写在前面
本系列推文为《R for Data Science (2)》的中文翻译版本。所有内容都通过开源免费的方式上传至Github,欢迎大家参与贡献,详细信息见:
Books-zh-cn 项目介绍:
Books-zh-cn:开源免费的中文书籍社区
r4ds-zh-cn Github 地址:
https://github.com/Books-zh-cn/r4ds-zh-cn
r4ds-zh-cn 网站地址:
https://books-zh-cn.github.io/r4ds-zh-cn/
目录
-
7.1 介绍
-
7.2 从文件读取数据
7.1 介绍
使用 R 包提供的数据是学习数据科学工具的好方法,但您希望在某个时候将所学到的知识应用到自己的数据中。在本章中,您将学习将数据文件读入 R 的基础知识。
具体来说,本章将重点关注读取纯文本矩形文件。我们将从处理列名称、类型和缺失数据等功能的实用建议开始。然后,您将了解如何同时从多个文件读取数据以及将数据从 R 写入文件。最后,您将学习如何在 R 中手工制作 data frames。
7.1.1 先决条件
在本章中,您将学习如何使用 readr 包在 R 中加载平面文件,该包是 tidyverse 核心的一部分。
library(tidyverse)7.2 从文件读取数据
首先,我们将重点关注最常见的矩形数据文件类型:CSV,它是逗号分隔值(comma-separated values)的缩写。简单的 CSV 文件如下所示。第一行,通常称为标题行,给出列名称,接下来的六行提供数据。各列由逗号分隔。
Student ID,Full Name,favourite.food,mealPlan,AGE
1,Sunil Huffmann,Strawberry yoghurt,Lunch only,4
2,Barclay Lynn,French fries,Lunch only,5
3,Jayendra Lyne,N/A,Breakfast and lunch,7
4,Leon Rossini,Anchovies,Lunch only,
5,Chidiegwu Dunkel,Pizza,Breakfast and lunch,five
6,Güvenç Attila,Ice cream,Lunch only,6Table 7.1 显示了与表格相同的数据的表示形式。
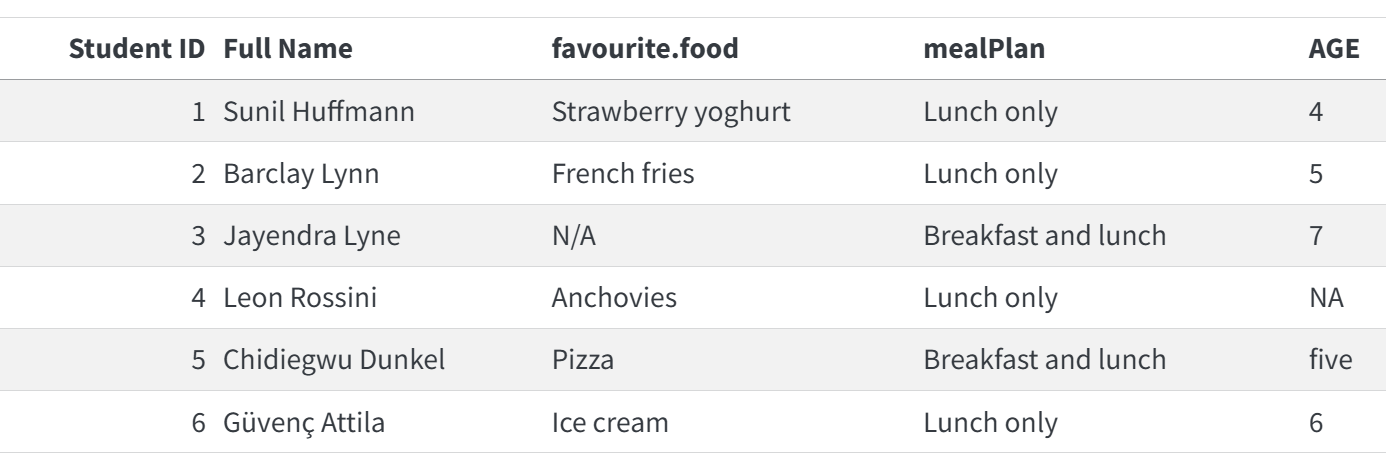
Table 7.1: 来自 students.csv 文件数据作为表格。
我们可以使用 read_csv() 将该文件读入 R。第一个参数是最重要的:文件的路径。您可以将路径视为文件的地址:该文件名为 students.csv,位于 data 文件夹中。
students <- read_csv("data/students.csv")
#> Rows: 6 Columns: 5
#> ── Column specification ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> Delimiter: ","
#> chr (4): Full Name, favourite.food, mealPlan, AGE
#> dbl (1): Student ID
#>
#> ℹ Use `spec()` to retrieve the full column specification for this data.
