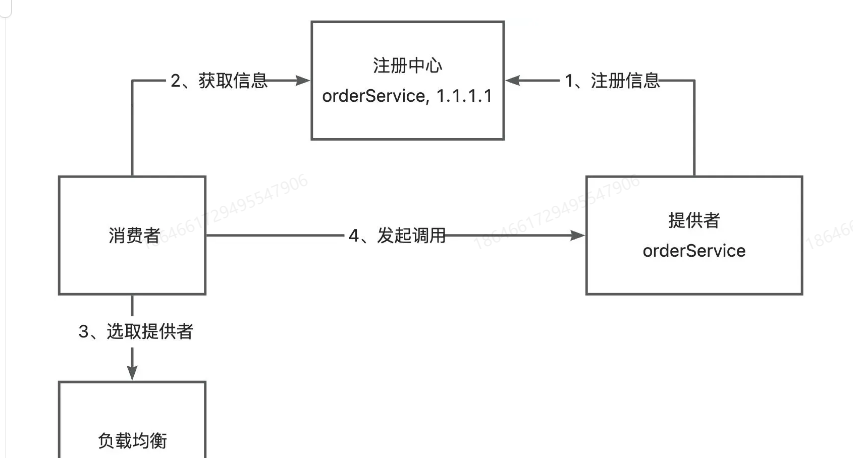
容错机制
如果服务调用失败,应该如何处理呢?
为了保证分布式系统的高可用,我们通常会给服务的调用增加一定的容错机制,比如失败重试、降级调用其他接口等等。
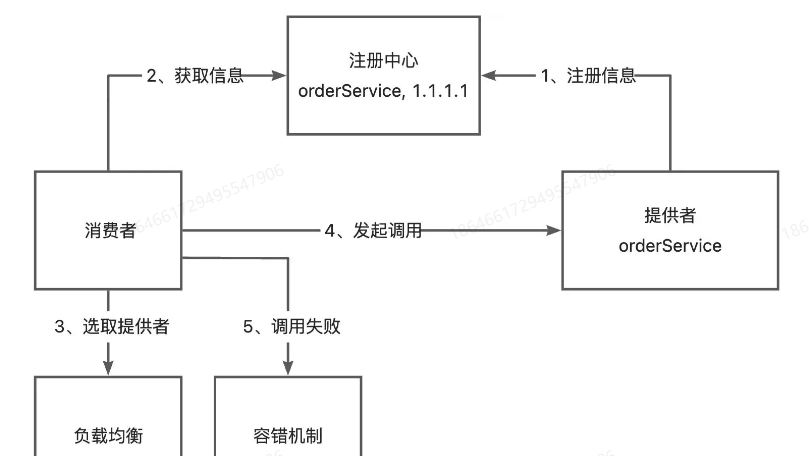
案例
消费者
java
public class EasyConsumerExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 静态代理
// UserService userService = new UserServiceProxy();
// 动态代理
UserService userService = ServiceProxyFactory.getProxy(UserService.class);
User user = new User();
user.setName("123");
// 调用
User newUser = userService.getUser(user);
if (newUser != null) {
System.out.println(newUser.getName());
} else {
System.out.println("user == null");
}
}
}
java
public class UserServiceProxy implements UserService {
@Override
public User getUser(User user) {
// 指定序列化器
final Serializer serializer = new JdkSerializer();
// 构造请求
RpcRequest rpcRequest = RpcRequest.builder()
.serviceName(UserService.class.getName())
.methodName("getUser")
.parameterTypes(new Class[]{User.class})
.args(new Object[]{user})
.build();
try {
// 序列化(Java 对象 => 字节数组)
byte[] bodyBytes = serializer.serialize(rpcRequest);
// 发送请求
try (HttpResponse httpResponse = HttpRequest.post("http://localhost:8080")
.body(bodyBytes)
.execute()) {
byte[] result = httpResponse.bodyBytes();
// 反序列化(字节数组 => Java 对象)
RpcResponse rpcResponse = serializer.deserialize(result, RpcResponse.class);
return (User) rpcResponse.getData();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}提供者
java
public class EasyProviderExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 注册服务
LocalRegistry.register(UserService.class.getName(), UserServiceImpl.class);
// 启动 web 服务
HttpServer httpServer = new VertxHttpServer();
httpServer.doStart(8080);
}
}
java
public class VertxHttpServer implements HttpServer {
/**
* 启动服务器
*
* @param port
*/
public void doStart(int port) {
// 创建 Vert.x 实例
Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx();
// 创建 HTTP 服务器
io.vertx.core.http.HttpServer server = vertx.createHttpServer();
// 处理请求
server.requestHandler(new HttpServerHandler());
// 启动 HTTP 服务器并监听指定端口
server.listen(port, result -> {
if (result.succeeded()) {
System.out.println("Server is now listening on port " + port);
} else {
System.err.println("Failed to start server: " + result.cause());
}
});
}
}
java
public class HttpServerHandler implements Handler<HttpServerRequest> {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServerRequest request) {
// 指定序列化器
final Serializer serializer = SerializerFactory.getInstance(RpcApplication.getRpcConfig().getSerializer());
// 记录日志
System.out.println("Received request: " + request.method() + " " + request.uri());
// 异步处理 HTTP 请求
Serializer finalSerializer = serializer;
request.bodyHandler(body -> {
byte[] bytes = body.getBytes();
RpcRequest rpcRequest = null;
try {
rpcRequest = finalSerializer.deserialize(bytes, RpcRequest.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 构造响应结果对象
RpcResponse rpcResponse = new RpcResponse();
// 如果请求为 null,直接返回
if (rpcRequest == null) {
rpcResponse.setMessage("rpcRequest is null");
doResponse(request, rpcResponse, finalSerializer);
return;
}
try {
// 获取要调用的服务实现类,通过反射调用
Class<?> implClass = LocalRegistry.get(rpcRequest.getServiceName());
Method method = implClass.getMethod(rpcRequest.getMethodName(), rpcRequest.getParameterTypes());
