SpringMVC2
接收参数的常用注解
- RequestParam注解
作用:把请求中的指定名称的参数传递给控制器中的形参赋值
属性:
value:请求参数中的名称,指定请求参数名与方法参数名的映射关系(解决名称不一致的问题);
required:请求参数中是否必须提供此参数,默认值是true,表示必须提供请求参数,若未传会抛异常,设为false则允许为空;
defaultValue:如果没有传请求参数,使用该默认值。
java
package com.qcby.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/dept")
public class DeptController {
/**
* RequestParam注解
*/
@RequestMapping("/save1.do")
public String save(@RequestParam(value = "username", required = false, defaultValue = "abc") String name) {
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
return "suc";
}
}- RequestBody注解
作用:将整个请求体的内容作为字符串接收(注意:get方法不可以)
required属性:表示是否必须有请求体,默认值是true
@requestBody注解常用的使用方式有两种:
- 将json格式的数据绑定到对应的实体类中
后端@RequestBody注解对应的类在将HTTP的输入流(含请求体)装配到目标类(即:@RequestBody后面 的类)时,会根据json字符串中的key来匹配对应实体类的属性,如果匹配一致且json中的该key对应的值符合(或可转换为)实体类的对应属性的类型要求时,会调用实体类的setter方法将值赋给该属性; - 将json格式的数据按照key值分别赋值在对应的字符串中
使用method="post"提交时,参数不会拼在 URL 后面,而是被封装到请求体(Request Body)中,格式为 key=value&key=value。
html
<h3>请求参数绑定(@RequestBody注解方式一)</h3>
<form action="/dept/save2.do" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="sname" /><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" name="aaa"/><br/>
</form>
<h3>请求参数绑定(@RequestBody注解方式二)</h3>
<form action="/dept/save3.do" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="sname" /><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" name="aaa"/><br/>
</form>
java
package com.qcby.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/dept")
public class DeptController {
/**
* RequestBody注解,绑定到对应的实体类中
*/
@RequestMapping("/save2.do")
public String save2(@RequestBody String body){
System.out.println("请求体内容:"+body);
return "suc";
}
/**
* RequestBody注解,别赋值在对应的字符串中
*/
@RequestMapping("/save3.do")
public String getUser(@RequestBody String sname,@RequestBody String age){
System.out.println(sname);
System.out.println(age);
return "suc";
}
}打印结果:

- RequestHeader注解
作用:获取指定请求头的信息
value属性:请求头的名称
servlet 中获取指定请求头信息的方式:
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
/**
* servlet提供的获取请求头信息
*/
