一、前言
在分布式消息中间件RocketMQ的架构中,Broker扮演着核心的消息存储和转发枢纽角色。它直接承担了生产者的消息投递、消费者的消息拉取以及消息的持久化存储等核心职责,其稳定性和性能直接决定了整个消息集群的服务质量。
本文将深入剖析RocketMQ 4.9.8版本中Broker服务的启动过程源码。我们将从启动脚本的入口BrokerStartup开始,一步步揭开Broker如何初始化其核心控制器BrokerController、如何加载配置与元数据、如何构建高性能的存储引擎和网络通信层,最终如何向NameServer完成注册,正式对外提供服务的完整过程。通过本次源码之旅,您不仅能清晰了解到Broker的内部组成,更能深刻理解RocketMQ高可用、高性能背后的设计哲学。
二、BrokerController的核心组件
Broker核心启动类是BrokerController它里面包含很多重要的组件,是它们共同协作完成Broker的功能,其中比较核心的组件有TopicConfigManager(管理Topic配置) 、ConsumerOffsetManager (管理消费进度)、SubscriptionGroupManager(管理订阅关系)、 MessageStore(消息存储核心引擎)、RemotingServer(处理客户端请求)、BrokerOuterAPI(与Namesrv交互)、PullRequestHoldService(长轮询服务)、各种ThreadPoolExecuto(处理不同业务的线程池) 、ScheduledExecutorService(执行定时任务),其中MessageStore是能否成功恢复并承载消息流量的关键所在,它里面也有一些核心组件,它们分别是CommitLog(消息存储主体, 顺序写) 、 MappedFileQueue(管理所有MappedFile, 文件队列) 、MappedFile(物理的文件表示类,CommitLog文件、ConsumeQueue 文件) 、ConsumeQueue(消费逻辑队列)。
下面以两张图展示BrokerController的核心组件。
图1:BrokerController 核心组件构成图
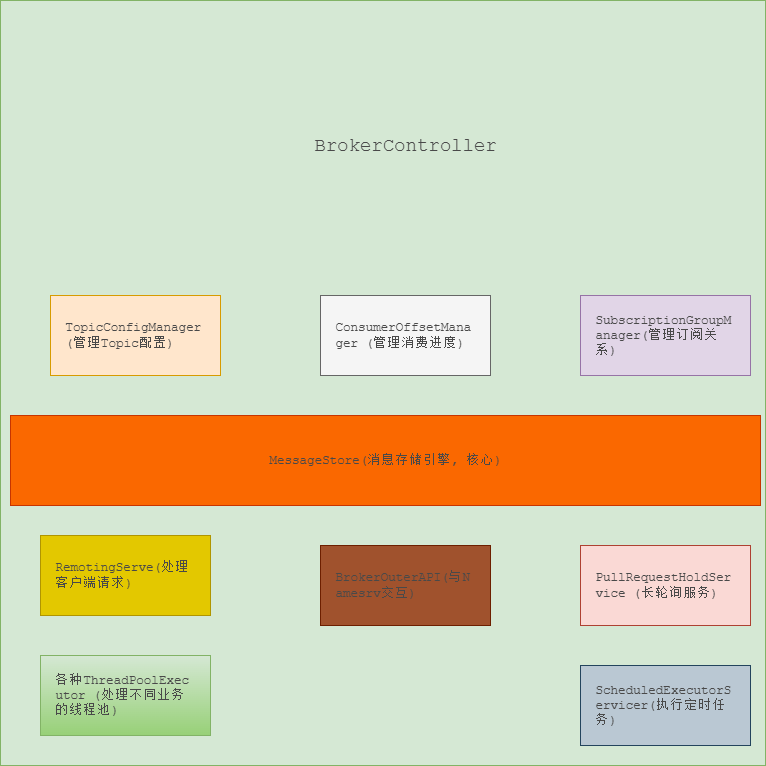
图2:消息存储(MessageStore)核心体系图

三、BrokerController创建和启动过程
Broker启动的入口地址在org.apache.rocketmq.broker.BrokerStartup的main方法中,该方法源码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
start(createBrokerController(args));
}这里面调用的是createBrokerController方法就是为了创建BrokerController对象,该方法源码如下:
public static BrokerController createBrokerController(String[] args) {
System.setProperty(RemotingCommand.REMOTING_VERSION_KEY, Integer.toString(MQVersion.CURRENT_VERSION));
try {
//解析命令行参数
// ... (省略具体的解析代码)
final BrokerConfig brokerConfig = new BrokerConfig();
brokerConfig.setNamesrvAddr("127.0.0.1:9876");
final NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig = new NettyServerConfig();
final NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig = new NettyClientConfig();
nettyClientConfig.setUseTLS(Boolean.parseBoolean(System.getProperty(TLS_ENABLE,
String.valueOf(TlsSystemConfig.tlsMode == TlsMode.ENFORCING))));
nettyServerConfig.setListenPort(10911);
final MessageStoreConfig messageStoreConfig = new MessageStoreConfig();
if (BrokerRole.SLAVE == messageStoreConfig.getBrokerRole()) {
int ratio = messageStoreConfig.getAccessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio() - 10;
messageStoreConfig.setAccessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio(ratio);
}
//解析命令行参数
// ... (省略具体的解析代码)
if (null == brokerConfig.getRocketmqHome()) {
System.out.printf("Please set the %s variable in your environment to match the location of the RocketMQ installation", MixAll.ROCKETMQ_HOME_ENV);
System.exit(-2);
}
String namesrvAddr = brokerConfig.getNamesrvAddr();
if (null != namesrvAddr) {
try {
String[] addrArray = namesrvAddr.split(";");
for (String addr : addrArray) {
RemotingUtil.string2SocketAddress(addr);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.printf(
"The Name Server Address[%s] illegal, please set it as follows, \"127.0.0.1:9876;192.168.0.1:9876\"%n",
namesrvAddr);
System.exit(-3);
}
}
switch (messageStoreConfig.getBrokerRole()) {
case ASYNC_MASTER:
case SYNC_MASTER:
brokerConfig.setBrokerId(MixAll.MASTER_ID);
break;
case SLAVE:
if (brokerConfig.getBrokerId() <= 0) {
System.out.printf("Slave's brokerId must be > 0");
System.exit(-3);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
if (messageStoreConfig.isEnableDLegerCommitLog()) {
brokerConfig.setBrokerId(-1);
}
messageStoreConfig.setHaListenPort(nettyServerConfig.getListenPort() + 1);
LoggerContext lc = (LoggerContext) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory();
JoranConfigurator configurator = new JoranConfigurator();
configurator.setContext(lc);
lc.reset();
System.setProperty("brokerLogDir", "");
if (brokerConfig.isIsolateLogEnable()) {
System.setProperty("brokerLogDir", brokerConfig.getBrokerName() + "_" + brokerConfig.getBrokerId());
}
if (brokerConfig.isIsolateLogEnable() && messageStoreConfig.isEnableDLegerCommitLog()) {
System.setProperty("brokerLogDir", brokerConfig.getBrokerName() + "_" + messageStoreConfig.getdLegerSelfId());
}
configurator.doConfigure(brokerConfig.getRocketmqHome() + "/conf/logback_broker.xml");
//解析命令行参数
// ... (省略具体的解析代码)
final BrokerController controller = new BrokerController(
brokerConfig,
nettyServerConfig,
nettyClientConfig,
messageStoreConfig);
// remember all configs to prevent discard
controller.getConfiguration().registerConfig(properties);
boolean initResult = controller.initialize();
if (!initResult) {
controller.shutdown();
System.exit(-3);
}
return controller;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(-1);
}
return null;
}创建Broker的配置类BrokerConfig,这个配置类的成员属性有很多,下面以表格方式列举一些主要的属性。
| 成员属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| brokerId | Broker 的 ID,主为 0,从为非 0 |
| brokerClusterName | Broker 所属的集群名,默认是DefaultCluster |
| namesrvAddr | NameServer 地址,多个用分号隔开 |
| defaultTopicQueueNums | 自动创建 Topic 时默认的队列数(默认 8) |
| autoCreateTopicEnable | 是否允许自动创建 Topic(默认 true) |
| autoCreateSubscriptionGroup | 是否允许自动创建订阅组(默认 true) |
| brokerIP1 | Broker 对外暴露的 IP 地址(默认读取本地) |
创建NettyServerConfig类,它主要是Broker作为服务器端Netty的配置参数,下面以表格方式列举一些主要的属性。
| 参数名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| listenPort | 10911 | Broker 对外服务的监听端口(必须开放给 Producer 和 Consumer) |
| serverWorkerThreads | 8 | Netty 工作线程数,用于处理网络读写 |