#> ℹ Specify the column types or set `show_col_types = FALSE` to quiet this message.如果项目的 data 文件夹中有 students.csv 文件,则上面的代码将起作用。您可以从 https://pos.it/r4ds-students-csv 下载 students.csv 文件,也可以使用以下命令直接从该 URL 读取它:
students <- read_csv("https://pos.it/r4ds-students-csv")当您运行 read_csv() 时,它会打印一条消息,告诉您数据的行数和列数、使用的分隔符(delimiter)以及列规范(按列包含的数据类型组织的列名称)。它还打印出一些有关检索完整列规范以及如何消除此消息的信息。该消息是 readr 不可或缺的一部分,我们将在 Section 7.3 中返回它。
7.2.1 实用建议
读入数据后,第一步通常涉及以某种方式对其进行转换,以便更容易在其余分析中使用。考虑到这一点,让我们再看一下 students 数据。
students
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> `Student ID` `Full Name` favourite.food mealPlan AGE
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 1 Sunil Huffmann Strawberry yoghurt Lunch only 4
#> 2 2 Barclay Lynn French fries Lunch only 5
#> 3 3 Jayendra Lyne N/A Breakfast and lunch 7
#> 4 4 Leon Rossini Anchovies Lunch only <NA>
#> 5 5 Chidiegwu Dunkel Pizza Breakfast and lunch five
#> 6 6 Güvenç Attila Ice cream Lunch only 6在 favourite.food 列中,有一堆食物项目,然后是字符串 N/A,这应该是真正的 NA,R 会识别为 "not available"。我们可以使用 na 参数来解决这个问题。默认情况下,read_csv() 仅将该数据集中的空字符串("")识别为 NAs,我们希望它也识别字符串 "N/A"。
students <- read_csv("data/students.csv", na = c("N/A", ""))
students
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> `Student ID` `Full Name` favourite.food mealPlan AGE
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 1 Sunil Huffmann Strawberry yoghurt Lunch only 4
#> 2 2 Barclay Lynn French fries Lunch only 5
#> 3 3 Jayendra Lyne <NA> Breakfast and lunch 7
#> 4 4 Leon Rossini Anchovies Lunch only <NA>
#> 5 5 Chidiegwu Dunkel Pizza Breakfast and lunch five
#> 6 6 Güvenç Attila Ice cream Lunch only 6您可能还会注意到 Student ID 和 Full Name 列周围有反引号。这是因为它们包含空格,违反了 R 变量名称的通常规则; 它们是非语法(non-syntactic )名称。要引用这些变量,您需要用反引号将它们括起来,`````:
students |>
rename(
student_id = `Student ID`,
full_name = `Full Name`
)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> student_id full_name favourite.food mealPlan AGE
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 1 Sunil Huffmann Strawberry yoghurt Lunch only 4
#> 2 2 Barclay Lynn French fries Lunch only 5
#> 3 3 Jayendra Lyne <NA> Breakfast and lunch 7
#> 4 4 Leon Rossini Anchovies Lunch only <NA>
#> 5 5 Chidiegwu Dunkel Pizza Breakfast and lunch five
#> 6 6 Güvenç Attila Ice cream Lunch only 6另一种方法是使用 janitor::clean_names() 来使用一些启发式方法将它们一次性全部变成 snake case。
students |> janitor::clean_names()
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> student_id full_name favourite_food meal_plan age
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
#> 1 1 Sunil Huffmann Strawberry yoghurt Lunch only 4
#> 2 2 Barclay Lynn French fries Lunch only 5
#> 3 3 Jayendra Lyne <NA> Breakfast and lunch 7
#> 4 4 Leon Rossini Anchovies Lunch only <NA>
#> 5 5 Chidiegwu Dunkel Pizza Breakfast and lunch five
#> 6 6 Güvenç Attila Ice cream Lunch only 6读入数据后的另一个常见任务是考虑变量类型。例如,meal_plan 是一个具有一组已知可能值的分类变量,在 R 中应表示为一个因子(factor):
students |>
janitor::clean_names() |>
mutate(meal_plan = factor(meal_plan))
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> student_id full_name favourite_food meal_plan age
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <fct> <chr>
#> 1 1 Sunil Huffmann Strawberry yoghurt Lunch only 4
#> 2 2 Barclay Lynn French fries Lunch only 5
#> 3 3 Jayendra Lyne <NA> Breakfast and lunch 7
#> 4 4 Leon Rossini Anchovies Lunch only <NA>
#> 5 5 Chidiegwu Dunkel Pizza Breakfast and lunch five