Object result = method.invoke(implClass.newInstance(), rpcRequest.getArgs());
// 封装返回结果
rpcResponse.setData(result);
rpcResponse.setDataType(method.getReturnType());
rpcResponse.setMessage("ok");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
rpcResponse.setMessage(e.getMessage());
rpcResponse.setException(e);
}
// 响应
doResponse(request, rpcResponse, finalSerializer);
});
}
/**
* 响应
*
* @param request
* @param rpcResponse
* @param serializer
*/
void doResponse(HttpServerRequest request, RpcResponse rpcResponse, Serializer serializer) {
HttpServerResponse httpServerResponse = request.response()
.putHeader("content-type", "application/json");
try {
// 序列化
byte[] serialized = serializer.serialize(rpcResponse);
httpServerResponse.end(Buffer.buffer(serialized));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
httpServerResponse.end(Buffer.buffer());
}
}
}补充
动态代理
无侵入式的给方法增强功能
invoke方法的执行时机,当你调用代理对象的方法时,这个调用会被重定向到InvocationHandler的invoke方法。设计模式被称为"延迟加载"
三要素
- 真正干活的对象
- 代理对象
- 利用代理调用方法
切记一点:代理可以增强或者拦截的方法都在接口中,接口需要写在newProxyInstance的第二个参数里。
案例
java
public interface Star {
//我们可以把所有想要被代理的方法定义在接口当中
//唱歌
public abstract String sing(String name);
//跳舞
public abstract void dance();
}
java
public class BigStar implements Star {
private String name;
public BigStar() {
}
public BigStar(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//唱歌
@Override
public String sing(String name){
System.out.println(this.name + "正在唱" + name);
return "谢谢";
}
//跳舞
@Override
public void dance(){
System.out.println(this.name + "正在跳舞");
}
/**
* 获取
* @return name
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* 设置
* @param name
*/
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return "BigStar{name = " + name + "}";
}
}
java
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
需求:
外面的人想要大明星唱一首歌
1. 获取代理的对象
代理对象 = ProxyUtil.createProxy(大明星的对象);
2. 再调用代理的唱歌方法
代理对象.唱歌的方法("只因你太美");
*/
//1. 获取代理的对象
BigStar bigStar = new BigStar("鸡哥");
Star proxy = ProxyUtil.createProxy(bigStar);
//2. 调用唱歌的方法
String result = proxy.sing("只因你太美");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
java
/*
*
* 类的作用:
* 创建一个代理
*
* */
public class ProxyUtil {
/*
*
* 方法的作用:
* 给一个明星的对象,创建一个代理
*
* 形参:
* 被代理的明星对象
*
* 返回值:
* 给明星创建的代理
*
*
*
* 需求:
* 外面的人想要大明星唱一首歌
* 1. 获取代理的对象
* 代理对象 = ProxyUtil.createProxy(大明星的对象);
* 2. 再调用代理的唱歌方法
* 代理对象.唱歌的方法("只因你太美");
* */
public static Star createProxy(BigStar bigStar){
/* java.lang.reflect.Proxy类:提供了为对象产生代理对象的方法:
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)
参数一:用于指定用哪个类加载器,去加载生成的代理类
参数二:指定接口,这些接口用于指定生成的代理长什么,也就是有哪些方法
参数三:用来指定生成的代理对象要干什么事情*/
Star star = (Star) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
ProxyUtil.class.getClassLoader(),//参数一:用于指定用哪个类加载器,去加载生成的代理类
new Class[]{Star.class},//参数二:指定接口,这些接口用于指定生成的代理长什么,也就是有哪些方法
//参数三:用来指定生成的代理对象要干什么事情
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/*
* 参数一:代理的对象
* 参数二:要运行的方法 sing
* 参数三:调用sing方法时,传递的实参
* */
if("sing".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("准备话筒,收钱");
}else if("dance".equals(method.getName())){
System.out.println("准备场地,收钱");
}
//去找大明星开始唱歌或者跳舞
//代码的表现形式:调用大明星里面唱歌或者跳舞的方法
return method.invoke(bigStar,args);
}
}
);
return star;
}
}