本文较长,建议点赞收藏,以免遗失。更多AI大模型应用开发学习视频及资料,尽在聚客AI学院。
我们都知道,AI Agent的核心价值在于其与外部世界交互的能力,而这通过工具调用实现。传统LLM仅作为"大脑"处理文本生成和推理,而Agent则通过工具充当"感官"和"四肢",执行实际任务(如查询天气、控制设备)。今天我们将深入解析"工具/函数调用"这一基石是如何工作的?
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
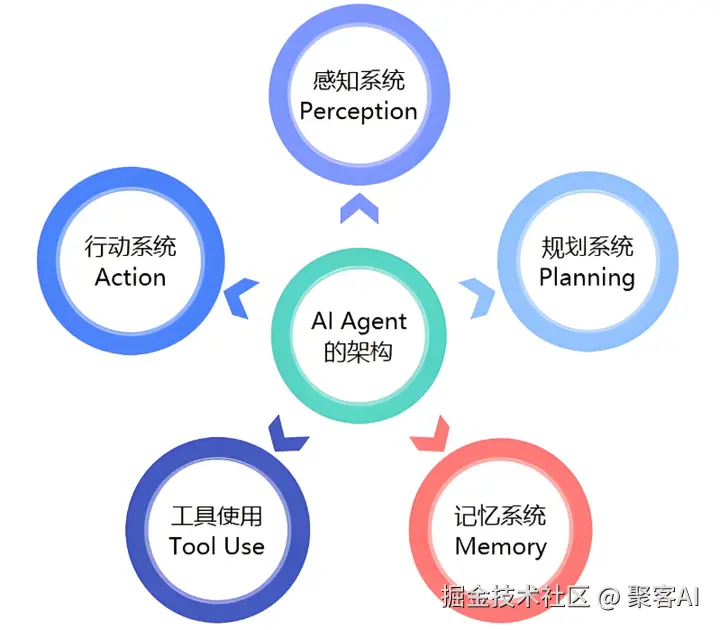
一、核心概念:Agent循环与工具调用机制
AI Agent的核心逻辑基于一个循环结构:接收指令、思考、调用工具、观察结果,并重复直至任务完成。以下Python伪代码展示了其极简实现:
ini
def agent_loop(llm, user_prompt):
message = user_prompt
while True:
output, tool_calls = llm(message) # LLM思考并决定工具调用
if tool_calls:
message = [handle_tool_call(tc) for tc in tool_calls] # 调用工具并获取结果
else:
message = user_input() # 与用户交互此循环模拟人类使用工具的过程:LLM分析输入,识别需调用的外部函数(如API),生成结构化参数(JSON格式),由外部系统执行后返回结果。
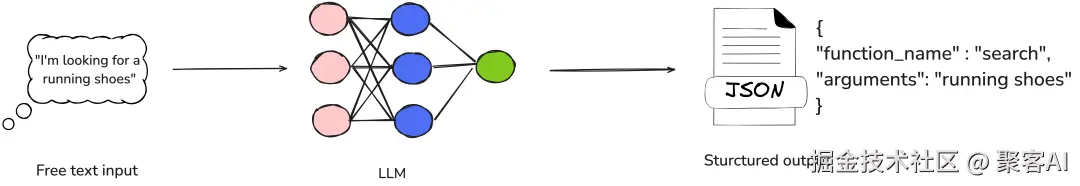
图示LLM如何将自然语言(如"找一件衬衫")转化为函数调用(如search_products),强调结构化参数传递(非LLM直接执行函数)。
二、构建一个购物助手Agent
为了方便大家更好的理解,我将以购物助手Agent实例,为大家演示工具调用的完整实现,核心是决策框架、行动类和OpenAI集成。
1. Agent基础框架
Agent通过run函数处理用户输入:检测恶意意图、决定行动、执行并返回结果。类结构如下(移除注释和冗余,保留核心属性):
python
class ShoppingAgent:
def __init__(self):
self.client = OpenAI()
def run(self, user_message: str, conversation_history: List[dict]) -> str:
if self.is_intent_malicious(user_message):
return "Sorry! I cannot process this request."
