你可以使用 C++ 中的 std::queue 或 std::deque 来实现一个固定长度的队列(大小为 NUM_OBJ),当从尾部添加新对象时,如果队列已满,则自动移除头部的对象。这类似于一个"滑动窗口"或"循环缓冲区"。虽然 std::queue 默认不支持遍历和直接控制大小,但也可以实现类似逻辑。对于频繁的头部删除操作,std::deque 或 std::queue (基于 deque) 通常是更高效的选择。
适用于批量添加场景。
✅ 总结
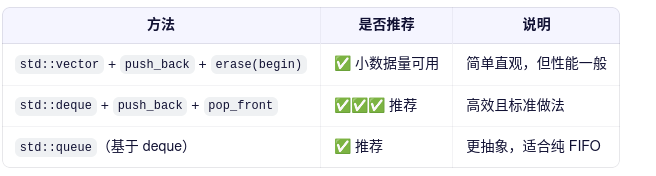
1、使用 std::deque 的完整 C++ 实现:
cpp
深色版本
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <string>
const int NUM_OBJ = 5; // 设置队列的最大长度
class ObjectQueue {
private:
std::deque<std::string> queue; // 使用 deque 支持头尾操作
public:
// 从尾部添加对象
void addObject(const std::string& obj) {
if (queue.size() >= NUM_OBJ) {
// 如果队列已满,移除头部对象
queue.pop_front();
}
queue.push_back(obj); // 添加新对象到尾部
}
// 打印当前队列内容
void printQueue() const {
std::cout << "当前队列: ";
for (const auto& obj : queue) {
std::cout << obj << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// 获取当前队列大小
size_t size() const {
return queue.size();
}
};
int main() {
ObjectQueue objQueue;
// 模拟添加对象
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i) {
std::string obj = "Obj" + std::to_string(i);
objQueue.addObject(obj);
objQueue.printQueue();
}
return 0;
}输出示例:
深色版本
当前队列: Obj1
当前队列: Obj1 Obj2
当前队列: Obj1 Obj2 Obj3
当前队列: Obj1 Obj2 Obj3 Obj4
当前队列: Obj1 Obj2 Obj3 Obj4 Obj5
当前队列: Obj2 Obj3 Obj4 Obj5 Obj6
当前队列: Obj3 Obj4 Obj5 Obj6 Obj7
当前队列: Obj4 Obj5 Obj6 Obj7 Obj8
说明:
使用 std::deque 是因为它支持高效的头部和尾部插入/删除。
当队列大小达到 NUM_OBJ(这里是 5)时,每次添加新元素都会先移除最前面的元素。
你可以将 std::string 替换为任何你想要的对象类型(如自定义类)。替代方案:使用 std::queue
2、使用std::queue 的C++完整实现:
cpp
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
const int NUM_OBJ = 5;
std::queue<std::string> q;
void addObject(const std::string& obj) {
if (q.size() >= NUM_OBJ) {
q.pop(); // 移除头部
}
q.push(obj); // 添加到尾部
}但 std::queue 不支持遍历,所以调试和打印不方便。推荐使用 std::deque。
如果你需要线程安全、对象拷贝控制或更复杂的类型,可以进一步扩展这个类。需要我加上这些功能吗?