| serverCallbackExecutorThreads | 0 | 业务回调线程池大小(为 0 时使用 publicExecutor) |
| serverSelectorThreads | 3 | Netty Selector 线程数,负责处理连接请求 |
| serverOnewaySemaphoreValue | 256 | Oneway 请求并发信号量限制(如发送消息不需要响应) |
| serverChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds | 120 | 空闲连接最大存活时间,超时会关闭连接 |
| serverSocketSndBufSize | 0 | Socket 发送缓冲区大小(0 代表使用系统默认) |
| serverSocketRcvBufSize | 0 | Socket 接收缓冲区大小 |
创建NettyClientConfig类,它主要用于配置客户端(Producer / Consumer)网络通信的相关参数,属于内部优化和性能调优的重要部分,下面以表格方式列举一些主要的属性。
| 字段名 | 类型 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| clientWorkerThreads | int | 4 | 客户端工作线程数(用于处理回调逻辑) |
| clientOnewaySemaphoreValue | int | 65535 | 单向请求信号量限制(控制并发量) |
| connectTimeoutMillis | int | 3000 | 建立 TCP 连接的超时时间(单位:毫秒) |
| channelNotActiveInterval | int | 60_000 | 连接空闲时间,超过后会关闭(单位:毫秒) |
| clientChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds | int | 120 | Channel 最大空闲时间,单位:秒 |
| clientSocketSndBufSize | int | Netty 默认 | Socket 发送缓冲区大小 |
| clientSocketRcvBufSize | int | Netty 默认 | Socket 接收缓冲区大小 |
| useTLS | boolean | false | 是否启用 TLS 安全传输 |
创建MessageStoreConfig类,它是消息存储配置类,它控制着 CommitLog、ConsumeQueue、Index 文件的存储行为,下面以表格方式列举一些主要的属性。
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| storePathRootDir | ${user.home}/store | 根目录,commitlog、consumequeue 等都在这个目录下 |
| storePathCommitLog | ${storePathRootDir}/commitlog | CommitLog 的存储路径 |
| mappedFileSizeCommitLog | 1 GB | CommitLog 每个文件的大小 |
| mappedFileSizeConsumeQueue | 6000000 | ConsumeQueue 文件大小(每个队列的索引文件) |
| flushIntervalCommitLog | 500ms | CommitLog 刷盘间隔 |
| flushCommitLogTimed | false | 是否定时 flush,false 表示用 group commit |
| deleteWhen | 04 | 删除过期文件的时间点(凌晨4点) |
| fileReservedTime | 72 小时 | 文件保留时间 |
| maxTransferBytesOnMessageInMemory | 256KB | 内存中转最大字节数 |
| maxTransferCountOnMessageInMemory | 32 | 内存中转最大消息条数 |
| flushDiskType | FlushDiskType.ASYNC_FLUSH | Flush 类型(ASYNC_FLUSH、SYNC_FLUSH)。 |
| accessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio | 40 | 控制消息消费时优先从内存中读取的最大比例 |
` if (BrokerRole.SLAVE == messageStoreConfig.getBrokerRole()) { int ratio = messageStoreConfig.getAccessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio() - 10; messageStoreConfig.setAccessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio(ratio); `
这代码判断当 broker 是 SLAVE 时:
- RocketMQ 通过
-10的方式,把accessMessageInMemoryMaxRatio比例下调,比如从 40 降到 30,以降低对内存的依赖。 - 目的是为了减少 SLAVE 读取内存中的数据,更倾向于从磁盘加载数据。
创建BrokerController对象,它是 RocketMQ Broker 的核心控制器类 ,可以认为它是整个 Broker 服务的 "大脑",负责协调和管理 Broker 的所有核心组件和生命周期,调用构造方法把BrokerConfig、NettyServerConfig、NettyClientConfig、MessageStoreConfig对象传入。
它的构造函数源码如下:
public BrokerController(
final BrokerConfig brokerConfig,
final NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig,
final NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig,
final MessageStoreConfig messageStoreConfig
) {
this.brokerConfig = brokerConfig;
this.nettyServerConfig = nettyServerConfig;
this.nettyClientConfig = nettyClientConfig;
this.messageStoreConfig = messageStoreConfig;
this.consumerOffsetManager = messageStoreConfig.isEnableLmq() ? new LmqConsumerOffsetManager(this) : new ConsumerOffsetManager(this);
this.topicConfigManager = messageStoreConfig.isEnableLmq() ? new LmqTopicConfigManager(this) : new TopicConfigManager(this);
this.pullMessageProcessor = new PullMessageProcessor(this);
this.pullRequestHoldService = messageStoreConfig.isEnableLmq() ? new LmqPullRequestHoldService(this) : new PullRequestHoldService(this);
this.messageArrivingListener = new NotifyMessageArrivingListener(this.pullRequestHoldService);
this.consumerIdsChangeListener = new DefaultConsumerIdsChangeListener(this);
this.consumerManager = new ConsumerManager(this.consumerIdsChangeListener);
this.consumerFilterManager = new ConsumerFilterManager(this);
this.producerManager = new ProducerManager();
this.clientHousekeepingService = new ClientHousekeepingService(this);
this.broker2Client = new Broker2Client(this);
this.subscriptionGroupManager = messageStoreConfig.isEnableLmq() ? new LmqSubscriptionGroupManager(this) : new SubscriptionGroupManager(this);
this.brokerOuterAPI = new BrokerOuterAPI(nettyClientConfig);
this.slaveSynchronize = new SlaveSynchronize(this);
this.sendThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getSendThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.putThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getPutThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.pullThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getPullThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.replyThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getReplyThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.queryThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getQueryThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.clientManagerThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getClientManagerThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.consumerManagerThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getConsumerManagerThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.heartbeatThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getHeartbeatThreadPoolQueueCapacity());