@RequestMapping("/save7.do")
public String save7(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
System.out.println(request.getParameter("username"));
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String headerName = (String) headerNames.nextElement();
String headerValue = request.getHeader(headerName);
System.out.println(headerName + ": " + headerValue);
}
return "suc";
}
}request 是 HttpServletRequest 类型的对象,代表客户端发送的 HTTP 请求,Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames(); 即通过 getHeaderNames() 获取所有 HTTP 请求头名称的枚举对象,while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) { ... } 循环遍历枚举对象,其中 hasMoreElements() 表示判断是否还有未处理的请求头名称,headerNames.nextElement(); 获取下一个请求头的名称,request.getHeader(headerName); 根据名称获取对应的请求头值。
html
<h3>获取请求头信息(servlet提供)</h3>
<form action="/user/save7.do" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" /><br/>
</form>打印结果:
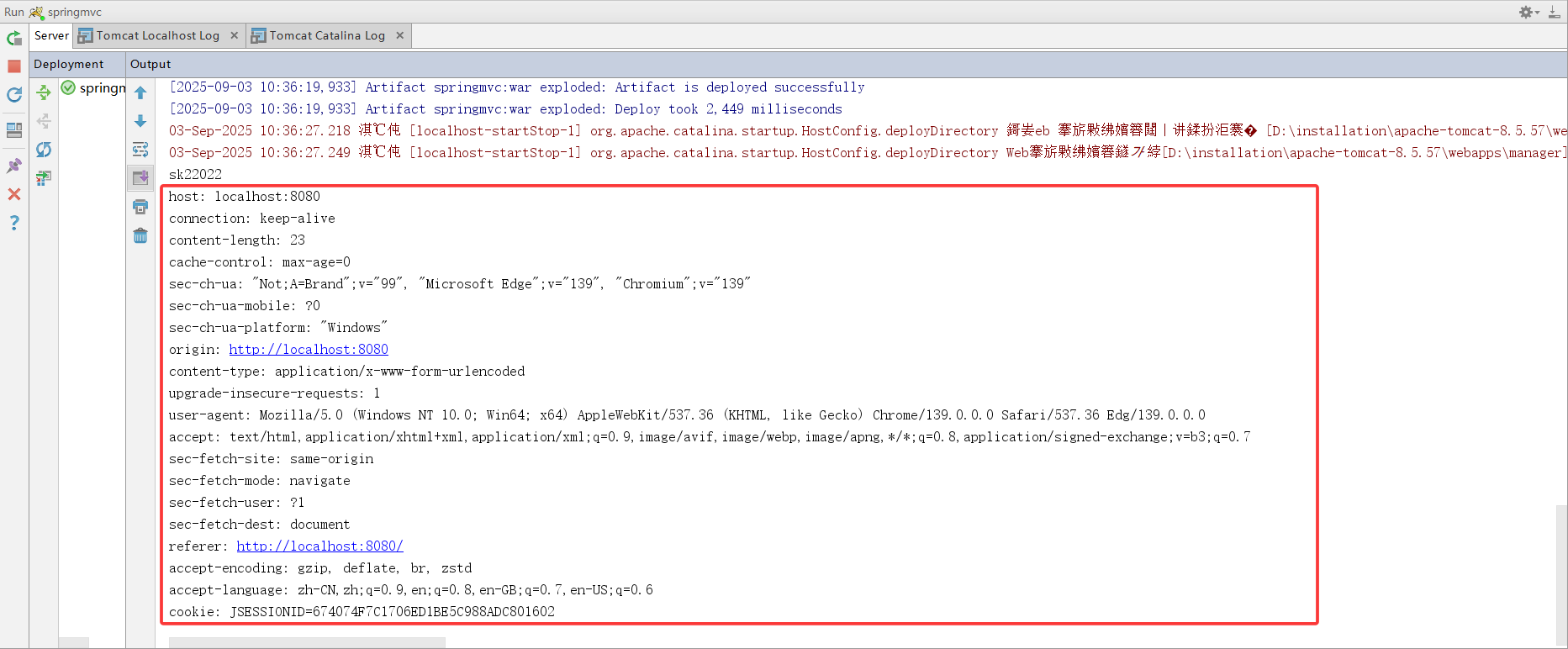
Spring 框架提供的 @RequestHeader 注解用于获取请求头中指定字段的值
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
/**
* @RequestHeader 注解
*/
@RequestMapping("/save8.do")
public String save8(@RequestHeader("cookie") String headerValue) {
System.out.println(headerValue);
return "suc";
}
}其中参数"cookie"表示获取请求头中名为Cookie的字段,注意是获取整个Cookie请求头的原始字符串
html
<h3>获取请求头信息(@RequestHeader 注解)</h3>
<form action="/user/save8.do" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" /><br/>
</form>打印结果:
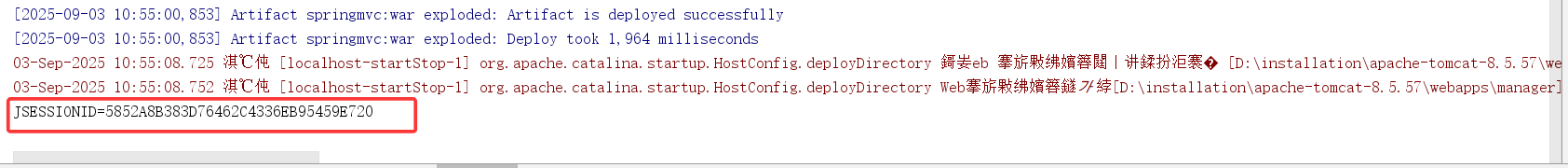
- CookieValue注解
作用:用于从请求携带的Cookie中直接获取指定名称Cookie的值
value属性:cookie的名称
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
/**
* CookieValue注解
*/
@RequestMapping("/save9.do")
public String save9(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID") String cookie){
System.out.println("值:"+cookie);
return "suc";
}
}@CookieValue 注解会自动从所有Cookie中提取指定名称(value = "JSESSIONID")的单个Cookie的具体值
html
<h3>获取请求头cookie信息(@CookieValue 注解)</h3>
<form action="/user/save9.do" method="post">
姓名:<input type="text" name="username" /><br/>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age" /><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交" /><br/>