代码模式
C++编程,使用std::vector<>完成,末端添加元素,同时头端删除元素,并且位置总元素数为NUM_OBJ
在 C++ 中使用 std::vector 来实现"从尾部添加、从头部删除"并且保持总元素数不超过 NUM_OBJ 的功能是可行的,但需要注意:std::vector 从头部删除元素(erase(begin()))效率较低(O(n)),因为需要移动所有后续元素。不过,如果你对性能要求不高或 NUM_OBJ 很小,这是可以接受的。
✅ 使用 std::vector 实现固定长度队列(FIFO)
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
const int NUM_OBJ = 5; // 固定最大元素数量
class FixedVectorQueue {
private:
std::vector<std::string> vec;
public:
// 从尾部添加元素,如果超过 NUM_OBJ,则从头部移除多余元素
void addAtBack(const std::string& obj) {
vec.push_back(obj); // 添加到尾部
// 如果超过最大长度,从头部删除多余元素
if (vec.size() > NUM_OBJ) {
vec.erase(vec.begin()); // 删除第一个元素(效率 O(n))
}
}
// 打印当前 vector 内容
void print() const {
std::cout << "队列: ";
for (const auto& item : vec) {
std::cout << item << " ";
}
std::cout << " (size=" << vec.size() << ")" << std::endl;
}
// 获取当前大小
size_t size() const {
return vec.size();
}
// 清空
void clear() {
vec.clear();
}
};
int main() {
FixedVectorQueue queue;
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i) {
std::string obj = "Obj" + std::to_string(i);
queue.addAtBack(obj);
queue.print();
}
return 0;
}✅ 输出结果:
深色版本
队列: Obj1 (size=1)
队列: Obj1 Obj2 (size=2)
队列: Obj1 Obj2 Obj3 (size=3)
队列: Obj1 Obj2 Obj3 Obj4 (size=4)
队列: Obj1 Obj2 Obj3 Obj4 Obj5 (size=5)
队列: Obj2 Obj3 Obj4 Obj5 Obj6 (size=5)
队列: Obj3 Obj4 Obj5 Obj6 Obj7 (size=5)
队列: Obj4 Obj5 Obj6 Obj7 Obj8 (size=5)
⚠️ 注意事项
vec.erase(vec.begin()) 是 O(n) 操作,不推荐用于频繁操作或大 NUM_OBJ。
若追求性能,应使用 std::deque 或循环缓冲区。
但若 NUM_OBJ 很小(如 ≤ 10),std::vector 的缓存友好性可能弥补性能损失。✅ 替代优化思路(避免频繁 erase)
你可以只保留 NUM_OBJ 个最新元素,通过判断后批量删除头部多个元素(虽然仍是 O(n),但减少调用次数):
cpp
void addAtBack(const std::string& obj) {
vec.push_back(obj);
// 一次性删除所有超出部分(可能多个)
while (vec.size() > NUM_OBJ) {
vec.erase(vec.begin());
}
}如果你坚持使用 std::vector,上面的代码完全满足你的需求:尾部添加,头部删除,始终保持最多 NUM_OBJ 个元素。
使用模板类(支持任意类型)或加入线程实现:
C++编程,使用std::vector<>完成,末端添加元素,同时头端删除元素,并且位置总元素数为NUM_OBJ。这是一个使用 std::vector 实现固定大小队列逻辑的 C++ 程序。它会在末端添加新元素,并在必要时从头端移除旧元素,以确保容器中的元素总数不超过 NUM_OBJ。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> // For std::copy (used in the manual shift example)
// Define the maximum number of objects the vector can hold
const int NUM_OBJ = 5;
// Function to add an element to the end and remove from the front if necessary
// using vector::erase for head removal (less efficient for large vectors)
void addAndMaintainSizeErase(std::vector<int>& vec, int new_element) {
vec.push_back(new_element);
// If the size exceeds the limit, remove elements from the front
while (vec.size() > NUM_OBJ) {
vec.erase(vec.begin()); // erase the first element, O(n) operation
}
}
// Alternative function to add an element to the end and remove from the front
// by manually shifting elements (also O(n), but demonstrates the concept)
void addAndMaintainSizeShift(std::vector<int>& vec, int new_element) {
if (vec.size() >= NUM_OBJ) {
// Shift all elements one position to the left, overwriting the first element
// std::copy is safe for overlapping ranges in this direction
if (vec.size() > 1) {