this.endTransactionThreadPoolQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(this.brokerConfig.getEndTransactionPoolQueueCapacity());
this.brokerStatsManager = messageStoreConfig.isEnableLmq() ? new LmqBrokerStatsManager(this.brokerConfig.getBrokerClusterName(), this.brokerConfig.isEnableDetailStat()) : new BrokerStatsManager(this.brokerConfig.getBrokerClusterName(), this.brokerConfig.isEnableDetailStat());
this.setStoreHost(new InetSocketAddress(this.getBrokerConfig().getBrokerIP1(), this.getNettyServerConfig().getListenPort()));
this.brokerFastFailure = new BrokerFastFailure(this);
this.configuration = new Configuration(
log,
BrokerPathConfigHelper.getBrokerConfigPath(),
this.brokerConfig, this.nettyServerConfig, this.nettyClientConfig, this.messageStoreConfig
);
}-
初始化成员变量ConsumerOffsetManager对象,它是管理消费进度的类。
-
初始化成员变量TopicConfigManager对象,它是管理管理Topic配置的类。
-
初始化成员变量SubscriptionGroupManager对象,它是管理消费者订阅关系的类。
-
初始化成员变量PullMessageProcessor对象,它用于处理消费者拉取请求。
-
初始化成员变量PullRequestHoldService对象,它是RocketMQ中长轮询机制的核心,主要用于挂起消费者的拉取请求(pull request),直到有新消息到达或超时再返回,防止增加网络IO压力。
-
初始化成员变量NotifyMessageArrivingListener对象, 是 RocketMQ 中用于 长轮询(Long Polling)消息拉取机制 的一个 消息到达通知接口 ,配合
PullRequestHoldService使用,主要目的是在新消息到达时及时唤醒挂起的消息拉取请求。 -
初始化成员变量ConsumerManager
/ProducerManager,它主要是管理客户端连接的消费者/生产者。 -
ClientHousekeepingService对象主要是检查客户端连接是否存活,清理无效连接。
-
BrokerOuterAPI对象主要是Broker 对 NameServer 的注册、更新等封装。
-
SlaveSynchronize对象主要是从节点向主节点同步配置信息。
-
初始化多个请求处理队列,用于绑定线程池,支撑并发处理:
- sendThreadPoolQueue 发送消息请求。
- pullThreadPoolQueue 消费者拉取消息。
- clientManagerThreadPoolQueue 客户端管理任务。
- heartbeatThreadPoolQueue 心跳包处理等。
好了到此处BrokerController对象初始化完成,然后开始调用其initialize方法,该方法源码如下:
public boolean initialize() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
boolean result = this.topicConfigManager.load();
result = result && this.consumerOffsetManager.load();
result = result && this.subscriptionGroupManager.load();
result = result && this.consumerFilterManager.load();
if (result) {
try {
this.messageStore =
new DefaultMessageStore(this.messageStoreConfig, this.brokerStatsManager, this.messageArrivingListener,
this.brokerConfig);
if (messageStoreConfig.isEnableDLegerCommitLog()) {
DLedgerRoleChangeHandler roleChangeHandler = new DLedgerRoleChangeHandler(this, (DefaultMessageStore) messageStore);
((DLedgerCommitLog)((DefaultMessageStore) messageStore).getCommitLog()).getdLedgerServer().getdLedgerLeaderElector().addRoleChangeHandler(roleChangeHandler);
}
this.brokerStats = new BrokerStats((DefaultMessageStore) this.messageStore);
//load plugin
MessageStorePluginContext context = new MessageStorePluginContext(messageStoreConfig, brokerStatsManager, messageArrivingListener, brokerConfig);
this.messageStore = MessageStoreFactory.build(context, this.messageStore);
this.messageStore.getDispatcherList().addFirst(new CommitLogDispatcherCalcBitMap(this.brokerConfig, this.consumerFilterManager));
} catch (IOException e) {
result = false;
log.error("Failed to initialize", e);
}
}
result = result && this.messageStore.load();
if (result) {
this.remotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(this.nettyServerConfig, this.clientHousekeepingService);
NettyServerConfig fastConfig = (NettyServerConfig) this.nettyServerConfig.clone();
fastConfig.setListenPort(nettyServerConfig.getListenPort() - 2);
this.fastRemotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(fastConfig, this.clientHousekeepingService);
this.sendMessageExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getSendMessageThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getSendMessageThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.sendThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("SendMessageThread_"));
this.putMessageFutureExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getPutMessageFutureThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getPutMessageFutureThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.putThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("PutMessageThread_"));
this.pullMessageExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getPullMessageThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getPullMessageThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.pullThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("PullMessageThread_"));
this.replyMessageExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getProcessReplyMessageThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getProcessReplyMessageThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.replyThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("ProcessReplyMessageThread_"));
this.queryMessageExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getQueryMessageThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getQueryMessageThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.queryThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("QueryMessageThread_"));
this.adminBrokerExecutor =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(this.brokerConfig.getAdminBrokerThreadPoolNums(), new ThreadFactoryImpl(
"AdminBrokerThread_"));
