目录
力扣.1054距离相等的条形码
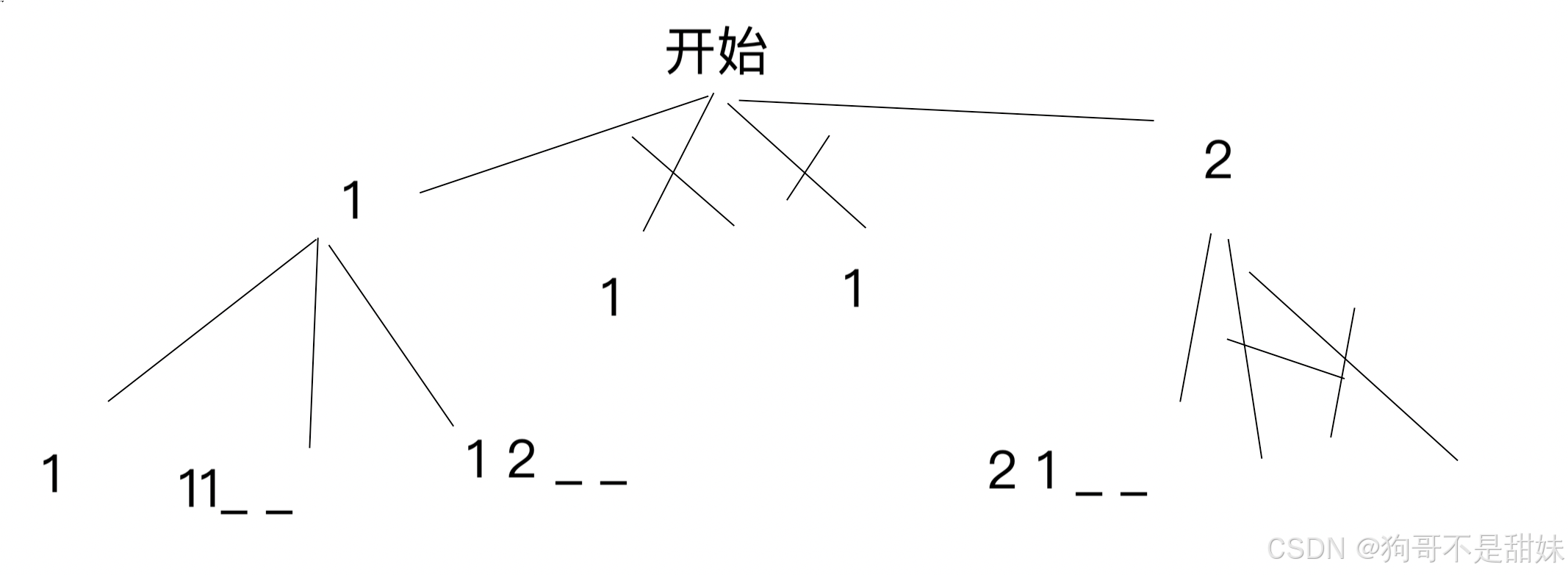
是否策略正确
但是假如 1 2 2 此时 1_2 此时中间只能填写2,但是就不对了,所以,限定条件,先处理出现次数最多的次数,其余无所谓
2_2
证明:题目一定有解,性质:两个两个一组
(n+1)/2组,出现次数最多的次数,一定是小于(n+1)/2个,那么
假如出现次数最多的,等于(n+1)/2,一定正确
第二个,最多的,小于(n+1)/2, 假如你 前面 o _ o_ o_ o_ x_ x_x 假如你第二个没填写完,就还是x,但是你不可能说是x填重复的,换句话,x绝对不可能绕过一圈来再次相邻,
class Solution { public int[] rearrangeBarcodes(int[] barcodes) { Arrays.sort(barcodes); int n=barcodes.length; Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap<>(); int[]a=new int[n]; int max=0; int maxcount=0; //第一个点,该定义变量就去定义,不要老想着优化 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ map.put(barcodes[i],map.getOrDefault(barcodes[i],0)+1); if(maxcount<map.get(barcodes[i])){ max=barcodes[i]; maxcount=map.get(barcodes[i]); } } //先处理出现次数最多的那个数字 int index=0; //统计处那个字符数字最多,然后给他填上 //最难的一步就是maxcount你是否能理清楚 for(int i=0;i<maxcount;i++){ a[index]=max; index+=2; } //处理剩下的数,可以直接删除,也可以遍历时候跳过,不要太纠结 map.remove(max); for(int x:map.keySet()){ for(int i=0;i<map.get(x);i++){ if(index>=n) index=1; a[index]=x; index+=2; } } return a; } }
力扣767.重构字符串
跟上面那个题思路一样,只需要进行一个判断,是否满足条件就行。
max>(n+1)/2的情况下,就返回空字符串
class Solution {
public String reorganizeString(String s) {
HashMap<Character,Integer>map=new HashMap<>();//(n+1)/2
char[]a=s.toCharArray();
int n=a.length;
char max=a[0];
int maxCount=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
map.put(a[i],map.getOrDefault(a[i],0)+1);
if(maxCount<map.get(a[i])){
max=a[i];
maxCount=map.get(a[i]);
}
}
if(maxCount>(n+1)/2)return "";
else{
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
int index=0;
for(int i=0;i<maxCount;i++){
a[index]=max;
index+=2;
}
map.remove(max);
for(char x:map.keySet()){
for(int i=0;i<map.get(x);i++){
if(index>=n)index=1;
a[index]=x;
index+=2;
}
}
return sb.append(a).toString();
}
}
}力扣47.全排列II
1.同一个节点都所有分支中,相同的元素只可以选择一次
同一个数只能使用一次
并且我们需要对数组,进行一个排序,去确定 check[i]==true||nums[i]与nums[i-1]是否相同
同一层的话,不用考虑 check[i-1]==false
考虑不合法的分支(这里的i不可以等于0,0一定合法,不用判断)