std::copy(vec.begin() + 1, vec.end(), vec.begin());
}
// Then replace the last element with the new one
vec.back() = new_element;
} else {
// If not full, simply add to the end
vec.push_back(new_element);
}
}
// Generic print function for the vector
template <typename T>
void printVector(const std::vector<T>& vec) {
std::cout << "Vector contents (size=" << vec.size() << "): ";
for (const T& item : vec) {
std::cout << item << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> myVector;
std::cout << "--- Using addAndMaintainSizeErase ---" << std::endl;
// Demonstrate adding elements
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; ++i) {
std::cout << "Adding element: " << i << std::endl;
addAndMaintainSizeErase(myVector, i);
printVector(myVector);
}
myVector.clear(); // Reset for the next example
std::cout << "\n--- Using addAndMaintainSizeShift ---" << std::endl;
// Demonstrate adding elements with the shift method
for (int i = 10; i <= 17; ++i) {
std::cout << "Adding element: " << i << std::endl;
addAndMaintainSizeShift(myVector, i);
printVector(myVector);
}
return 0;
}代码解释:
const int NUM_OBJ = 5;: 定义了向量应保持的最大元素数量。
addAndMaintainSizeErase 函数:
使用 vec.push_back(new_element) 将新元素添加到向量末尾。
然后检查 vec.size()。如果它超过了 NUM_OBJ,则使用 vec.erase(vec.begin()) 删除第一个元素。
while 循环确保如果一次添加导致多个元素超出限制(虽然 push_back 一次只加一个),也能全部处理。对于单次 push_back,if 语句也足够。
注意: vec.erase(vec.begin()) 是一个 O(n) 操作,因为它需要将所有后续元素向前移动一位。
addAndMaintainSizeShift 函数:
这是另一种实现方式,手动移动元素。
如果向量已满 (vec.size() >= NUM_OBJ),它使用 std::copy 将从第二个元素到最后一个元素的内容复制到从第一个位置开始的位置,有效地"删除"了第一个元素并将其他元素左移。
然后,它直接将新元素赋值给向量的最后一个位置 (vec.back() = new_element)。
如果向量未满,则直接 push_back。
这种方法避免了 erase 的开销(但仍需要移动元素,所以复杂度仍然是 O(n))。
printVector 模板函数: 一个通用的辅助函数,用于打印任何类型 T 的 std::vector 的内容和大小。
main 函数:
创建一个 std::vector<int> 实例 myVector。
首先演示使用 addAndMaintainSizeErase 方法,循环添加元素 1 到 8,并在每次添加后打印向量状态。
然后清空向量,并演示使用 addAndMaintainSizeShift 方法,添加元素 10 到 17。输出示例:
深色版本
--- Using addAndMaintainSizeErase ---
Adding element: 1
Vector contents (size=1): 1
Adding element: 2
Vector contents (size=2): 1 2
Adding element: 3
Vector contents (size=3): 1 2 3
Adding element: 4
Vector contents (size=4): 1 2 3 4
Adding element: 5
Vector contents (size=5): 1 2 3 4 5
Adding element: 6
Vector contents (size=5): 2 3 4 5 6
Adding element: 7
Vector contents (size=5): 3 4 5 6 7
Adding element: 8
Vector contents (size=5): 4 5 6 7 8
--- Using addAndMaintainSizeShift ---
Adding element: 10
Vector contents (size=1): 10
Adding element: 11
Vector contents (size=2): 10 11
Adding element: 12
Vector contents (size=3): 10 11 12
Adding element: 13
Vector contents (size=4): 10 11 12 13
Adding element: 14
Vector contents (size=5): 10 11 12 13 14
Adding element: 15
Vector contents (size=5): 11 12 13 14 15
Adding element: 16
Vector contents (size=5): 12 13 14 15 16
Adding element: 17
Vector contents (size=5): 13 14 15 16 17 这个程序清晰地展示了如何使用 std::vector 来模拟一个固定大小的队列行为。请记住,对于频繁的头部删除操作,std::deque 或 std::queue (基于 deque) 通常是更高效的选择。