this.clientManageExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getClientManageThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getClientManageThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.clientManagerThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("ClientManageThread_"));
this.heartbeatExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getHeartbeatThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getHeartbeatThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.heartbeatThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("HeartbeatThread_", true));
this.endTransactionExecutor = new BrokerFixedThreadPoolExecutor(
this.brokerConfig.getEndTransactionThreadPoolNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getEndTransactionThreadPoolNums(),
1000 * 60,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
this.endTransactionThreadPoolQueue,
new ThreadFactoryImpl("EndTransactionThread_"));
this.consumerManageExecutor =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(this.brokerConfig.getConsumerManageThreadPoolNums(), new ThreadFactoryImpl(
"ConsumerManageThread_"));
this.registerProcessor();
final long initialDelay = UtilAll.computeNextMorningTimeMillis() - System.currentTimeMillis();
final long period = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24;
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.getBrokerStats().record();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("schedule record error.", e);
}
}, initialDelay, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.consumerOffsetManager.persist();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("schedule persist consumerOffset error.", e);
}
}, 1000 * 10, this.brokerConfig.getFlushConsumerOffsetInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.consumerFilterManager.persist();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("schedule persist consumer filter error.", e);
}
}, 1000 * 10, 1000 * 10, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.protectBroker();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("protectBroker error.", e);
}
}, 3, 3, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.printWaterMark();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("printWaterMark error.", e);
}
}, 10, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
log.info("dispatch behind commit log {} bytes", BrokerController.this.getMessageStore().dispatchBehindBytes());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("schedule dispatchBehindBytes error.", e);
}
}, 1000 * 10, 1000 * 60, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (this.brokerConfig.getNamesrvAddr() != null) {
this.brokerOuterAPI.updateNameServerAddressList(this.brokerConfig.getNamesrvAddr());
log.info("Set user specified name server address: {}", this.brokerConfig.getNamesrvAddr());
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.brokerOuterAPI.updateNameServerAddressList(BrokerController.this.brokerConfig.getNamesrvAddr());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask updateNameServerAddr exception", e);
}
}, 1000 * 10, 1000 * 60 * 2, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else if (this.brokerConfig.isFetchNamesrvAddrByAddressServer()) {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.brokerOuterAPI.fetchNameServerAddr();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask fetchNameServerAddr exception", e);
}
}, 1000 * 10, 1000 * 60 * 2, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
if (!messageStoreConfig.isEnableDLegerCommitLog()) {
if (BrokerRole.SLAVE == this.messageStoreConfig.getBrokerRole()) {
if (this.messageStoreConfig.getHaMasterAddress() != null && this.messageStoreConfig.getHaMasterAddress().length() >= 6) {
this.messageStore.updateHaMasterAddress(this.messageStoreConfig.getHaMasterAddress());
this.updateMasterHAServerAddrPeriodically = false;
} else {
this.updateMasterHAServerAddrPeriodically = true;
}
} else {
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
try {
BrokerController.this.printMasterAndSlaveDiff();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("schedule printMasterAndSlaveDiff error.", e);
}
}, 1000 * 10, 1000 * 60, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
if (TlsSystemConfig.tlsMode != TlsMode.DISABLED) {
// Register a listener to reload SslContext
try {
fileWatchService = new FileWatchService(
new String[] {
TlsSystemConfig.tlsServerCertPath,
TlsSystemConfig.tlsServerKeyPath,
TlsSystemConfig.tlsServerTrustCertPath
},
new FileWatchService.Listener() {
boolean certChanged, keyChanged = false;
@Override
public void onChanged(String path) {
if (path.equals(TlsSystemConfig.tlsServerTrustCertPath)) {
log.info("The trust certificate changed, reload the ssl context");
reloadServerSslContext();
}
if (path.equals(TlsSystemConfig.tlsServerCertPath)) {
certChanged = true;
}
if (path.equals(TlsSystemConfig.tlsServerKeyPath)) {
keyChanged = true;
}
if (certChanged && keyChanged) {
log.info("The certificate and private key changed, reload the ssl context");
certChanged = keyChanged = false;
reloadServerSslContext();
}
}
private void reloadServerSslContext() {
((NettyRemotingServer) remotingServer).loadSslContext();