#> 6 6 Güvenç Attila Ice cream Lunch only 6请注意,meal_plan 变量中的值保持不变,但变量名称下方表示的变量类型已从 character (<chr>) 更改为 factor ()。您将在 Chapter 16 中了解有关 factors 的更多信息。
在分析这些数据之前,您可能需要修复 age 和 id 列。目前,age 是一个 character 变量,因为其中一个观测结果被输入为 five,而不是数字 5。我们将在 Chapter 20 中讨论解决此问题的详细信息。
students <- students |>
janitor::clean_names() |>
mutate(
meal_plan = factor(meal_plan),
age = parse_number(if_else(age == "five", "5", age))
)
students
#> # A tibble: 6 × 5
#> student_id full_name favourite_food meal_plan age
#> <dbl> <chr> <chr> <fct> <dbl>
#> 1 1 Sunil Huffmann Strawberry yoghurt Lunch only 4
#> 2 2 Barclay Lynn French fries Lunch only 5
#> 3 3 Jayendra Lyne <NA> Breakfast and lunch 7
#> 4 4 Leon Rossini Anchovies Lunch only NA
#> 5 5 Chidiegwu Dunkel Pizza Breakfast and lunch 5
#> 6 6 Güvenç Attila Ice cream Lunch only 6这里的一个新函数是 if_else(),它有三个参数。第一个参数 test 应该是一个逻辑向量。当 test 为 TRUE 时,结果将包含第二个参数 yes 的值;当 test 为 FALSE 时,结果将包含第三个参数 no 的值。这里我们说如果 age 是字符串 "five",则将其设为 "5",如果不是则将其保留为 age。您将在 Chapter 12 中了解有关 if_else() 和逻辑向量的更多信息。
7.2.2 其他参数
我们还需要提及其他几个重要的参数,如果我们首先向您展示一个方便的技巧,它们将更容易演示:read_csv() 可以读取您创建的文本字符串并像 CSV 文件一样格式化:
read_csv(
"a,b,c
1,2,3
4,5,6"
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> a b c
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 2 3
#> 2 4 5 6通常,read_csv() 使用数据的第一行作为列名,这是一个非常常见的约定。但文件顶部包含几行 metadata 的情况并不少见。您可以使用 skip = n 跳过前 n 行,或使用 comment = "#" 删除所有以(例如)# 开头的行:
read_csv(
"The first line of metadata
The second line of metadata
x,y,z
1,2,3",
skip = 2
)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> x y z
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 2 3
read_csv(
"# A comment I want to skip
x,y,z
1,2,3",
comment = "#"
)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 3
#> x y z
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 2 3在其他情况下,数据可能没有列名称。您可以使用 col_names = FALSE 告诉 read_csv() 不要将第一行视为标题,而是从 X1 到 Xn 按顺序标记它们:
read_csv(
"1,2,3
4,5,6",
col_names = FALSE
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> X1 X2 X3
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 2 3
#> 2 4 5 6或者,您可以向 col_names 传递一个字符向量,该向量将用作列名称:
read_csv(
"1,2,3
4,5,6",
col_names = c("x", "y", "z")
)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> x y z
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 2 3
#> 2 4 5 6阅读实践中遇到的大多数 CSV 文件时,您只需要了解这些参数即可。(对于其余的,您需要仔细检查 .csv 文件并阅读 read_csv() 的许多其他参数的文档。)
7.2.3 其他文件类型
一旦掌握了 read_csv(),使用 readr 的其他函数就很简单了;只需要知道要使用哪个函数即可:
-
read_csv2()读取以分号分隔的(semicolon-separated)文件。 这些使用;而不是,来分隔字段,并且在使用,作为小数点标记的国家/地区很常见。 -
read_tsv()读取制表符分隔的(tab-delimited)文件。 -
read_delim()读取带有任何分隔符的文件,如果您未指定分隔符,则会尝试自动猜测分隔符。 -
read_fwf()读取固定宽度的文件。 您可以使用fwf_widths()按宽度指定字段,或使用fwf_positions()按字段位置指定字段。 -
read_table()读取固定宽度文件的常见变体,其中列由空格分隔。 -
read_log()读取 Apache 风格的日志文件。
7.2.4 练习
-
您将使用什么函数来读取字段以 "|" 分隔的文件?
-
除了
file、skip和comment之外,read_csv()和read_tsv()还有哪些其他参数的共同点? -
read_fwf()最重要的参数是什么? -
有时 CSV 文件中的字符串包含逗号。 为了防止它们引起问题,它们需要被引号字符包围,例如
"或'。默认情况下,read_csv()假设引号字符为"。 要将以下文本读入数据框中,您需要为read_csv()指定什么参数?"x,y\n1,'a,b'" -
确定以下每个内联 CSV 文件的问题所在。 运行代码时会发生什么?
read_csv("a,b\n1,2,3\n4,5,6") read_csv("a,b,c\n1,2\n1,2,3,4") read_csv("a,b\n\"1") read_csv("a,b\n1,2\na,b") read_csv("a;b\n1;3") -
通过以下方式练习引用以下数据框中的非语法名称:
a. 提取名为
1的变量。b. 绘制
1与2的散点图。c. 创建一个名为
3的新列,即2除以1。d. 将列重命名为
one、two和three。annoying <- tibble( `1` = 1:10, `2` = `1` * 2 + rnorm(length(`1`)) )
--------------- 未完待续 ---------------
本期翻译贡献:
@TigerZ生信宝库