</form>打印结果:
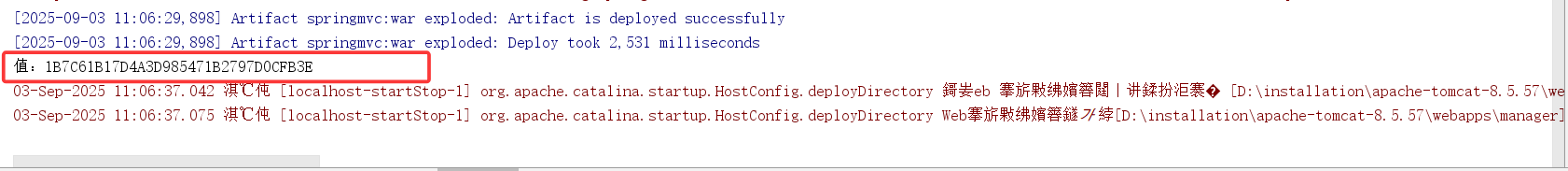
- PathVaribale注解
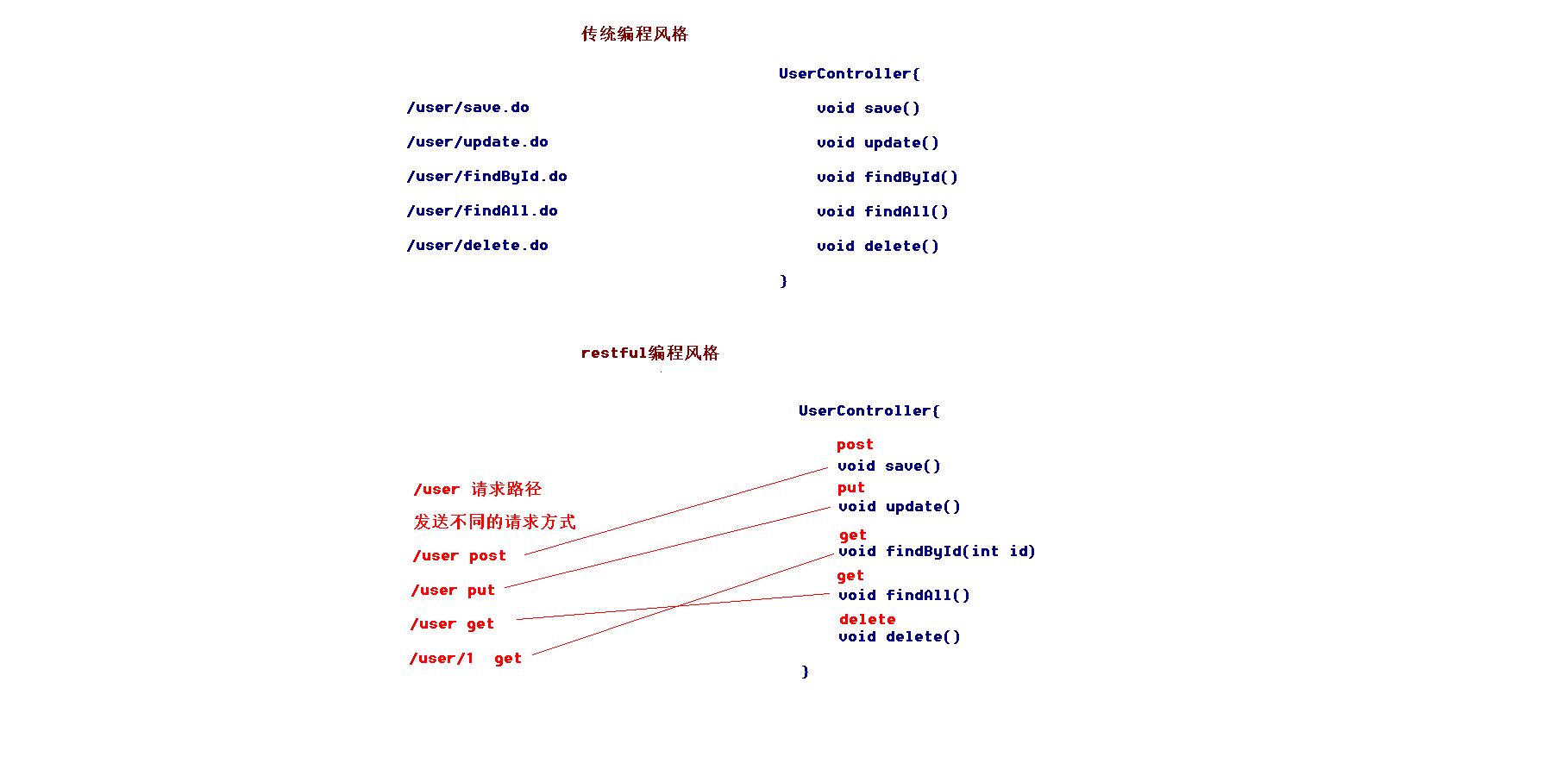
作用:获取 URL 路径中的占位符参数(适用于 RESTful 风格的 URL)
例如:url中有/delete/{id},{id}就是占位符
value属性:指定url中的占位符名称,若方法参数名与占位符名一致可省略
Restful 风格的 URL:请求路径一样,可以根据不同的请求方式去执行后台的不同方法
@GetMapping:映射 GET 请求,用于查询资源
@PostMapping:映射 POST 请求,用于创建新资源
@PutMapping:映射 PUT 请求,用于全量更新资源
@DeleteMapping:映射 DELETE 请求,用于删除资源
restful风格的URL优点:结构清晰、符合标准、易于理解、扩展方便
java
package com.qcby.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
//@RequestMapping("/emp")
public class EmpController{
/**
* 保存
*/
@RequestMapping(path ="/emp",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(){
System.out.println("保存员工...");
return "suc";
}
/**
* 查询所有
*/
@RequestMapping(path ="/emp", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String findAll(){
System.out.println("查询员工...");
return "suc";
}
/**
* 查询所有
*/
@RequestMapping(path = "/emp/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String findById(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id){
System.out.println("通过id查询员工..."+id);
return "suc";
}
}
html
<h3>Restful风格的URL</h3>
<form action="/emp" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="保存员工"><br/>
</form>
<form action="/emp" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="查询员工"><br/>
</form>
<form action="/emp/1" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="通过id查询员工"><br/>
</form>打印结果:

响应数据和结果视图
- 返回String
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
/**
* 返回字符串(常用)
*/
@RequestMapping("/save1.do")
public String save1(){
System.out.println("执行了save1...");
return "suc";
}
}- 返回值是void
如果控制器的方法返回值编写成void,SpringMVC 不会自动进行视图解析或数据处理,默认查找JSP页面没有找到,执行程序报404的异常
解决方式:可以使用请求转发或者重定向跳转到指定的页面,而非依赖 Spring MVC 的视图解析器自动跳转
需要使用 Servlet 规范中的原生 API 获取请求信息和处理响应,三种常见的响应方式:
- 通过 HttpServletRequest 的 getRequestDispatcher() 方法实现请求转发,可以访问/WEB-INF目录下的资源,以及可以携带request域中的数据到目标资源;
- 通过 HttpServletResponse 的 sendRedirect() 方法实现重定向,需要注意的是不能直接访问/WEB-INF目录下的资源,且request域中的数据会丢失;