((NettyRemotingServer) fastRemotingServer).loadSslContext();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("FileWatchService created error, can't load the certificate dynamically");
}
}
initialTransaction();
initialAcl();
initialRpcHooks();
}
return result;
}这个方法总结下拉主要做了以下事情:
-
加载本地配置文件
- 读取Topic配置文件(
TopicConfigManager) - 读取消费者消费偏移量配置文件(
ConsumerOffsetManager) - 读取订阅分组配置文件(
SubscriptionGroupManager) - 读取消费者过滤配置文件(
ConsumerFilterManager)
- 读取Topic配置文件(
-
创建消息存储类(DefaultMessageStore)
-
创建Broker服务端通信类
NettyRemotingServer(这个类在我Netty源码中已经分析过了) -
创建了很多定时任务线程池
- 每隔24小时打印前一天生产和消费数量
- 每隔5s将消费者offset持久化
- 每隔10s将消费过滤信息持久化
- 每隔3min,检查消费者消费进度
- 每隔1s打印发送线程池队列信息
5.创建文件监听器
6.初始化事务相关服务
7.初始化权限相关服务
8.初始化RPC调用钩子函数
这个方法里面还初始化了很多线程池对象,下面一一例举一下:
-
ExecutorService sendMessageExecutor表示处理发送消息请求线程池,默认线程数量:min(处理器数量,4)。 -
ExecutorService putMessageFutureExecutor表示生产者推送消息处理完成线程池,默认线程数量:min(处理器数量,4)* 。 -
ExecutorService pullMessageExecutor表示消费者拉取消息线程池,默认线程数量:16+处理器数量*2。 -
ExecutorService replyMessageExecutor表示消费者消费消息响应线程池,默认线程数量:16+处理器数量*2。 -
ExecutorService queryMessageExecutor表示查询消息线程池:默认线程池数量:8+处理器数量。 -
ExecutorService adminBrokerExecutor表示 broker管理线程池,默认线程数量:16。 -
ExecutorService clientManageExecutor表示客户端管理线程池。 -
ExecutorService heartbeatExecutor表示心跳处理线程池。 -
ExecutorService endTransactionExecutor表示事务处理线程池。 -
ExecutorService consumerManageExecutor表示消费者管理线程池。
调用registerProcessor方法将请求处理器注册,注册到RemotingServer的成员变量HashMap<Integer, Pair<NettyRequestProcessor, ExecutorService>> 上,key是Request,value是Pair里面有成员变量Processor、ExecutorService,后续处理Netty请求就需要用到这些处理器。
这里要重点说明一下DefaultMessageStore 创建过程,它是整个消息存储子系统的核心入口类,它承担了消息写入、消息查询、消息恢复等关键职责。它的内部核心成员变量是 CommitLog ,可以理解为 RocketMQ 的"消息写入日志文件",所有消息的真实内容(消息体 + 消息属性等)都会顺序写入到 CommitLog 文件中,这些文件才是消息的物理存储。
为了高效地管理 CommitLog,CommitLog 内部又持有一个 MappedFileQueue 对象,它可以看作是文件的队列管理器:
-
一个 MappedFileQueue 由多个 MappedFile 组成;
-
每个 MappedFile 实际上对应着磁盘上的一个 CommitLog 文件(默认大小 1G);
-
当一个文件写满后,就会自动创建下一个文件,形成一个逻辑上连续、物理上分段的日志序列。
RocketMQ 并不是直接用传统 I/O 来读写 CommitLog 文件,而是通过 mmap(内存映射) 的方式,把磁盘文件映射到内核的 PageCache。这样设计有几个好处:
-
顺序写极致性能:消息写入 CommitLog 时,实际上只是顺序地往 PageCache 里写数据,由内核异步刷盘,写入速度几乎接近内存操作。
-
零拷贝加速读取:消费者拉消息时,可以直接利用 PageCache + mmap 将数据"暴露"为用户态可访问的内存区域,不需要多次拷贝。
-
文件切分管理:通过 MappedFileQueue 管理多个 MappedFile,不仅可以方便文件的顺序写入,还能支持按偏移量快速定位消息(逻辑偏移 → 物理偏移 → CommitLog)。
MappedFile其实是封装了mmap的操作,下面我们来看一下它的init方法是如果管理CommitLog文件的。
private void init(final String fileName, final int fileSize) throws IOException { this.fileName = fileName; this.fileSize = fileSize; this.file = new File(fileName); this.fileFromOffset = Long.parseLong(this.file.getName()); boolean ok = false; ensureDirOK(this.file.getParent()); try { this.fileChannel = new RandomAccessFile(this.file, "rw").getChannel(); this.mappedByteBuffer = this.fileChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, fileSize); TOTAL_MAPPED_VIRTUAL_MEMORY.addAndGet(fileSize); TOTAL_MAPPED_FILES.incrementAndGet(); ok = true; } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { log.error("Failed to create file " + this.fileName, e); throw e; } catch (IOException e) { log.error("Failed to map file " + this.fileName, e); throw e; } finally { if (!ok && this.fileChannel != null) { this.fileChannel.close(); } } }
根据文件名创建File对象,然后创建了RandomAccessFile随机读取文件对象,设置为读写模式,调用getChannel方法获取FileChannel对象然后调用map方法获取MappedByteBuffer对象,它就是真正的内存映射,应用程序操作 MappedByteBuffer 就相当于直接操作内核页缓存,减少了 JVM 堆和内核之间的拷贝。后续存储消息和读取消息都是通过此对象进行操作的,等分析时候再详细的说明。
此时createBrokerController方法执行完成开始调用BrokerStartup的start,该方法源码如下:
public static BrokerController start(BrokerController controller) {
try {
controller.start();
String tip = "The broker[" + controller.getBrokerConfig().getBrokerName() + ", "
+ controller.getBrokerAddr() + "] boot success. serializeType=" + RemotingCommand.getSerializeTypeConfigInThisServer();
if (null != controller.getBrokerConfig().getNamesrvAddr()) {
tip += " and name server is " + controller.getBrokerConfig().getNamesrvAddr();
}
log.info(tip);
System.out.printf("%s%n", tip);
return controller;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(-1);
}
return null;
}里面调用的是BrokerController的start方法,该方法源码如下:
public void start() throws Exception {
if (this.messageStore != null) {
this.messageStore.start();
}
if (this.remotingServer != null) {
this.remotingServer.start();
}
if (this.fastRemotingServer != null) {
this.fastRemotingServer.start();
}
if (this.fileWatchService != null) {
this.fileWatchService.start();
}
if (this.brokerOuterAPI != null) {
this.brokerOuterAPI.start();
}
if (this.pullRequestHoldService != null) {
this.pullRequestHoldService.start();
}
if (this.clientHousekeepingService != null) {
this.clientHousekeepingService.start();
}
if (!messageStoreConfig.isEnableDLegerCommitLog()) {
startProcessorByHa(messageStoreConfig.getBrokerRole());
handleSlaveSynchronize(messageStoreConfig.getBrokerRole());
this.registerBrokerAll(true, false, true);
}
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
BrokerController.this.registerBrokerAll(true, false, brokerConfig.isForceRegister());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("registerBrokerAll Exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 10, Math.max(10000, Math.min(brokerConfig.getRegisterNameServerPeriod(), 60000)), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (this.brokerStatsManager != null) {