check[i]==true ||(i!=0&&nums[i]==nums[i-1]&&check[i-1]==false)
假如i位置是true代表当前位置已经被使用了,或者,当前位置的前一个没有被使用,但是我和你是在一层,换句话说,我们属于一层,那么就应该剪枝
考虑合法的分支(这里面的i是可以等于0的(
check[i]=false&&(nums[i]!=nums[i-1]||check[i-1]==true(此时的条件是a[i]=a[i-1]) )
class Solution { List<List<Integer>>ret=new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer>ans=new ArrayList<>(); boolean[]check; int n; //伴随着就是如何剪枝 public void dfs(int pos,int []nums){ if(pos==n){ ret.add(new ArrayList<>(ans)); return ;} for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if((check[i]==true)||(i!=0&&check[i-1]==false&&nums[i]==nums[i-1])){continue;} check[i]=true; ans.add(nums[i]); dfs(pos+1,nums); ans.remove(ans.size()-1); check[i]=false;; } } public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { n=nums.length; Arrays.sort(nums); check=new boolean[n]; dfs(0,nums); return ret; } }
力扣980.不同路径III
step++,然后到达终点之后,路径++,然后不断递增就好
这个要注意,最后才调用这个函数要让step走完
class Solution {
int pathCount=0;
int[]dx={0,0,1,-1};
int[]dy={1,-1,0,0};
int n;
int m;
int step;
boolean[][]vis;
public void dfs(int count,int[][]grid,int i,int j){
if(grid[i][j]==2){
if(count==step)pathCount++;
return;
}
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=i+dx[k];
int y=j+dy[k];
if(
x>=0&&x<n&&y>=0&&y<m
&&vis[x][y]==false
&&(grid[x][y]==0||grid[x][y]==2)
){
vis[x][y]=true;
dfs(count+1,grid,x,y);
vis[x][y]=false;
}
}
}
public int uniquePathsIII(int[][] grid) {
n=grid.length;
m=grid[0].length;
vis=new boolean[n][m];
int bx=0;
int by=0;
//这么判断是否走完全了
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(grid[i][j]==1){
bx=i;
by=j;
vis[bx][by]=true;
}
else if(grid[i][j]==0||grid[i][j]==2)step++;
}
}
dfs(0,grid,bx,by);
return pathCount;
}
}力扣509.斐波那契数列(记忆化搜索)
存储在map,假如有值,直接返回,就不用再去递归了。
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer>map=new HashMap<>();
public int dfs(int n){
if(map.containsKey(n)){
return map.get(n);
}
map.put(n,dfs(n-1)+dfs(n-2));
return map.get(n);
}
public int fib(int n) {
map.put(0,0);
map.put(1,1);
return dfs(n);
}
}