- 通过 HttpServletResponse 的输出流直接向客户端输出数据,不经过其他资源跳转。
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
/**
* 返回值是void
*/
@RequestMapping("/save2.do")
public void save2(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("执行了save2...");
//请求转发
request.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/pages/suc.jsp").forward(request,response);
//重定向, request.getContextPath() 用于获取上下文路径
//response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");
// 使用response对象直接向客户端输出响应数据
//response.getWriter().print("hello");
return;
}
}- 返回值是ModelAndView对象
ModelAndView 是 SpringMVC 提供的一个对象,可同时封装模型数据和视图信息,适合需要在一个对象中同时处理数据和视图的场景
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
/**
* 返回ModelAndView对象
*/
@RequestMapping("/save3.do")
public ModelAndView save3(){
System.out.println("执行了save3...");
// 创建mv对象
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
// 把一些数据,存储到mv对象中
mv.addObject("msg","用户名或者密码已经存在");
// 设置逻辑视图的名称
mv.setViewName("suc");
// 也支持redirect/forward
// mv.setViewName("redirect:/index.jsp");
return mv;
}
}补充另一种拆开的方式,返回值是String,视图解析器跳转至对应视图,参数列表中携带model来返回数据内容,代码示例:
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/mtype")
public class MtypeController {
@RequestMapping("/list")
public String selectpage(MtypeQuery mq, Model model){
Page<Mtype> page = mtypeService.selectObjectByCondition(mq);
model.addAttribute("page", page);
return "mtype";
}
}- SpringMVC 框架提供的forward请求转发
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
/**
* 返回String
* SpringMVC框架提供的请求转发
*/
@RequestMapping("/save4.do")
public String save4(){
System.out.println("执行了save4...");
return "forward:/WEB-INF/pages/suc.jsp";
}
}- SpringMVC 框架提供的redirect请求转发
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
/**
* 返回String
* SpringMVC框架提供的重定向
*/
@RequestMapping("/save5.do")
public String save5(){
System.out.println("执行了save5...");
return "redirect:save1.do";
// 也可重定向到外部URL但无法访问WEB-INF下的资源
//return "redirect:https://www.baidu.com";
}
}前端编写
xml
<h3>请求转发与重定向</h3>
<form action="/redict/save1.do" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="执行"><br/>