this.brokerStatsManager.start();
}
if (this.brokerFastFailure != null) {
this.brokerFastFailure.start();
}
}这里面可以看出调用各个组件的start方法,主要是启动Broker的Netty服务器端和客户端、启动长轮询处理服务、客户端活跃连接扫描服务,然后每隔30秒发送一下心跳给NameSrv,处理逻辑是registerBrokerAll方法,该方法源码如下:
public synchronized void registerBrokerAll(final boolean checkOrderConfig, boolean oneway, boolean forceRegister) {
TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper = this.getTopicConfigManager().buildTopicConfigSerializeWrapper();
if (!PermName.isWriteable(this.getBrokerConfig().getBrokerPermission())
|| !PermName.isReadable(this.getBrokerConfig().getBrokerPermission())) {
ConcurrentHashMap<String, TopicConfig> topicConfigTable = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
for (TopicConfig topicConfig : topicConfigWrapper.getTopicConfigTable().values()) {
TopicConfig tmp =
new TopicConfig(topicConfig.getTopicName(), topicConfig.getReadQueueNums(), topicConfig.getWriteQueueNums(),
this.brokerConfig.getBrokerPermission());
topicConfigTable.put(topicConfig.getTopicName(), tmp);
}
topicConfigWrapper.setTopicConfigTable(topicConfigTable);
}
if (forceRegister || needRegister(this.brokerConfig.getBrokerClusterName(),
this.getBrokerAddr(),
this.brokerConfig.getBrokerName(),
this.brokerConfig.getBrokerId(),
this.brokerConfig.getRegisterBrokerTimeoutMills())) {
doRegisterBrokerAll(checkOrderConfig, oneway, topicConfigWrapper);
}
}调用的是doRegisterBrokerAll方法,该方法源码如下:
private void doRegisterBrokerAll(boolean checkOrderConfig, boolean oneway,
TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper) {
List<RegisterBrokerResult> registerBrokerResultList = this.brokerOuterAPI.registerBrokerAll(
this.brokerConfig.getBrokerClusterName(),
this.getBrokerAddr(),
this.brokerConfig.getBrokerName(),
this.brokerConfig.getBrokerId(),
this.getHAServerAddr(),
topicConfigWrapper,
Lists.newArrayList(),
oneway,
this.brokerConfig.getRegisterBrokerTimeoutMills(),
this.brokerConfig.isCompressedRegister());
if (registerBrokerResultList.size() > 0) {
RegisterBrokerResult registerBrokerResult = registerBrokerResultList.get(0);
if (registerBrokerResult != null) {
if (this.updateMasterHAServerAddrPeriodically && registerBrokerResult.getHaServerAddr() != null) {
this.messageStore.updateHaMasterAddress(registerBrokerResult.getHaServerAddr());
}
this.slaveSynchronize.setMasterAddr(registerBrokerResult.getMasterAddr());
if (checkOrderConfig) {
this.getTopicConfigManager().updateOrderTopicConfig(registerBrokerResult.getKvTable());
}
}
}
}又调用的是this.brokerOuterAPI.registerBrokerAll方法,该方法源码如下:
public List<RegisterBrokerResult> registerBrokerAll(
final String clusterName,
final String brokerAddr,
final String brokerName,
final long brokerId,
final String haServerAddr,
final TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper,
final List<String> filterServerList,
final boolean oneway,
final int timeoutMills,
final boolean compressed) {
final List<RegisterBrokerResult> registerBrokerResultList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
List<String> nameServerAddressList = this.remotingClient.getNameServerAddressList();
if (nameServerAddressList != null && nameServerAddressList.size() > 0) {
final RegisterBrokerRequestHeader requestHeader = new RegisterBrokerRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setBrokerAddr(brokerAddr);
requestHeader.setBrokerId(brokerId);
requestHeader.setBrokerName(brokerName);
requestHeader.setClusterName(clusterName);
requestHeader.setHaServerAddr(haServerAddr);
requestHeader.setCompressed(compressed);
RegisterBrokerBody requestBody = new RegisterBrokerBody();
requestBody.setTopicConfigSerializeWrapper(topicConfigWrapper);
requestBody.setFilterServerList(filterServerList);
final byte[] body = requestBody.encode(compressed);
final int bodyCrc32 = UtilAll.crc32(body);
requestHeader.setBodyCrc32(bodyCrc32);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(nameServerAddressList.size());
for (final String namesrvAddr : nameServerAddressList) {
brokerOuterExecutor.execute(() -> {
try {
RegisterBrokerResult result = registerBroker(namesrvAddr, oneway, timeoutMills, requestHeader, body);
if (result != null) {
registerBrokerResultList.add(result);
}
log.info("register broker[{}]to name server {} OK", brokerId, namesrvAddr);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("registerBroker Exception, {}", namesrvAddr, e);
} finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
});
}
try {
countDownLatch.await(timeoutMills, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
return registerBrokerResultList;
}先创建头部对象RegisterBrokerRequestHeader,设置broker的地址、brokerId、brokerName、clusterName等信息,创建请求体对象 RegisterBrokerBody,设置topicConfigSerializeWrapper、filterServerList属性,把RegisterBrokerBody对象编码成body,然后 调用UtilAll.crc32方法得到bodyCrc32设置到头部对象RegisterBrokerRequestHeader,调用registerBroker方法,该方法源码如下:
private RegisterBrokerResult registerBroker(
final String namesrvAddr,
final boolean oneway,
final int timeoutMills,
final RegisterBrokerRequestHeader requestHeader,
final byte[] body
) throws RemotingCommandException, MQBrokerException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException,
InterruptedException {