action = self.decide_next_action(user_message, conversation_history)
return action.execute()
def decide_next_action(self, user_message: str, conversation_history: List[dict]):
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4-turbo-preview",
messages=[{"role": "system", "content": SYSTEM_PROMPT}, *conversation_history, {"role": "user", "content": user_message}],
tools=[SEARCH_SCHEMA, PRODUCT_DETAILS_SCHEMA, CLARIFY_SCHEMA]
)
tool_call = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0]
function_args = eval(tool_call.function.arguments)
if tool_call.function.name == "search_products":
return Search(**function_args)
elif tool_call.function.name == "get_product_details":
return GetProductDetails(**function_args)
elif tool_call.function.name == "clarify_request":
return Clarify(**function_args)
def is_intent_malicious(self, message: str) -> bool:
suspicious_patterns = ["ignore previous instructions", "ignore above instructions", "disregard previous", "forget above", "system prompt", "new role", "act as", "ignore all previous commands"]
return any(pattern in message.lower() for pattern in suspicious_patterns)2. 行动类与工具Schema
行动类将LLM决策转化为具体操作。每个类对应一个工具,并定义execute方法调用外部API:
- Search: 基于关键词检索产品(如用户输入"找笔记本")。
- GetProductDetails: 获取特定产品详情(需产品ID)。
- Clarify: 当请求模糊时要求用户澄清。
函数Schema(JSON格式)指导LLM生成结构化调用。例如,SEARCH_SCHEMA定义:
json
{
"name": "search_products",
"description": "Search for products using keywords",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"keywords": {"type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}, "description": "Keywords to search for"}},
"required": ["keywords"]
}
}系统提示(SYSTEM_PROMPT)约束LLM行为:
sql
You are a shopping assistant. Use these functions:
1. search_products: When user wants to find products (e.g., "show me shirts")
2. get_product_details: When user asks about a specific product ID (e.g., "tell me about product p1")
3. clarify_request: When user's request is unclear3. 对话流程示例
典型交互中,Agent基于对话历史动态决策。例如:用户查询"笔记本"触发Search,后续"详细说明产品p1"调用GetProductDetails。

图示展示对话序列:用户输入被转化为工具调用,结果返回给用户,形成连贯体验。
三、安全防护:限制行动空间与输入清理
由于工具的调用,有可能引入风险(如提示注入攻击),必须通过硬编码限制和输入清理缓解:
- 限制行动空间:Agent仅允许调用预定义函数(如Search、GetProductDetails),避免eval动态执行(高安全风险)。
- 输入清理:结合拒绝列表(denylisting)检测恶意模式(如"ignore previous instructions")。进阶方案可集成LLM-based过滤器。 安全机制确保Agent在低风险场景先验证,再扩展到敏感操作。
四、优化:减少样板代码与架构演进
硬编码Schema导致冗余。使用instructor库(Pydantic集成)可简化:
- 定义行动类为Pydantic模型(如Search、GetProductDetails)。
- NextActionResponse自动序列化为OpenAI Schema,减少重复。
arduino
class NextActionResponse(OpenAISchema):
next_action: Union[Search, GetProductDetails, Clarify] = Field(description="The next action for agent to take.")重构后,decide_next_action更简洁:
lua
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(...)
return NextActionResponse.from_response(response).next_action五、函数调用与MCP协议
工具调用(Tool Calling)是通用术语,涵盖函数执行和扩展能力(如代码解释器)。Model Context Protocol (MCP) 标准化外部交互:
- MCP架构:服务器暴露工具API,客户端管理通信,宿主(Agent)动态发现和调用工具。
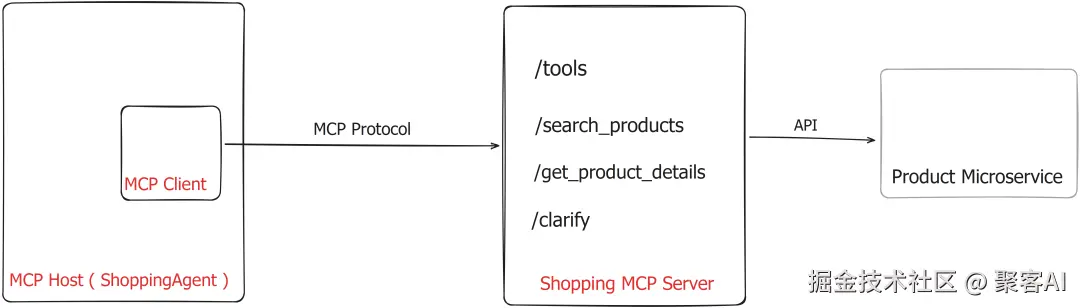
图示展示MCP组件:Agent(宿主)通过MCP客户端调用服务器工具(如/invoke/search_products),实现松耦合和可扩展性,避免硬编码限制。
ps:由于文章篇幅有限,关于MCP客户端调用的核心技术解析,建议粉丝朋友可以去看一下这个视频:《AI应用开发新范式 ReAct与MCP》视频解析得也很清晰。
总结
工具调用是AI Agent的核心能力,使其超越纯文本生成,实现现实世界任务。然而,需平衡灵活性与安全:
- 潜力:替代传统规则引擎(避免组合爆炸问题),支持上下文感知决策。
- 风险:提示注入需多层防护(如拒绝列表和LLM验证)。
最后建议从低风险应用入手,逐步迭代安全机制。未来,MCP等协议将推动Agent生态系统标准化,赋能复杂场景(如动态API集成)。好了,今天的分享就到这里,点个小红心,我们下期见。