</form>
<form action="/redict/save2.do" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="执行"><br/>
</form>
<form action="/redict/save3.do" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="执行"><br/>
</form>
<form action="/redict/save4.do" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="执行"><br/>
</form>
<form action="/redict/save5.do" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="执行"><br/>
</form>打印结果:
- ResponseBody响应json数据(重要)
首先需要导入坐标依赖,引入JSON 序列化依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>@ResponseBody的使用本质是 "标记返回值需转为响应体",ResponseBody响应json数据后台代码编写有三种方式,使得返回值会被序列化为 JSON
第一种方式 @ResponseBody 注解加到返回值前
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
/**
* ResponseBody响应json数据(重要)
* 异步的数据交互
*/
@RequestMapping("/save6.do")
public @ResponseBody User save6(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println(user);
// 模拟,调用业务层代码
user.setUsername("hello");
user.setAge(100);
// 把user对象转换成json字符串,再响应,response.getWriter().print()
return user;
}
}第二种方式 @ResponseBody 注解加到方法上
java
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/redict")
public class ReController {
// 方法上单独使用@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/save7.do")
@ResponseBody // 仅当前方法返回数据(不跳转视图)
public User save7(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
user.setUsername("hello");
user.setAge(100);
return user; // 返回的User对象会被转换为JSON响应
}
}第三种方式 @ResponseBody 注解加到类上,即类上使用@RestController,等价于@Controller + @ResponseBody
java
package com.qcby.controller;
import com.qcby.model.User;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class TestController {
// 方法上无需再添加@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/save1.do")
public User save6(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println(user);
user.setUsername("hello");
user.setAge(100);
return user; // 返回的User对象会被转换为JSON响应
}
}前端jsp代码编写
html
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>请求参数绑定</title>