RemotingCommand request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.REGISTER_BROKER, requestHeader);
request.setBody(body);
if (oneway) {
try {
this.remotingClient.invokeOneway(namesrvAddr, request, timeoutMills);
} catch (RemotingTooMuchRequestException e) {
}
return null;
}
RemotingCommand response = this.remotingClient.invokeSync(namesrvAddr, request, timeoutMills);
assert response != null;
switch (response.getCode()) {
case ResponseCode.SUCCESS: {
RegisterBrokerResponseHeader responseHeader =
(RegisterBrokerResponseHeader) response.decodeCommandCustomHeader(RegisterBrokerResponseHeader.class);
RegisterBrokerResult result = new RegisterBrokerResult();
result.setMasterAddr(responseHeader.getMasterAddr());
result.setHaServerAddr(responseHeader.getHaServerAddr());
if (response.getBody() != null) {
result.setKvTable(KVTable.decode(response.getBody(), KVTable.class));
}
return result;
}
default:
break;
}
throw new MQBrokerException(response.getCode(), response.getRemark(), requestHeader == null ? null : requestHeader.getBrokerAddr());
}创建RemotingCommand对象,设置该对象的成员属性类型是int的code值是(requestCode.REGISTER_BROKER,即103)、成员属性类型CommandCustomHeader的CommandCustomHeader值是RegisterBrokerRequestHeader 设置body值是requestBody.encode(compressed),接着调用NettyRemotingClient的invokeSync方法,该方法源码如下:
public RemotingCommand invokeSync(String addr, final RemotingCommand request, long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Channel channel = this.getAndCreateChannel(addr);
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
try {
doBeforeRpcHooks(addr, request);
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeSync call the addr[" + addr + "] timeout");
}
RemotingCommand response = this.invokeSyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime);
doAfterRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), request, response);
return response;
} catch (RemotingSendRequestException e) {
log.warn("invokeSync: send request exception, so close the channel[{}]", addr);
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw e;
} catch (RemotingTimeoutException e) {
if (nettyClientConfig.isClientCloseSocketIfTimeout()) {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
log.warn("invokeSync: close socket because of timeout, {}ms, {}", timeoutMillis, addr);
}
log.warn("invokeSync: wait response timeout exception, the channel[{}]", addr);
throw e;
}
} else {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw new RemotingConnectException(addr);
}
}先调用getAndCreateChannel方法创建Netty的Channel对象,便于和服务器端进行通信,该方法源码如下:
private Channel getAndCreateChannel(final String addr) throws RemotingConnectException, InterruptedException {
if (null == addr) {
return getAndCreateNameserverChannel();
}
ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {
return cw.getChannel();
}
return this.createChannel(addr);
}然后这个方法调用的是createChannel方法,该方法源码如下:
private Channel createChannel(final String addr) throws InterruptedException {
ChannelWrapper cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
if (cw != null && cw.isOK()) {
return cw.getChannel();
}
if (this.lockChannelTables.tryLock(LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
try {
boolean createNewConnection;
cw = this.channelTables.get(addr);
if (cw != null) {
if (cw.isOK()) {
return cw.getChannel();
} else if (!cw.getChannelFuture().isDone()) {
createNewConnection = false;
} else {
this.channelTables.remove(addr);
createNewConnection = true;
}
} else {
createNewConnection = true;
}
if (createNewConnection) {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = this.bootstrap.connect(RemotingHelper.string2SocketAddress(addr));
log.info("createChannel: begin to connect remote host[{}] asynchronously", addr);
cw = new ChannelWrapper(channelFuture);
this.channelTables.put(addr, cw);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("createChannel: create channel exception", e);
} finally {
this.lockChannelTables.unlock();
}
} else {
log.warn("createChannel: try to lock channel table, but timeout, {}ms", LOCK_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
}
if (cw != null) {
ChannelFuture channelFuture = cw.getChannelFuture();
if (channelFuture.awaitUninterruptibly(this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())) {
if (cw.isOK()) {
log.info("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] success, {}", addr, channelFuture.toString());
return cw.getChannel();
} else {
log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[" + addr + "] failed, " + channelFuture, channelFuture.cause());
}
} else {
log.warn("createChannel: connect remote host[{}] timeout {}ms, {}", addr, this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis(),
channelFuture.toString());
}
}
return null;
}首次执行时候会调用到ChannelFuture channelFuture = this.bootstrap.connect(RemotingHelper.string2SocketAddress(addr));创建一个ChannelFuture对象, 包装成ChannelWrapper对象,放到ConcurrentMap<String, ChannelWrapper> channelTables对象上,调用channelFuture.awaitUninterruptibly(this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis()) 等待this.nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis()这个时间看Channel是否创建完成,如果完成返回Channel对象,否则返回null。
回到invokeSync方法,得到Channel以后就可以往服务器端写入数据,调用的是invokeSyncImpl方法,该方法源码如下:
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
responseTable.remove(opaque);
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return responseCommand;
} finally {
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}创建ResponseFuture对象,代表是未来的对象,可能是没写入完成的对象,放入到ConcurrentMap<Integer, ResponseFuture> responseTable对象中,异步调用Channel的writeAndFlush方法进行写入服务端,如果写入成功会回调ChannelFutureListener对象的operationComplete方法表示写入成功,设置ResponseFuture对象的sendRequestOK属性为true,否则设置为false并设置失败原因。
如果异步没执行完成会调用RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);阻塞等待直到超时,如果得到的RemotingCommand是null,抛出RemotingTimeoutException异常,如果没有就正常返回RemotingCommand,有没有这样疑问RemotingCommand对象是从哪里的得来的那,它是Netty写入服务器端以后服务器端返回的对象,这块我们稍后做分析。
我们再来看一下NameSrv服务端收到注册请求的逻辑是什么样的,上一篇文章分析过NettyRemotingServer的实例化工厂,他是Netty服务器端的启动对象,它注册了一个NettyServerHandler,它实现了ChannelInboundHandler接口,并且它是NettyRemotingServer的内部类,会调用channelRead0方法,该方法源码如下:
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand msg) throws Exception {
processMessageReceived(ctx, msg);
}然后调用的是processMessageReceived方法,该方法是NettyRemotingServer父类的NettyRemotingAbstract方法,该方法源码如下:
public void processMessageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand msg) throws Exception {
final RemotingCommand cmd = msg;
if (cmd != null) {
switch (cmd.getType()) {
case REQUEST_COMMAND:
processRequestCommand(ctx, cmd);
break;
case RESPONSE_COMMAND:
processResponseCommand(ctx, cmd);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}这个RemotingCommand对象是NettyDecoder对象解析出来的,对服务器来说cmd.getType是REQUEST_COMMAND,经过一系列调用会调用到DefaultRequestProcessor的registerBrokerWithFilterServer方法,该方法源码如下:
public RemotingCommand registerBrokerWithFilterServer(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request)
throws RemotingCommandException {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RegisterBrokerResponseHeader.class);
final RegisterBrokerResponseHeader responseHeader = (RegisterBrokerResponseHeader) response.readCustomHeader();
final RegisterBrokerRequestHeader requestHeader =
(RegisterBrokerRequestHeader) request.decodeCommandCustomHeader(RegisterBrokerRequestHeader.class);
.................................
RegisterBrokerResult result = this.namesrvController.getRouteInfoManager().registerBroker(
requestHeader.getClusterName(),
requestHeader.getBrokerAddr(),
requestHeader.getBrokerName(),
requestHeader.getBrokerId(),
requestHeader.getHaServerAddr(),
registerBrokerBody.getTopicConfigSerializeWrapper(),
registerBrokerBody.getFilterServerList(),
ctx.channel());
responseHeader.setHaServerAddr(result.getHaServerAddr());
responseHeader.setMasterAddr(result.getMasterAddr());
byte[] jsonValue = this.namesrvController.getKvConfigManager().getKVListByNamespace(NamesrvUtil.NAMESPACE_ORDER_TOPIC_CONFIG);
response.setBody(jsonValue);
response.setCode(ResponseCode.SUCCESS);
response.setRemark(null);
return response;
}可以看出在这里创建的RemotingCommand的响应对象,创建完响应对象以后会回调一个匿名的RemotingResponseCallback对象,它的源码如下:
final RemotingResponseCallback callback = new RemotingResponseCallback() {
@Override
public void callback(RemotingCommand response) {
doAfterRpcHooks(remoteAddr, cmd, response);
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
if (response != null) {
response.setOpaque(opaque);
response.markResponseType();
response.setSerializeTypeCurrentRPC(cmd.getSerializeTypeCurrentRPC());
try {
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("process request over, but response failed", e);
log.error(cmd.toString());
log.error(response.toString());
}
} else {
}
}
}
};可以看出调用ctx.writeAndFlush(response)向客户端写出响应对象。
回调Broker端的Netty客户端的处理逻辑,它会调用NettyRemotingClient的内部类NettyClientHandler的channelRead0方法,channelRead0方法同样调用了processMessageReceived方法,该方法源码如下:
public void processMessageReceived(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand msg) throws Exception {
final RemotingCommand cmd = msg;
if (cmd != null) {
switch (cmd.getType()) {
case REQUEST_COMMAND:
processRequestCommand(ctx, cmd);
break;
case RESPONSE_COMMAND:
processResponseCommand(ctx, cmd);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}对于客户端来说服务端像客户端写入最终会调用到该方法的case RESPONSE_COMMAND逻辑,然后调用的是processResponseCommand,该方法源码如下:
public void processResponseCommand(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = responseTable.get(opaque);
if (responseFuture != null) {
responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);
responseTable.remove(opaque);
if (responseFuture.getInvokeCallback() != null) {
executeInvokeCallback(responseFuture);
} else {
responseFuture.putResponse(cmd);
responseFuture.release();
}
} else {
log.warn("receive response, but not matched any request, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()));
log.warn(cmd.toString());
}
}这里就是取出之前ResponseFuture对象然后设置响应对象RemotingCommand responseCommand,上面阻塞等待就是判断这个对象是否为null,如果不为null说明注册到NameSrv成功了,否则就是失败的。
四、结语
通过对BrokerStartup启动流程的源码分析,我们可以清晰地看到,一个RocketMQ Broker实例的启动是一个精密而复杂 的过程。它不仅仅是简单地启动一个服务端口,而是包含了配置解析、模块初始化、资源加载、网络服务构建、定时任务调度、高可用准备以及与协调组件注册等一系列关键操作。
从BrokerController这个"大脑"的构建,到MessageStore存储引擎的初始化,再到通过NettyRemotingServer提供网络服务,最后通过BrokerOuterAPI与NameServer集群保持心跳。每一个步骤都体现了RocketMQ在架构设计上对可靠性、可用性和性能的极致追求。
理解Broker的启动过程,是理解其消息存储、刷盘、复制、负载均衡等一切高级功能的基础。