<%--引入jq,使用阿里云的jQuery CDN(无integrity校验,稳定可靠) --%>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/jquery@3.6.0/dist/jquery.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script>
// 页面加载
$(function(){
// 单击事件
$("#btn1").click(function(){
// 发送ajax的请求
$.ajax({
type: "post",
url: "/redict/save6.do",
contentType:"application/json;charset=UTF-8",
data:'{"username":"haha","age":"20"}',
dataType: "json",
success:function(d){
// 编写很多代码
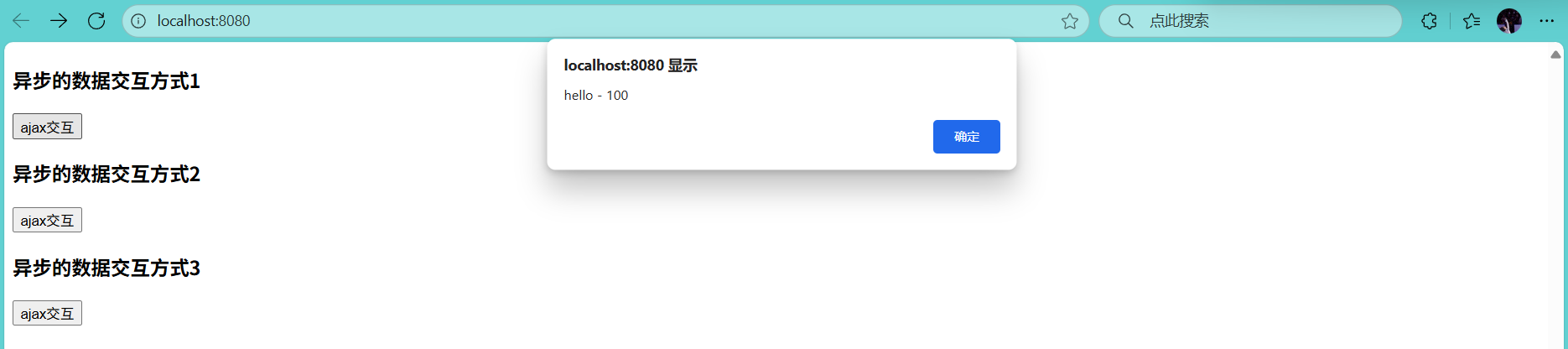
alert(d.username+" - "+d.age);
}
});
});
$("#btn2").click(function(){
// 发送ajax的请求
$.ajax({
type: "post",
url: "/redict/save7.do",
contentType:"application/json;charset=UTF-8",
data:'{"username":"haha","age":"20"}',
dataType: "json",
success:function(d){
// 编写很多代码
alert(d.username+" - "+d.age);
}
});
});
$("#btn3").click(function(){
// 发送ajax的请求
$.ajax({
type: "post",
url: "/test/save1.do",
contentType:"application/json;charset=UTF-8",
data:'{"username":"haha","age":"20"}',
dataType: "json",
success:function(d){
// 编写很多代码
alert(d.username+" - "+d.age);
}
});
});
});
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2>响应数据和结果视图</h2>
<h3>返回值是String</h3>
<a href="/redict/save1.do" >返回String</a><br/>
<h3>返回值是void</h3>
<a href="/redict/save2.do" >返回void</a><br/>
<h3>返回值是ModelAndView</h3>
<a href="/redict/save3.do" >返回ModelAndView</a><br/>
<h3>请求转发返回值是String</h3>
<a href="/redict/save4.do" >返回值是String</a><br/>
<h3>重定向返回值是String</h3>
<a href="/redict/save5.do" >返回值是String</a><br/>
<h3>异步的数据交互方式1</h3>
<input type="button" value="ajax交互" id="btn1"><br/>
<h3>异步的数据交互方式2</h3>
<input type="button" value="ajax交互" id="btn2"><br/>
<h3>异步的数据交互方式3</h3>
<input type="button" value="ajax交互" id="btn3"><br/>
</body>
</html>需要注意的是 DispatcherServlet 会拦截到所有的资源,导致静态资源也会被拦截到,从而不能被使用,需要配置静态资源不进行拦截,在 springmvc.xml 配置文件添加如下配置:
xml
<!-- 设置静态资源不过滤 -->
<mvc:resources location="/css/" mapping="/css/**"/> <!-- 样式 -->
<mvc:resources location="/images/" mapping="/images/**"/> <!-- 图片 -->
<mvc:resources location="/js/" mapping="/js/**"/> <!-- javascript -->location元素表示webapp目录下的包下的所有文件,mapping元素表示以/static开头的所有请求路径
响应结果:
后端打印结果:
